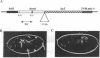
Abstract
The Drosophila morphogen dorsal, KBF1, NF-kappa B, and the proto-oncogene c-rel belong to the rel family of transcription factors whose function is regulated post-translationally by selective nuclear import. In the early Drosophila embryo, dorsal protein is proposed to be retained in the cytoplasm through its interaction with cactus protein. The maternal dorsal group genes constitute a signal transduction pathway, which results in targeting cytoplasmic dorsal protein into the nuclei of the syncytial blastoderm embryo, in a ventral-to-dorsal gradient. The asymmetric transcriptional regulation of zygotic genes along the dorsoventral axis by the dorsal morphogen gradient establishes embryonic dorsoventral polarity. In the lymphocytes, the functional equivalent of cactus is I kappa B, which appears to retain NF-kappa B in the cytoplasm. This retention is relieved by extracellular signals in tissue culture. NF-kappa B and rel proteins each are known to function as oligomeric complexes. Here we present genetic and biochemical evidence for the existence and functional importance of an oligomeric dorsal complex in vivo.
Full text
PDF

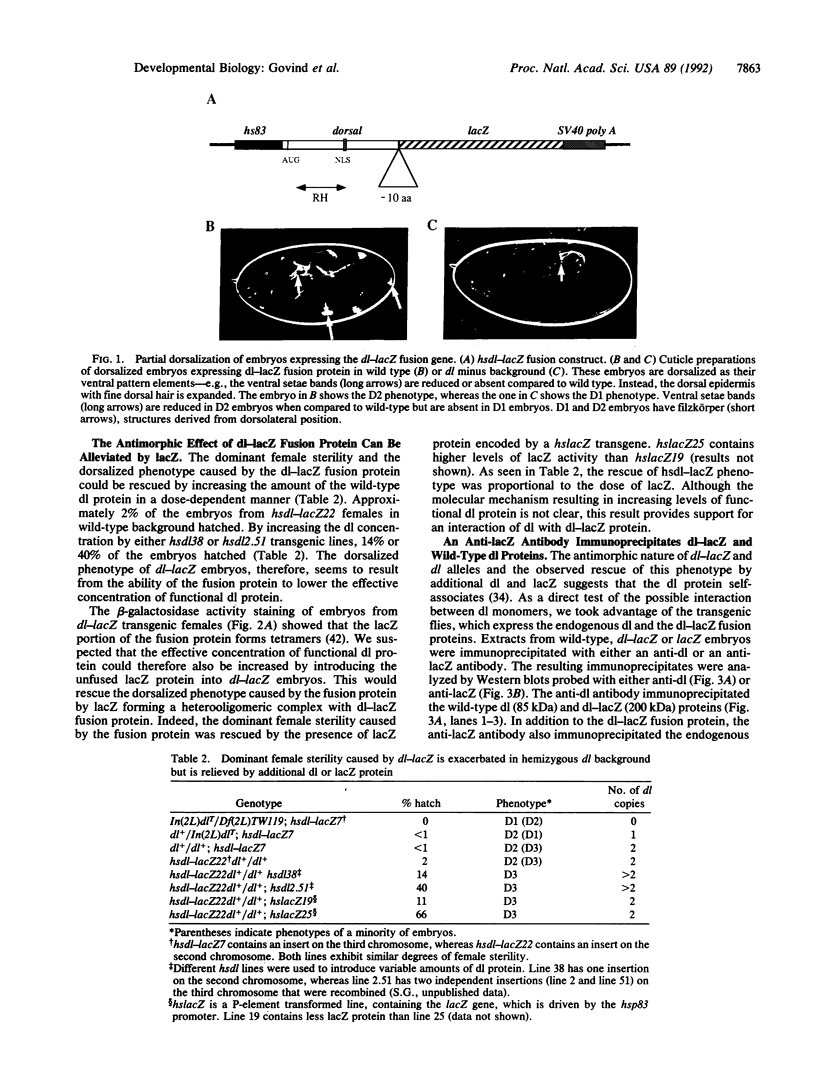

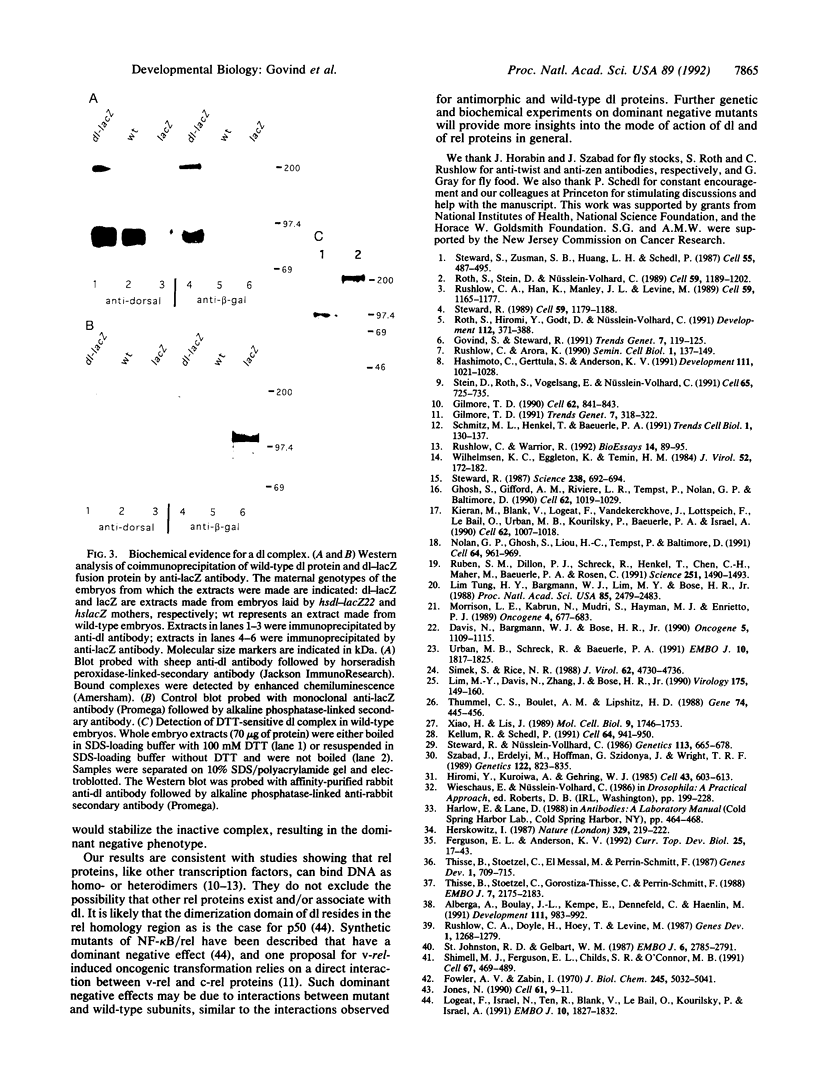
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alberga A., Boulay J. L., Kempe E., Dennefeld C., Haenlin M. The snail gene required for mesoderm formation in Drosophila is expressed dynamically in derivatives of all three germ layers. Development. 1991 Apr;111(4):983–992. doi: 10.1242/dev.111.4.983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis J. N., Bargmann W., Bose H. R., Jr Identification of protein complexes containing the c-rel proto-oncogene product in avian hematopoietic cells. Oncogene. 1990 Aug;5(8):1109–1115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson E. L., Anderson K. V. Dorsal-ventral pattern formation in the Drosophila embryo: the role of zygotically active genes. Curr Top Dev Biol. 1991;25:17–43. doi: 10.1016/s0070-2153(08)60410-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fowler A. V., Zabin I. The amino acid sequence of beta galactosidase. I. Isolation and composition of tryptic peptides. J Biol Chem. 1970 Oct 10;245(19):5032–5041. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh S., Gifford A. M., Riviere L. R., Tempst P., Nolan G. P., Baltimore D. Cloning of the p50 DNA binding subunit of NF-kappa B: homology to rel and dorsal. Cell. 1990 Sep 7;62(5):1019–1029. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90276-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore T. D. Malignant transformation by mutant Rel proteins. Trends Genet. 1991 Oct;7(10):318–322. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(91)90421-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore T. D. NF-kappa B, KBF1, dorsal, and related matters. Cell. 1990 Sep 7;62(5):841–843. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90257-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Govind S., Steward R. Dorsoventral pattern formation in Drosophila: signal transduction and nuclear targeting. Trends Genet. 1991 Apr;7(4):119–125. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(91)90456-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto C., Gerttula S., Anderson K. V. Plasma membrane localization of the Toll protein in the syncytial Drosophila embryo: importance of transmembrane signaling for dorsal-ventral pattern formation. Development. 1991 Apr;111(4):1021–1028. doi: 10.1242/dev.111.4.1021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herskowitz I. Functional inactivation of genes by dominant negative mutations. Nature. 1987 Sep 17;329(6136):219–222. doi: 10.1038/329219a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiromi Y., Kuroiwa A., Gehring W. J. Control elements of the Drosophila segmentation gene fushi tarazu. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):603–613. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90232-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones N. Transcriptional regulation by dimerization: two sides to an incestuous relationship. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):9–11. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90207-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellum R., Schedl P. A position-effect assay for boundaries of higher order chromosomal domains. Cell. 1991 Mar 8;64(5):941–950. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90318-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kieran M., Blank V., Logeat F., Vandekerckhove J., Lottspeich F., Le Bail O., Urban M. B., Kourilsky P., Baeuerle P. A., Israël A. The DNA binding subunit of NF-kappa B is identical to factor KBF1 and homologous to the rel oncogene product. Cell. 1990 Sep 7;62(5):1007–1018. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90275-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim M. Y., Davis N., Zhang J. Y., Bose H. R., Jr The v-rel oncogene product is complexed with cellular proteins including its proto-oncogene product and heat shock protein 70. Virology. 1990 Mar;175(1):149–160. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90195-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logeat F., Israël N., Ten R., Blank V., Le Bail O., Kourilsky P., Israël A. Inhibition of transcription factors belonging to the rel/NF-kappa B family by a transdominant negative mutant. EMBO J. 1991 Jul;10(7):1827–1832. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07708.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison L. E., Kabrun N., Mudri S., Hayman M. J., Enrietto P. J. Viral rel and cellular rel associate with cellular proteins in transformed and normal cells. Oncogene. 1989 Jun;4(6):677–683. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nolan G. P., Ghosh S., Liou H. C., Tempst P., Baltimore D. DNA binding and I kappa B inhibition of the cloned p65 subunit of NF-kappa B, a rel-related polypeptide. Cell. 1991 Mar 8;64(5):961–969. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90320-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth S., Hiromi Y., Godt D., Nüsslein-Volhard C. cactus, a maternal gene required for proper formation of the dorsoventral morphogen gradient in Drosophila embryos. Development. 1991 Jun;112(2):371–388. doi: 10.1242/dev.112.2.371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth S., Stein D., Nüsslein-Volhard C. A gradient of nuclear localization of the dorsal protein determines dorsoventral pattern in the Drosophila embryo. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):1189–1202. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90774-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruben S. M., Dillon P. J., Schreck R., Henkel T., Chen C. H., Maher M., Baeuerle P. A., Rosen C. A. Isolation of a rel-related human cDNA that potentially encodes the 65-kD subunit of NF-kappa B. Science. 1991 Mar 22;251(5000):1490–1493. doi: 10.1126/science.2006423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rushlow C. A., Han K., Manley J. L., Levine M. The graded distribution of the dorsal morphogen is initiated by selective nuclear transport in Drosophila. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):1165–1177. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90772-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rushlow C., Arora K. Dorsal ventral polarity and pattern formation in the Drosophila embryo. Semin Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;1(3):137–149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rushlow C., Doyle H., Hoey T., Levine M. Molecular characterization of the zerknüllt region of the Antennapedia gene complex in Drosophila. Genes Dev. 1987 Dec;1(10):1268–1279. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.10.1268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rushlow C., Warrior R. The rel family of proteins. Bioessays. 1992 Feb;14(2):89–95. doi: 10.1002/bies.950140204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz M. L., Henkel T., Baeuerle P. A. Proteins controlling the nuclear uptake of NF-kappa B, Rel and dorsal. Trends Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;1(5):130–137. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(91)90118-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimell M. J., Ferguson E. L., Childs S. R., O'Connor M. B. The Drosophila dorsal-ventral patterning gene tolloid is related to human bone morphogenetic protein 1. Cell. 1991 Nov 1;67(3):469–481. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90522-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simek S., Rice N. R. p59v-rel, the transforming protein of reticuloendotheliosis virus, is complexed with at least four other proteins in transformed chicken lymphoid cells. J Virol. 1988 Dec;62(12):4730–4736. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.12.4730-4736.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Johnston R. D., Gelbart W. M. Decapentaplegic transcripts are localized along the dorsal-ventral axis of the Drosophila embryo. EMBO J. 1987 Sep;6(9):2785–2791. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02574.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein D., Roth S., Vogelsang E., Nüsslein-Volhard C. The polarity of the dorsoventral axis in the Drosophila embryo is defined by an extracellular signal. Cell. 1991 May 31;65(5):725–735. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90381-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steward R. Dorsal, an embryonic polarity gene in Drosophila, is homologous to the vertebrate proto-oncogene, c-rel. Science. 1987 Oct 30;238(4827):692–694. doi: 10.1126/science.3118464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steward R., Nüsslein-Volhard C. The genetics of the dorsal-Bicaudal-D region of Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 1986 Jul;113(3):665–678. doi: 10.1093/genetics/113.3.665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steward R. Relocalization of the dorsal protein from the cytoplasm to the nucleus correlates with its function. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):1179–1188. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90773-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steward R., Zusman S. B., Huang L. H., Schedl P. The dorsal protein is distributed in a gradient in early Drosophila embryos. Cell. 1988 Nov 4;55(3):487–495. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90035-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szabad J., Erdélyi M., Hoffmann G., Szidonya J., Wright T. R. Isolation and characterization of dominant female sterile mutations of Drosophila melanogaster. II. Mutations on the second chromosome. Genetics. 1989 Aug;122(4):823–835. doi: 10.1093/genetics/122.4.823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thisse B., Stoetzel C., Gorostiza-Thisse C., Perrin-Schmitt F. Sequence of the twist gene and nuclear localization of its protein in endomesodermal cells of early Drosophila embryos. EMBO J. 1988 Jul;7(7):2175–2183. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03056.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thummel C. S., Boulet A. M., Lipshitz H. D. Vectors for Drosophila P-element-mediated transformation and tissue culture transfection. Gene. 1988 Dec 30;74(2):445–456. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90177-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tung H. Y., Bargmann W. J., Lim M. Y., Bose H. R., Jr The v-rel oncogene product is complexed to a 40-kDa phosphoprotein in transformed lymphoid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2479–2483. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urban M. B., Schreck R., Baeuerle P. A. NF-kappa B contacts DNA by a heterodimer of the p50 and p65 subunit. EMBO J. 1991 Jul;10(7):1817–1825. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07707.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilhelmsen K. C., Eggleton K., Temin H. M. Nucleic acid sequences of the oncogene v-rel in reticuloendotheliosis virus strain T and its cellular homolog, the proto-oncogene c-rel. J Virol. 1984 Oct;52(1):172–182. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.1.172-182.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiao H., Lis J. T. Heat shock and developmental regulation of the Drosophila melanogaster hsp83 gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;9(4):1746–1753. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.4.1746. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]