Abstract
von Willebrand factor interaction with glycoprotein Ib alpha (GPIb alpha) plays a critical role in the initial phase of platelet adhesion at high shear rates, and it may also play a role in platelet thrombus formation in partially occluded arteries. Previous studies have indicated that two peptides, Cys-474--Pro-488 (peptide 153) and Ser-692--Pro-708 (peptide 154), inhibit von Willebrand factor--GPIb alpha interaction. We have expressed a recombinant fragment of von Willebrand factor, Leu-504--Lys-728 [corrected], with a single intrachain disulfide bond linking residues Cys-509--Cys-695 and examined its ability to inhibit von Willebrand factor--GPIb alpha interactions and platelet adhesion at high shear forces. This recombinant fragment, named VCL, inhibits ristocetin-induced, botrocetin-induced, and asialo-von Willebrand factor-induced platelet aggregation and binding to platelets at an IC50 = 0.011-0.260 microM, significantly lower than the IC50 of peptide 153 or 154, IC50 = 86-700 microM. Peptides 153 and 154 did not result in any inhibition of platelet adhesion (IC50 greater than 500 microM). In contrast, VCL inhibited 50% of platelet adhesion at 0.94 microM and at 7.6 microM inhibited greater than 80% of platelet adhesion to human umbilical artery subendothelium at high shear forces. VCL inhibited the contact and spreading of platelets and also caused a marked decrease in thrombus formation. These studies indicate that VCL may be an effective antithrombotic agent in preventing arterial thrombus formation in areas of high shear force.
Full text
PDF

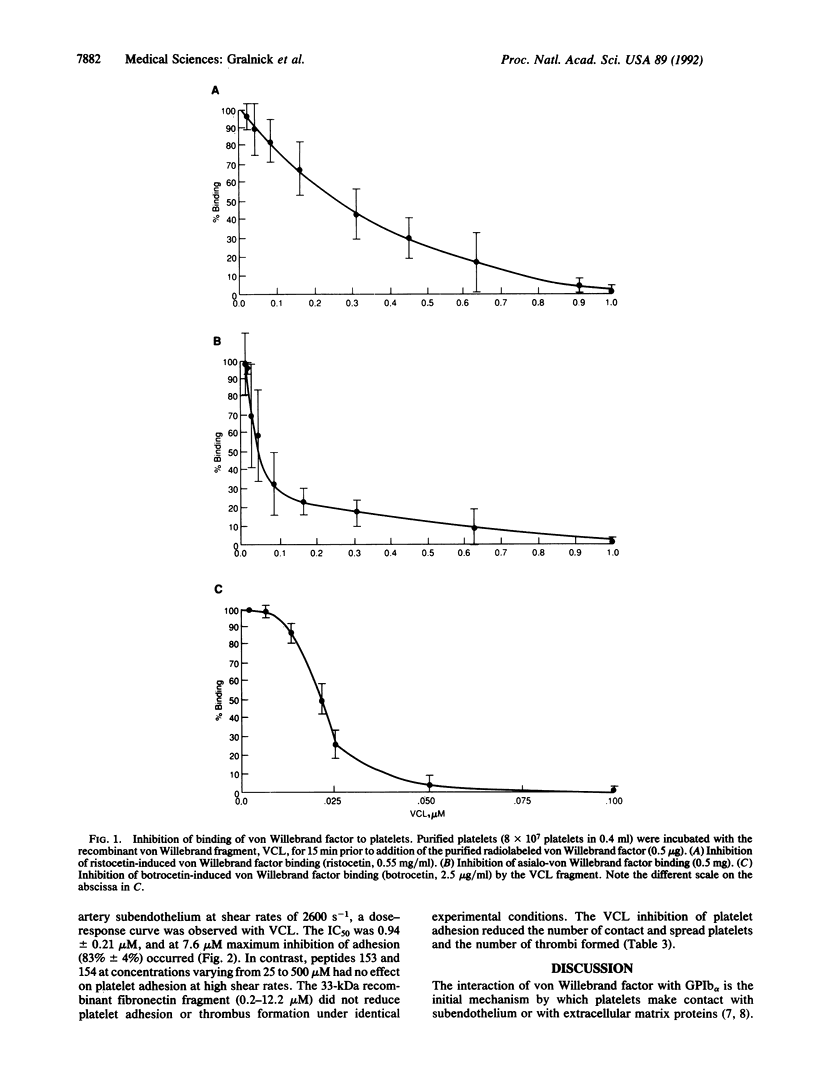
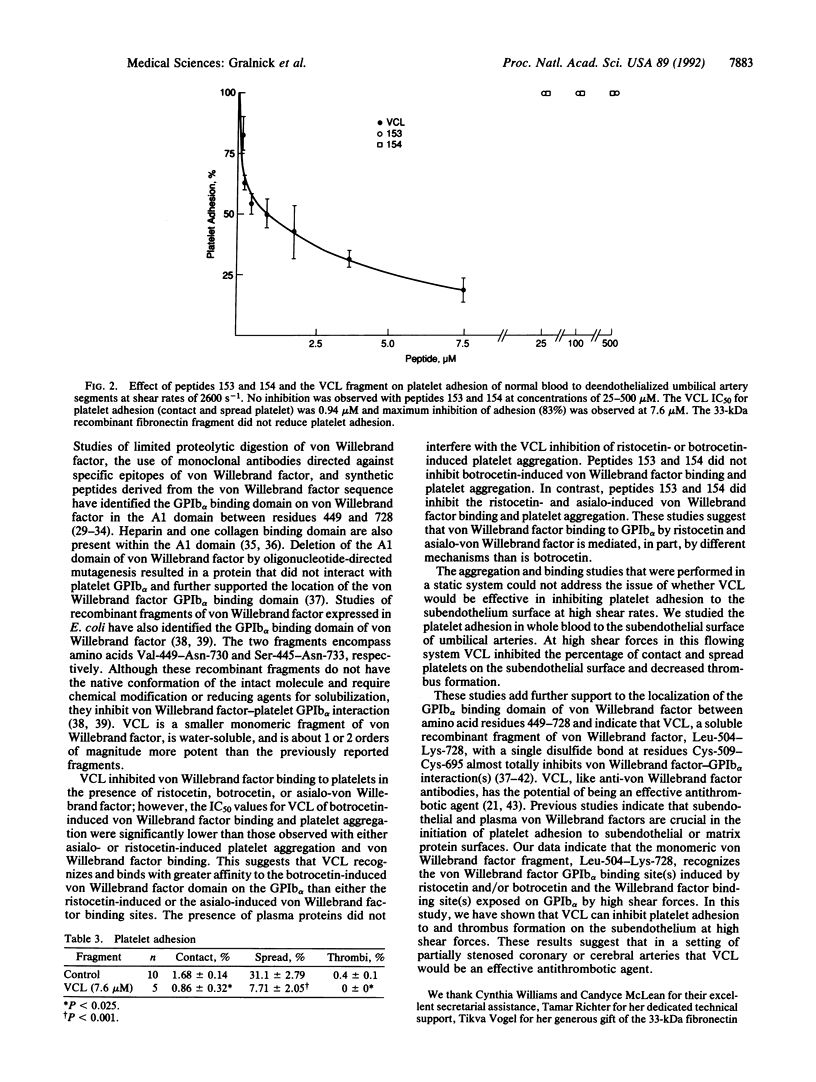

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bellinger D. A., Nichols T. C., Read M. S., Reddick R. L., Lamb M. A., Brinkhous K. M., Evatt B. L., Griggs T. R. Prevention of occlusive coronary artery thrombosis by a murine monoclonal antibody to porcine von Willebrand factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(22):8100–8104. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.22.8100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinkhous K. M., Read M. S., Reddick R. L., Griggs T. R. Pathophysiology of platelet-aggregating von Willebrand factor: applications of the venom coagglutinin vWF assay. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1981;370:191–204. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1981.tb29732.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coller B. S., Peerschke E. I., Scudder L. E., Sullivan C. A. Studies with a murine monoclonal antibody that abolishes ristocetin-induced binding of von Willebrand factor to platelets: additional evidence in support of GPIb as a platelet receptor for von Willebrand factor. Blood. 1983 Jan;61(1):99–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooney K. A., Nichols W. C., Bruck M. E., Bahou W. F., Shapiro A. D., Bowie E. J., Gralnick H. R., Ginsburg D. The molecular defect in type IIB von Willebrand disease. Identification of four potential missense mutations within the putative GpIb binding domain. J Clin Invest. 1991 Apr;87(4):1227–1233. doi: 10.1172/JCI115123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer M., Fytlovitch S., Amit B., Wortzel A., Beck Y. A constitutive expression vector system driven by the deo P1P2 promoters of Escherichia coli. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 1990 Jul;33(4):424–428. doi: 10.1007/BF00176658. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimura Y., Holland L. Z., Ruggeri Z. M., Zimmerman T. S. The von willebrand factor domain-mediating botrocetin-induced binding to glycoprotein IB lies between Val449 and Lys728. Blood. 1987 Oct;70(4):985–988. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimura Y., Titani K., Holland L. Z., Roberts J. R., Kostel P., Ruggeri Z. M., Zimmerman T. S. A heparin-binding domain of human von Willebrand factor. Characterization and localization to a tryptic fragment extending from amino acid residue Val-449 to Lys-728. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 5;262(4):1734–1739. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimura Y., Titani K., Holland L. Z., Russell S. R., Roberts J. R., Elder J. H., Ruggeri Z. M., Zimmerman T. S. von Willebrand factor. A reduced and alkylated 52/48-kDa fragment beginning at amino acid residue 449 contains the domain interacting with platelet glycoprotein Ib. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 5;261(1):381–385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuster V., Fass D. N., Kaye M. P., Josa M., Zinsmeister A. R., Bowie E. J. Arteriosclerosis in normal and von Willebrand pigs: long-term prospective study and aortic transplantation study. Circ Res. 1982 Nov;51(5):587–593. doi: 10.1161/01.res.51.5.587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuster W., Bowie E. J., Lewis J. C., Fass D. N., Owen C. A., Jr, Brown A. L. Resistance to arteriosclerosis in pigs with von Willebrand's disease. Spontaneous and high cholesterol diet-induced arteriosclerosis. J Clin Invest. 1978 Mar;61(3):722–730. doi: 10.1172/JCI108985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girma J. P., Chopek M. W., Titani K., Davie E. W. Limited proteolysis of human von Willebrand factor by Staphylococcus aureus V-8 protease: isolation and partial characterization of a platelet-binding domain. Biochemistry. 1986 Jun 3;25(11):3156–3163. doi: 10.1021/bi00359a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girma J. P., Kalafatis M., Piétu G., Lavergne J. M., Chopek M. W., Edgington T. S., Meyer D. Mapping of distinct von Willebrand factor domains interacting with platelet GPIb and GPIIb/IIIa and with collagen using monoclonal antibodies. Blood. 1986 May;67(5):1356–1366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grainick H. R., Williams S. B., Coller B. S. Asialo von Willebrand factor interactions with platelets. Interdependence of glycoproteins Ib and IIb/IIIa for binding and aggregation. J Clin Invest. 1985 Jan;75(1):19–25. doi: 10.1172/JCI111673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gralnick H. R., Williams S. B., Coller B. S. Fibrinogen competes with von Willebrand factor for binding to the glycoprotein IIb/IIIa complex when platelets are stimulated with thrombin. Blood. 1984 Oct;64(4):797–800. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda Y., Handa M., Kawano K., Kamata T., Murata M., Araki Y., Anbo H., Kawai Y., Watanabe K., Itagaki I. The role of von Willebrand factor and fibrinogen in platelet aggregation under varying shear stress. J Clin Invest. 1991 Apr;87(4):1234–1240. doi: 10.1172/JCI115124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence J. B., Gralnick H. R. Monoclonal antibodies to the glycoprotein IIb-IIIa epitopes involved in adhesive protein binding: effects on platelet spreading and ultrastructure on human arterial subendothelium. J Lab Clin Med. 1987 Apr;109(4):495–503. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence J. B., Kramer W. S., McKeown L. P., Williams S. B., Gralnick H. R. Arginine-glycine-aspartic acid- and fibrinogen gamma-chain carboxyterminal peptides inhibit platelet adherence to arterial subendothelium at high wall shear rates. An effect dissociable from interference with adhesive protein binding. J Clin Invest. 1990 Nov;86(5):1715–1722. doi: 10.1172/JCI114896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moake J. L., Turner N. A., Stathopoulos N. A., Nolasco L. H., Hellums J. D. Involvement of large plasma von Willebrand factor (vWF) multimers and unusually large vWF forms derived from endothelial cells in shear stress-induced platelet aggregation. J Clin Invest. 1986 Dec;78(6):1456–1461. doi: 10.1172/JCI112736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohri H., Fujimura Y., Shima M., Yoshioka A., Houghten R. A., Ruggeri Z. M., Zimmerman T. S. Structure of the von Willebrand factor domain interacting with glycoprotein Ib. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 5;263(34):17901–17904. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohri H., Yoshioka A., Zimmerman T. S., Ruggeri Z. M. Isolation of the von Willebrand factor domain interacting with platelet glycoprotein Ib, heparin, and collagen and characterization of its three distinct functional sites. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 15;264(29):17361–17367. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols T. C., Bellinger D. A., Johnson T. A., Lamb M. A., Griggs T. R. von Willebrand's disease prevents occlusive thrombosis in stenosed and injured porcine coronary arteries. Circ Res. 1986 Jul;59(1):15–26. doi: 10.1161/01.res.59.1.15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols T. C., Bellinger D. A., Tate D. A., Reddick R. L., Read M. S., Koch G. G., Brinkhous K. M., Griggs T. R. von Willebrand factor and occlusive arterial thrombosis. A study in normal and von Willebrand's disease pigs with diet-induced hypercholesterolemia and atherosclerosis. Arteriosclerosis. 1990 May-Jun;10(3):449–461. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.10.3.449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pareti F. I., Niiya K., McPherson J. M., Ruggeri Z. M. Isolation and characterization of two domains of human von Willebrand factor that interact with fibrillar collagen types I and III. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 5;262(28):13835–13841. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piétu G., Meulien P., Cherel G., Diaz J., Baruch D., Courtney M., Meyer D. Production in Escherichia coli of a biologically active subfragment of von Willebrand factor corresponding to the platelet glycoprotein Ib, collagen and heparin binding domains. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Nov 15;164(3):1339–1347. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)91816-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randi A. M., Rabinowitz I., Mancuso D. J., Mannucci P. M., Sadler J. E. Molecular basis of von Willebrand disease type IIB. Candidate mutations cluster in one disulfide loop between proposed platelet glycoprotein Ib binding sequences. J Clin Invest. 1991 Apr;87(4):1220–1226. doi: 10.1172/JCI115122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Read M. S., Shermer R. W., Brinkhous K. M. Venom coagglutinin: an activator of platelet aggregation dependent on von Willebrand factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4514–4518. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddick R. L., Griggs T. R., Lamb M. A., Brinkhous K. M. Platelet adhesion to damaged coronary arteries: Comparison in normal and von Willebrand disease swine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(16):5076–5079. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.16.5076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth G. J., Titani K., Hoyer L. W., Hickey M. J. Localization of binding sites within human von Willebrand factor for monomeric type III collagen. Biochemistry. 1986 Dec 30;25(26):8357–8361. doi: 10.1021/bi00374a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruggeri Z. M., Bader R., de Marco L. Glanzmann thrombasthenia: deficient binding of von Willebrand factor to thrombin-stimulated platelets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(19):6038–6041. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.19.6038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakariassen K. S., Nievelstein P. F., Coller B. S., Sixma J. J. The role of platelet membrane glycoproteins Ib and IIb-IIIa in platelet adherence to human artery subendothelium. Br J Haematol. 1986 Aug;63(4):681–691. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1986.tb07552.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawada Y., Fass D. N., Katzmann J. A., Bahn R. C., Bowie E. J. Hemostatic plug formation in normal and von Willebrand pigs: the effect of the administration of cryoprecipitate and a monoclonal antibody to Willebrand factor. Blood. 1986 May;67(5):1229–1239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sixma J. J., Schiphorst M. E., Verweij C. L., Pannekoek H. Effect of deletion of the A1 domain of von Willebrand factor on its binding to heparin, collagen and platelets in the presence of ristocetin. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Mar 14;196(2):369–375. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb15826.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugimoto M., Ricca G., Hrinda M. E., Schreiber A. B., Searfoss G. H., Bottini E., Ruggeri Z. M. Functional modulation of the isolated glycoprotein Ib binding domain of von Willebrand factor expressed in Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1991 May 28;30(21):5202–5209. doi: 10.1021/bi00235a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ware J., Dent J. A., Azuma H., Sugimoto M., Kyrle P. A., Yoshioka A., Ruggeri Z. M. Identification of a point mutation in type IIB von Willebrand disease illustrating the regulation of von Willebrand factor affinity for the platelet membrane glycoprotein Ib-IX receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 1;88(7):2946–2950. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.7.2946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss H. J., Tschopp T. B., Baumgartner H. R., Sussman I. I., Johnson M. M., Egan J. J. Decreased adhesion of giant (Bernard-Soulier) platelets to subendothelium. Further implications on the role of the von Willebrand factor in hemostasis. Am J Med. 1974 Dec;57(6):920–925. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(74)90170-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss H. J., Turitto V. T., Baumgartner H. R. Effect of shear rate on platelet interaction with subendothelium in citrated and native blood. I. Shear rate--dependent decrease of adhesion in von Willebrand's disease and the Bernard-Soulier syndrome. J Lab Clin Med. 1978 Nov;92(5):750–764. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss H. J., Turitto V. T., Baumgartner H. R. Platelet adhesion and thrombus formation on subendothelium in platelets deficient in glycoproteins IIb-IIIa, Ib, and storage granules. Blood. 1986 Feb;67(2):322–330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



