Abstract
Oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) has been estimated to be the sixth most common cancer worldwide. The distant metastasis plays a critical role in the management and prognosis in oral cancer patients. Regarding the distant metastasis from the oral cancer, the hypopharynx is the most common primary site, followed by the base of tongue and anterior tongue. The present review article analyzes the characteristics of the distant metastases from the oral cavity from 1937 to 2015.
Key words: Incidence, metastasis, molecular biology, oral cancer
INTRODUCTION
Oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) has been estimated to be the sixth most common cancer worldwide.[1] The distant metastasis plays a critical role in the management and prognosis of oral cancer patients.[2] Regarding the distant metastasis from the oral cancer, the hypopharynx is the most common primary site (60%), followed by the base of tongue (53%) and anterior tongue (50%).[3]
The present article reviews the characteristics of distant metastases from the oral cavity to analyze all available information in the English language literature from 1937 to 2015. Metastases from the major salivary glands are not included in this review. In addition, metastasis to the cervical lymph nodes was not included.
BIOLOGY OF METASTASIS
Metastasis means the spread of the disease from one organ to another not directly connected to it. Cancer cells enter the vascular or lymphatic channels.[4] Metastasis starts from detaching the cancer cells from the primary site, spreading in the tissue, moving away through the extracellular matrix, invading blood vessels, and settling in the microvasculature, and finally, extravasating through the vessel wall and proliferating in the recipient tissue.[5] Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) promotes metastasis due to loss of cell–cell adhesion and secretion of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) to degrade the extracellular matrix (ECM).[6,7,8] Anoikis, a specific form of apoptosis, occurs after detachment of the cells from the ECM[9] and facilitates metastasis.[10] Angiogenesis is another step for cancer metastasis as tumor cells should be transported via blood and/or lymph vessels.[11] Overexpression of vascular endothelial growth factors (VEGFs) has been reported in the cancers.[12] Tumor cells lining blood vessels “mosaic vessels” or “vasculogenic mimicry” may be another way for spreading cancer cells.[13] After surviving the immune system, the tumor cells extravasate into the organ parenchyma to establish a micrometastasis.[14]
There are a few theories about the mechanism of metastasis. First, the “organ selection” theory suggesting the growth factors in the metastatic site may determine the establishment of successful metastasis. The second theory “adhesion theory” proposes that tissue specific adhesion molecules, expressing on endothelial cells of target organs, set up a pre-metastatic niche by anchoring migrating cancer cells to develop a metastatic tumor. Another is the “chemoattraction theory” that suggests that cancer cells express chemokine receptors.[15] Another theory proposes that the site and histopathological type of the primary cancer determine the organ distribution patterns, which first was reported by Paget in 1889, who proposed the concept of “seed” for metastatic tumor cells and of “soil” for the secondary site.[16] A pre-metastatic niche is a recently suggested concept, and according to the concept, prior to colonization, the primary tumor induces the remodelling of an organ microenvironment by circulating tumor cells (CTCs). Then, a metastatic niche is produced to support disseminated tumor cells (DTCs) to localize them.[17,18] A metastatic niche is a microenvironment that supports and facilitates the invasion and growth of metastasis.[19] Finally, there is a new theory that explains the relationship between the primary and metastatic sites as a bidirectional pathway, rather than unidirectional. According to this theory, the surviving cancer cells in the secondary tumor site have the ability to return to the primary site to accelerate the primary tumor progression.[20,21]
RESULTS
Of the 107 case reports of distant metastasis, 67 were in men and 36 in women. The male and female patients' age ranged from 20–92 and 6–79 years, respectively. Distant soft tissue metastases most commonly occurred in the lung with 23 cases, followed by the heart with 10 cases. Metastasis to different bones occurred in 23 cases, with a higher incidence to vertebral bones in 11 cases. In 8 cases, the primary and secondary tumors were discovered at the same time. In 16 cases, the distant metastasis occurred bilaterally, and in 2 cases there were multiple metastases. In 13 cases, the distant metastasis occurred in the contralateral side. In 6 cases, the distant metastasis was the first sign of the presence of a malignancy. In 47 cases, the distant metastasis occurred in more than one site, more commonly in the lung with 22 cases. The most common histologic type was SCC with 55 cases for soft tissue metastases, and ameloblastoma with 23 cases for jaw bone metastases. In addition, there were 18 cases of distant metastasis from the oral cavity minor salivary gland tumors.
The details are summarized in Tables 1–3 to aid comparison.
Table 1.
Demographic characteristics of distant metastasis from the oral cancer among 67 males
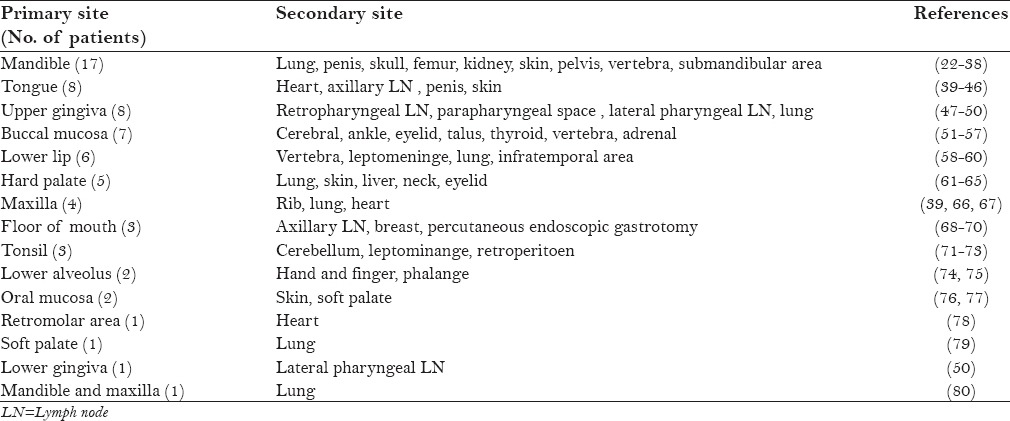
Table 3.
Demographic characteristics of distant metastasis from the oral cancer among patients with unknown gender
Table 2.
Demographic characteristics of distant metastasis from the oral cancer among 36 females

DISCUSSION
There is a high risk of developing a second primary tumor in oral cancer patients.[111] Distant metastasis is another problem with oral cancer which is not so common and correlates with advanced stages of oral cancer.[112] Although the tongue is considered to be the most common site for cancer development, the present review indicated that the gingiva was the most frequent primary site for distant metastasis. A previous study showed that the rate of distant metastasis from the tongue was 4.1%, and was lower than that from upper gingiva carcinomas (6.6%).[113] The lip cancer comprises 30% of the oral cancer and 2.06% of all cancer cases.[114,115] The lip carcinoma shows regional lymph node metastasis in 3–29% of cases. In the present review, only 1 case of lip carcinoma metastasis to the lung has been found.
Although amelolastoma is histologically a benign and slow growing tumor mostly in the mandible, it can metastasize to the cervical lymph nodes and distant sites.[116] In the present review, 22 cases (20.5%) of distant metastasis from ameloblastoma have been reported. In 15 cases (68%), the distant metastasis was developed in the lungs. In addition, there was a case of mandibular ameloblastoma, metastasiazing to the eye. Metastatic head and neck tumor to the brain is the rare.[69] A previous study has shown that metastasis to the brain occurred in 6% of head and neck cancer patients.[117] In the current review, metastasis to the brain and skull was detected in 10 (9.3%) cases.
In conclusion, distant metastasis from the oral cavity is not so common an event, however, because it mostly occurs in the advanced stages of a malignancy, careful examination of the patient during primary cancer treatment has a significant impact on a patient's life.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
REFERENCES
- 1.Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P. Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 2005;55:74–108. doi: 10.3322/canjclin.55.2.74. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Takes RP, Rinaldo A, Silver CE, Haigentz M, Jr, Woolgar JA, Triantafyllou A, et al. Distant metastases from head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Part I. Basic aspects. Oral Oncol. 2012;48:775–9. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2012.03.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Kotwall C, Sako K, Razack MS, Rao U, Bakamjian V, Shedd DP. Metastatic patterns in squamous cell cancer of the head and neck. Am J Surg. 1987;154:439–42. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(89)90020-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Irani S. Metastasis to head and neck area: A 16-year retrospective study. Am J Otolaryngol. 2011;32:24–7. doi: 10.1016/j.amjoto.2009.09.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Spano D, Heck C, De Antonellis P, Christofori G, Zollo M. Molecular networks that regulate cancer metastasis. Semin Cancer Biol. 2012;22:234–49. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2012.03.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Derksen PW, Liu X, Saridin F, van der Gulden H, Zevenhoven J, Evers B, et al. Somatic inactivation of E-cadherin and p53 in mice leads to metastatic lobular mammary carcinoma through induction of anoikis resistance and angiogenesis. Cancer Cell. 2006;10:437–49. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2006.09.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Irani S, Salajegheh A, Smith RA, Lam AK. A review of the profile of endothelin axis in cancer and its management. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2014;89:314–21. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2013.08.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Jechlinger M, Grunert S, Tamir IH, Janda E, Ludemann S, Waerner T, et al. Expression profiling of epithelial plasticity in tumor progression. Oncogene. 2003;22:7155–69. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1206887. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Chiarugi P, Giannoni E. Anoikis: A necessary death program for anchorage-dependent cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 2008;76:1352–64. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2008.07.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Geiger TR, Peeper DS. The neurotrophic receptor TrkB in anoikis resistance and metastasis: A perspective. Cancer Res. 2005;65:7033–6. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-0709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Gimbrone MA, Jr, Leapman SB, Cotran RS, Folkman J. Tumor dormancy in vivo by prevention of neovascularization. J Exp Med. 1972;136:261–76. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.2.261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Irani S, Salajegheh A, Gopalan V, Smith RA, Lam AK. Expression profile of endothelin 1 and its receptor endothelin receptor A in papillary thyroid carcinoma and their correlations with clinicopathologic characteristics. Ann Diagn Pathol. 2014;18:43–8. doi: 10.1016/j.anndiagpath.2013.11.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Chang YS, di Tomaso E, McDonald DM, Jones R, Jain RK, Munn LL. Mosaic blood vessels in tumors: Frequency of cancer cells in contact with flowing blood. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000;97:14608–13. doi: 10.1073/pnas.97.26.14608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Fidler IJ. Critical factors in the biology of human cancer metastasis: Twenty-eighth G.H.A. Clowes memorial award lecture. Cancer Res. 1990;50:6130–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Hoon DS, Ferris R, Tanaka R, Chong KK, Alix-Panabieres C, Pantel K. Molecular mechanisms of metastasis. J Surg Oncol. 2011;103:508–17. doi: 10.1002/jso.21690. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Paget S. The distribution of secondary growths in cancer of the breast.1889. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1989;8:98–101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Psaila B, Lyden D. The metastatic niche: Adapting the foreign soil. Nature Rev Cancer. 2009;9:285–93. doi: 10.1038/nrc2621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Erler JT, Bennewith KL, Cox TR, Lang G, Bird D, Koong A, et al. Hypoxia-induced lysyl oxidase is a critical mediator of bone marrow cell recruitment to form the premetastatic niche. Cancer Cell. 2009;15:35–44. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2008.11.012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Zoccoli A, Iuliani M, Pantano F, Imperatori M, Intagliata S, Vincenzi B, et al. Premetastatic niche: Ready for new therapeutic interventions? Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2012;16(Suppl 2):S119–29. doi: 10.1517/14728222.2012.656092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Comen E, Norton L, Massague J. Clinical implications of cancer self-seeding. Nature Rev Clin Oncol. 2011;8:369–77. doi: 10.1038/nrclinonc.2011.64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Kim MY, Oskarsson T, Acharyya S, Nguyen DX, Zhang XH, Norton L, et al. Tumor self-seeding by circulating cancer cells. Cell. 2009;139:1315–26. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.11.025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Ghiam A, Al Zahrani A, Feld R. A case of recurrent metastatic ameloblastoma and hypercalcaemia successfully treated with carboplatin and paclitaxel: Long survival and prolonged stable disease. Ecancermedicalscience. 2013;7:323. doi: 10.3332/ecancer.2013.323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Phillips SD, Corio RL, Brem H, Mattox D. Ameloblastoma of the mandible with intracranial metastasis. A case study. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1992;118:861–3. doi: 10.1001/archotol.1992.01880080083018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.White RM, Patterson JW. Distant skin metastases in a long-term survivor of malignant ameloblastoma. J Cutan Pathol. 1986;13:383–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0560.1986.tb00474.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Ciment LM, Ciment AJ. Malignant ameloblastoma metastatic to the lungs 29 years after primary resection: A case report. Chest. 2002;121:1359–61. doi: 10.1378/chest.121.4.1359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Oka K, Fukui M, Yamashita M, Takeshita I, Fujii K, Kitamura K, et al. Mandibular ameloblastoma with intracranial extension and distant metastasis. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 1986;88:303–9. doi: 10.1016/s0303-8467(86)80051-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Chiu GA, Woodwards RT, Benatar B, Hall R. Mandibular central mucoepidermoid carcinoma with distant metastasis. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2012;41:361–3. doi: 10.1016/j.ijom.2011.10.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Amzerin M, Fadoukhair Z, Belbaraka R, Iraqui M, Boutayeb S, M'Rabti H, et al. Metastatic ameloblastoma responding to combination chemotherapy: Case report and review of the literature. J Med Case Rep. 2011;5:491. doi: 10.1186/1752-1947-5-491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Hayakawa K, Hayashi E, Aoyagi T, Hata M, Kuramoto C, Tonogi M, et al. Metastatic malignant ameloblastoma of the kidneys. Int J Urol. 2004;11:424–6. doi: 10.1111/j.1442-2042.2004.00822.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Campbell D, Jeffrey RR, Wallis F, Hulks G, Kerr KM. Metastatic pulmonary ameloblastoma. An unusual case. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2003;41:194–6. doi: 10.1016/s0266-4356(03)00046-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Cardoso Guimaraes G, Rodrigues De Souza R, Paiva Gadelha Guimaraes A, Filho WD, Valeschka De Matos Granja N, Karan Kalil R, et al. Penile metastasis of chondrosarcoma of the jaw. Urology. 2003;61:837. doi: 10.1016/s0090-4295(02)02431-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Shamim T, Varghese VI, Shameena PM, Sudha S. Primary intraosseous adenoid cystic carcinoma of the mandible with lung metastasis: A case report. J Oral Sci. 2008;50:95–8. doi: 10.2334/josnusd.50.95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Georgakas I, Lazaridou M, Dimitrakopoulos I, Tilaveridis I, Sekouli A, Papakosta D, et al. Pulmonary metastasis in a 65-year-old man with mandibular ameloblastoma: A case report and review of the literature. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2012;70:1109–13. doi: 10.1016/j.joms.2011.04.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Mano T, Wada N, Uchida K, Muraki Y, Nagatsuka H, Ueyama Y. Central adenoid cystic carcinoma of the mandible with multiple bone metastases: Case report. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2010;68:446–51. doi: 10.1016/j.joms.2009.07.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Luo DY, Feng CJ, Guo JB. Pulmonary metastases from an Ameloblastoma: Case report and review of the literature. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2012;40:e470–4. doi: 10.1016/j.jcms.2012.03.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Devenney-Cakir B, Dunfee B, Subramaniam R, Sundararajan D, Mehra P, Spiegel J, et al. Ameloblastic carcinoma of the mandible with metastasis to the skull and lung: Advanced imaging appearance including computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging and positron emission tomography computed tomography. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 2010;39:449–53. doi: 10.1259/dmfr/29356719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Golubovic M, Petrovic M, Jelovac DB, Nenezic DU, Antunovic M. Malignant ameloblastoma metastasis to the neck--Radiological and pathohistological dilemma. Vojnosanit Pregl. 2012;69:444–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Nguyen BD. Malignant ameloblastoma with thoracic vertebral metastasis: PET/CT and MR imaging. Clin Nucl Med. 2005;30:450–2. doi: 10.1097/01.rlu.0000163382.16320.6b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Oo AL, Yamaguchi S, Iwaki H, Amagasa T. Axillary nodal metastasis from oral and maxillofacial cancers: A report of 3 cases. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2004;62:1019–24. doi: 10.1016/j.joms.2003.08.042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Hans S, Chauvet D, Sadoughi B, Brasnu DF. Cardiac metastasis after squamous cell carcinoma of the base of tongue. Am J Otolaryngol. 2009;30:206–8. doi: 10.1016/j.amjoto.2008.03.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Chaux A, Amin M, Cubilla AL, Young RH. Metastatic tumors to the penis: A report of 17 cases and review of the literature. Int Surg Pathol. 2011;19:597–606. doi: 10.1177/1066896909350468. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Rivkin A, Meara JG, Li KK, Potter C, Wenokur R. Squamous cell metastasis from the tongue to the myocardium presenting as pericardial effusion. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1999;120:593–5. doi: 10.1053/hn.1999.v120.a84489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Macri GF, Greco A, Gallo A, Fusconi M, Marinelli C, de Vincentiis M. Use of electrochemotherapy in a case of neck skin metastasis of oral squamous cell carcinoma: Case report and considerations. Head Neck. 2014;36:E86–90. doi: 10.1002/hed.23552. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Nagata S, Ota K, Nagata M, Shinohara M. Cardiac metastasis of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2012;41:1458–62. doi: 10.1016/j.ijom.2012.07.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.McKeag N, Hall V, Johnston N, McClements B. Cardiac metastasis from a squamous cell carcinoma of the tongue in the absence of local recurrence. Ulster Med J. 2013;82:193–4. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Adelson RT, Ducic Y. Metastatic head and neck carcinoma to a percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy site. Head Neck. 2005;27:339–43. doi: 10.1002/hed.20159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Kimura Y, Hanazawa T, Sano T, Okano T. Lateral retropharyngeal node metastasis from carcinoma of the upper gingiva and maxillary sinus. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1998;19:1221–4. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Umeda M, Minamikawa T, Yokoo S, Komori T. Metastasis of maxillary carcinoma to the parapharyngeal space: Rationale and technique for concomitant en bloc parapharyngeal dissection. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2002;60:408–13. doi: 10.1053/joms.2002.31253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Martı'neza EA AF, Sánchez Silesc M, Jornetc PL. Melanoma of the oral mucosa with cerebral metastasis: A clinical case. Oral Oncol Extra. 2005;41:30–3. [Google Scholar]
- 50.Umeda M, Shigeta T, Takahashi H, Kataoka T, Oguni A, Minamikawa T, et al. Metastasis to the lateral retropharyngeal lymph node from squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity: Report of three cases. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surgery. 2009;38:1004–8. doi: 10.1016/j.ijom.2009.04.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Leimert M, Juratli TA, Lindner C, Geiger KD, Gerber J, Schackert G, et al. An extremely rare, remote intracerebral metastasis of oral cavity cancer: A case report. Case Rep Med. 2013;2013:257046. doi: 10.1155/2013/257046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Suhag V, Sunita BS, Sridhar PS, Rautray D, Singh HP, Kallur KG, et al. Carcinoma Buccal Mucosa with Metastasis to Left Adrenal. Med J Armed Forces India. 2011;67:80–2. doi: 10.1016/S0377-1237(11)80027-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Pichi B, Marchesi P, Manciocco V, Ruscito P, Pellini R, Cristalli G, et al. Carcinoma of the buccal mucosa metastasizing to the talus. J Craniofac Surg. 2009;20:1142–5. doi: 10.1097/SCS.0b013e3181abb469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Thomas M, Bhatt V, James G, Ayshford C. Metastasis to the thyroid from oral squamous cell carcinoma. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2009;47:500–1. doi: 10.1016/j.bjoms.2009.01.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Asproudis I, Gorezis S, Aspiotis M, Tsanou E, Kitsiou E, Merminga E, et al. Orbital metastasis from verrucous carcinoma of the oral cavity: Case report and review of the literature. In vivo. 2007;21:909–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Mathew BS, Jayasree K, Madhavan J, Nair MK, Rajan B. Skeletal metastases and bone marrow infiltration from squamous cell carcinoma of the buccal mucosa. Oral Oncology. 1997;33:454–5. doi: 10.1016/s0964-1955(97)00043-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Ho KK, Lin HY, Chao HL, Lin CS. Unusual distant metastatic lesion from buccal carcinoma mimics refractory gouty arthritis. Oral Oncol Extra. 2005;41:303–5. [Google Scholar]
- 58.Vahtsevanos K, Ntomouchtsis A, Andreadis C, Patrikidou A, Karakinaris G, Mangoudi D, et al. Distant bone metastases from carcinoma of the lip: A report of four cases. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2007;36:180–5. doi: 10.1016/j.ijom.2006.07.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Sullivan LM, Smee R. Leptomeningeal carcinomatosis from perineural invasion of a lip squamous cell carcinoma. Australas Radiol. 2006;50:262–6. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1673.2006.01577.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Olusanya AA, Akadiri OA, Akinmoladun VI, Adeyemi BF. Polymorphous low grade adenocarcinoma: Literature review and report of lower lip lesion with suspected lung metastasis. J Maxillofac Oral Surg. 2011;10:60–3. doi: 10.1007/s12663-011-0185-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Hong HJ, Byeon HK, Bae SH, Park AY, Choi EC, Choi HS. Carcinoma ex pleomorphic adenoma in the oral cavity: A huge oral cavity mass with neck metastasis. J Craniofac Surg. 2013;24:e543–6. doi: 10.1097/SCS.0b013e31829ac5f9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Gutmann SM, Weiss JS, Albert DM. Choroidal metastasis of adenocystic carcinoma of the salivary gland. Br J Ophthalmol. 1986;70:100–3. doi: 10.1136/bjo.70.2.100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Herd MK, Murugaraj V, Ghataura SS, Brennan PA, Anand R. Low-grade mucoepidermoid carcinoma of the palate-a previously unreported case of metastasis to the liver. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2012;70:2343–6. doi: 10.1016/j.joms.2011.11.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Sun J, Gao Q, Fan VT. Multifocal cutaneous metastases from squamous cell carcinoma of hard palate. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2012;41:807–9. doi: 10.1016/j.ijom.2011.12.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Matsuoka K. Oral malignant melanoma detected after resection of amelanotic pulmonary metastasis. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2013;4:1169–72. doi: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2013.10.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Lopez Guerra JL, Foro Arnalot P, Algara Lopez M. Breast metastases from a floor of the mouth carcinoma. Clin Transl Oncol. 2008;10:522–4. doi: 10.1007/s12094-008-0244-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Ananth S, Amin M. Implantation of oral squamous cell carcinoma at the site of a percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy: A case report. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2002;40:125–30. doi: 10.1054/bjom.2001.0740. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Biswal BM, Goyal M, Prasad RR, Lal P, Sharma R, Mohanti BK, et al. Leptomeningeal carcinomatosis from carcinoma of the palatine tonsil. Australas Radiol. 1998;42:66–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1673.1998.tb00567.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Djalilian HR, Tekin M, Hall WA, Adams GL. Metastatic head and neck squamous cell carcinoma to the brain. Auris Nasus Larynx. 2002;29:47–54. doi: 10.1016/s0385-8146(01)00113-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Hofmann U, O'Connor JP, Biyani CS, Harnden P, Selby P, Weston PM. Retroperitoneal metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the tonsil (with elevated beta human chorionic gonadotrophin): A misdiagnosis as extra-gonadal germ cell tumour. J Laryngol Otol. 2006;120:885–7. doi: 10.1017/S0022215106001642. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Lin Y, He JF, Li ZY, Liu JH. Ameloblastoma with varied sites of metastasis: Report of two cases and literature review. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2014;42:e301–4. doi: 10.1016/j.jcms.2013.10.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Zwahlen RA, Vogt P, Fischer FS, Gratz KW. Case report: Myocardial metastasis of a maxillary malignant ameloblastoma. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2003;61:731–4. doi: 10.1053/joms.2003.50146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Berger AJ, Son J, Desai NK. Malignant ameloblastoma: Concurrent presentation of primary and distant disease and review of the literature. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2012;70:2316–26. doi: 10.1016/j.joms.2011.11.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Viswanathan PN, Rangad F, Roul RK. J Hand Surg Br. 1996;21:544–6. doi: 10.1016/s0266-7681(96)80062-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Shrivastava R, Singh KK, Umbarker BR, Karle R, Shrivastava M. Phalange metastasis from carcinoma of alveolus. Indian J Dent Res. 2009;20:496–8. doi: 10.4103/0970-9290.59452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Watanabe T, Yoshida Y, Yamamoto O. Cutaneous metastasis of squamous cell carcinoma of oral mucosa with a purpura-like appearance with tumor thrombosis in lymphatic vessels. Dermatol Surgery. 2010;36:1491–2. doi: 10.1111/j.1524-4725.2010.01667.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Vaidya AM, Vaidya AM, Petruzzelli GJ, McClatchey KD. Isolated submandibular gland metastasis from oral cavity squamous cell carcinoma. Am J Otolaryngol. 1999;20:172–5. doi: 10.1016/s0196-0709(99)90067-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Tsai YT, Kuo SW, Hao SP. Cardiac tamponade: A rare presentation from a rare metastatic site in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2010;267:1483–5. doi: 10.1007/s00405-010-1304-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Akan H, Yildiz L, Unal R. Carcinoma ex pleomorphic adenoma of the minor salivary gland with pulmonary metastasis. Diagn Interv Radiol. 2008;14:3–5. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Onerci M, Yilmaz T, Dogan R, Sungur A. Pulmonary metastasectomy in the treatment of recurrent ameloblastoma of the maxilla and mandible: A case report. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2001;258:25–7. doi: 10.1007/s004050000293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Hayashi N, Iwata J, Masaoka N, Ueno H, Ohtsuki Y, Moriki T. Ameloblastoma of the mandible metastasizing to the orbit with malignant transformation. A histopathological and immunohistochemical study. Virchows Arch. 1997;430:501–7. doi: 10.1007/s004280050061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Rayatt SS, Dancey AL, Fagan J, Srivastava S. Axillary metastases from recurrent oral carcinoma. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2004;42:264–6. doi: 10.1016/j.bjoms.2003.12.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Basu S, Shet T, Awasare S. Bilateral adrenal metastases and metastatic subcutaneous deposit in the chest wall from osteosarcoma of the mandible: Utility of 18F-FDG-PET. Hell J Nucl Med. 2009;12:51–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Senra GS, Pereira AC, Murilo dos Santos L, Carvalho YR, Brandao AA. Malignant ameloblastoma metastasis to the lung: A case report. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2008;105:e42–6. doi: 10.1016/j.tripleo.2007.09.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Kumar M, Fasanmade A, Barrett AW, Mack G, Newman L, Hyde NC. Metastasising clear cell odontogenic carcinoma: A case report and review of the literature. Oral Oncol. 2003;39:190–4. doi: 10.1016/s1368-8375(02)00012-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Takeuchi S, Kobayashi K, Minakawa T, Azumi T, Fukushima M. Metastatic ameloblastoma of the skull. Surg Neurol. 1981;15:182–5. doi: 10.1016/0090-3019(81)90136-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Henderson JM, Sonnet JR, Schlesinger C, Ord RA. Pulmonary metastasis of ameloblastoma: Case report and review of the literature. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 1999;88:170–6. doi: 10.1016/s1079-2104(99)70113-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Dissanayake RK, Jayasooriya PR, Siriwardena DJ, Tilakaratne WM. Review of metastasizing (malignant) ameloblastoma (METAM): Pattern of metastasis and treatment. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2011;111:734–41. doi: 10.1016/j.tripleo.2010.12.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Ueta E, Yoneda K, Ohno A, Osaki T. Intraosseous carcinoma arising from mandibular ameloblastoma with progressive invasion and pulmonary metastasis. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1996;25:370–2. doi: 10.1016/s0901-5027(06)80033-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Park HR, Min JH, Huh KH, Yi WJ, Heo MS, Lee SS, et al. Distant metastasis of intraosseous dentinogenic ghost cell tumour to the donor site of a bone graft. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 2013;42:20120172. doi: 10.1259/dmfr.20120172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.McDermott M, Gamis AS, el-Mofty S, Dehner LP. Adenocarcinoma of minor salivary gland origin with skeletal metastasis in a child. Pediatr Pathol Lab Med. 1996;16:89–98. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Weissferdt A, Langman G. An intracapsular carcinoma ex pleomorphic adenoma with lung metastases composed exclusively of benign elements: Histological evidence of a continuum between metastasizing pleomorphic adenoma and carcinoma ex pleomorphic adenoma. Pathol Res Pract. 2010;206:480–3. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2009.07.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Schwender FT, Wollner I, Kunju LP, Nakhleh RE, Chan KM. Squamous cell carcinoma of the buccal mucosa with metastases to the pericardial cavity, lung and thyroid. Oral Oncol. 2002;38:114–6. doi: 10.1016/s1368-8375(01)00021-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Ettl T, Kleinheinz J, Mehrotra R, Schwarz S, Reichert TE, Driemel O. The buccal minor salivary glands as starting point for a metastasizing adenocarcinoma--Report of a case. Head Face Med. 2008;4:16. doi: 10.1186/1746-160X-4-16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Zatterstrom U, Thor A, Nordgren H. Cervical metastasis from Spitz nevus of the buccal mucosa. Melanoma Res. 2008;18:36–9. doi: 10.1097/CMR.0b013e3282f356e4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Desai SR, Angarkar NN, Patil NJ, Dombale VD, Kulkarni SR. Primary malignant melanoma of left buccal mucosa with metastasis in thyroid: A case report. Indian J Pathol Microbiol. 2007;50:385–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Mitra S, Kundu S, Pattari SK, Ghosal AG. Metastatic pleural effusion: A rare presentation of salivary gland adenoid cystic carcinoma. Indian J Chest Dis Allied Sci. 2011;53:107–10. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Rednam S, Hicks J, Levy ML, Pappo AS. Metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the oropharynx in a child with a mutation in the Connexin 26 gene. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2011;33:387–9. doi: 10.1097/MPH.0b013e3181e65c1c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Thennavan A, Rao L, Radhakrishnan R. Polymorphous low-grade adenocarcinoma of maxillary alveolus metastasising to the abdomen: The role of immunomarkers in diagnosis. BMJ Case Rep 2013. 2013 doi: 10.1136/bcr-2013-009633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Okami J, Tomita Y, Higashiyama M, Kodama K. Solitary pulmonary metastasis of mucoepidermoid carcinoma of the palate 43 years after the initial treatment. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2009;9:728–9. doi: 10.1510/icvts.2009.211755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Hannen EJ, Bulten J, Festen J, Wienk SM, de Wilde PC. Polymorphous low grade adenocarcinoma with distant metastases and deletions on chromosome 6q23-qter and 11q23-qter: A case report. J Clin Pathol. 2000;53:942–5. doi: 10.1136/jcp.53.12.942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Shukla GP, Pant MC, Husain N, Gupta D, Bisht SS, Gupta S, Verma J. Bilateral Renal Metastases In Oral Leiomyosarcoma: A Case Report. Internet J Radiol. 2010;11:3. [Google Scholar]
- 103.Onwuchekwa J, Banchs J. Early cardiac metastasis from squamous cell carcinoma of the tongue in 2 patients. Tex Heart Inst J. 2012;39:565–7. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Sa YJ, Sim SB, Kim TJ, Moon SW, Park CB. Late-developing tongue adenoid cystic carcinoma after pulmonary metastasectomy: A case report. World J Surg Oncol. 2014;12:102. doi: 10.1186/1477-7819-12-102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Dobelbower MC, Nabell L, Markert J, Carroll W, Said-Al-Naief N, Meredith R. Cancer of the tonsil presenting as central nervous system metastasis: A case report. Head Neck. 2009;31:127–30. doi: 10.1002/hed.20834. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Munshi A, Sharma R, Iyer VK, Chander B, Rath GK. Carcinoma of the tonsil with bilateral breast metastasis: A rare presentation. Australas Radiol. 2005;49:519–21. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1673.2005.01504.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Zemann W, Feichtinger M, Kowatsch E, Schanbacher M, Karcher H. Cardiac metastasis after squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity: Case report. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2007;45:425–6. doi: 10.1016/j.bjoms.2005.12.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Torre W, Comellas M, Cuesta M. Massive pleural effusion as isolated manifestation of metastatic spread of salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma. Respir Med. 1997;91:169–70. doi: 10.1016/s0954-6111(97)90053-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Poovaneswaran S, Paleri V, Charlton F, Dobrowsky W, Kelly C. Cutaneous metastases from head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Med J Malaysia. 2012;67:430–2. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Carlson ER, Ord RA. Vertebral metastases from oral squamous cell carcinoma. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2002;60:858–62. doi: 10.1053/joms.2002.33851. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Irani S, Monsef Esfahani A, Bidari Zerehpoush F. Detection of Helicobacterpylori in Oral Lesions. J Dent Res Dent Clin Dent Prospects. 2013;7:230–7. doi: 10.5681/joddd.2013.037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Betka J. Distant metastases from lip and oral cavity cancer. ORL J Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec. 2001;63:217–21. doi: 10.1159/000055744. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Osaki T, Yoneda K, Yamamoto T, Kimura T, Matuoka H, Sakai H, et al. Clinical investigation on pulmonary metastasis of head and neck carcinomas. Oncology. 2000;59:196–203. doi: 10.1159/000012161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Heller KS, Shah JP. Carcinoma of the lip. Am J Surg. 1979;138:600–3. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(79)90427-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Salgarelli AC, Sartorelli F, Cangiano A, Collini M. Treatment of lower lip cancer: An experience of 48 cases. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2005;34:27–32. doi: 10.1016/j.ijom.2004.01.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Adebayo ET, Fomete B, Adekeye EO. Delayed soft tissue recurrence after treatment of ameloblastoma in a black African: Case report and review of the literature. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2011;39:615–8. doi: 10.1016/j.jcms.2010.05.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Posner JB, Chernik NL. Intracranial metastases from systemic cancer. Adv Neurol. 1978;19:579–92. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


