Abstract
Aims:
The present study aimed to compare apical sealing ability between GuttaFlow and AH Plus.
Materials and Method:
Eighty extracted human maxillary anterior teeth with fully formed apex and straight root were collected for this study. The root canals were cleaned and shaped using a standard step back preparation to size 60# master apical file at the established working length and divided into four groups: Group 1, GuttaFlow sealer with gutta-percha; Group 2, AH Plus sealer with gutta-percha; Group 3, positive control group (Teeth were instrumented and left without obturation); Group 4, negative control group (Teeth were totally coated with nail varnish) Dye leakage was carried out. Statistical analysis was done using the Statistical Package for the Social Sciences software and Student's unpaired t-test.
Results:
The GuttaFlow group had a mean leakage of 1.38 mm whereas AH Plus had a mean of 1.425 mm. The standard deviation of GuttaFlow and AH Plus were 0.3861 and 0.3226, respectively. Student's unpaired t-test disclosed no significant difference (P < 0.05) between the groups.
Conclusion:
None of the sealers used in the study could completely seal the apical foramen to have a fluid-tight seal. GuttaFlow and AH Plus showed no statistically significant difference in microleakage; the better result was shown by GuttaFlow.
Key words: AH Plus, apical leakage, GuttaFlow, sealer
INTRODUCTION
Obliteration of the root canal space with an inert filling material, formation of a hermetic seal, and elimination of any portal entry or exit to periapical tissues have been suggested as objectives for effective endodontic treatment.[1]
A key to successful endodontics and a major aim of modern nonsurgical root canal treatment is to seal completely both the apical and coronal routes of potential leakage and maintain the disinfected status achieved by chemical or mechanical cleaning and to prevent reinfection and passage of bacterial byproducts, allowing the periodontium to maintain its integrity and to achieve healing.[2]
The method most commonly recommended for obturation is the use of a large mass of solid and inert material (gutta-percha) associated with an endodontic sealer applied using the lateral-condensation obturation technique.[3]
For complete sealing of the canal, the root canal sealer is required to have bonding capability with the dentin of the root canal. Advances in adhesives have endorsed attempts to reduce leakage by bonding to root canal walls. Total-etch adhesives have been used with resin cements as one of alternative root filling materials. The results demonstrated that dentin adhesives significantly reduced apical leakage. Self-etching primers have conjointly been tested for bonding to root canal dentin.[4]
Various materials used as sealers have been tested from time to time to evaluate their sealing abilities to fulfill the objective of obtaining a hermetic apical seal.
The purpose of this study is to compare systematically the apical sealing ability provided by two endodontic sealers, namely, GuttaFlow and AH Plus using a dye penetration method.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Eighty extracted human maxillary anterior teeth with fully formed apex and straight root were collected for this study. All the teeth were stored in 4% formalin until the sample was completed. Organic debris was removed by storing teeth in 5.25% sodium hypochlorite for 8 h. Subsequently, they were washed with tap water for 1 h and stored in saline until use.
The most common and most scientific method of sample size calculation is power analysis. This method is one of the methods used for calculating sample size for clinical studies and clinical trials. Simple calculation was carried out manually with the help of the same formula, sample size = 2 SD2 (1.96 + 0.842)2/d2.
Exclusion criteria
Incompletely formed root apex
Evident root fracture
Bifurcating canals
Calcified canals
Pulp stones.
Inclusion criteria
Caries-free teeth
Type I root canal anatomy.
With the help of a diamond disk with water splash coolant, teeth were decoronated to obtain a standardized length of 15 mm, following pulp extirpation with barbed broach, a size 15 K file was inserted into canal until it was seen at the apical foramen to check for apical patency. Working length was determined to be 1 mm short of that position. Root canals were cleaned and shaped using standard step back preparation to size 60# master apical file at the established working length. 5.25% sodium hypochlorite and saline was used for irrigation between instrumentation and dried with paper points. The teeth were randomly divided into four groups of 20 each.
Groups
Teeth were divided into (20 samples containing each)
Group 1 – GuttaFlow sealer with gutta-percha
Group 2 – AH Plus sealer with gutta-percha
Group 3 – Positive control group (teeth were instrumented and left without obturation)
Group 4 – Negative control group (teeth were completely coated with nail varnish).
Canal filling
The prepared teeth were filled by using the lateral compaction technique. Endodontic sealers were mixed and used according to manufacturer's instructions, and introduced into the canal space using Lentulo spiral filler.
Group 1: GuttaFlow sealer with gutta-percha
Twenty teeth in group 1 were obturated with cold lateral condensation. A standardized ISO No. 60 Master Cone guttapercha was fitted up to the working length. GuttaFlow sealer was mixed according to the manufacturer's instructions and introduced into the canal. The apical part of master gutta-percha cone was coated with sealer and placed into the canal. The master cone was laterally condensed by finger spreader, inserted 1 mm short of working length space created by the spreader, and was filled with auxiliary gutta-percha point. The procedure was repeated until gutta-percha point could not be introduced more than 3 mm into the root canal. Excess gutta-percha was trimmed with a hot plastic instrument and was condensed with a plugger.
Group 2: AH-Plus sealer with gutta-percha
AH Plus sealer was mixed according to the manufacturer's instructions and placed in the canal using a lentulospiral to the working length. The master cone was selected to fit the canal snugly, was coated with AH Plus, and laterally condensed with finger spreaders. Coronal surplus of gutta-percha was removed by heat and the gutta-percha was compacted.
Group 3: Positive control group
Teeth were instrumented and left without obturation.
Group 4: Negative control group
Teeth were completely coated with nail varnish.
Following obturation of each group, gutta-percha was removed from the coronal 2 mm of the obturated root canals with a warm instrument after the sealer had hardened and the coronal end of all canals were sealed with glass ionomer cement.
The teeth were stored in an incubator in 100% humidity at 37°C for 48 h to ensure complete setting of the sealers. Root surfaces of all the samples except negative control were coated with two coats of nail varnish except apical 2 mm. Dye leakage procedure was carried out.
Linear dye leakage method
All the root surfaces of all the teeth were thoroughly dried and coated with two coats of nail varnish, except at the apical 2 mm of the root, with each coat being allowed to dry before the subsequent one was applied.
These samples were suspended in dye, i.e., 1% methylene blue in a glass container for 72 h at 37°C in the incubator. The sample were suspended in the dye in a vertical direction with the help of a sticky wax so that the dye can penetrate by capillary action.
After removal from the dye, the teeth were washed under running tap water to remove excess dye and nail varnish was removed using bard parker blade.
A demineralization and clearing process was carried out. The teeth were demineralized by placing in 5% nitric acid solution; the acid was changed daily for 5 days. The teeth were dehydrated in 70, 80, 90%, and absolute alcohol for 1 h in each concentration. By immersing the teeth in methyl salicylate solution, clearing process was completed.
The samples were then examined under stereomicroscope (magnification: 4–40×) for the evaluation of dye penetration. Single examiner measured the extent of microleakage. The dye penetration scores were recorded and tabulated, and statistical analysis was carried out.
RESULTS
The study was performed to evaluate the apical sealing ability between GuttaFlow and AH Plus. The efficacy was evaluated based on the dye penetration test. This in-vitro study was conducted to evaluate the apical sealing ability between GuttaFlow and AH Plus.
In this study, a total of 80 maxillary anterior teeth were used. They were divided into four groups. The first and second group consisted of 20 samples each, and the third and fourth group had 20 samples each. The first and second group served as GuttFlow and AH Plus, respectively. The third and fourth group served as positive and negative controls, respectively.
The original values of apical microleakage for the two sealers were recorded. [Table 1; Graph 1] The group AH Plus showed more leakage values than the GuttaFlow group. Mean leakage values and standard deviation (SD) for apical leakage of GuttaFlow and AH Plus are shown in Table 2. The results showed that the GuttaFlow group had a mean leakage of 1.38 mm whereas AH Plus had a mean of 1.425 mm [Table 1 and Graph 2]. The SD of GuttaFlow and AH Plus were 0.3861 and 0.3226, respectively [Table 1 and Graph 3].
Table 1.
Descriptive table of dye leakage
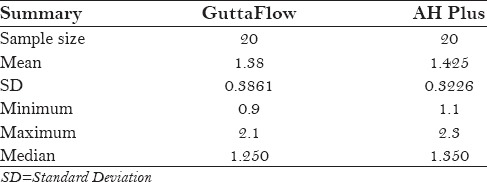
Graph 1.
Original values (in mm) of apical microleakage. (1. Guttaflow Group, 2. AH Plus group)
Table 2.
Comparison of GuttaFlow and AH Plus with respect to microleakage values by Student's unpaired t-test

Graph 2.
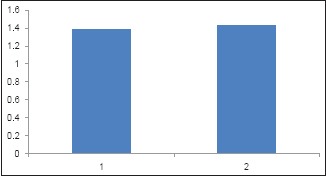
Comparison of GuttaFlow and AH Plus with respect to mean microleakage. (1. Guttaflow Group, 2. AHPlus)
Graph 3.
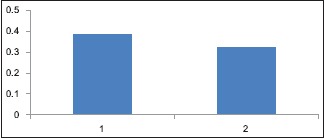
Standard deviation of apical microleakage of both groups. (1. Guttaflow Group, 2. AH Plus Group)
Statistical analysis done using the Statistical Package for Social Sciences software and Student's unpaired t-test disclosed no significant difference (P > 0.05) between the groups [Table 2].
DISCUSSION
The goal of root canal filling is to prevent the ingress of microorganisms and their byproducts along the root canal.[5] Three-dimensional obturation of root canal including apical seal greatly depends on the sealing ability of the obturating material and the root canal sealer.[6] The latter has a significant influence on microleakage of root canal obturation.[7]
A new silicone-based sealer (GuttaFlow) has been introduced as one of various roots filling material. GuttaFlow is 2 in 1 cold, fluid obturation system that mixes sealer and gutta-percha together. It consists of a polymer matrix, which is filled with very finely ground gutta-percha. Polydimethylsiloxane has been utilized in the dental field for many years, especially in prosthodontics, as an impression material with only limited dimensional change in setting expansion. The finely ground gutta-percha powder and the silicone-based matrix are dispensed homogeneously after mixing. Laboratory investigations indicate setting expansion of 0.2%, biocompatibility.[8,9]
GuttaFlow contains nanosilver. Nanosilver is metallic silver that is uniformly dispersed on the surface of the filling. The corrosion or color changes in GuttaFlow are not caused by the chemical type and concentration of the nanosilver. There is adequate nanosilver in the material to avert further spread of bacteria, and nanosilver is highly biocompatible.[10]
AH Plus (Dentsply Maillefer, Ballaigues, Switzerland) is an epoxy-based endodontic sealer that is used with gutta-percha. It consists of a paste-to-paste system, supplied in two tubes in a double barrel syringe. AH Plus contains silicone oils along with other ingredients. AH Plus has a film thickness of approximately 25 mm, which is clearly below the value of less than 50 mm required by the ISO standard for root canal sealing materials.[11]
In this dye leakage study, methylene blue dye was used because it shows a high sensitivity and its particles are of a similar dimension to microorganisms and their metabolites.[12,13]
In the present study, dye penetration was observed in all specimens except the negative control teeth. Statistical analysis revealed that the lowest dye penetration was in Group 1 (GuttaFlow) followed by (in ascending order of dye penetration) Group 2 (AH Plus), and the positive control. Group 2 showed a mean linear dye penetration of 1.425 mm, whereas Group 1 showed a mean linear dye penetration of 1.38 mm. The difference between the mean linear dye penetration between Groups I and II was not statistically significant.
The null hypothesis of the present study was partially accepted because the results showed that the sealing ability of AH plus was similar to that of the GuttaFlow within acceptable limits. The most likely explanation for low mean leakage scores in Group I would be the setting expansion of GuttaFlow by 0.2%, as claimed by manufacturers, and validated in studies.[14,15]
The presence of fine sized gutta-percha particles (nanoparticles less than 30 µ) further bestows increased flowability to GuttaFlow, resulting in better coating capacity and adaptation to root canal walls, as well as into dentinal tubules.[16,17]
Leakage of AH Plus may be rippled from inadequate bonding between the sealer and the gutta-percha point, allowing fluid to pass at the interface. This possibility is in agreement with the results of Tay et al.[18]
One in vitro study compared the microleakage of three sealers, namely, endosequence bioceramic (BC) sealer, AH Plus, and Epiphany, suggesting that newly introduced BC and Epiphany sealers sealed better compared to AH Plus Sealer.[19]
In one comparative study of apical sealing ability of a new resin-based obturation system (Resilion) with AH 26, it was found that there was no significant difference between both the materials.[20]
Study limitations
This is an in vitro study; further in-vivo studies should be conducted to correlate with the present study.
Future research directions
The sealers serve as filler for the canal irregularities as well as minor defects between the canal wall and the filling material. They seal the lateral and the accessory canals and assist in microbial control. Further studies should aim for a better sealing ability on basis of this research platform. This study will be helpful for researchers to work in a most important direction i.e., apical seal on which the success of root canal treatment depends.
CONCLUSION
With the results obtained after evaluation and comparison of the sealing ability of GuttaFlow with AH Plus sealers, it could be concluded that
Two experimental groups showed comparable apical leakage
Dye penetration was observed in all the specimens, except the negative control. This shows that none of the sealers used in the study could completely seal the apical foramen to have a fluid-tight seal
Though GuttaFlow and AH Plus showed no statistically significant difference in microleakage, the better result was shown by GuttaFlow
GuttaFlow seems to be a promising filling material because of the good sealing ability, ease of handling, and application of the material. The results of dye penetration studies only indicate the comparative sealing ability of root canal fillings in vitro and they do not indicate their ability to prevent the ingress of bacteria into filled root canals in vivo
Further in vivo studies need to be done to correlate with the present study.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
REFERENCES
- 1.Evans JT, Simon JH. Evaluation of the apical seal produced by injected thermoplasticized Gutta-percha in the absence of smear layer and root canal sealer. J Endod. 1986;12:100–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Anantula K, Ganta AK. Evaluation and comparison of sealing ability of three different obturation techniques – Lateral condensation, Obtura II, and GuttaFlow: An in vitro study. J Conserv Dent. 2011;14:57–61. doi: 10.4103/0972-0707.80748. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Schilder H. Filling root canals in three dimensions.1967. J Endod. 2006;32:281–90. doi: 10.1016/j.joen.2006.02.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Imai Y, Komabayashi T. Properties of a new inject table type of root canal filling resin with adhesiveness to dentin. J Endod. 2002;29:20–3. doi: 10.1097/00004770-200301000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.European Society of Endodontology. Quality guidelines for endodontic treatment: Consensus report of the European Society of Endodontology. Int Endod J. 2006;39:921–30. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2591.2006.01180.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Kulkarni G. Apical seal between adhesive root canal obturation system and gutta-percha/ah-plus sealer: An in vitro comparison study. J Evid Based Med. Healthc. 2016;3 [Google Scholar]
- 7.Petschelt A, Ebert J, Hickel R. The tightness of root fillings in smear-free root canals. Dtsch Zahnarztl Z. 1988;43:884–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Accardo C, Himel VT, Lallier TE. A novel GuttaFlow sealer supports cell survival and attachment. J Endod. 2014;40:231–4. doi: 10.1016/j.joen.2013.08.029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Bouillaguet S, Wataha JC, Lockwood PE, Galgano C, Golay A, Krejci I. Cytotoxicity and sealing properties of four classes of endodontic sealers evaluated by succinic dehydrogenase activity and confocal laser scanning microscopy. Eur J Oral Sci. 2004;112:182–7. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0722.2004.00115.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.De-Deus G, Brandão MC, Fidel RA, Fidel SR. The sealing ability of GuttaFlow in oval-shaped canals: An ex vivo study using a polymicrobial leakage model. Int Endod J. 2007;40:794–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2591.2007.01295.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Tyagi S, Mishra P, Tyagi P. Evolution of root canal sealers: An insight story. Eur J Gen Dent. 2013;2:199–218. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Matloff IR, Jensen JR, Singer L, Tabibi A. A comparison of methods used in root canal sealability studies. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1982;53:203–8. doi: 10.1016/0030-4220(82)90288-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Kersten HW, Moorer WR. Particles and molecules in endodontic leakage. Int Endod J. 1989;22:118–24. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2591.1989.tb00909.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Ørstavik D, Nordahl I, Tibballs JE. Dimensional change following setting of root canal sealer materials. Dent Mater. 2001;17:512–9. doi: 10.1016/s0109-5641(01)00011-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Elayouti A, Achleithner C, Lost C, Weiger R. Homogeneity and adaptation of a new gutta-percha paste to root canal walls. J Endod. 2005;31:687–90. doi: 10.1097/01.don.0000157991.83577.e0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Gernhardt CR, Kruger T, Bekes K, Schaller HG. Apical sealing ability of 2 epoxy resin-based sealers used with root canal obturation techniques based on warm gutta-percha compared to cold lateral condensation. Quintessence Int. 2007;38:229–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Punia SK, Nadig P, Punia V. An in vitro assessment of apical microleakage in root canals obturated with gutta-flow, resilon, thermafil and lateral condensation: A stereomicroscopic study. J Conserv Dent. 2011;14:173–7. doi: 10.4103/0972-0707.82629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Bouillaguet S, Shaw L, Barthelemy J, Krejci I, Wataha JC. Long-term sealing ability of Pulp Canal Sealer, AH-Plus, GuttaFlow and Epiphany. Int Endod J. 2008;41:219–26. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2591.2007.01343.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Pawar SS, Pujar MA, Makandar SD. Evaluation of the apical sealing ability of bioceramic sealer, AH plus & epiphany: An in vitro study. J Conserv Dent. 2014;17:579–82. doi: 10.4103/0972-0707.144609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Kishan KV, Hegde V. Comparative analysis of sealing ability of a new resin based obturation system using two different techniques- An in vitro study. Indian J Dent Sci. 2015;7:28–30. [Google Scholar]


