Abstract
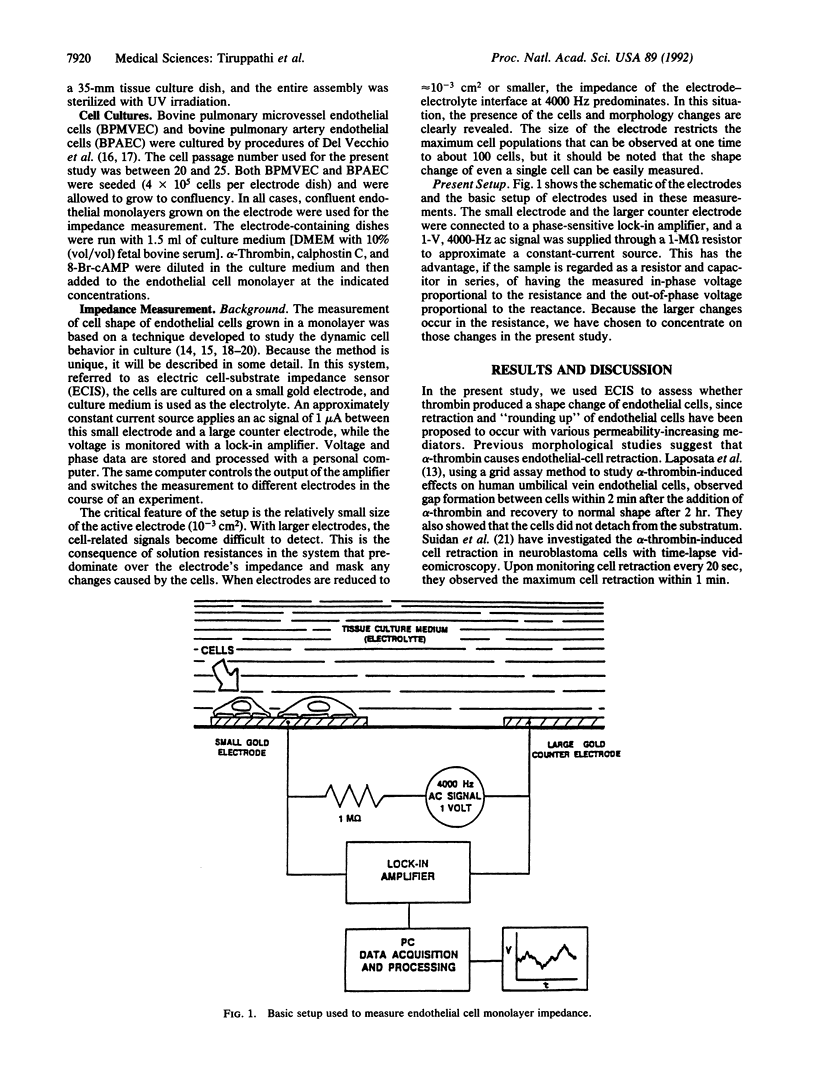
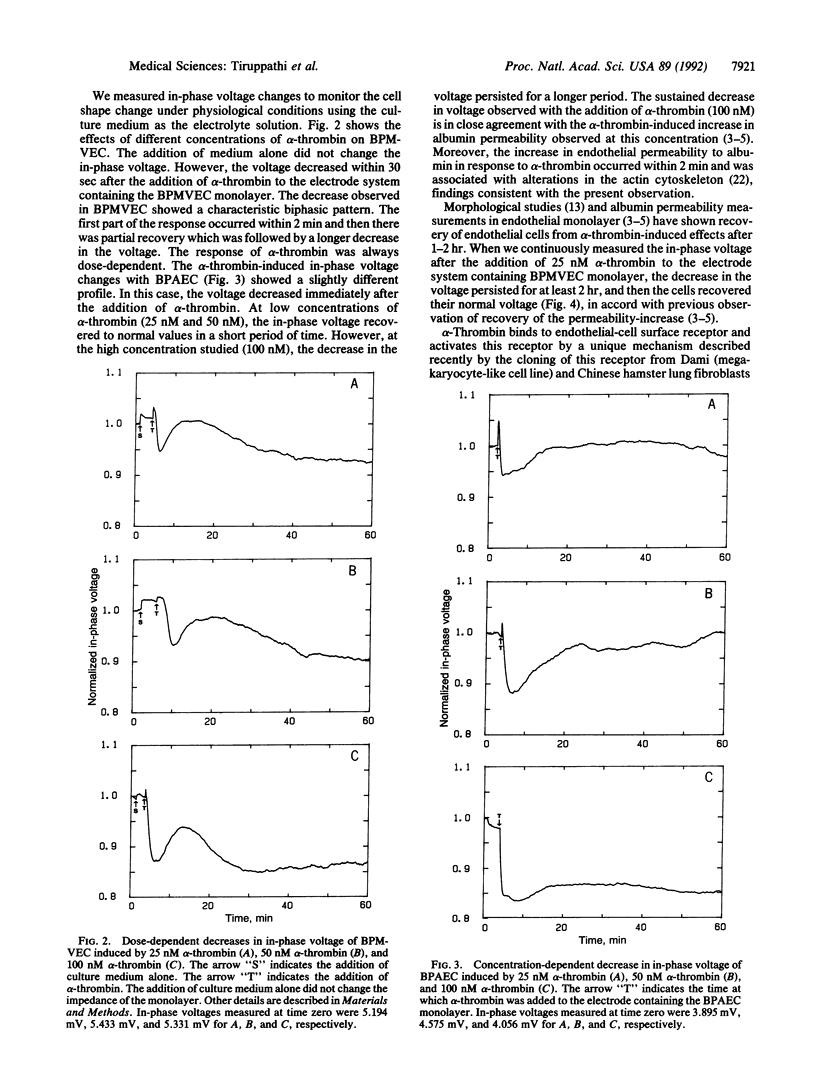
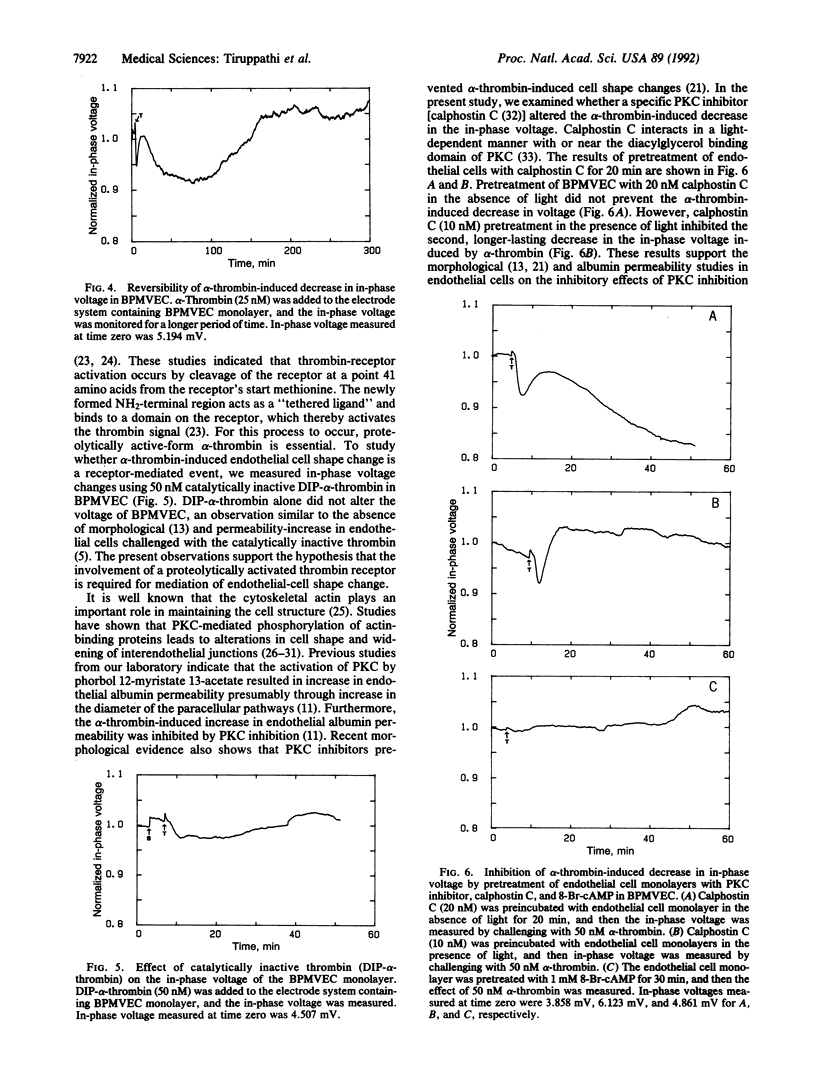
We have developed an electrical method to study endothelial cell shape changes in real time in order to examine the mechanisms of alterations in the endothelial barrier function. Endothelial shape changes were quantified by using a monolayer of endothelial cells grown on a small (10(-3) cm2) evaporated gold electrode and measuring the changes in electrical impedance. Bovine pulmonary microvessel endothelial cells and bovine pulmonary artery endothelial cells were used to study the effects of alpha-thrombin on cell-shape dynamics by the impedance measurement. alpha-Thrombin produced a dose-dependent decrease in impedance that occurred within 0.5 min in both cell types, indicative of retraction of endothelial cells and widening of interendothelial junctions because of "rounding up" of the cells. The alpha-thrombin-induced decrease in impedance persisted for approximately 2 hr, after which the value recovered to basal levels. Pretreatment of endothelial cells with the protein kinase C inhibitor, calphostin C, or with 8-bromoadenosine 3',5'-cyclic monophosphate prevented the decreased impedance, suggesting that the endothelial cell change is modulated by activation of second-messenger pathways. The alpha-thrombin-induced decrease in impedance was in agreement with the previously observed increases in transendothelial albumin permeability and evidence of formation of intercellular gaps after alpha-thrombin challenge. The impedance measurement may be a valuable in vitro method for the assessment of mechanisms of decreased endothelial barrier function occurring with inflammatory mediators. Since the rapidly occurring changes in endothelial cell shape in response to mediators such as thrombin are mediated activation of second-messenger pathways, the ability to monitor endothelial cell dynamics in real time may provide insights into the signal-transduction events mediating the increased endothelial permeability.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aschner J. L., Lennon J. M., Fenton J. W., 2nd, Aschner M., Malik A. B. Enzymatic activity is necessary for thrombin-mediated increase in endothelial permeability. Am J Physiol. 1990 Oct;259(4 Pt 1):L270–L275. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1990.259.4.L270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruns R. F., Miller F. D., Merriman R. L., Howbert J. J., Heath W. F., Kobayashi E., Takahashi I., Tamaoki T., Nakano H. Inhibition of protein kinase C by calphostin C is light-dependent. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Apr 15;176(1):288–293. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)90922-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burridge K., Fath K., Kelly T., Nuckolls G., Turner C. Focal adhesions: transmembrane junctions between the extracellular matrix and the cytoskeleton. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1988;4:487–525. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.04.110188.002415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bussolino F., Camussi G., Aglietta M., Braquet P., Bosia A., Pescarmona G., Sanavio F., D'Urso N., Marchisio P. C. Human endothelial cells are target for platelet-activating factor. I. Platelet-activating factor induces changes in cytoskeleton structures. J Immunol. 1987 Oct 1;139(7):2439–2446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casnocha S. A., Eskin S. G., Hall E. R., McIntire L. V. Permeability of human endothelial monolayers: effect of vasoactive agonists and cAMP. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1989 Nov;67(5):1997–2005. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1989.67.5.1997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crone C. Modulation of solute permeability in microvascular endothelium. Fed Proc. 1986 Feb;45(2):77–83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Del Vecchio P. J., Siflinger-Birnboim A., Shepard J. M., Bizios R., Cooper J. A., Malik A. B. Endothelial monolayer permeability to macromolecules. Fed Proc. 1987 Jun;46(8):2511–2515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galdal K. S., Evensen S. A., Nilsen E. Thrombin-induced shape changes of cultured endothelial cells: metabolic and functional observations. Thromb Res. 1983 Oct 1;32(1):57–66. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(83)90154-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia J. G., Siflinger-Birnboim A., Bizios R., Del Vecchio P. J., Fenton J. W., 2nd, Malik A. B. Thrombin-induced increase in albumin permeability across the endothelium. J Cell Physiol. 1986 Jul;128(1):96–104. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041280115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giaever I., Keese C. R. Micromotion of mammalian cells measured electrically. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 1;88(17):7896–7900. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.17.7896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giaever I., Keese C. R. Monitoring fibroblast behavior in tissue culture with an applied electric field. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(12):3761–3764. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.12.3761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giaever I., Keese C. R. Use of electric fields to monitor the dynamical aspect of cell behavior in tissue culture. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 1986 Feb;33(2):242–247. doi: 10.1109/TBME.1986.325896. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang C. K., Devanney J. F., Kennedy S. P. Vimentin, a cytoskeletal substrate of protein kinase C. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Feb 15;150(3):1006–1011. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(88)90728-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi E., Nakano H., Morimoto M., Tamaoki T. Calphostin C (UCN-1028C), a novel microbial compound, is a highly potent and specific inhibitor of protein kinase C. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Mar 15;159(2):548–553. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)90028-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowolenko M., Keese C. R., Lawrence D. A., Giaever I. Measurement of macrophage adherence and spreading with weak electric fields. J Immunol Methods. 1990 Feb 20;127(1):71–77. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(90)90342-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langeler E. G., van Hinsbergh V. W. Norepinephrine and iloprost improve barrier function of human endothelial cell monolayers: role of cAMP. Am J Physiol. 1991 May;260(5 Pt 1):C1052–C1059. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1991.260.5.C1052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laposata M., Dovnarsky D. K., Shin H. S. Thrombin-induced gap formation in confluent endothelial cell monolayers in vitro. Blood. 1983 Sep;62(3):549–556. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch J. J., Ferro T. J., Blumenstock F. A., Brockenauer A. M., Malik A. B. Increased endothelial albumin permeability mediated by protein kinase C activation. J Clin Invest. 1990 Jun;85(6):1991–1998. doi: 10.1172/JCI114663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malik A. B., Lynch J. J., Cooper J. A. Endothelial barrier function. J Invest Dermatol. 1989 Aug;93(2 Suppl):62S–67S. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12581072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitra P., Keese C. R., Giaever I. Electric measurements can be used to monitor the attachment and spreading of cells in tissue culture. Biotechniques. 1991 Oct;11(4):504–510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullin J. M., O'Brien T. G. Effects of tumor promoters on LLC-PK1 renal epithelial tight junctions and transepithelial fluxes. Am J Physiol. 1986 Oct;251(4 Pt 1):C597–C602. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1986.251.4.C597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ojakian G. K. Tumor promoter-induced changes in the permeability of epithelial cell tight junctions. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):95–103. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90274-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver J. A. Adenylate cyclase and protein kinase C mediate opposite actions on endothelial junctions. J Cell Physiol. 1990 Dec;145(3):536–542. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041450321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson B. T. Permeability: theory vs. practice in lung research. Am J Physiol. 1992 Mar;262(3 Pt 1):L243–L256. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1992.262.3.L243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen U. B., Vouret-Craviari V., Jallat S., Schlesinger Y., Pagès G., Pavirani A., Lecocq J. P., Pouysségur J., Van Obberghen-Schilling E. cDNA cloning and expression of a hamster alpha-thrombin receptor coupled to Ca2+ mobilization. FEBS Lett. 1991 Aug 19;288(1-2):123–128. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)81017-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotrosen D., Gallin J. I. Histamine type I receptor occupancy increases endothelial cytosolic calcium, reduces F-actin, and promotes albumin diffusion across cultured endothelial monolayers. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 1):2379–2387. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shasby D. M., Lind S. E., Shasby S. S., Goldsmith J. C., Hunninghake G. W. Reversible oxidant-induced increases in albumin transfer across cultured endothelium: alterations in cell shape and calcium homeostasis. Blood. 1985 Mar;65(3):605–614. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siflinger-Birnboim A., Cooper J. A., del Vecchio P. J., Lum H., Malik A. B. Selectivity of the endothelial monolayer: effects of increased permeability. Microvasc Res. 1988 Nov;36(3):216–227. doi: 10.1016/0026-2862(88)90023-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stelzner T. J., Weil J. V., O'Brien R. F. Role of cyclic adenosine monophosphate in the induction of endothelial barrier properties. J Cell Physiol. 1989 Apr;139(1):157–166. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041390122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suidan H. S., Stone S. R., Hemmings B. A., Monard D. Thrombin causes neurite retraction in neuronal cells through activation of cell surface receptors. Neuron. 1992 Feb;8(2):363–375. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90302-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vu T. K., Hung D. T., Wheaton V. I., Coughlin S. R. Molecular cloning of a functional thrombin receptor reveals a novel proteolytic mechanism of receptor activation. Cell. 1991 Mar 22;64(6):1057–1068. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90261-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werth D. K., Niedel J. E., Pastan I. Vinculin, a cytoskeletal substrate of protein kinase C. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 10;258(19):11423–11426. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamasaki H., Enomoto T., Martel N., Shiba Y., Kanno Y. Tumour promoter-mediated reversible inhibition of cell-cell communication (electrical coupling). Relationship with phorbol ester binding and de novo macromolecule synthesis. Exp Cell Res. 1983 Jul;146(2):297–308. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(83)90132-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Lanerolle P., Nishikawa M. Regulation of embryonic smooth muscle myosin by protein kinase C. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 5;263(19):9071–9074. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



