Abstract
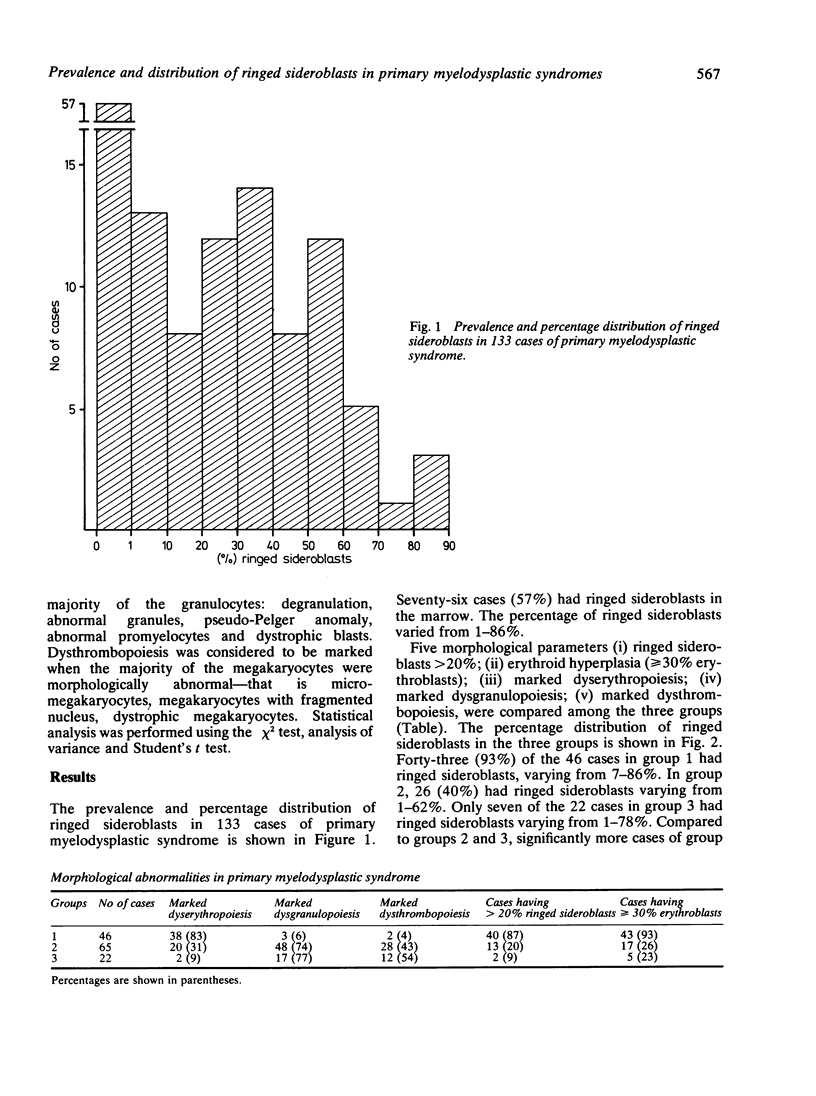
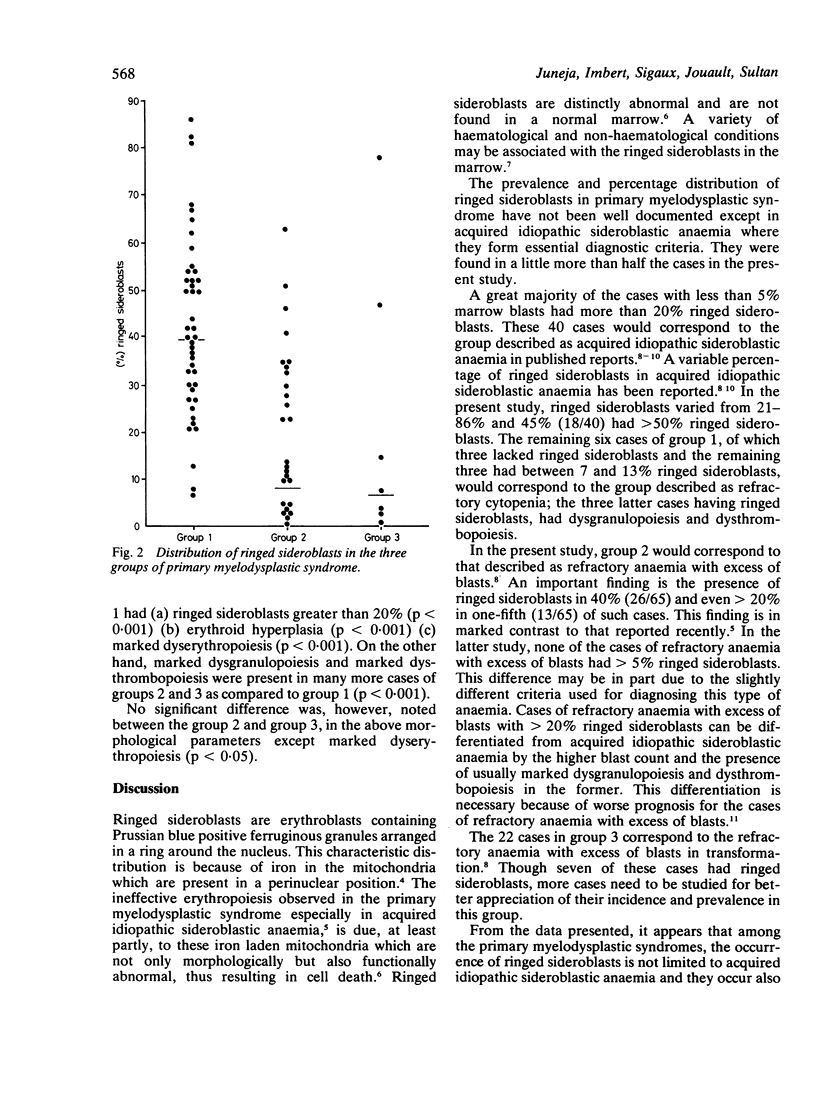
In order to determine the prevalence and percentage distribution of ringed sideroblasts in primary myelodysplastic syndromes, the results of Prussian blue staining were analysed in 133 cases. Ringed sideroblasts ranging from 1 to 86% of cells were found in 76 (57%) cases. The cases of primary myelodysplastic syndrome corresponding to the group entitled "acquired idiopathic sideroblastic anaemia" had between 21 and 86% ringed sideroblasts; these were also found in 40% (26/65) cases corresponding to refractory anaemia with excess of blasts. Seven of the 22 cases having morphological features of refractory anaemia with excess of blasts in transformation had ringed sideroblasts. It would appear that cases of acquired idiopathic sideroblastic anaemia have at least 20% ringed sideroblasts; they also seem to occur frequently in refractory anaemia with excess of blasts.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BESSIS M. C., JENSEN W. N. SIDEROBLASTIC ANAEMIA, MITOCHONDRIA AND ERYTHROBLASTIC IRON. Br J Haematol. 1965 Jan;11:49–51. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1965.tb00083.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett J. M., Catovsky D., Daniel M. T., Flandrin G., Galton D. A., Gralnick H. R., Sultan C. Proposals for the classification of the myelodysplastic syndromes. Br J Haematol. 1982 Jun;51(2):189–199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottomley S. S. Sideroblastic anaemia. Clin Haematol. 1982 Jun;11(2):389–409. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartwright G. E., Deiss A. Sideroblasts, siderocytes, and sideroblastic anemia. N Engl J Med. 1975 Jan 23;292(4):185–193. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197501232920405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cazzola M., Barosi G., Berzuini C., Dacco M., Orlandi E., Stefanelli M., Ascari E. Quantitative evaluation of erythropoietic activity in dysmyelopoietic syndromes. Br J Haematol. 1982 Jan;50(1):55–62. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1982.tb01890.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng D. S., Kushner J. P., Wintrobe M. M. Idiopathic refractory sideroblastic anemia: incidence and risk factors for leukemic transformation. Cancer. 1979 Aug;44(2):724–731. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197908)44:2<724::aid-cncr2820440245>3.0.co;2-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Classification of acute leukemia. Ann Intern Med. 1977 Dec;87(6):740–753. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-87-6-740. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigaux F., Richard M. F., Imbert M., Sultan C. Les anémies sidéroblastiques acquises idiopathiques. Pathol Biol (Paris) 1979 Sep;27(7):421–432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


