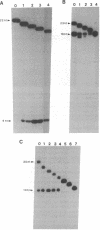
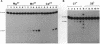Abstract
Nucleotide sequence and metal ion requirements for Mn(2+)-dependent self-cleavage of an RNA 31 nucleotides long [Dange, V., Van Atta, R. B. & Hecht, S. M. (1990) Science 248, 585-588] were examined by analysis of the site-specific cleavage activity of substitution and deletion mutants as well as complexes assembled from fragments of this RNA. A complex of UUU and GAAACp allows specific cleavage between G and A at 37 degrees C and pH 7.5. Additional nucleotides flanking the oligonucleotides in the minimal complex are not necessary for the cleavage reaction to take place but can affect the rate of the reaction. The 2'-OH groups of uridine residues do not participate in catalysis since both poly(U) and poly(dU) can promote the specific cleavage reaction in trans. Cd2+ ions can also promote the specific cleavage reaction and Mg2+ ions (which are inactive alone), under certain conditions, can enhance the Mn(2+)-induced cleavage of RNA.
Full text
PDF


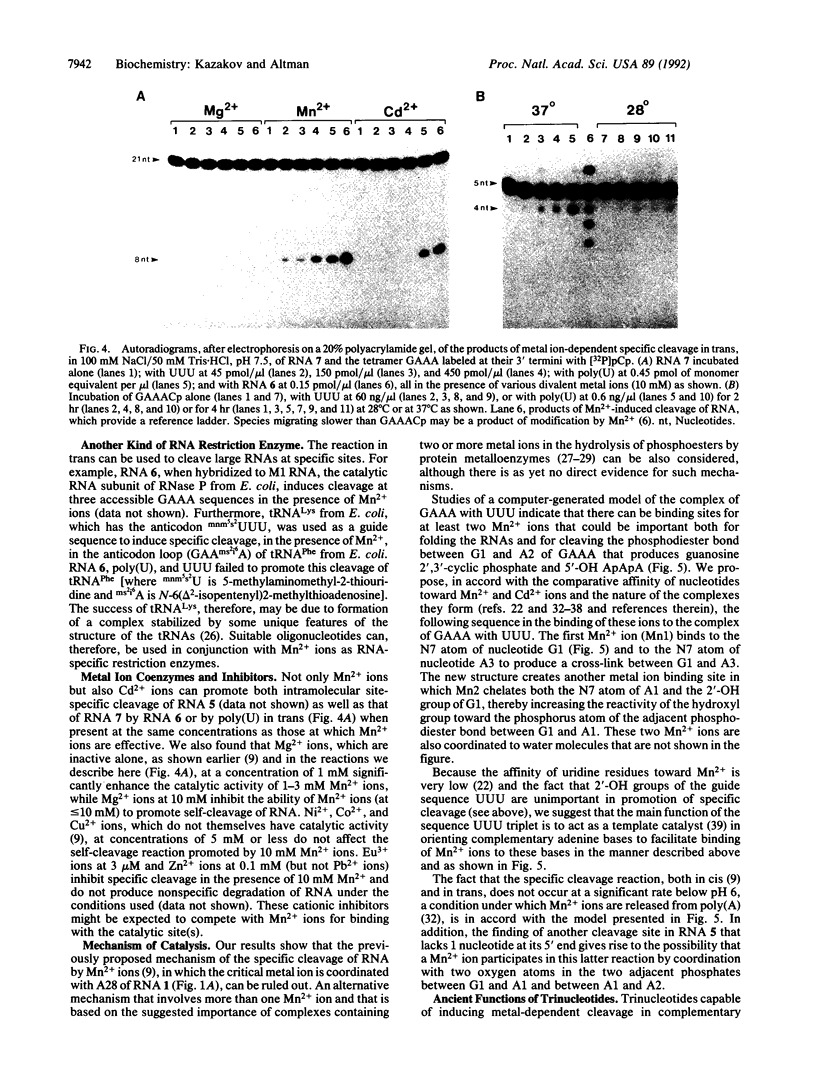

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beese L. S., Steitz T. A. Structural basis for the 3'-5' exonuclease activity of Escherichia coli DNA polymerase I: a two metal ion mechanism. EMBO J. 1991 Jan;10(1):25–33. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07917.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown R. S., Dewan J. C., Klug A. Crystallographic and biochemical investigation of the lead(II)-catalyzed hydrolysis of yeast phenylalanine tRNA. Biochemistry. 1985 Aug 27;24(18):4785–4801. doi: 10.1021/bi00339a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohn M., Danchin A., Grunberg-Manago M. Proton magnetic relaxation studies of marganous complexes of transfer RNA and related compounds. J Mol Biol. 1969 Jan 14;39(1):199–217. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90342-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahm S. C., Uhlenbeck O. C. Role of divalent metal ions in the hammerhead RNA cleavage reaction. Biochemistry. 1991 Oct 1;30(39):9464–9469. doi: 10.1021/bi00103a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dange V., Van Atta R. B., Hecht S. M. A Mn2(+)-dependent ribozyme. Science. 1990 May 4;248(4955):585–588. doi: 10.1126/science.2185542. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EISINGER J., FAWAZ-ESTRUP F., SHULMAN R. G. BINDING OF MN2+ TO NUCLEIC ACIDS. J Chem Phys. 1965 Jan 1;42:43–53. doi: 10.1063/1.1695717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FELSENFELD G., RICH A. Studies on the formation of two- and three-stranded polyribonucleotides. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1957 Dec;26(3):457–468. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(57)90091-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forster A. C., Davies C., Sheldon C. C., Jeffries A. C., Symons R. H. Self-cleaving viroid and newt RNAs may only be active as dimers. Nature. 1988 Jul 21;334(6179):265–267. doi: 10.1038/334265a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forster A. C., Jeffries A. C., Sheldon C. C., Symons R. H. Structural and ionic requirements for self-cleavage of virusoid RNAs and trans self-cleavage of viroid RNA. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1987;52:249–259. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1987.052.01.030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardiner K. J., Marsh T. L., Pace N. R. Ion dependence of the Bacillus subtilis RNase P reaction. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 10;260(9):5415–5419. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granot J., Feigon J., Kearns D. R. Interactions of DNA with divalent metal ions. I. 31P-NMR studies. Biopolymers. 1982 Jan;21(1):181–201. doi: 10.1002/bip.360210115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosshans C. A., Cech T. R. Metal ion requirements for sequence-specific endoribonuclease activity of the Tetrahymena ribozyme. Biochemistry. 1989 Aug 22;28(17):6888–6894. doi: 10.1021/bi00443a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrier-Takada C., Altman S. Structure in solution of M1 RNA, the catalytic subunit of ribonuclease P from Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1984 Dec 18;23(26):6327–6334. doi: 10.1021/bi00321a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrier-Takada C., Haydock K., Allen L., Altman S. Metal ion requirements and other aspects of the reaction catalyzed by M1 RNA, the RNA subunit of ribonuclease P from Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1986 Apr 8;25(7):1509–1515. doi: 10.1021/bi00355a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrier-Takada C., Lumelsky N., Altman S. Specific interactions in RNA enzyme-substrate complexes. Science. 1989 Dec 22;246(4937):1578–1584. doi: 10.1126/science.2480641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrier-Takada C., McClain W. H., Altman S. Cleavage of tRNA precursors by the RNA subunit of E. coli ribonuclease P (M1 RNA) is influenced by 3'-proximal CCA in the substrates. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):219–224. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90543-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herschlag D., Piccirilli J. A., Cech T. R. Ribozyme-catalyzed and nonenzymatic reactions of phosphate diesters: rate effects upon substitution of sulfur for a nonbridging phosphoryl oxygen atom. Biochemistry. 1991 May 21;30(20):4844–4854. doi: 10.1021/bi00234a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jack A., Ladner J. E., Rhodes D., Brown R. S., Klug A. A crystallographic study of metal-binding to yeast phenylalanine transfer RNA. J Mol Biol. 1977 Apr 15;111(3):315–328. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80054-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazakov S., Altman S. Site-specific cleavage by metal ion cofactors and inhibitors of M1 RNA, the catalytic subunit of RNase P from Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 15;88(20):9193–9197. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.20.9193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim E. E., Wyckoff H. W. Reaction mechanism of alkaline phosphatase based on crystal structures. Two-metal ion catalysis. J Mol Biol. 1991 Mar 20;218(2):449–464. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90724-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labuda D., Grosjean H., Striker G., Pörschke D. Codon:anticodon and anticodon:anticodon interaction: evaluation of equilibrium and kinetic parameters of complexes involving a g:u wobble. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Sep 27;698(3):230–236. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(82)90152-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan J. F., Uhlenbeck O. C. Synthesis of small RNAs using T7 RNA polymerase. Methods Enzymol. 1989;180:51–62. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(89)80091-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orgel L. E. RNA catalysis and the origins of life. J Theor Biol. 1986 Nov 21;123(2):127–149. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5193(86)80149-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pieken W. A., Olsen D. B., Benseler F., Aurup H., Eckstein F. Kinetic characterization of ribonuclease-resistant 2'-modified hammerhead ribozymes. Science. 1991 Jul 19;253(5017):314–317. doi: 10.1126/science.1857967. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pyle A. M., McSwiggen J. A., Cech T. R. Direct measurement of oligonucleotide substrate binding to wild-type and mutant ribozymes from Tetrahymena. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8187–8191. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D., Burgin A. B., Haas E. S., Pace N. R. Influence of metal ions on the ribonuclease P reaction. Distinguishing substrate binding from catalysis. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 5;267(4):2429–2436. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhlenbeck O. C. A small catalytic oligoribonucleotide. Nature. 1987 Aug 13;328(6131):596–600. doi: 10.1038/328596a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent J. B., Crowder M. W., Averill B. A. Hydrolysis of phosphate monoesters: a biological problem with multiple chemical solutions. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Mar;17(3):105–110. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(92)90246-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada A., Akasaka K., Hatano H. Proton and phosphorus-31 magnetic relaxation studies on the interaction of polyriboadenylic acid with Mn2+. Biopolymers. 1976 Jul;15(7):1315–1331. doi: 10.1002/bip.1976.360150708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang J. H., Perreault J. P., Labuda D., Usman N., Cedergren R. Mixed DNA/RNA polymers are cleaved by the hammerhead ribozyme. Biochemistry. 1990 Dec 25;29(51):11156–11160. doi: 10.1021/bi00503a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaug A. J., Kent J. R., Cech T. R. Reactions of the intervening sequence of the Tetrahymena ribosomal ribonucleic acid precursor: pH dependence of cyclization and site-specific hydrolysis. Biochemistry. 1985 Oct 22;24(22):6211–6218. doi: 10.1021/bi00343a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]