Abstract
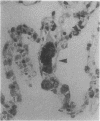
Sections of lung from four maternal deaths have been stained with an antibody raised to human keratin. This method has been found to be a more sensitive technique for determining amniotic fluid emboli than other special stains and has shown a higher incidence than expected.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ATTWOOD H. D. The histological diagnosis of amniotic-fluid embolism. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1958 Jul;76(1):211–215. doi: 10.1002/path.1700760124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Attwood H. D. Amniotic fluid embolism. Pathol Annu. 1972;7:145–172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOUGLAS G. W., THOMAS L., CARR M., CULLEN N. M., MORRIS R. Trophoblast in the circulating blood during pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1959 Nov;78:960–973. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9378(16)36649-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs E., Green H. The expression of keratin genes in epidermis and cultured epidermal cells. Cell. 1978 Nov;15(3):887–897. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90273-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guidotti R. J., Grimes D. A., Cates W., Jr Fatal amniotic fluid embolism during legally induced abortion, United States, 1972 to 1978. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1981 Oct 1;141(3):257–261. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9378(16)32629-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roche W. D., Jr, Norris H. J. Detection and significance of maternal pulmonary amniotic fluid embolism. Obstet Gynecol. 1974 May;43(5):729–731. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlegel R., Banks-Schlegel S., Pinkus G. S. Immunohistochemical localization of keratin in normal human tissues. Lab Invest. 1980 Jan;42(1):91–96. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]