Abstract
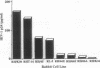
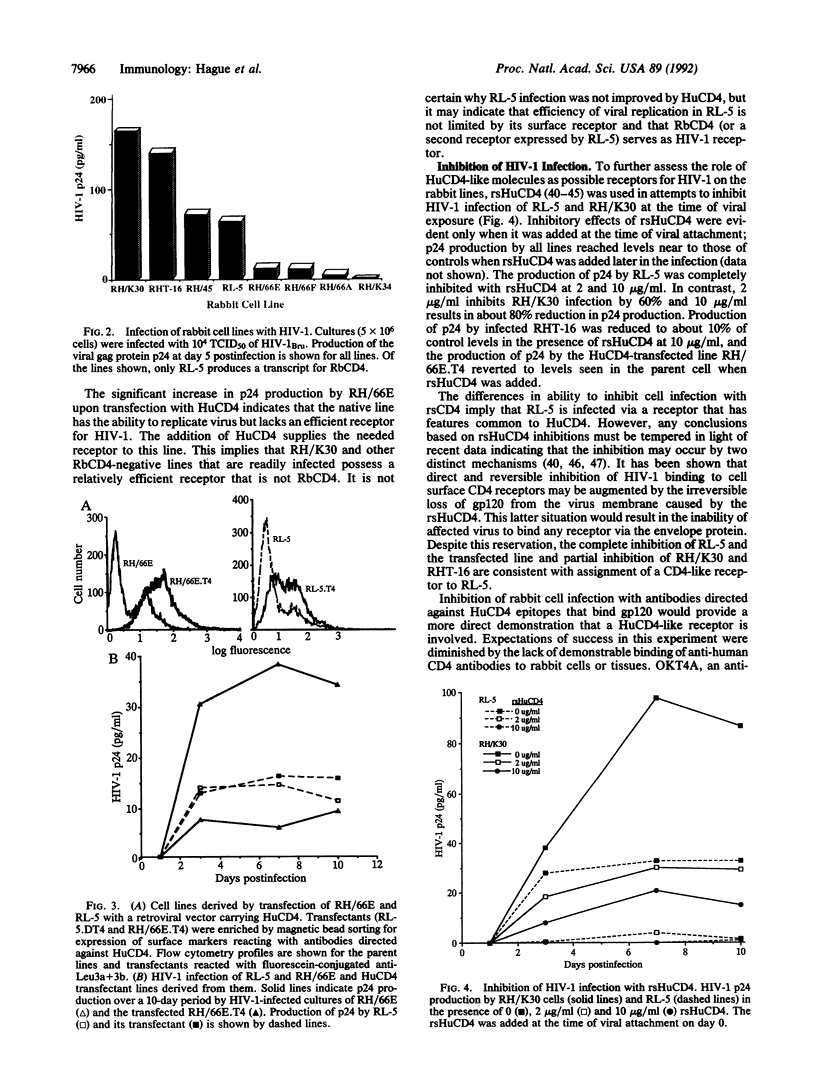
Human CD4 (HuCD4) is the principal receptor for human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) in human cell infection. Susceptibility of rabbit cell lines to infection with HIV-1 raised questions concerning whether a CD4 homolog serves as HIV-1 receptor on rabbit cells. Sequence comparisons of rabbit CD4 (RbCD4) cloned from a rabbit thymus cDNA library showed that 6 of the 18 residues implicated in HIV-1 binding by CD4 differ between the human and rabbit proteins. No correlation between RbCD4 expression by rabbit cell lines and their ability to support HIV-1 infection was seen. Transfection of RbCD4-negative, HTLV-I-transformed cell lines with HuCD4 significantly enhanced HIV-1 infectivity, suggesting that these lines lack a receptor present on other RbCD4-negative lines that produce high levels of p24 in their native state. Inhibition of HIV-1 infection with soluble HuCD4 was demonstrated for all rabbit lines tested, but complete inhibition was obtained only with a rabbit T-cell line expressing RbCD4 and with HuCD4 transfectants. The results suggest that HIV-1 infection of the RbCD4-positive line proceeds through a receptor similar to HuCD4 but that an additional receptor or receptors may serve this purpose in RbCD4-negative lines.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arthos J., Deen K. C., Chaikin M. A., Fornwald J. A., Sathe G., Sattentau Q. J., Clapham P. R., Weiss R. A., McDougal J. S., Pietropaolo C. Identification of the residues in human CD4 critical for the binding of HIV. Cell. 1989 May 5;57(3):469–481. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90922-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashkenazi A., Presta L. G., Marsters S. A., Camerato T. R., Rosenthal K. A., Fendly B. M., Capon D. J. Mapping the CD4 binding site for human immunodeficiency virus by alanine-scanning mutagenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(18):7150–7154. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.18.7150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodsky M. H., Warton M., Myers R. M., Littman D. R. Analysis of the site in CD4 that binds to the HIV envelope glycoprotein. J Immunol. 1990 Apr 15;144(8):3078–3086. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camerini D., Seed B. A CD4 domain important for HIV-mediated syncytium formation lies outside the virus binding site. Cell. 1990 Mar 9;60(5):747–754. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90089-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cao Y. Z., Friedman-Kien A. E., Huang Y. X., Li X. L., Mirabile M., Moudgil T., Zucker-Franklin D., Ho D. D. CD4-independent, productive human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection of hepatoma cell lines in vitro. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):2553–2559. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.2553-2559.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capon D. J., Ward R. H. The CD4-gp120 interaction and AIDS pathogenesis. Annu Rev Immunol. 1991;9:649–678. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.09.040191.003245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhary V. K., Mizukami T., Fuerst T. R., FitzGerald D. J., Moss B., Pastan I., Berger E. A. Selective killing of HIV-infected cells by recombinant human CD4-Pseudomonas exotoxin hybrid protein. Nature. 1988 Sep 22;335(6188):369–372. doi: 10.1038/335369a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark S. J., Jefferies W. A., Barclay A. N., Gagnon J., Williams A. F. Peptide and nucleotide sequences of rat CD4 (W3/25) antigen: evidence for derivation from a structure with four immunoglobulin-related domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(6):1649–1653. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.6.1649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalgleish A. G., Beverley P. C., Clapham P. R., Crawford D. H., Greaves M. F., Weiss R. A. The CD4 (T4) antigen is an essential component of the receptor for the AIDS retrovirus. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):763–767. doi: 10.1038/312763a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel M. D., Meléndez L. V., Hunt R. D., King N. W., Anver M., Fraser C. E., Barahona H., Baggs R. B. Herpesvirus saimiri: VII. Induction of malignant lymphoma in New Zealand white rabbits. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1974 Dec;53(6):1803–1807. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deen K. C., McDougal J. S., Inacker R., Folena-Wasserman G., Arthos J., Rosenberg J., Maddon P. J., Axel R., Sweet R. W. A soluble form of CD4 (T4) protein inhibits AIDS virus infection. Nature. 1988 Jan 7;331(6151):82–84. doi: 10.1038/331082a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dimitrov D. S., Willey R. L., Martin M. A., Blumenthal R. Kinetics of HIV-1 interactions with sCD4 and CD4+ cells: implications for inhibition of virus infection and initial steps of virus entry into cells. Virology. 1992 Apr;187(2):398–406. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90441-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filice G., Cereda P. M., Varnier O. E. Infection of rabbits with human immunodeficiency virus. Nature. 1988 Sep 22;335(6188):366–369. doi: 10.1038/335366a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher R. A., Bertonis J. M., Meier W., Johnson V. A., Costopoulos D. S., Liu T., Tizard R., Walker B. D., Hirsch M. S., Schooley R. T. HIV infection is blocked in vitro by recombinant soluble CD4. Nature. 1988 Jan 7;331(6151):76–78. doi: 10.1038/331076a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folks T., Benn S., Rabson A., Theodore T., Hoggan M. D., Martin M., Lightfoote M., Sell K. Characterization of a continuous T-cell line susceptible to the cytopathic effects of the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS)-associated retrovirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4539–4543. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon M. R., Truckenmiller M. E., Recker D. P., Dickerson D. R., Kuta E., Kulaga H., Kindt T. J. Evidence for HIV-1 infection in rabbits. A possible model for AIDS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1990;616:270–280. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1990.tb17847.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman S. D., Tourvieille B., Parnes J. R. Structure of the mouse gene encoding CD4 and an unusual transcript in brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7644–7648. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7644. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart T. K., Kirsh R., Ellens H., Sweet R. W., Lambert D. M., Petteway S. R., Jr, Leary J., Bugelski P. J. Binding of soluble CD4 proteins to human immunodeficiency virus type 1 and infected cells induces release of envelope glycoprotein gp120. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 15;88(6):2189–2193. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.6.2189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hussey R. E., Richardson N. E., Kowalski M., Brown N. R., Chang H. C., Siliciano R. F., Dorfman T., Walker B., Sodroski J., Reinherz E. L. A soluble CD4 protein selectively inhibits HIV replication and syncytium formation. Nature. 1988 Jan 7;331(6151):78–81. doi: 10.1038/331078a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kindt T. J., Hirsch V. M., Johnson P. R., Sawasdikosol S. Animal models for acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Adv Immunol. 1992;52:425–474. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60880-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klatzmann D., Champagne E., Chamaret S., Gruest J., Guetard D., Hercend T., Gluckman J. C., Montagnier L. T-lymphocyte T4 molecule behaves as the receptor for human retrovirus LAV. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):767–768. doi: 10.1038/312767a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulaga H., Folks T. M., Rutledge R., Kindt T. J. Infection of rabbit T-cell and macrophage lines with human immunodeficiency virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4455–4459. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulaga H., Folks T., Rutledge R., Truckenmiller M. E., Gugel E., Kindt T. J. Infection of rabbits with human immunodeficiency virus 1. A small animal model for acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. J Exp Med. 1989 Jan 1;169(1):321–326. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.1.321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lasky L. A., Nakamura G., Smith D. H., Fennie C., Shimasaki C., Patzer E., Berman P., Gregory T., Capon D. J. Delineation of a region of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 gp120 glycoprotein critical for interaction with the CD4 receptor. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):975–985. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90524-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li X. L., Moudgil T., Vinters H. V., Ho D. D. CD4-independent, productive infection of a neuronal cell line by human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J Virol. 1990 Mar;64(3):1383–1387. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.3.1383-1387.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lonberg N., Gettner S. N., Lacy E., Littman D. R. Mouse brain CD4 transcripts encode only the COOH-terminal half of the protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):2224–2228. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.2224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maddon P. J., Dalgleish A. G., McDougal J. S., Clapham P. R., Weiss R. A., Axel R. The T4 gene encodes the AIDS virus receptor and is expressed in the immune system and the brain. Cell. 1986 Nov 7;47(3):333–348. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90590-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maddon P. J., Littman D. R., Godfrey M., Maddon D. E., Chess L., Axel R. The isolation and nucleotide sequence of a cDNA encoding the T cell surface protein T4: a new member of the immunoglobulin gene family. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):93–104. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80105-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDougal J. S., Klatzmann D. R., Maddon P. J. CD4-gp120 interactions. Curr Opin Immunol. 1991 Aug;3(4):552–558. doi: 10.1016/0952-7915(91)90020-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyoshi I., Yoshimoto S., Taguchi H., Kubonishi I., Fujishita M., Ohtsuki Y., Shiraishi Y., Akagi T. Transformation of rabbit lymphocytes with T-cell leukemia virus. Gan. 1983 Feb;74(1):1–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore J. P., McKeating J. A., Weiss R. A., Sattentau Q. J. Dissociation of gp120 from HIV-1 virions induced by soluble CD4. Science. 1990 Nov 23;250(4984):1139–1142. doi: 10.1126/science.2251501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norimine J., Miyazawa T., Kawaguchi Y., Tohya Y., Kai C., Mikami T. A cDNA encoding feline CD4 has a unique repeat sequence downstream of the V-like region. Immunology. 1992 Jan;75(1):74–79. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson A., Seed B. Genetic analysis of monoclonal antibody and HIV binding sites on the human lymphocyte antigen CD4. Cell. 1988 Jul 1;54(1):65–72. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90180-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popovic M., Sarin P. S., Robert-Gurroff M., Kalyanaraman V. S., Mann D., Minowada J., Gallo R. C. Isolation and transmission of human retrovirus (human t-cell leukemia virus). Science. 1983 Feb 18;219(4586):856–859. doi: 10.1126/science.6600519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Recker D. P., Kulaga H., Dorsett D., Folks T., Kindt T. J. A monocyte-derived factor interferes with detection of reverse transcriptase in HIV-1 infection. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1991 Jan;7(1):73–81. doi: 10.1089/aid.1991.7.73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sattentau Q. J., Arthos J., Deen K., Hanna N., Healey D., Beverley P. C., Sweet R., Truneh A. Structural analysis of the human immunodeficiency virus-binding domain of CD4. Epitope mapping with site-directed mutants and anti-idiotypes. J Exp Med. 1989 Oct 1;170(4):1319–1334. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.4.1319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. H., Byrn R. A., Marsters S. A., Gregory T., Groopman J. E., Capon D. J. Blocking of HIV-1 infectivity by a soluble, secreted form of the CD4 antigen. Science. 1987 Dec 18;238(4834):1704–1707. doi: 10.1126/science.3500514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tateno M., Gonzalez-Scarano F., Levy J. A. Human immunodeficiency virus can infect CD4-negative human fibroblastoid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(11):4287–4290. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.11.4287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tourvieille B., Gorman S. D., Field E. H., Hunkapiller T., Parnes J. R. Isolation and sequence of L3T4 complementary DNA clones: expression in T cells and brain. Science. 1986 Oct 31;234(4776):610–614. doi: 10.1126/science.3094146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traunecker A., Lüke W., Karjalainen K. Soluble CD4 molecules neutralize human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Nature. 1988 Jan 7;331(6151):84–86. doi: 10.1038/331084a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tseng C. K., Hughes M. A., Hsu P. L., Mahoney S., Duvic M., Sell S. Syphilis superinfection activates expression of human immunodeficiency virus I in latently infected rabbits. Am J Pathol. 1991 May;138(5):1149–1164. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner J. M., Brodsky M. H., Irving B. A., Levin S. D., Perlmutter R. M., Littman D. R. Interaction of the unique N-terminal region of tyrosine kinase p56lck with cytoplasmic domains of CD4 and CD8 is mediated by cysteine motifs. Cell. 1990 Mar 9;60(5):755–765. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90090-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward R. H., Capon D. J., Jett C. M., Murthy K. K., Mordenti J., Lucas C., Frie S. W., Prince A. M., Green J. D., Eichberg J. W. Prevention of HIV-1 IIIB infection in chimpanzees by CD4 immunoadhesin. Nature. 1991 Aug 1;352(6334):434–436. doi: 10.1038/352434a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe M., Boyson J. E., Lord C. I., Letvin N. L. Chimpanzees immunized with recombinant soluble CD4 develop anti-self CD4 antibody responses with anti-human immunodeficiency virus activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 1;89(11):5103–5107. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.11.5103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamura Y., Kotani M., Chowdhury M. I., Yamamoto N., Yamaguchi K., Karasuyama H., Katsura Y., Miyasaka M. Infection of human CD4+ rabbit cells with HIV-1: the possibility of the rabbit as a model for HIV-1 infection. Int Immunol. 1991 Nov;3(11):1183–1187. doi: 10.1093/intimm/3.11.1183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]