Abstract
Background
The time course of blood lactate levels could be helpful to assess a patient’s response to therapy. Although the focus of published studies has been largely on septic patients, many other studies have reported serial blood lactate levels in different groups of acutely ill patients.
Methods
We performed a systematic search of PubMed, Science Direct, and Embase until the end of February 2016 plus reference lists of relevant publications. We selected all observational and interventional studies that evaluated the capacity of serial blood lactate concentrations to predict outcome. There was no restriction based on language. We excluded studies in pediatric populations, experimental studies, and studies that did not report changes in lactate values or all-cause mortality rates. We separated studies according to the type of patients included. We collected data on the number of patients, timing of lactate measurements, minimum lactate level needed for inclusion if present, and suggested time interval for predictive use.
Results
A total of 96 studies met our criteria: 14 in general ICU populations, five in general surgical ICU populations, five in patients post cardiac surgery, 14 in trauma patients, 39 in patients with sepsis, four in patients with cardiogenic shock, eight in patients after cardiac arrest, three in patients with respiratory failure, and four in other conditions. A decrease in lactate levels over time was consistently associated with lower mortality rates in all subgroups of patients. Most studies reported changes over 6, 12 or 24 hrs, fewer used shorter time intervals. Lactate kinetics did not appear very different in patients with sepsis and other types of patients. A few studies suggested that therapy could be guided by these measurements.
Conclusions
The observation of a better outcome associated with decreasing blood lactate concentrations was consistent throughout the clinical studies, and was not limited to septic patients. In all groups, the changes are relatively slow, so that lactate measurements every 1–2 hrs are probably sufficient in most acute conditions. The value of lactate kinetics appears to be valid regardless of the initial value.
Background
Since the early studies by Weil and others [1–3], blood lactate concentrations have been used widely as a marker of altered tissue perfusion in critically ill patients [4]. In physiological conditions, about 1500 mmol of lactate is produced daily from various organs, including the muscle, the intestine, the red blood cells, the brain, and the skin [5]. Lactate is metabolized by the liver (about 60 %), the kidneys (about 30 %), and other organs [5]. The normal blood lactate concentration is around 1 mEq/l [6]. Even minor increases in lactate concentrations to >1.5 mEq/l are associated with higher mortality rates [6, 7]. The exact pathophysiologic mechanisms of hyperlactatemia have been much debated, because the condition does not always simply reflect the development of anaerobic metabolism [8]. In sepsis in particular, metabolic alterations can contribute to elevated blood lactate concentrations, including increased glycolysis, catecholamine-stimulated Na–K pump activity, alterations in pyruvate dehydrogenase activity, and reduced lactate clearance primarily as a result of liver hypoperfusion. Regardless of these mechanisms, hyperlactatemia is a hallmark characteristic of shock states [4, 9] and the degree of increase in lactate concentrations is directly related to the severity of the shock state and to mortality rates [10, 11].
As for the blood levels of any substance, elevated lactate levels can be the result of increased production, reduced elimination, or both. A dynamic evaluation of serial lactate concentrations may thus be more informative than a single value. This concept of repeating blood lactate concentrations over time as an indicator of response to therapy was first proposed in 1983 [12], based on an idea raised after a publication by Orringer et al. in 1977 [13] showing that the decrease in lactate levels after cessation of grand mal seizures was actually quite rapid, with a half-life of about 50 % in 1 hr. Many studies have since emphasized that changes in lactate over the first hrs of treatment may represent a valuable monitoring tool. Some studies have even proposed integrating changes in lactate concentrations as a target in therapeutic protocols [14–17] or including them as one of the sepsis resuscitation “bundles” [18]. A number of investigators have used the term “lactate clearance” to describe decreasing lactate levels, but this is incorrect for two reasons. The first is that the changes in lactate concentrations over time reflect changes in production and in elimination. The decrease in lactate over time may reflect decreased (over)production more than increased clearance by the liver and other organs [19, 20]. The specific study of lactate clearance would require intravenous injection of radiolabeled lactate, as has been done in several studies [21, 22]. The second reason why use of the term is incorrect is that “clearance” or “elimination” implies a progressive normalization of blood lactate concentrations, which is too simplistic. Blood lactate concentrations can have a complex evolution and may even increase over time (Fig. 1), a situation that one should then call “negative lactate clearance”.
Fig. 1.
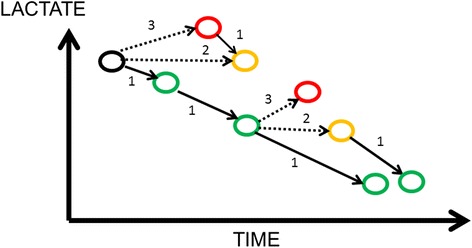
Schematic showing some of the possible evolutions of blood lactate levels over time: decreasing (1), remaining stable (2), or increasing (3). Dashed lines represent an unfavorable course and suggest the need for treatment to be reviewed, if this has not already been done, because the current management is likely ineffective
We performed a literature search on this subject to address several questions. First, is the observation of a better prognosis with decreasing lactate concentrations a consistent finding in all types of critically ill patient? Second, although some studies have suggested that repeated lactate measurements may be particularly useful in sepsis, can similar observations be made in other acute disease states or even in heterogeneous groups of critically ill patients? Third, how fast should lactate concentrations decrease in optimal conditions and is there any particular time interval that could be recommended? Fourth, some studies in emergency medicine considered only patients with lactate values > 4 mEq/l as an at-risk population, but is this approach valid? In other words, is the study of lactate kinetics more useful when lactate concentrations exceed a given value?
Methods
We searched databases of PubMed, Science Direct, and Embase until the end of February 2016 to identify studies that evaluated the capacity of serial blood lactate concentrations to predict outcome, using the search terms “Lactate levels” OR “lactate clearance” AND “shock” OR “critically ill” AND “mortality”. We included original prospective or retrospective clinical studies. There was no restriction based on language. We excluded studies in pediatric populations, experimental studies, case reports, and studies that did not report changes over time in lactate values or relationship of changes in lactate concentrations to all-cause mortality rates. We had no restriction on the initial location in the hospital (e.g., ICU, trauma unit, emergency room, operating room). We also checked the reference lists of included articles to capture any references missed during the search. We classified the different adult populations into general ICU patients, general surgical ICU patients, cardiac surgery patients, trauma patients, patients with sepsis, patients with cardiogenic shock, post-cardiac arrest patients, patients with respiratory failure, and others.
Results
A total of 96 studies met our inclusion criteria (Fig. 2, Table 1).
Fig. 2.
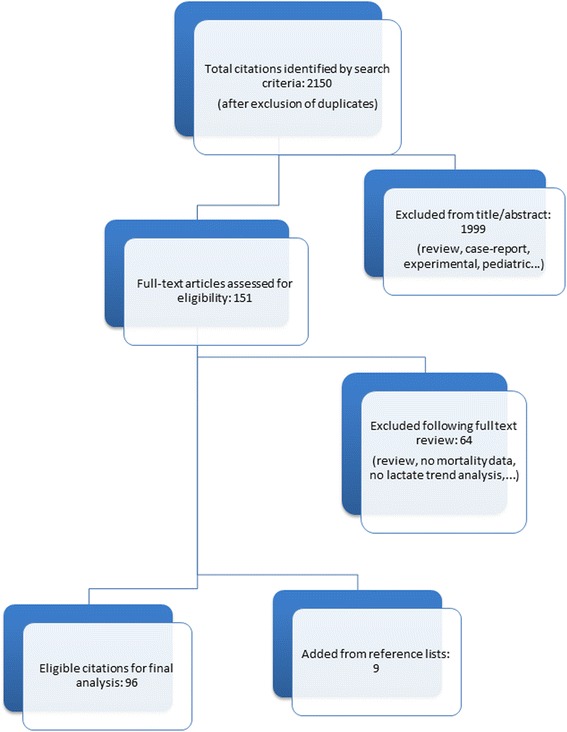
Prisma diagram
Table 1.
Included studies according to population type
| First author, year [reference] | Number of patients | Study design | Initial minimum lactate for patient inclusion | Timing of measurements | Suggested time interval | Comments | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| General ICU/emergency department | |||||||
| Observational | |||||||
| 1. | Vincent, 1983 [12] | 17 | Prospective | ≥4 | Every 20 min during first 2 h of ICU treatment | 1 h | Decrease >10 % associated with survival |
| 2. | Cowan, 1984 [23] | 30 | Prospective | – | 3 h, 24 h | 3 h | Change in lactate predictive of outcome but less so than simple hemodynamic variables |
| 3. | Suistomaa, 2000 [24] | 100 | Prospective | – | Every 2 h for 24 h | 6 h | Failure to decrease lactate at 6 h associated with higher mortality |
| 4. | Jansen, 2008 [31] | 106 | Prospective | – | Variable (at ambulance pickup and at ER arrival) | — | Decrease in lactate independently associated with decreased hazard of death |
| 5. | Wang, 2009 [25] | 101 | NR | ≥2 | 12 h, 24 h | 12 h | Decrease ≤10 % associated with increased mortality |
| 6. | Jansen, 2009 [26] | 394 | Prospective | – | 12 h, 24 h | 12 h | Decrease in lactate only of prognostic value in patients with sepsis |
| 7. | Krishna, 2009 [27] | 50 | Prospective | – | 12 h, 24 h, 36 h | 24 h, 36 h | Decreasing levels associated with survival |
| 8. | Soliman, 2010 [28] | 433 | Prospective | – | 24 h, 48 h | 24 h | Higher lactate concentrations at 24 and 48 h after admission associated with decreased survival |
| 9. | Nichol, 2010 [6] | 7155 | Retrospective | – | Variable | 24 h | Time-weighted average lactate over 24 h independent predictor of mortality |
| 10. | Nichol, 2011 [10] | 5041 | Retrospective | – | Variable | 24 h | Time-weighted average lactate and change in lactate over 24 h independent predictors of hospital mortality |
| 11. | van Beest, 2013 [29] | 2251 | Retrospective | – | Variable | 6 h | Normalization of lactate <6 h after ICU admission associated with better hospital survival than normalization of lactate >6 hrs |
| 12. | Zhang, 2014 [30] | 6291 | Retrospective | >2 | Variable | Variable | Normalization and speed of normalization related to outcome |
| 13. | Haas, 2016 [11] | 400 | Retrospective | >10 | Variable | 12 h | No decrease in lactate over 12 h associated with increased mortality |
| Interventional | |||||||
| 14. | Jansen, 2010 [15] | 348 | Prospective | ≥3.0 | 2 h | 8 h | Objective was to decrease lactate by 20 % or more per 2 h for the initial 8 h of ICU stay. Lactate-guided therapy was independently associated with reduced hospital mortality |
| Surgical ICU | |||||||
| 15. | McNelis, 2001 [32] | 95 | Retrospective | – | 8-h intervals until lactate normalized | Variable | Time to lactate normalization predictive of outcome |
| 16. | Husain, 2003 [33] | 137 | Retrospective | – | Variable | Variable | Time to lactate normalization independent predictor of mortality |
| 17. | Meregalli, 2004 [34] | 44 | Prospective | – | 12 h, 24 h, 48 h | 48 h | Blood lactate concentrations decreased with time in survivors, but remained stable in nonsurvivors |
| 18. | Cardinal Fernandez, 2009 [35] | 108 | Prospective | >2 | 6 h | 6 h | Decrease in lactate by >40 % associated with increased survival |
| 19. | Ibrahim, 2013 [36] | 322 | Prospective | – | 8 h, 16 h, 24 h | 16 h | Percent change in blood lactate at 16 h independent predictor of postoperative mortality |
| Cardiac surgery | |||||||
| 20. | Lindsay, 2013 [37] | 1291 | Retrospective | – | Variable | Variable | Longer predicted time to reach normal lactate (<1.5 mmol/l) associated with increased mortality |
| 21. | Hajjar, 2013 [38] | 502 | Prospective | – | 6 h, 12 h | 6 h, 12 h | Failure to decrease lactate associated with major complications, including death |
| 22. | Park, 2014 [39] | 115 | Retrospective | – | 6 h, 12 h, 24 h | 6 h, 12 h, 24 h | Lack of decrease in lactate predictive of mortality |
| 23. | Lopez-Delgado, 2015 [40] | 2935 | Prospective | – | 6 h, 12 h, 24 h | 24 h | Later peak in lactate associated with higher hospital and long-term mortality |
| 24. | Li, 2015 [41] | 123 | Retrospective | – | 6 h, 12 h | 12 h | Lactate decrease predictive of in-hospital mortality in patients receiving ECMO |
| Trauma | |||||||
| Observational | |||||||
| 25. | Abramson, 1993 [42] | 76 | Prospective | – | 8 h, 16 h, 24 h, 36 h, 48 h | 24 h | Normalization of lactate by 24 h associated with 100 % survival |
| 26. | Manikis, 1995 [43] | 129 | Retrospective | – | At least three times a day | Variable | Duration of hyperlactatemia correlated with the development of organ failure but not with mortality |
| 27. | Holm, 2000 [44] | 21 | Prospective | – | 12 h, 24 h, 48 h, 72 h | Variable | Decreasing lactate levels associated with survival |
| 28. | Cerovic, 2003 [45] | 98 | Prospective | – | Twice daily during first 2 days and once daily during next 3 days | Variable | Reduced lactate levels in survivors |
| 29. | Kamolz, 2005 [46] | 166 | Prospective | – | Variable | 24 h | Higher mortality in patients with initial lactate > 2 mmol/l if lactate not normalized at 24 h |
| 30. | Billeter, 2009 [47] | 1032 | Retrospective | – | Variable | 24 h | Delayed or absent decrease in lactate associated with infectious complications but not mortality |
| 31. | Regnier, 2012 [48] | 281 | Prospective | – | 2 h, 4 h | 2 h | Early normalization of lactate independent predictor of survival |
| 32. | Dubendorfer, 2013 [49] | 724 | Retrospective | – | Variable | Variable | In patients without traumatic brain injury, decrease in lactate impaired in nonsurvivors |
| 33. | Odom, 2013 [50] | 623 | Retrospective | ≥4 | 6 h | 6 h | Lower decrease in lactate at 6 h independently predictive of increased risk of death |
| 34. | Heinonen, 2014 [51] | 610 | Retrospective | – | Variable | Variable | Failure to normalize lactate associated with increased mortality |
| 35. | Freitas, 2015 [52] | 117 | Retrospective | – | 6 h | 6 h | No correlation between decrease in lactate and mortality |
| 36. | Dezman, 2015 [53] | 3887 | Retrospective | ≥3 | Variable | Variable | No decrease in lactate independent predictor of 24-h mortality |
| Interventional | |||||||
| 37. | Blow, 1999 [55] | 79 | Retrospective | – | Variable | 24 h | Failure to decrease lactate associated with increased mortality |
| 38. | Claridge, 2000 [56] | 364 | Prospective | – | Variable | 12 h | Increase in infections, length of stay, and mortality if lactate did not normalize by 12 h |
| Sepsis | |||||||
| Observational | |||||||
| 39. | Bakker, 1991 [57] | 48 | Prospective | >2 | Variable | Variable | Only survivors had a significant decrease in blood lactate concentrations during the course of septic shock |
| 40. | Friedman, 1995 [58] | 35 | Prospective | >2 | 4 h, 24 h | Variable | Lactate remained high in nonsurvivors and progressively decreased in survivors |
| 41. | Bernardin, 1996 [59] | 32 | Prospective | – | 24 h | 24 h | Greater decrease in lactate in survivors |
| 42. | Marecaux, 1996 [60] | 38 | Prospective | >2 | 24 h, 48 h | 24 h, 48 h | Greater decrease in lactate in survivors |
| 43. | Bakker, 1996 [61] | 87 | Prospective | >2 | Variable | Variable | Duration of lactic acidosis best discriminant of survival |
| 44. | Kobayashi, 2001 [62] | 22 | Prospective | – | Every 4 hours for 4 days | Variable | Decrease in lactate associated with survival |
| 45. | Nguyen, 2004 [63] | 111 | Prospective | – | 6 h | 6 h | Decrease in lactate ≥10 % associated with lower 60-day mortality |
| 46. | Nguyen, 2007 [64] | 330 | Prospective | – | Variable | 6 h | Decreased odds ratio for mortality in patients with decreased lactate |
| 47. | Phua, 2008 [65] | 72 | Prospective | – | 24 h, 48 h | 24 h | Increase in lactate predictive of mortality |
| 48. | Yang, 2009 [66] | 105 | Prospective | – | 6 h, 24 h, 72 h | 6 h | Decrease in lactate at 6 h ≥30 % was independent predictor of survival |
| 49. | Arnold, 2009 [67] | 166 | Retrospective | – | 6 h | 6 h | Lactate decrease by less than 10 % independent predictor of in-hospital death |
| 50. | Nguyen, 2010 [68] | 220 | Retrospective | – | 6 h | 6 h | Larger decrease in lactate associated with decreased mortality up to 12 months |
| 51. | Nguyen, 2011 [18] | 556 | Prospective | – | 12 h | 12 h | Any decrease in lactate within 12 h from baseline or an initial lactate <2 mmol/l independently associated with reduced mortality |
| 52. | Puskarich, 2012 [69] | 203 | Retrospective analysis of data from [16] | – | 2 h, 4 h, 6 h | 6 h | ≥10 % decrease in lactate during resuscitation associated with decreased mortality |
| 53. | Zanaty, 2012 [70] | 53 | Prospective | – | 6 h | 6 h | <15 % decrease in lactate independent predictor of mortality |
| 54. | Puskarich, 2013 [71] | 187 | Retrospective analysis of data from [16] | – | At least two lactate measurements in first 6 h | 6 h | Lactate normalization in 6 h stronger independent predictor of survival than decrease in lactate by ≥50 % |
| 55. | Walker, 2013 [72] | 78 | Retrospective | – | 6 h | 6 h | Decrease in lactate independently associated with mortality, with optimal cut-off of 36 % |
| 56. | Liu, 2013 [73] | 9190 | Retrospective | ≥2 | 4 h, 8 h, 12 h | 12 h | Reduced mortality in patients with more than 60 % lactate improvement at 12 h. |
| 57. | Marty, 2013 [74] | 94 | Prospective | – | 6 h, 12 h, 24 h | 24 h | Decrease in lactate at 24 h independently correlated to survival |
| 58. | Park, 2014 [75] | 25 | Prospective | – | 6 h, 12 h, 18 h, 24 h, 48 h | 48 h | Normalization independent predictor of survival |
| 59. | Permpikul, 2014 [76] | 51 | Prospective | – | 6 h | 6 h | Lactate decrease associated with reduced 28-day mortality |
| 60. | Bao, 2015 [77] | 94 | Retrospective | – | 3 h, 6 h, 24 h | 24 h | 24-h lactate decrease predictive of outcome |
| 61. | Galbois, 2015 [78] | 42 | Prospective | – | 6 h, 12 h, 18 h, 24 h | 6 h | Lesser decrease in lactate associated with 14-day mortality |
| 62. | Lee, 2015 [79] | 109 | Retrospective | >3.3 | 6 h, 24 h, 48 h | 6 h, 24 h, 48 h | Decrease in lactate of <10 % in the first 6 h, 24 h, and 48 h independently associated with mortality |
| 63. | Dettmer, 2015 [17] | 243 | Retrospective | ≥4 | Variable | Variable | Greater reduction in lactate associated with decreased 28-day mortality |
| 64. | Lokhandwala, 2015 [80] | 74 | Retrospective | ≥4 | Variable | Variable | Lactate decrease < 4 mmol/l associated with increased hospital morality |
| 65. | Wang, 2015 [81] | 115 | Prospective | – | 6 h, 12 h, 18 h, 24 h | 24 h | Lower lactate area score and percentage decrease in lactate associated with increased mortality |
| 66. | Bhat, 2015 [82] | 207 | Retrospective | – | Variable | Variable | Higher mortality in patients with no decrease in lactate |
| 67. | Chertoff, 2016 [83] | 229 | Retrospective | – | 24-48 h | 24-48 h | Lower decrease in plasma lactate 24–48 h after initiation of treatment was associated with higher 30-day mortality |
| 68. | Drumheller, 2016 [84] | 411 | Retrospective | ≥4 | Variable | Variable | Decrease in lactate independently associated with decreased risk of death |
| 69. | He, 2016 [85] | 84 | Prospective | – | 8 h | 8 h | Patients with lactate decrease ≥10 % had lower ICU mortality than those with lactate decrease <10 % |
| 70. | Ha, 2016 [86] | 208 | – | 6 h, 24 h | 24 h | Low decrease in lactate at 6 and 24 h independently associated with hospital mortality, but 24-h lactate decrease had higher discriminatory power | |
| 71. | Bolvardi, 2016 [87] | 90 | Prospective | – | 6 h | 6 h | Lactate decrease <10 % associated with increased mortality |
| 72. | Amir, 2016 [88] | 202 | Prospective | – | 6 h | 6 h | Lactate decrease ≥10 % not associated with mortality |
| Interventional | |||||||
| 73. | Jones, 2010 [16] | 300 | Prospective | – | Variable | Variable | No differences in in-hospital mortality using management to normalize lactate compared with management to normalize ScvO2 |
| 74. | Tian, 2012 [89] | 62 | Prospective | – | Variable | 48 h | 28-day mortality rates lower in patients with 30 % decrease in lactate target than in those with 10 % decrease in lactate target and controls |
| 75. | Yu, 2013 [90] | 50 | Prospective | – | 3 h, 6 h, 72 h | 6 h, 72 h | No differences in in-hospital mortality using management targeted at 10 % lactate decrease compared with management to normalize ScvO2 |
| 76. | Lyu, 2015 [91] | 100 | Prospective | – | 1 h, 2 h, 3 h, 4 h, 5 h, 6 h | 6 h | 28-day mortality independently associated with lactate decrease <10 % |
| 77. | Kuan, 2016 [92] | 122 | Prospective | ≥3 | Variable | 3 h | Lactate decrease >20 % associated with decreased mortality |
| Cardiogenic shock | |||||||
| 78. | Attana, 2012 [93] | 51 | Prospective | – | 12 h | 12 h | Decrease in lactate by <10 % predicts higher risk of death |
| 79. | Attana, 2013 [94] | 63 | Prospective | – | 12 h | 12 h | Nonsurvivors had smaller decrease in lactate |
| 80. | Park, 2014 [95] | 96 | Retrospective | – | Variable | 48 h | Lactate decrease <70 % independent predictor of hospital mortality |
| 81. | Guenther, 2014 [96] | 41 | retrospective | – | Variable | 6 h | Increased lactate concentrations at 6 h associated with nonsurvival after ECMO |
| Cardiac arrest | |||||||
| 82. | Kliegel, 2004 [97] | 394 | Retrospective | – | 24 h, 48 h | 48 h | Persistent hyperlactatemia predictive or poor prognosis |
| 83. | Donnino, 2007 [98] | 79 | Retrospective | – | 6 h, 12 h | 12 h | Decrease in lactate independent predictor of hospital survival |
| 84. | Arnalich, 2010 [99] | 85 | Prospective | – | 6 h | 6 h | Decrease in lactate significantly higher in 24-h survivors compared with nonsurvivors |
| 85. | Le Guen, 2011 [100] | 51 | Prospective | – | 1 h | 1 h | Decrease in blood lactate >10 % significantly different in survivors and nonsurvivors treated with ECMO |
| 86. | Starodub, 2013 [101] | 199 | Retrospective | – | 6 h, 12 h, 24 h | 12 h, 24 h | Change in lactate over time not predictive of survival but lower mean lactate levels at 12 and 24 h associated with increased survival |
| 87. | Donnino, 2014 [102] | 100 | Prospective | – | 12 h, 24 h | 12 h | Greater percentage decrease independently associated with survival |
| 88. | Riveiro, 2015 [103] | 54 | Prospective | – | 6 h, 12 h, 24 h, 48 h, 72 h | 6 h | Decrease in lactate predictive of 28-day survival |
| 89. | Williams, 2016 [104] | 167 | Retrospective | – | Variable | 4 h | More rapid decrease in lactate in survivors |
| Respiratory failure | |||||||
| 90. | Zhao, 2010 [105] | 110 | Prospective | – | 6 h | 6 h | Lactate decrease ≥10 % associated with improved survival |
| 91. | Wu, 2012 [106] | 27 | Prospective | – | 12 h, 24 h, 48 h, 72 h | 12 h, 24 h, 48 h, 72 h | Smaller decrease in lactate predictive of outcome |
| 92. | Zang, 2014 [107] | 43 | Prospective | – | 6 h | 6 h | Decrease in lactate independent predictor of survival in patients treated by ECMO |
| Others | |||||||
| 93. | Scott, 2010 [110] | 95 | Prospective | – | 1 h, 2 h, 6 h, 24 h | 2 h | Lactate decrease <15 % predictive of poor outcome (hospital mortality or endotracheal intubation) in patients with cardiorespiratory insufficiency |
| 94. | Wu, 2011 [109] | 222 | Prospective | – | 6 h | 6 h | Lactate decrease of <24.8 % at 6 h associated with higher incidence of liver graft failure and mortality |
| 95. | Lui, 2013 [108] | 204 | Prospective | ≥2 | 12 h | 12 h | Smaller decrease in lactate associated with increased mortality in patients with paraquat poisoning |
| 96. | Mohamed, 2014 [111] | 46 | Prospective | – | 8 h, 24 h | 24 h | Mortality greater if <40 % decrease in lactate |
EMCO extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, ER emergency room, h hours, NR not reported, ScvO 2 central venous oxygen saturation
General ICU patients
Observational studies
We identified 13 observational studies in heterogeneous critically ill populations [6, 10–12, 23–31]. All of these studies indicated that nonsurvivors had persistently higher lactate concentrations over time than survivors. Only one study [26] reported that lactate reduction during the first 24 hrs of ICU stay was useful only in septic patients, but not in patients with hemorrhage or other conditions.
The suggested optimal timing of lactate measurements was not precisely defined in several of the studies that evaluated the course of lactate concentrations over time. The studies that did include a time interval usually selected 6, 12 or even 24 hrs.
Interventional studies
An interventional trial of 348 patients by Jansen et al. [15] targeted a lactate decrease of at least 20 % in 2 hrs for the initial 8 hrs of treatment in ICU patients with an initial lactate ≥ 3 mEq/l. This strategy was associated with a lower mortality rate in the lactate-guided therapy group after adjustment for predefined risk factors (hazard ratio (HR), 0.61; confidence interval (CI), 0.43–0.87).
Surgical patients
We identified five observational studies conducted in general surgical ICU patients [32–36]. Failure of lactate concentrations to decrease over time was associated with worse outcomes in all studies.
After cardiac surgery
There were five observational studies in cardiac surgery patients [37–41], including two studies in patients treated with extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) post cardiac surgery [39, 41]. All studies consistently demonstrated differences in changes in lactate concentration between survivors and nonsurvivors.
Trauma patients
Observational studies
We identified twelve observational studies in trauma patients [42–53]. Three retrospective studies reported no association of change in lactate levels with mortality [43, 47, 52], although Manikis et al. [43] reported that the duration of hyperlactatemia was associated with the development of organ failure and Billeter et al. [47] noted that delayed or no reduction in blood lactate was associated with increased infectious complications. Several small studies used relatively long time intervals of 12–24 hrs [45, 54]. One study reported that repeated lactate after 2 hrs could be valuable [48] and a retrospective study proposed a time limit of 6 hrs [50].
Interventional studies
In a retrospective analysis of a small prospective cohort managed according to a protocol to normalize blood lactate levels, Blow et al. [55] reported that failure to normalize blood lactate levels (<2.5 mmol/l) was associated with increased morbidity and mortality. In an interventional study by Claridge et al. [56], patients were managed according to the same protocol targeted at reducing lactate levels to <2.4 mmol/l. Failure to achieve this target was associated with increased risk of infection, increased length of stay, and increased mortality.
Patients with sepsis
Observational studies
We found thirty four observational studies in patients with sepsis [17, 18, 57–88]. One study reported that a decrease in lactate levels of ≥10 % was not associated with mortality [88], but this study was conducted in a low-resource setting, such that resuscitation may not have been optimal as acknowledged by the authors. Several studies reported that 6-hrly changes could be a useful guide [63, 64, 66, 67, 69–72, 78].
Interventional studies
One interventional study by Jones et al. [16] compared resuscitation based on lactate concentrations with a target of obtaining a >10 % decrease from the initial value with resuscitation based on achieving central venous oxygen saturation (ScvO2) ≥ 70 %; there were no differences in outcome between the two strategies. In an analysis of patients in this trial who had simultaneous lactate and ScvO2 measurements, Puskarich et al. [69] concluded that failure to achieve the target lactate decrease was associated with a worse prognosis than failure to achieve the ScvO2 target. In a small Chinese study [89], patients randomized to a 30 % decrease in lactate target had better 28-day survival than those randomized to a 10 % target or to control, and in another small study [90] there were no differences in in-hospital mortality using management targeted at a 10 % decrease in lactate compared with management to normalize ScvO2. Two other Chinese studies reported that patients randomized to lactate-directed therapy had improved outcomes [91, 92].
Patients with cardiogenic shock
There were four studies in patients with cardiogenic shock [93–96], all showing that lactate concentrations decreased more in survivors than in nonsurvivors.
After cardiac arrest
We identified eight observational studies [97–104] in post-cardiac arrest patients. All but one [101] of these studies demonstrated differences in changes in lactate concentration between survivors and nonsurvivors.
Patients with acute respiratory failure
We found three observational studies in patients with acute respiratory failure [105–107], all showing that decreasing lactate levels were predictive of survival.
Other conditions
Changes in lactate concentrations were also reported following paraquat poisoning [108], after liver transplantation [109], in patients with acute cardiorespiratory failure [110], and in patients with severe community-acquired pneumonia [111]. All studies indicated the value of repeated lactate concentrations in these patient populations.
Discussion
Our literature review clearly supports the value of serial lactate measurements in the evaluation of critically ill patients and their response to therapy. This observation was similar across all studies and in all categories of patients, without being restricted to those with sepsis. We found only one study which suggested that evaluating the time course of lactate concentrations would be useful in sepsis patients but not in other conditions [26], and just five studies reporting no predictive effect of decrease in lactate levels over time on mortality [43, 47, 52, 88, 101] although two of these did suggest a relationship with morbidity outcomes [43, 47]. Repeated lactate concentrations can also help separate patients with complications, such as neurological complications after cardiac arrest [112, 113] or after surgery [38]. A meta-analysis of these data is complicated by the heterogeneity of the populations and the different timings of the measurements, but the data are very consistent across studies.
Increased lactate concentrations can be due to factors other than cellular hypoxia, so the decrease in blood lactate concentrations may not just be the result of improvements in cellular oxygen availability. For example, beta-adrenergic stimulation may contribute to increased lactate production [114]. A recent study indicated the reverse phenomenon; that is, the increase in lactate concentrations seen in patients with sepsis may be blunted in patients previously treated with beta-blocking agents [115]. The infusion of lactate-containing intravenous solutions may also potentially complicate the interpretation of blood lactate concentrations [116], although the amount of fluid infused must be very large to have such an effect [117]. A recent study also reported that lactate levels decrease more slowly in patients with a positive blood alcohol level, thus complicating evaluation of blood lactate levels in these patients [118].
Because lactate is primarily metabolized in the liver, liver dysfunction may alter lactate clearance. Thus, some studies have questioned whether blood lactate concentrations can be used to indicate tissue hypoperfusion in critically ill patients with hepatic dysfunction. However, patients with stable cirrhosis have normal lactate concentrations [8]. Kruse et al. [119] analyzed the incidence of hyperlactatemia in patients with liver disease and showed that lactic acidosis was associated with clinical evidence of shock and increased hospital mortality. Chiolero et al. [120] reported that major hepatectomy was not associated with any global changes in lactate clearance, although lactate half-life was prolonged. A recent experimental study indicated that liver hypoperfusion is unlikely to contribute to increased blood lactate concentrations [121]. In patients with paracetamol-induced acute liver failure, higher lactate concentrations were associated with more severe organ failure and mortality [122].
Some investigators have compared lactate and ScvO2 or combined the two measures. Lactate is usually a better prognostic marker [69]. But is it actually necessary to choose? In an interventional study in patients with sepsis, Jones et al. [16] reported no differences in outcomes for patients managed according to lactate concentrations or to ScvO2 values, but it is difficult to evaluate how these measurements really guided therapy because there were no differences in administered treatments during the first 72 hrs. In post-cardiac surgery patients, Polonen et al. [14] reported better outcomes when ScvO2 and lactate concentrations were targeted together than in control patients. The most convincing evidence in favor of lactate as a target comes from the study by Jansen et al. [15] in which outcomes were improved in patients treated to a target of a 20 % decrease in lactate concentrations. Nevertheless, the relatively slow changes in lactate make it difficult to interpret these results—the trend analysis is more a marker of effective treatment than a target in itself.
Although changes in blood lactate kinetics were clearly significant after 6 hrs in many studies and after 12 hrs in most, it is currently not possible to define the best time interval between lactate measurements. The normal reduction in lactate concentrations when overproduction of lactate abruptly ceases after grand mal seizures is about 50 % in 1 hr [13]. Although Levraut et al. [21] suggested that lactate clearance may be decreased in septic patients, Revelly et al. [22] reported similar values in patients with sepsis and in healthy volunteers.
The rate of lactate decrease in optimal treatment conditions is quite variable. In the best conditions, blood lactate concentrations decreased by more than 10 % in 1 hr in patients who responded rapidly to resuscitation [12] or by 10–20 % in 2 hrs [15]. A study by Hernandez et al. [123] suggested a >50 % decrease in lactate concentrations during the first 6 hrs of resuscitation in patients with septic shock. Although some systems now allow the quasi-continuous measurement of lactate concentrations, determinations every 1–2 hrs are probably sufficient; in the interventional study by Jansen et al. [15] the protocol was to measure blood lactate every 2 hrs. Even though serial blood lactate concentrations have been suggested to guide therapy, our review underlines that changes in lactate over time are relatively slow, taking place over hrs, and this may be too slow to guide therapy. Serial lactate concentrations should serve as a regular control, similar to how in the past a navigator would consult a compass from time to time to ensure that their boat was still heading in the right direction. If lactate concentrations do not normalize over time, the need for changes in therapy should be considered.
Conclusion
Our systematic literature review has provided the following answers to our initial questions. First, observation of a better prognosis with decreasing lactate concentrations is consistent throughout the literature. Second, these observations are not specific to septic patients, but apply to all common situations of hyperlactatemia and in heterogeneous patient populations. Third, the changes are relatively slow, and it is difficult to provide recommendations about the speed of decrease in lactate concentrations in the best conditions. Clearly repeating measurements every 12 hrs can generally separate those who will do well from those who are likely to die, but shorter time intervals may be helpful. On the basis of our observations, we would recommend checking blood lactate concentrations as often as every 1–2 hrs in acute conditions. Fourth, the study of lactate kinetics appears to be valid regardless of the initial value and not only in patients with severe hyperlactatemia.
Abbreviations
ECMO, extracorporeal membrane oxygenation; ScvO2, central venous oxygen saturation
Acknowledgements
None.
Funding
Institutional funds only.
Availability of supporting data
Not applicable.
Authors’ contributions
AQeS and LC performed the literature search and drafted the manuscript. J-LV and FST reviewed the article for critical content. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Contributor Information
Jean-Louis Vincent, Email: jlvincent@intensive.org.
Amanda Quintairos e Silva, Email: amandaqsilva@gmail.com.
Lúcio Couto, Jr, Email: luciocouto@hotmail.com.
Fabio S. Taccone, Email: ftaccone@ulb.ac.be
References
- 1.Broder G, Weil MH. Excess lactate: an index of reversibility of shock in human patients. Science. 1964;143:1457–9. doi: 10.1126/science.143.3613.1457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Weil MH, Afifi AA. Experimental and clinical studies on lactate and pyruvate as indicators of the severity of acute circulatory failure (shock) Circulation. 1970;41:989–1001. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.41.6.989. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Peretz DI, McGregor M, Dossetor JB. Lactic acidosis: a clinically significant aspect of shock. Can Med Assoc J. 1964;90:673–5. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Vincent JL, De Backer D. Circulatory shock. N Engl J Med. 2013;369:1726–34. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra1208943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Levy B. Lactate and shock state: the metabolic view. Curr Opin Crit Care. 2006;12:315–21. doi: 10.1097/01.ccx.0000235208.77450.15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Nichol AD, Egi M, Pettila V, Bellomo R, French C, Hart G, et al. Relative hyperlactatemia and hospital mortality in critically ill patients: a retrospective multi-centre study. Crit Care. 2010;14:R25. doi: 10.1186/cc8888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Singer M, Deutschman CS, Seymour CW, Shankar-Hari M, Annane D, Bauer M, et al. The Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3) JAMA. 2016;315:801–10. doi: 10.1001/jama.2016.0287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Kraut JA, Madias NE. Lactic acidosis. N Engl J Med. 2014;371:2309–19. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra1309483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Cecconi M, De Backer D, Antonelli M, Beale R, Bakker J, Hofer C, et al. Consensus on circulatory shock and hemodynamic monitoring. Task force of the European Society of Intensive Care Medicine. Intensive Care Med. 2014;40:1795–815. doi: 10.1007/s00134-014-3525-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Nichol A, Bailey M, Egi M, Pettila V, French C, Stachowski E, et al. Dynamic lactate indices as predictors of outcome in critically ill patients. Crit Care. 2011;15:R242. doi: 10.1186/cc10497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Haas SA, Lange T, Saugel B, Petzoldt M, Fuhrmann V, Metschke M, et al. Severe hyperlactatemia, lactate clearance and mortality in unselected critically ill patients. Intensive Care Med. 2016;42:202–10. doi: 10.1007/s00134-015-4127-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Vincent JL, Dufaye P, Berre J, Leeman M, Degaute JP, Kahn RJ. Serial lactate determinations during circulatory shock. Crit Care Med. 1983;11:449–51. doi: 10.1097/00003246-198306000-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Orringer CE, Eustace JC, Wunsch CD, Gardner LB. Natural history of lactic acidosis after grand-mal seizures. A model for the study of an anion-gap acidosis not associated with hyperkalemia. N Engl J Med. 1977;297:796–9. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197710132971502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Polonen P, Ruokonen E, Hippelainen M, Poyhonen M, Takala J. A prospective, randomized study of goal-oriented hemodynamic therapy in cardiac surgical patients. Anesth Analg. 2000;90:1052–9. doi: 10.1097/00000539-200005000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Jansen TC, van Bommel J, Schoonderbeek FJ, Sleeswijk Visser SJ, van der Klooster JM, Lima AP, et al. Early lactate-guided therapy in intensive care unit patients: a multicenter, open-label, randomized controlled trial. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2010;182:752–61. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200912-1918OC. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Jones AE, Shapiro NI, Trzeciak S, Arnold RC, Claremont HA, Kline JA. Lactate clearance vs central venous oxygen saturation as goals of early sepsis therapy: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2010;303:739–46. doi: 10.1001/jama.2010.158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Dettmer M, Holthaus CV, Fuller BM. The impact of serial lactate monitoring on emergency department resuscitation interventions and clinical outcomes in severe sepsis and septic shock: an observational cohort study. Shock. 2015;43:55–61. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0000000000000260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Nguyen HB, Kuan WS, Batech M, Shrikhande P, Mahadevan M, Li CH, et al. Outcome effectiveness of the severe sepsis resuscitation bundle with addition of lactate clearance as a bundle item: a multi-national evaluation. Crit Care. 2011;15:R229. doi: 10.1186/cc10469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Vincent JL. Serial blood lactate levels reflect both lactate production and clearance. Crit Care Med. 2015;43:e209. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000000906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Vincent JL. Lactic acidosis. N Engl J Med. 2015;372:1077–8. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1500327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Levraut J, Ciebiera JP, Chave S, Rabary O, Jambou P, Carles M, et al. Mild hyperlactatemia in stable septic patients is due to impaired lactate clearance rather than overproduction. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1998;157:1021–6. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.157.4.9705037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Revelly JP, Tappy L, Martinez A, Bollmann M, Cayeux MC, Berger MM, et al. Lactate and glucose metabolism in severe sepsis and cardiogenic shock. Crit Care Med. 2005;33:2235–40. doi: 10.1097/01.CCM.0000181525.99295.8F. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Cowan BN, Burns HJ, Boyle P, Ledingham IM. The relative prognostic value of lactate and haemodynamic measurements in early shock. Anaesthesia. 1984;39:750–5. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2044.1984.tb06516.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Suistomaa M, Ruokonen E, Kari A, Takala J. Time-pattern of lactate and lactate to pyruvate ratio in the first 24 hrs of intensive care emergency admissions. Shock. 2000;14:8–12. doi: 10.1097/00024382-200014010-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Wang H, Wu DW, Chen XM, Li C, Ding SF, Zhai Q, et al. Relationship between blood lactic level, lactic clearance, duration of lacticemia and prognosis of critically ill patients in intensive care unit. Zhongguo Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2009;21:357–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Jansen TC, van Bommel J, Mulder PG, Lima AP, van der Hoven B, Rommes JH, et al. Prognostic value of blood lactate levels: does the clinical diagnosis at admission matter? J Trauma. 2009;66:377–85. doi: 10.1097/TA.0b013e3181648e2f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Krishna U, Joshi SP, Modh M. An evaluation of serial blood lactate measurement as an early predictor of shock and its outcome in patients of trauma or sepsis. Indian J Crit Care Med. 2009;13:66–73. doi: 10.4103/0972-5229.56051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Soliman HM, Vincent JL. Prognostic value of admission serum lactate concentrations in intensive care unit patients. Acta Clin Belg. 2010;65:176–81. doi: 10.1179/acb.2010.037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.van Beest PA, Brander L, Jansen SP, Rommes JH, Kuiper MA, Spronk PE. Cumulative lactate and hospital mortality in ICU patients. Ann Intensive Care. 2013;3:6. doi: 10.1186/2110-5820-3-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Zhang Z, Chen K, Ni H, Fan H. Predictive value of lactate in unselected critically ill patients: an analysis using fractional polynomials. J Thorac Dis. 2014;6:995–1003. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2072-1439.2014.07.01. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Jansen TC, van Bommel J, Mulder PG, Rommes JH, Schieveld SJ, Bakker J. The prognostic value of blood lactate levels relative to that of vital signs in the pre-hospital setting: a pilot study. Crit Care. 2008;12:R160. doi: 10.1186/cc7159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.McNelis J, Marini CP, Jurkiewicz A, Szomstein S, Simms HH, Ritter G, et al. Prolonged lactate clearance is associated with increased mortality in the surgical intensive care unit. Am J Surg. 2001;182:481–5. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9610(01)00755-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Husain FA, Martin MJ, Mullenix PS, Steele SR, Elliott DC. Serum lactate and base deficit as predictors of mortality and morbidity. Am J Surg. 2003;185:485–91. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9610(03)00044-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Meregalli A, Oliveira RP, Friedman G. Occult hypoperfusion is associated with increased mortality in hemodynamically stable, high-risk, surgical patients. Crit Care. 2004;8:R60–5. doi: 10.1186/cc2423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Cardinal Fernandez PA, Olano E, Acosta C, Bertullo H, Albornoz H, Bagnulo H. Prognostic value of lactate clearance in the first 6 hrs of intensive medicine course. Med Intensiva. 2009;33:166–70. doi: 10.1016/S0210-5691(09)71212-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Ibrahim WA, Ahmed AS. Serial estimations of blood lactate predict postoperative outcome in cancer patients undergoing head and neck surgeries. Egyptian J Anaesth. 2013;29:149–54. doi: 10.1016/j.egja.2012.10.003. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Lindsay AJ, Xu M, Sessler DI, Blackstone EH, Bashr CA. Lactate clearance time and concentration linked to morbidity and death in cardiac surgical patients. Ann Thorac Surg. 2013;95:486–92. doi: 10.1016/j.athoracsur.2012.07.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Hajjar LA, Almeida JP, Fukushima JT, Rhodes A, Vincent JL, Osawa EA, et al. High lactate levels are predictors of major complications after cardiac surgery. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2013;146:455–60. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2013.02.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Park SJ, Kim SP, Kim JB, Jung SH, Choo SJ, Chung CH, et al. Blood lactate level during extracorporeal life support as a surrogate marker for survival. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2014;148:714–20. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2014.02.078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Lopez-Delgado JC, Esteve F, Javierre C, Torrado H, Rodriguez-Castro D, Carrio ML, et al. Evaluation of serial arterial lactate levels as a predictor of hospital and long-term mortality in patients after cardiac surgery. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2015;29:1441–53. doi: 10.1053/j.jvca.2015.04.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Li CL, Wang H, Jia M, Ma N, Meng X, Hou XT. The early dynamic behavior of lactate is linked to mortality in postcardiotomy patients with extracorporeal membrane oxygenation support: A retrospective observational study. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2015;149:1445–50. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2014.11.052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Abramson D, Scalea TM, Hitchcock R, Trooskin SZ, Henry SM, Greenspan J. Lactate clearance and survival following injury. J Trauma. 1993;35:584–8. doi: 10.1097/00005373-199310000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Manikis P, Jankowski S, Zhang H, Kahn RJ, Vincent JL. Correlation of serial blood lactate levels to organ failure and mortality after trauma. Am J Emerg Med. 1995;13:619–22. doi: 10.1016/0735-6757(95)90043-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Holm C, Melcer B, Horbrand F, Worl HH, von Donnersmarck GH, Muhlbauer W. Haemodynamic and oxygen transport responses in survivors and non-survivors following thermal injury. Burns. 2000;26:25–33. doi: 10.1016/S0305-4179(99)00095-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Cerovic O, Golubovic V, Spec-Marn A, Kremzar B, Vidmar G. Relationship between injury severity and lactate levels in severely injured patients. Intensive Care Med. 2003;29:1300–5. doi: 10.1007/s00134-003-1753-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Kamolz LP, Andel H, Schramm W, Meissl G, Herndon DN, Frey M. Lactate: early predictor of morbidity and mortality in patients with severe burns. Burns. 2005;31:986–90. doi: 10.1016/j.burns.2005.06.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Billeter A, Turina M, Seifert B, Mica L, Stocker R, Keel M. Early serum procalcitonin, interleukin-6, and 24-hr lactate clearance: useful indicators of septic infections in severely traumatized patients. World J Surg. 2009;33:558–66. doi: 10.1007/s00268-008-9896-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Regnier MA, Raux M, Le MY, Asencio Y, Gaillard J, Devilliers C, et al. Prognostic significance of blood lactate and lactate clearance in trauma patients. Anesthesiology. 2012;117:1276–88. doi: 10.1097/ALN.0b013e318273349d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Dubendorfer C, Billeter AT, Seifert B, Keel M, Turina M. Serial lactate and admission SOFA scores in trauma: an analysis of predictive value in 724 patients with and without traumatic brain injury. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2013;39:25–34. doi: 10.1007/s00068-012-0212-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Odom SR, Howell MD, Silva GS, Nielsen VM, Gupta A, Shapiro NI, et al. Lactate clearance as a predictor of mortality in trauma patients. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2013;74:999–1004. doi: 10.1097/TA.0b013e3182858a3e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Heinonen E, Hardcastle TC, Barle H, Muckart DJ. Lactate clearance predicts outcome after major trauma. Afr J Emerg Med. 2014;4:61–5. doi: 10.1016/j.afjem.2013.11.006. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Freitas AD, Franzon O. Lactate as predictor of mortality in polytrauma. Arq Bras Cir Dig. 2015;28:163–6. doi: 10.1590/S0102-67202015000300004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Dezman ZD, Comer AC, Smith GS, Narayan M, Scalea TM, Hirshon JM. Failure to clear elevated lactate predicts 24-hr mortality in trauma patients. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2015;79:580–5. doi: 10.1097/TA.0000000000000810. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Roumen RM, Redl H, Schlag G, Sandtner W, Koller W, Goris RJ. Scoring systems and blood lactate concentrations in relation to the development of adult respiratory distress syndrome and multiple organ failure in severely traumatized patients. J Trauma. 1993;35:349–55. doi: 10.1097/00005373-199309000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Blow O, Magliore L, Claridge JA, Butler K, Young JS. The golden hr and the silver day: detection and correction of occult hypoperfusion within 24 hrs improves outcome from major trauma. J Trauma. 1999;47:964–9. doi: 10.1097/00005373-199911000-00028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Claridge JA, Crabtree TD, Pelletier SJ, Butler K, Sawyer RG, Young JS. Persistent occult hypoperfusion is associated with a significant increase in infection rate and mortality in major trauma patients. J Trauma. 2000;48:8–14. doi: 10.1097/00005373-200001000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Bakker J, Coffernils M, Leon M, Gris P, Vincent JL. Blood lactate levels are superior to oxygen-derived variables in predicting outcome in human septic shock. Chest. 1991;99:956–62. doi: 10.1378/chest.99.4.956. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Friedman G, Berlot G, Kahn RJ, Vincent JL. Combined measurements of blood lactate concentrations and gastric intramucosal pH in patients with severe sepsis. Crit Care Med. 1995;23:1184–93. doi: 10.1097/00003246-199507000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Bernardin G, Pradier C, Tiger F, Deloffre P, Mattei M. Blood pressure and arterial lactate level are early indicators of short-term survival in human septic shock. Intensive Care Med. 1996;22:17–25. doi: 10.1007/BF01728326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Marecaux G, Pinsky MR, Dupont E, Kahn RJ, Vincent JL. Blood lactate levels are better prognostic indicators than TNF and IL-6 levels in patients with septic shock. Intensive Care Med. 1996;22:404–8. doi: 10.1007/BF01712155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Bakker J, Gris P, Coffernils M, Kahn RJ, Vincent JL. Serial blood lactate levels can predict the development of multiple organ failure following septic shock. Am J Surg. 1996;171:221–6. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9610(97)89552-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Kobayashi S, Gando S, Morimoto Y, Nanzaki S, Kemmotsu O. Serial measurement of arterial lactate concentrations as a prognostic indicator in relation to the incidence of disseminated intravascular coagulation in patients with systemic inflammatory response syndrome. Surg Today. 2001;31:853–9. doi: 10.1007/s005950170022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Nguyen HB, Rivers EP, Knoblich BP, Jacobsen G, Muzzin A, Ressler JA, et al. Early lactate clearance is associated with improved outcome in severe sepsis and septic shock. Crit Care Med. 2004;32:1637–42. doi: 10.1097/01.CCM.0000132904.35713.A7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Nguyen HB, Corbett SW, Steele R, Banta J, Clark RT, Hayes SR, et al. Implementation of a bundle of quality indicators for the early management of severe sepsis and septic shock is associated with decreased mortality. Crit Care Med. 2007;35:1105–12. doi: 10.1097/01.CCM.0000259463.33848.3D. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Phua J, Koay ES, Lee KH. Lactate, procalcitonin, and amino-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide versus cytokine measurements and clinical severity scores for prognostication in septic shock. Shock. 2008;29:328–33. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0b013e318150716b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Yang CS, Qiu HB, Huang YZ, Xie JF, Mo M, Liu SQ, et al. Prospective research on the prognosis of septic shock based on the change of lactate concentration in arterial blood. Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2009;47:685–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Arnold RC, Shapiro NI, Jones AE, Schorr C, Pope J, Casner E, et al. Multicenter study of early lactate clearance as a determinant of survival in patients with presumed sepsis. Shock. 2009;32:35–9. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0b013e3181971d47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Nguyen HB, Loomba M, Yang JJ, Jacobsen G, Shah K, Otero RM, et al. Early lactate clearance is associated with biomarkers of inflammation, coagulation, apoptosis, organ dysfunction and mortality in severe sepsis and septic shock. J Inflamm (Lond) 2010;7:6. doi: 10.1186/1476-9255-7-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Puskarich MA, Trzeciak S, Shapiro NI, Arnold RC, Heffner AC, Kline JA, et al. Prognostic value and agreement of achieving lactate clearance or central venous oxygen saturation goals during early sepsis resuscitation. Acad Emerg Med. 2012;19:252–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1553-2712.2012.01292.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Zanaty OM, Megahed M, Demerdash H, Swelem R. Delta neutrophil index versus lactate clearance: early markers for outcome prediction in septic shock patients. Alex J Med. 2012;48:327–33. doi: 10.1016/j.ajme.2012.05.003. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Puskarich MA, Trzeciak S, Shapiro NI, Albers AB, Heffner AC, Kline JA, et al. Whole blood lactate kinetics in patients undergoing quantitative resuscitation for severe sepsis and septic shock. Chest. 2013;143:1548–53. doi: 10.1378/chest.12-0878. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Walker CA, Griffith DM, Gray AJ, Datta D, Hay AW. Early lactate clearance in septic patients with elevated lactate levels admitted from the emergency department to intensive care: time to aim higher? J Crit Care. 2013;28:832–7. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrc.2013.02.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Liu V, Morehouse JW, Soule J, Whippy A, Escobar GJ. Fluid volume, lactate values, and mortality in sepsis patients with intermediate lactate values. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2013;10:466–73. doi: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.201304-099OC. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Marty P, Roquilly A, Vallee F, Luzi A, Ferre F, Fourcade O, et al. Lactate clearance for death prediction in severe sepsis or septic shock patients during the first 24 hrs in intensive care unit: an observational study. Ann Intensive Care. 2013;3:3. doi: 10.1186/2110-5820-3-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Park JH, Lee J, Park YS, Lee CH, Lee SM, Yim JJ, et al. Prognostic value of central venous oxygen saturation and blood lactate levels measured simultaneously in the same patients with severe systemic inflammatory response syndrome and severe sepsis. Lung. 2014;192:435–40. doi: 10.1007/s00408-014-9564-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Permpikul C, Sringam P, Tongyoo S. Therapeutic goal achievements during severe sepsis and septic shock resuscitation and their association with patients' outcomes. J Med Assoc Thai. 2014;97(Suppl 3):S176–83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Bao L, Zhang M, Yan P, Wu X, Shao J, Zheng R. Retrospective analysis of the value of arterial blood lactate level and its clearance rate on the prognosis of septic shock patients. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2015;27:38–42. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2015.01.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Galbois A, Bige N, Pichereau C, Boelle PY, Baudel JL, Bourcier S, et al. Exploration of skin perfusion in cirrhotic patients with septic shock. J Hepatol. 2015;62:549–55. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2014.10.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Lee SM, Kim SE, Kim EB, Jeong HJ, Son YK, An WS. Lactate clearance and vasopressor seem to be predictors for mortality in severe sepsis patients with lactic acidosis supplementing sodium bicarbonate: a retrospective analysis. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0145181. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0145181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Lokhandwala S, Moskowitz A, Lawniczak R, Giberson T, Cocchi MN, Donnino MW. Disease heterogeneity and risk stratification in sepsis-related occult hypoperfusion: a retrospective cohort study. J Crit Care. 2015;30:531–6. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrc.2015.01.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Wang H, Li Z, Yin M, Chen XM, Ding SF, Li C, et al. Combination of Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation II score, early lactate area, and N-terminal prohormone of brain natriuretic peptide levels as a predictor of mortality in geriatric patients with septic shock. J Crit Care. 2015;30:304–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrc.2014.11.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Bhat SR, Swenson KE, Francis MW, Wira CR. Lactate clearance predicts survival among patients in the emergency department with severe sepsis. West J Emerg Med. 2015;16:1118–26. doi: 10.5811/westjem.2015.10.27577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Chertoff J, Chisum M, Simmons L, King B, Walker M, Lascano J. Prognostic utility of plasma lactate measured between 24 and 48 h after initiation of early goal-directed therapy in the management of sepsis, severe sepsis, and septic shock. J Intensive Care. 2016;4:13. doi: 10.1186/s40560-016-0142-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Drumheller BC, Agarwal A, Mikkelsen ME, Sante SC, Weber AL, Goyal M, et al. Risk factors for mortality despite early protocolized resuscitation for severe sepsis and septic shock in the emergency department. J Crit Care. 2016;31:13–20. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrc.2015.10.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.He HW, Liu DW, Long Y, Wang XT. High central venous-to-arterial CO2 difference/arterial-central venous O2 difference ratio is associated with poor lactate clearance in septic patients after resuscitation. J Crit Care. 2016;31:76–81. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrc.2015.10.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Ha TS, Shin TG, Jo IJ, Hwang SY, Chung CR, Suh GY et al. Lactate clearance and mortality in septic patients with hepatic dysfunction. Am J Emerg Med. 2016;34:1011–15. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 87.Bolvardi E, Malmir J, Reihani H, Hashemian AM, Bahramian M, Khademhosseini P, et al. The role of lactate clearance as a predictor of organ dysfunction and mortality in patients with severe sepsis. Mater Sociomed. 2016;28:57–60. doi: 10.5455/msm.2016.28.57-60. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Amir A, Saulters KJ, Olum S, Pitts K, Parsons A, Churchill C et al. Outcomes of patients with severe sepsis after the first 6 hrs of resuscitation at a regional referral hospital in Uganda. J Crit Care. 2016;33:78–83. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 89.Tian HH, Han SS, Lv CJ, Wang T, Li Z, Hao D, et al. The effect of early goal lactate clearance rate on the outcome of septic shock patients with severe pneumonia. Zhongguo Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2012;24:42–5. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Yu B, Tian HY, Hu ZJ, Zhao C, Liu LX, Zhang Y, et al. Comparison of the effect of fluid resuscitation as guided either by lactate clearance rate or by central venous oxygen saturation in patients with sepsis. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2013;25:578–83. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2013.10.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Lyu X, Xu Q, Cai G, Yan J, Yan M. Efficacies of fluid resuscitation as guided by lactate clearance rate and central venous oxygen saturation in patients with septic shock. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2015;95:496–500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Kuan WS, Ibrahim I, Leong BS, Jain S, Lu Q, Cheung YB, et al. Emergency department management of sepsis patients: a randomized, goal-oriented, noninvasive sepsis trial. Ann Emerg Med. 2016;67:367–78. doi: 10.1016/j.annemergmed.2015.09.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Attana P, Lazzeri C, Chiostri M, Picariello C, Gensini GF, Valente S. Lactate clearance in cardiogenic shock following ST elevation myocardial infarction: a pilot study. Acute Card Care. 2012;14:20–6. doi: 10.3109/17482941.2011.655293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Attana P, Lazzeri C, Chiostri M, Picariello C, Gensini GF, Valente S. Strong-ion gap approach in patients with cardiogenic shock following ST-elevation myocardial infarction. Acute Card Care. 2013;15:58–62. doi: 10.3109/17482941.2013.776691. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Park TK, Yang JH, Choi SH, Song YB, Hahn JY, Choi JH, et al. Clinical outcomes of patients with acute myocardial infarction complicated by severe refractory cardiogenic shock assisted with percutaneous cardiopulmonary support. Yonsei Med J. 2014;55:920–7. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2014.55.4.920. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Guenther S, Theiss HD, Fischer M, Sattler S, Peterss S, Born F, et al. Percutaneous extracorporeal life support for patients in therapy refractory cardiogenic shock: initial results of an interdisciplinary team. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2014;18:283–91. doi: 10.1093/icvts/ivt505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Kliegel A, Losert H, Sterz F, Holzer M, Zeiner A, Havel C, et al. Serial lactate determinations for prediction of outcome after cardiac arrest. Medicine (Baltimore) 2004;83:274–9. doi: 10.1097/01.md.0000141098.46118.4c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Donnino MW, Miller J, Goyal N, Loomba M, Sankey SS, Dolcourt B, et al. Effective lactate clearance is associated with improved outcome in post-cardiac arrest patients. Resuscitation. 2007;75:229–34. doi: 10.1016/j.resuscitation.2007.03.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Arnalich F, Menendez M, Lagos V, Ciria E, Quesada A, Codoceo R, et al. Prognostic value of cell-free plasma DNA in patients with cardiac arrest outside the hospital: an observational cohort study. Crit Care. 2010;14:R47. doi: 10.1186/cc8934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Le Guen M, Nicolas-Robin A, Carreira S, Raux M, Leprince P, Riou B, et al. Extracorporeal life support following out-of-hospital refractory cardiac arrest. Crit Care. 2011;15:R29. doi: 10.1186/cc9976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Starodub R, Abella BS, Grossestreuer AV, Shofer FS, Perman SM, Leary M, et al. Association of serum lactate and survival outcomes in patients undergoing therapeutic hypothermia after cardiac arrest. Resuscitation. 2013;84:1078–82. doi: 10.1016/j.resuscitation.2013.02.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Donnino MW, Andersen LW, Giberson T, Gaieski DF, Abella BS, Peberdy MA, et al. Initial lactate and lactate change in post-cardiac arrest: a multicenter validation study. Crit Care Med. 2014;42:1804–11. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000000332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Riveiro DF, de Oliveira VM, Braunner JS, Vieira SR. Evaluation of serum lactate, central venous saturation, and venous-arterial carbon dioxide difference in the prediction of mortality in postcardiac arrest syndrome. J Intensive Care Med. 2015. [Epub ahead of print] [DOI] [PubMed]
- 104.Williams TA, Martin R, Celenza A, Bremner A, Fatovich D, Krause J, et al. Use of serum lactate levels to predict survival for patients with out-of-hospital cardiac arrest: a cohort study. Emerg Med Australas. 2016;28:171–8. doi: 10.1111/1742-6723.12560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Zhao YF, Lin Y, Zhu XL. Clinical significance of early lactate clearance rate in patients with respiratory failure. Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 2010;33:183–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Wu WH, Niu YY, Zhang CR, Xiao LB, Ye HS, Pan DM, et al. Combined APACH II score and arterial blood lactate clearance rate to predict the prognosis of ARDS patients. Asian Pac J Trop Med. 2012;5:656–60. doi: 10.1016/S1995-7645(12)60134-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Zang Z, Xu H, Dong L, Gao F, Yan J. Prognostic significance of early lactate clearance rate for severe acute respiratory failure patients on extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 2014;37:197–201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Liu XW, Ma T, Qu B, Ji Y, Liu Z. Prognostic value of initial arterial lactate level and lactate metabolic clearance rate in patients with acute paraquat poisoning. Am J Emerg Med. 2013;31:1230–5. doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2013.04.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Wu JF, Wu RY, Chen J, Ou-Yang B, Chen MY, Guan XD. Early lactate clearance as a reliable predictor of initial poor graft function after orthotopic liver transplantation. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2011;10:587–92. doi: 10.1016/S1499-3872(11)60100-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Scott S, Antonaglia V, Guiotto G, Paladino F, Schiraldi F. Two-hr lactate clearance predicts negative outcome in patients with cardiorespiratory insufficiency. Crit Care Res Pract. 2010;2010:917053. doi: 10.1155/2010/917053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Mohamed KAE, Ahmed DAE. Prognostic value of lactate clearance in severe community-acquired pneumonia. Egypt J Chest Dis Tuberc. 2014;63:1053–8. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcdt.2014.05.011. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Lee TR, Kang MJ, Cha WC, Shin TG, Sim MS, Jo IJ, et al. Better lactate clearance associated with good neurologic outcome in survivors who treated with therapeutic hypothermia after out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. Crit Care. 2013;17:R260. doi: 10.1186/cc13090. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Matsumoto H, Nihei S, Endo T, Kanazawa A, Arai H, Nagata K, et al. Examination of relationship between lactate clearance and neurologic outcome in cardiac arrest induced by ventricular fibrillation. J UOEH. 2014;36:11–6. doi: 10.7888/juoeh.36.11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Qvisth V, Hagstrom-Toft E, Enoksson S, Bolinder J. Catecholamine regulation of local lactate production in vivo in skeletal muscle and adipose tissue: role of -adrenoreceptor subtypes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008;93:240–6. doi: 10.1210/jc.2007-1313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Contenti J, Occelli C, Corraze H, Lemoel F, Levraut J. Long-term beta-blocker therapy decreases blood lactate concentration in severely septic patients. Crit Care Med. 2015;43:2616–22. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000001308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Orbegozo Cortes D, Rayo Bonor A, Vincent JL. Isotonic crystalloid solutions: a structured review of the literature. Br J Anaesth. 2014;112:968–81. doi: 10.1093/bja/aeu047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Didwania A, Miller J, Kassel D, Jackson EV, Jr, Chernow B. Effect of intravenous lactated Ringer's solution infusion on the circulating lactate concentration: Part 3. Results of a prospective, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Crit Care Med. 1997;25:1851–4. doi: 10.1097/00003246-199711000-00024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Dezman ZD, Comer AC, Narayan M, Scalea TM, Hirshon JM, Smith GS. Alcohol consumption decreases lactate clearance in acutely injured patients. Injury. 2016. [Epub ahead of print] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 119.Kruse JA, Zaidi SA, Carlson RW. Significance of blood lactate levels in critically ill patients with liver disease. Am J Med. 1987;83:77–82. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(87)90500-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Chiolero R, Tappy L, Gillet M, Revelly JP, Roth H, Cayeux C, et al. Effect of major hepatectomy on glucose and lactate metabolism. Ann Surg. 1999;229:505–13. doi: 10.1097/00000658-199904000-00009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Tapia P, Soto D, Bruhn A, Alegria L, Jarufe N, Luengo C, et al. Impairment of exogenous lactate clearance in experimental hyperdynamic septic shock is not related to total liver hypoperfusion. Crit Care. 2015;19:188. doi: 10.1186/s13054-015-0928-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Schmidt LE, Larsen FS. Prognostic implications of hyperlactatemia, multiple organ failure, and systemic inflammatory response syndrome in patients with acetaminophen-induced acute liver failure. Crit Care Med. 2006;34:337–43. doi: 10.1097/01.CCM.0000194724.70031.B6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Hernandez G, Luengo C, Bruhn A, Kattan E, Friedman G, Ospina-Tascon GA, et al. When to stop septic shock resuscitation: clues from a dynamic perfusion monitoring. Ann Intensive Care. 2014;4:30. doi: 10.1186/s13613-014-0030-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


