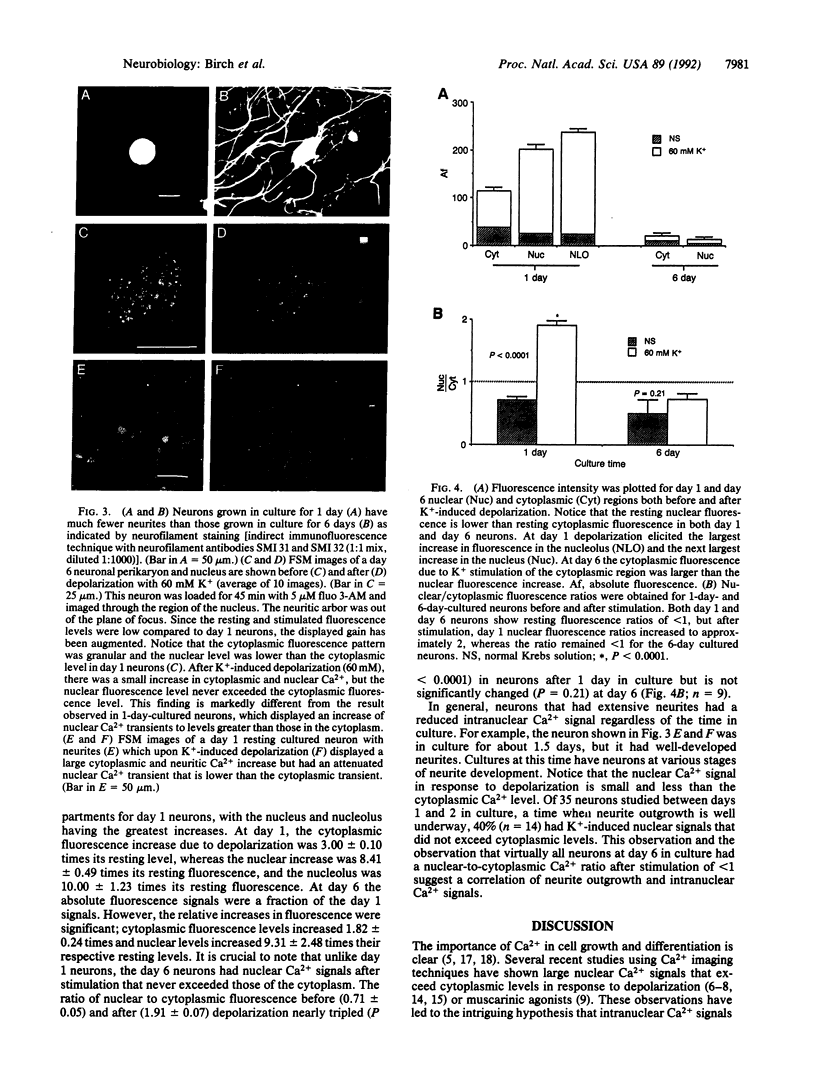
Abstract
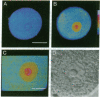
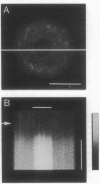
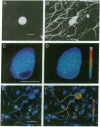
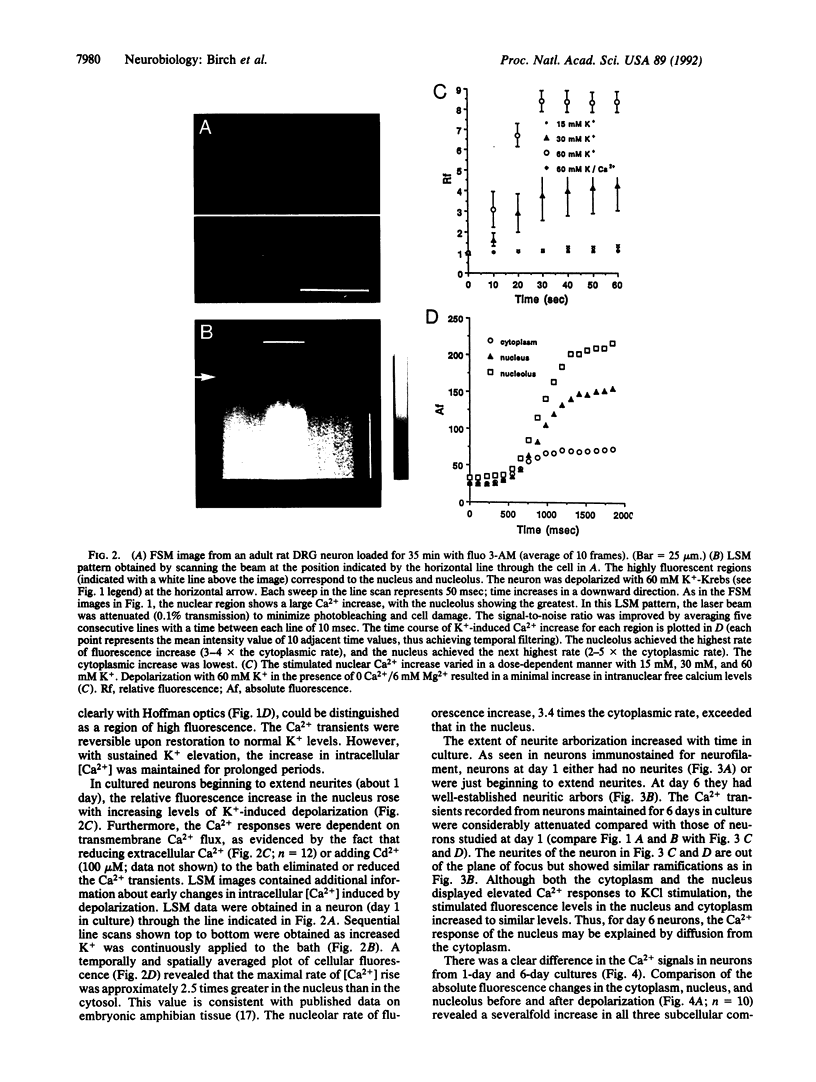
Depolarization-induced increases in cytoplasmic and intranuclear Ca2+ were visualized in adult mammalian dorsal root ganglion (DRG) neurons during different stages of neurite extension by using confocal laser scanning microscopy and the long-wavelength Ca2+ indicator dye fluo 3-AM (acetoxymethyl ester of fluo 3). In neurons beginning to extend neurites, depolarization led to pronounced increases in nuclear and nucleolar Ca2+ levels severalfold greater than corresponding increases in the cytoplasm. The nucleolar Ca2+ signal often exceeded that of the nucleus, indicating regional heterogeneity of the nucleus. The subcellular calcium transients were dependent on extracellular Ca2+ and the level of depolarization, indicating the importance of transmembrane Ca2+ fluxes in triggering the nuclear events. After neurite extension, the nuclear Ca2+ signals were attenuated and never exceeded cytoplasmic levels. These results indicate that activity-dependent modulation of intranuclear Ca2+ levels is greater in DRG neurons during early neurite extension. Given the importance of Ca2+ in gene expression, the results may be relevant to Ca(2+)-dependent nuclear events responsible for axonal regeneration.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Connor J. A., Kater S. B., Cohan C., Fink L. Ca2+ dynamics in neuronal growth cones: regulation and changing patterns of Ca2+ entry. Cell Calcium. 1990 Feb-Mar;11(2-3):233–239. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(90)90074-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fine R. E., Bray D. Actin in growing nerve cells. Nat New Biol. 1971 Nov 24;234(47):115–118. doi: 10.1038/newbio234115a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg M. E., Ziff E. B., Greene L. A. Stimulation of neuronal acetylcholine receptors induces rapid gene transcription. Science. 1986 Oct 3;234(4772):80–83. doi: 10.1126/science.3749894. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernández-Cruz A., Sala F., Adams P. R. Subcellular calcium transients visualized by confocal microscopy in a voltage-clamped vertebrate neuron. Science. 1990 Feb 16;247(4944):858–862. doi: 10.1126/science.2154851. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernández-Cruz A., Sala F., Connor J. A. Stimulus-induced nuclear Ca2+ signals in fura-2-loaded amphibian neurons. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1991;635:416–420. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1991.tb36514.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman P. N., Lasek R. J. The slow component of axonal transport. Identification of major structural polypeptides of the axon and their generality among mammalian neurons. J Cell Biol. 1975 Aug;66(2):351–366. doi: 10.1083/jcb.66.2.351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holliday J., Adams R. J., Sejnowski T. J., Spitzer N. C. Calcium-induced release of calcium regulates differentiation of cultured spinal neurons. Neuron. 1991 Nov;7(5):787–796. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90281-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holliday J., Spitzer N. C. Spontaneous calcium influx and its roles in differentiation of spinal neurons in culture. Dev Biol. 1990 Sep;141(1):13–23. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(90)90098-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao J. P., Harootunian A. T., Tsien R. Y. Photochemically generated cytosolic calcium pulses and their detection by fluo-3. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 15;264(14):8179–8184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kater S. B., Mills L. R. Regulation of growth cone behavior by calcium. J Neurosci. 1991 Apr;11(4):891–899. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.11-04-00891.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan J. I., Curran T. Role of ion flux in the control of c-fos expression. Nature. 1986 Aug 7;322(6079):552–555. doi: 10.1038/322552a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan J. I., Curran T. Stimulus-transcription coupling in neurons: role of cellular immediate-early genes. Trends Neurosci. 1989 Nov;12(11):459–462. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(89)90096-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Przywara D. A., Bhave S. V., Bhave A., Wakade T. D., Wakade A. R. Stimulated rise in neuronal calcium is faster and greater in the nucleus than the cytosol. FASEB J. 1991 Feb;5(2):217–222. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.5.2.2004666. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheng M., McFadden G., Greenberg M. E. Membrane depolarization and calcium induce c-fos transcription via phosphorylation of transcription factor CREB. Neuron. 1990 Apr;4(4):571–582. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90115-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. A., Becker P. L., Fay F. S. Regional changes in calcium underlying contraction of single smooth muscle cells. Science. 1987 Mar 27;235(4796):1644–1648. doi: 10.1126/science.3103219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]