Abstract
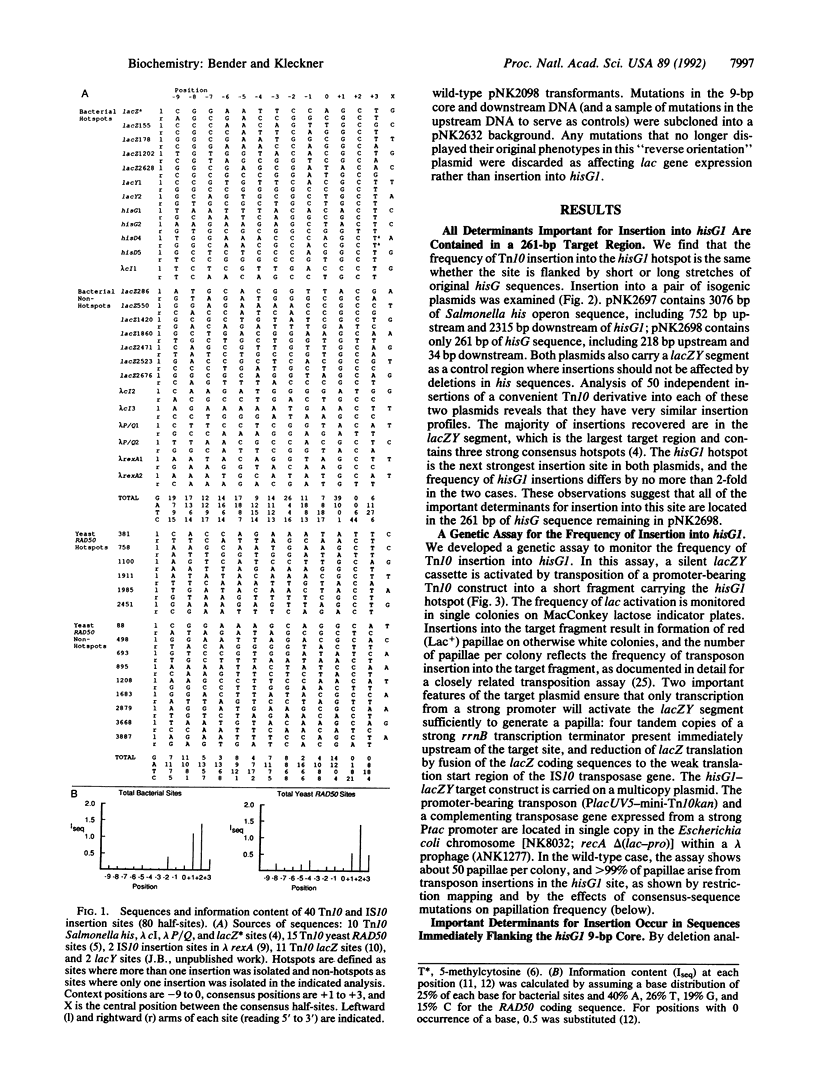
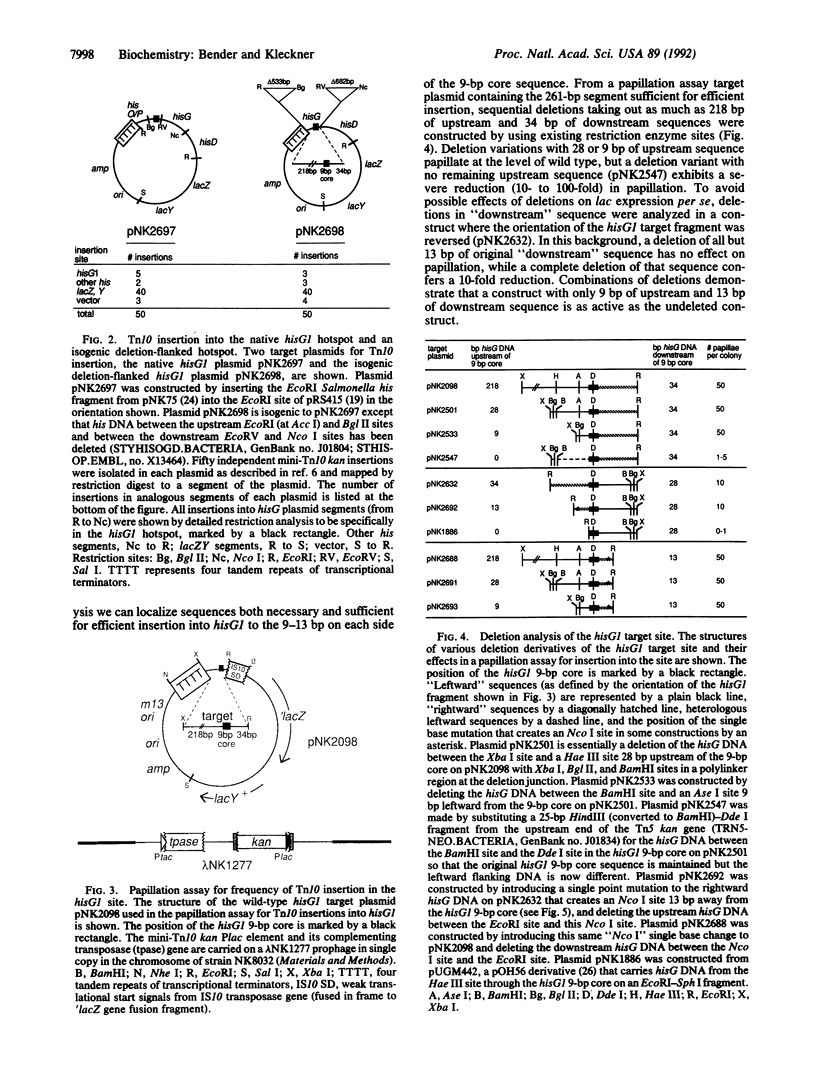
Transposon Tn10 inserts preferentially into particular "hotspots" that have been shown by sequence analysis to contain the symmetrical consensus sequence 5'-GCTNAGC-3'. This consensus is necessary but not sufficient to determine insertion specificity. We have mutagenized a known hotspot to identify other determinants for insertion into this site. This genetic dissection of the sequence context of a protein binding site shows that a second major determinant for Tn10 insertion specificity is contributed by the 6-9 base pairs that flank each end of the consensus sequence. Variations in these context base pairs can confer variations of at least 1000-fold in insertion frequency. There is no discernible consensus sequence for the context determinant, suggesting that sequence-specific protein-DNA contacts are not playing a major role. Taken together with previous work, the observations presented suggest a model for the interaction of transposase with the insertion site: symmetrically disposed subunits bind with specific contacts to the major groove of consensus-sequence base pairs, while flanking sequences influence the interaction through effects on DNA helix structure. We also show that the determinants important for insertion into a site are not important for transposition out of that site.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alves J., Pingoud A., Haupt W., Langowski J., Peters F., Maass G., Wolff C. The influence of sequences adjacent to the recognition site on the cleavage of oligodeoxynucleotides by the EcoRI endonuclease. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Apr 2;140(1):83–92. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08069.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bender J., Kleckner N. IS10 transposase mutations that specifically alter target site recognition. EMBO J. 1992 Feb;11(2):741–750. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05107.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bender J., Kuo J., Kleckner N. Genetic evidence against intramolecular rejoining of the donor DNA molecule following IS10 transposition. Genetics. 1991 Aug;128(4):687–694. doi: 10.1093/genetics/128.4.687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benjamin H. W., Kleckner N. Excision of Tn10 from the donor site during transposition occurs by flush double-strand cleavages at the transposon termini. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 15;89(10):4648–4652. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.10.4648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benjamin H. W., Kleckner N. Intramolecular transposition by Tn10. Cell. 1989 Oct 20;59(2):373–383. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90298-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brosius J., Dull T. J., Sleeter D. D., Noller H. F. Gene organization and primary structure of a ribosomal RNA operon from Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1981 May 15;148(2):107–127. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90508-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casadesus J., Roth J. R. Transcriptional occlusion of transposon targets. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 Apr;216(2-3):204–209. doi: 10.1007/BF00334357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniell E., Roberts R., Abelson J. Mutations in the lactose operon caused by bacteriophage Mu. J Mol Biol. 1972 Aug 14;69(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90019-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster T. J., Davis M. A., Roberts D. E., Takeshita K., Kleckner N. Genetic organization of transposon Tn10. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):201–213. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90285-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gamas P., Chandler M. G., Prentki P., Galas D. J. Escherichia coli integration host factor binds specifically to the ends of the insertion sequence IS1 and to its major insertion hot-spot in pBR322. J Mol Biol. 1987 May 20;195(2):261–272. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90648-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodrich J. A., Schwartz M. L., McClure W. R. Searching for and predicting the activity of sites for DNA binding proteins: compilation and analysis of the binding sites for Escherichia coli integration host factor (IHF). Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Sep 11;18(17):4993–5000. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.17.4993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halling S. M., Kleckner N. A symmetrical six-base-pair target site sequence determines Tn10 insertion specificity. Cell. 1982 Jan;28(1):155–163. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90385-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halling S. M., Simons R. W., Way J. C., Walsh R. B., Kleckner N. DNA sequence organization of IS10-right of Tn10 and comparison with IS10-left. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(8):2608–2612. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.8.2608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huisman O., Errada P. R., Signon L., Kleckner N. Mutational analysis of IS10's outside end. EMBO J. 1989 Jul;8(7):2101–2109. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03619.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huisman O., Kleckner N. A new generalizable test for detection of mutations affecting Tn10 transposition. Genetics. 1987 Jun;116(2):185–189. doi: 10.1093/genetics/116.2.185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huisman O., Raymond W., Froehlich K. U., Errada P., Kleckner N., Botstein D., Hoyt M. A. A Tn10-lacZ-kanR-URA3 gene fusion transposon for insertion mutagenesis and fusion analysis of yeast and bacterial genes. Genetics. 1987 Jun;116(2):191–199. doi: 10.1093/genetics/116.2.191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleckner N., Bender J., Gottesman S. Uses of transposons with emphasis on Tn10. Methods Enzymol. 1991;204:139–180. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)04009-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleckner N. DNA sequence analysis of Tn10 insertions: origin and role of 9 bp flanking repetitions during Tn10 translocation. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):711–720. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90087-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleckner N., Steele D. A., Reichardt K., Botstein D. Specificity of insertion by the translocatable tetracycline-resistance element Tn10. Genetics. 1979 Aug;92(4):1023–1040. doi: 10.1093/genetics/92.4.1023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. Y., Butler D., Kleckner N. Efficient Tn10 transposition into a DNA insertion hot spot in vivo requires the 5-methyl groups of symmetrically disposed thymines within the hot-spot consensus sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(22):7876–7880. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.22.7876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu A. L., Jack W. E., Modrich P. DNA determinants important in sequence recognition by Eco RI endonuclease. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 25;256(24):13200–13206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurer R., Meyer B., Ptashne M. Gene regulation at the right operator (OR) bacteriophage lambda. I. OR3 and autogenous negative control by repressor. J Mol Biol. 1980 May 15;139(2):147–161. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90302-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClarin J. A., Frederick C. A., Wang B. C., Greene P., Boyer H. W., Grable J., Rosenberg J. M. Structure of the DNA-Eco RI endonuclease recognition complex at 3 A resolution. Science. 1986 Dec 19;234(4783):1526–1541. doi: 10.1126/science.3024321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers R. M., Lerman L. S., Maniatis T. A general method for saturation mutagenesis of cloned DNA fragments. Science. 1985 Jul 19;229(4710):242–247. doi: 10.1126/science.2990046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin R. A., Modrich P. Substrate dependence of the mechanism of EcoRI endonuclease. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Aug;5(8):2991–2997. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.8.2991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider T. D., Stormo G. D., Gold L., Ehrenfeucht A. Information content of binding sites on nucleotide sequences. J Mol Biol. 1986 Apr 5;188(3):415–431. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90165-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeman N. C., Rosenberg J. M., Rich A. Sequence-specific recognition of double helical nucleic acids by proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Mar;73(3):804–808. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.3.804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons R. W., Houman F., Kleckner N. Improved single and multicopy lac-based cloning vectors for protein and operon fusions. Gene. 1987;53(1):85–96. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90095-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas M., Davis R. W. Studies on the cleavage of bacteriophage lambda DNA with EcoRI Restriction endonuclease. J Mol Biol. 1975 Jan 25;91(3):315–328. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90383-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




