Abstract
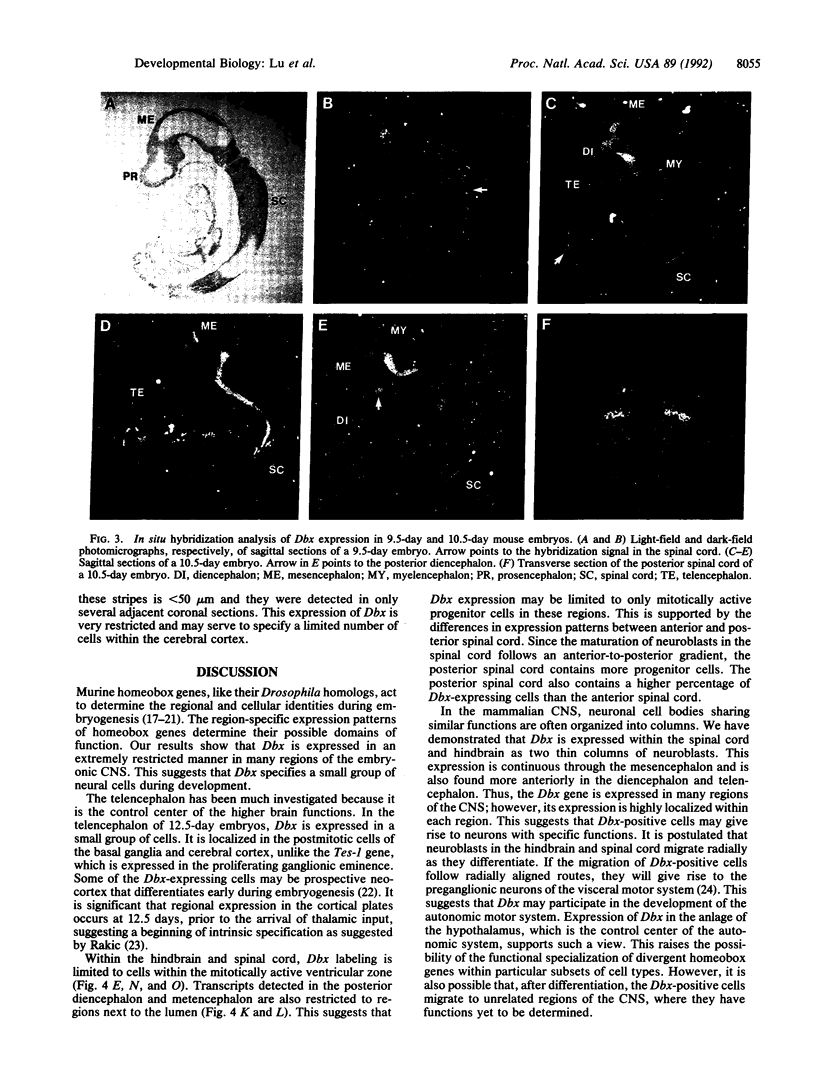
Homeobox genes specify regional identity during development. A homeobox sequence that we have named Dbx was isolated from 13.5-day embryonic mouse telencephalon cDNA. The Dbx homeodomain shows highest sequence homology to Drosophila H2.0 and chicken CHox E. We report here the expression pattern of Dbx during mouse embryogenesis. In situ hybridization analyses indicate that Dbx is expressed exclusively within the embryonic central nervous system in a highly restricted manner. Dbx transcripts are detected within a region of the prospective cerebral cortex of the midgestation telencephalon. Dbx is also expressed in the diencephalon as well as in two thin continuous columns of neuroblasts within the hindbrain and spinal cord. This expression is limited to regions of active mitosis. Dbx may act to specify subsets of neuroblasts during the development of the central nervous system.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen J. D., Lints T., Jenkins N. A., Copeland N. G., Strasser A., Harvey R. P., Adams J. M. Novel murine homeo box gene on chromosome 1 expressed in specific hematopoietic lineages and during embryogenesis. Genes Dev. 1991 Apr;5(4):509–520. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.4.509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balling R., Mutter G., Gruss P., Kessel M. Craniofacial abnormalities induced by ectopic expression of the homeobox gene Hox-1.1 in transgenic mice. Cell. 1989 Jul 28;58(2):337–347. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90848-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barad M., Jack T., Chadwick R., McGinnis W. A novel, tissue-specific, Drosophila homeobox gene. EMBO J. 1988 Jul;7(7):2151–2161. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03054.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bastian H., Gruss P. A murine even-skipped homologue, Evx 1, is expressed during early embryogenesis and neurogenesis in a biphasic manner. EMBO J. 1990 Jun;9(6):1839–1852. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08309.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogarad L. D., Utset M. F., Awgulewitsch A., Miki T., Hart C. P., Ruddle F. H. The developmental expression pattern of a new murine homeo box gene: Hox-2.5. Dev Biol. 1989 Jun;133(2):537–549. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(89)90056-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chisaka O., Capecchi M. R. Regionally restricted developmental defects resulting from targeted disruption of the mouse homeobox gene hox-1.5. Nature. 1991 Apr 11;350(6318):473–479. doi: 10.1038/350473a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis C. A., Joyner A. L. Expression patterns of the homeo box-containing genes En-1 and En-2 and the proto-oncogene int-1 diverge during mouse development. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12B):1736–1744. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12b.1736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He X., Treacy M. N., Simmons D. M., Ingraham H. A., Swanson L. W., Rosenfeld M. G. Expression of a large family of POU-domain regulatory genes in mammalian brain development. Nature. 1989 Jul 6;340(6228):35–41. doi: 10.1038/340035a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessel M., Gruss P. Murine developmental control genes. Science. 1990 Jul 27;249(4967):374–379. doi: 10.1126/science.1974085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Mouellic H., Lallemand Y., Brûlet P. Homeosis in the mouse induced by a null mutation in the Hox-3.1 gene. Cell. 1992 Apr 17;69(2):251–264. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90406-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lufkin T., Dierich A., LeMeur M., Mark M., Chambon P. Disruption of the Hox-1.6 homeobox gene results in defects in a region corresponding to its rostral domain of expression. Cell. 1991 Sep 20;66(6):1105–1119. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90034-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGinnis W., Garber R. L., Wirz J., Kuroiwa A., Gehring W. J. A homologous protein-coding sequence in Drosophila homeotic genes and its conservation in other metazoans. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):403–408. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90370-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murtha M. T., Leckman J. F., Ruddle F. H. Detection of homeobox genes in development and evolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10711–10715. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porteus M. H., Bulfone A., Ciaranello R. D., Rubenstein J. L. Isolation and characterization of a novel cDNA clone encoding a homeodomain that is developmentally regulated in the ventral forebrain. Neuron. 1991 Aug;7(2):221–229. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90260-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price M., Lemaistre M., Pischetola M., Di Lauro R., Duboule D. A mouse gene related to Distal-less shows a restricted expression in the developing forebrain. Nature. 1991 Jun 27;351(6329):748–751. doi: 10.1038/351748a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rakic P. Specification of cerebral cortical areas. Science. 1988 Jul 8;241(4862):170–176. doi: 10.1126/science.3291116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rangini Z., Ben-Yehuda A., Shapira E., Gruenbaum Y., Fainsod A. CHox E, a chicken homeogene of the H2.0 type exhibits dorso-ventral restriction in the proliferating region of the spinal cord. Mech Dev. 1991 Aug;35(1):13–24. doi: 10.1016/0925-4773(91)90037-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rentrop M., Knapp B., Winter H., Schweizer J. Aminoalkylsilane-treated glass slides as support for in situ hybridization of keratin cDNAs to frozen tissue sections under varying fixation and pretreatment conditions. Histochem J. 1986 May;18(5):271–276. doi: 10.1007/BF01676237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld M. G. POU-domain transcription factors: pou-er-ful developmental regulators. Genes Dev. 1991 Jun;5(6):897–907. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.6.897. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shashikant C. S., Utset M. F., Violette S. M., Wise T. L., Einat P., Einat M., Pendleton J. W., Schughart K., Ruddle F. H. Homeobox genes in mouse development. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 1991;1(3):207–245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolgemuth D. J., Behringer R. R., Mostoller M. P., Brinster R. L., Palmiter R. D. Transgenic mice overexpressing the mouse homoeobox-containing gene Hox-1.4 exhibit abnormal gut development. Nature. 1989 Feb 2;337(6206):464–467. doi: 10.1038/337464a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]