Supplemental Digital Content is available in the text
Abstract
Remote ischemic preconditioning (RIPC) has been proven to reduce the ischemia-reperfusion injury. However, its effect on children receiving congenital cardiac surgery (CCS) was inconsistent. We therefore performed the current meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials (RCTs) to comprehensively evaluate the effect of RIPC in pediatric patients undergoing CCS.
PubMed, Embase, and Cochrane library were searched to identify RCTs assessing the effect of RIPC in pediatric patients undergoing CCS. The outcomes included the duration of mechanical ventilation (MV), intensive care unit (ICU) length of stay, postoperative cardiac troponin (cTnI) level, hospital length of stay (HLOS), postoperative inotropic score, and mortality. Subgroup and sensitivity analysis were also performed as predesigned. The meta-analysis was performed with random-effects model despite of heterogeneity. Sensitivity and subgroup analysis were predesigned to identify the robustness of the pooled estimate.
Nine RCTs with 697 pediatric patients were included in the meta-analysis. Overall, RIPC failed to alter clinical outcomes of duration of MV (standard mean difference [SMD] −0.03, 95% confidence interval [CI] −0.23–0.17), ICU length of stay (SMD −0.22, 95% CI −0.47–0.04), or HLOS (SMD −0.14, 95% CI −0.55–0.26). Additionally, RIPC could not reduce postoperative cTnI (at 4–6 hours: SMD −0.25, 95% CI −0.73–0.23; P = 0.311; at 20–24 hours: SMD 0.09, 95% CI −0.51–0.68; P = 0.778) or postoperative inotropic score (at 4–6 hours: SMD −0.19, 95% CI −0.51–0.14; P = 0.264; at 24 hours: SMD −0.15, 95% CI −0.49–0.18; P = 0.365).
RIPC may have no beneficial effects in children undergoing CCS. However, this finding should be interpreted with caution because of heterogeneity and large-scale RCTs are still needed.
INTRODUCTION
Congenital heart disease (CHD) is the most common congenital anomaly with an incidence of approximately 0.9% and is a leading cause of mortality in neonates.1,2 With great advances in cardiothoracic surgery, 95% of neonates with CHD could survive to adulthood.3 Nevertheless, cardiopulmonary bypass was routinely used during congenital cardiac surgery (CCS)4 and could cause ischemia-reperfusion injury (IRI).5 IRI was associated with heart injuries, such as arrhythmia, myocardial stunning, low cardiac output, and perioperative myocardial infarction, especially for the immature newborn myocardium which was more vulnerable to apoptosis.6,7 Despite great progress in the underlying mechanism of myocardial IRI, numerous strategies to prevent heart injury are still disappointing.
Ischemic preconditioning (IPC) was reported to be a striking strategy that intermittent periods of myocardial ischemia could reduce the cardiac injury resulting from a subsequent prolonged period of ischemia.8 Consistently, the protection effect of IPC on ischemic injury was also confirmed in other organs in both animal and human.9–11 It was demonstrated that cardiac protection of IPC could be achieved by prevention against abnormal adenosine triphosphate production, mitochondrial swelling, and cell-membrane rupture.12,13 Additionally, IPC could induce expressions of nitric oxide synthase, cyclooxygenase 2, and antiapoptotic protein,12,14,15 to contribute to the cardiac protection. However, direct invasive IPC may be impractical and harmful in some clinical settings, and the access to temporarily occlude blood supply of the target organ is unavailable.16 Fortunately, transient ischemia in a remote tissue, namely remote ischemic preconditioning (RIPC), could also confer protection effect to target tissue from a subsequent lethal ischemia.17 RIPC shares the similar mechanism of IPC in cardiac protection, and it could also suppress the proinflammatory gene transcription and promote antiinflammation gene transcription.18
Three meta-analyses have demonstrated that RIPC could reduce the release of cardiac troponin (cTnI) in patients undergoing cardiac surgery.19–21 Specially, one of them, involving a total of 214 subjects, suggested that RIPC could provide cardiac protection in pediatric patients undergoing CCS.20 But in recent years, accumulating evidences of randomized controlled trials (RCTs)22–25 found that RIPC failed to show significant benefits on children undergoing CCS. Additionally, our previous meta-analysis found that RIPC could only benefit the clinical outcome of intensive care unit (ICU) length of stay rather than the others.26 The primary outcome of cTnI was included in our inclusion criteria, and the exclusion of studies assessing other clinical outcomes might cause inadequate statistical power.26 Considering the statistical power and controversial effects of RIPC on children undergoing CCS, therefore we performed this meta-analysis of RCTs focusing on all potential clinical outcomes to give a comprehensive evaluation of RIPC in pediatric patients undergoing CCS.
METHODS
We conducted and reported the current meta-analysis in accordance with the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-analysis statement (Additional file 1, http://links.lww.com/MD/A481).27 Since all analyses are on the basis of previous published studies, ethical approval and patient consent are not required.
Literature Search and Study Selection
PubMed, Embase, and Cochrane library were searched by 2 experienced authors independently, from the inception to July 2015 without any limitation. We combined MeSH and free-text terms to identify all potentially relevant studies with the following words: (“ischemic preconditioning” OR “myocardial ischemic preconditioning” OR “remote ischemic preconditioning” OR “limb ischemic preconditioning”) AND (“cardiovascular surgical procedures” OR “cardiac surgical procedures” OR “thoracic surgery” OR “ventricular septal defects” OR “atrial septal defects” OR “cardiopulmonary bypass” OR “cardiac surgery” OR “heart surgery”) AND (child OR children OR infants OR infant OR newborn OR newborns OR neonate OR neonates). The bibliographies of retrieved studies were also screened for other relevant studies, and the process was performed repeatedly until no additional eligible studies were added. Two authors independently selected the studies by screening titles/abstracts, and then full texts were acquired for further screening. Disputes were finally adjudicated by the 3rd author.
Inclusion criteria: population, pediatric patients undergoing CCS; intervention, RIPC; control, sham operation; outcome, no limitation; study design, RCTs.
Data Extraction and Outcomes
Two investigators independently extracted data by using a standardized spreadsheet, and the following information were extracted: first author, publication year, country, sample size, patient baseline characteristic, surgery type, intervention of RIPC, intervention of control, start time of RIPC, and study design/Jadad score. Data were extrapolated from figures as needed, and Data.Graph.Digitizer.v2.24 was used to digitize graphs and plots according to the instruction. Although essential data were missing or uncertain, the corresponding authors would be contacted. All extracted data were rechecked by the 3rd author and disagreements were resolved by negotiation.
The outcomes were the duration of mechanical ventilation (MV), ICU length of stay, postoperative cTnI level, hospital length of stay (HLOS), postoperative inotropic score, and mortality.
Quality Assessment
Methodological quality of the included RCTs was independently assessed by 2 investigators using the modified Jadad scale.28 The scale includes 4 items: the generation of random sequences (0–2 points), blinding method (0–2 points), concealment of allocation (0–2 points), and withdrawal and dropout (0–1 point). The quality score varies from 0 to 7 points, and a Jadad score >3 indicates a high-quality study. Discrepancies were resolved by discussion and adjudicated by the 3rd author.
Statistical Analysis
For all outcomes except mortality, standard mean differences (SMDs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were used to calculate the estimated pooled difference between RIPC and control groups. Since no death was observed in each group in 6 included studies, the effect of RIPC on mortality was only qualitatively described. For the purpose of meta-analysis, continuous variables expressed as medians with ranges were converted to the means and the variances by an elementary inequalities and approximations.29 The random-effects model with DerSimonian and Laird weights was used in all analysis. Statistical heterogeneity was tested by the I2 statistic and was considered to be low (I2 less than 50%), moderate (I2 between 50% and 75%), or high (I2 more than 75%).30 Sensitivity and subgroup analysis were predesigned to identify the robustness of the pooled estimate. The stratification factors for subgroups were children age (<1 vs >1 year), RIPC cycles (4 vs 3), and sample size (≥50 vs <50). Sensitivity analysis was performed via omitting 1 study and pooling the others in each turn. Additionally, sensitivity analysis was also conducted according to various inclusion criteria (children with ventricular septal defect [VSD], cyanosed children, RIPC in lower limb, RIPC after anesthesia, inflation pressure 15 mmHg > systolic arterial pressure [SAP], inflation pressure 30 mmHg > SAP, cTnI at postoperative 4 hours, cTnI at postoperative 6 hours, and cTnI at postoperative 24 hours). Publication bias was not evaluated because fewer than 10 publications were included.31 A 2-tailed P value less than 0.05 indicated a statistical significance. Stata 12.0 software (StataCorp, College Station, TX) was used for all statistical analysis.
RESULTS
Study Selection and Identification
A total of 185 publications were identified from the initial database search (PubMed [n = 49], Embase [n = 112], and Cochrane library [n = 24]). Of them, 48 were excluded owing to duplicate studies, 121were excluded by screening titles/abstracts. Among the remaining 16 articles, 6 conference abstracts were excluded for the duplicate publications of the included full texts, which were also confirmed by the corresponding authors. Additionally, one was excluded for focusing on the intervention of IPC but not RIPC.32 Finally, 9 eligible RCTs22–25,33–37 meeting the inclusion criteria were included in the meta-analysis. The process of identification of eligible RCTs is presented in Figure 1.
FIGURE 1.
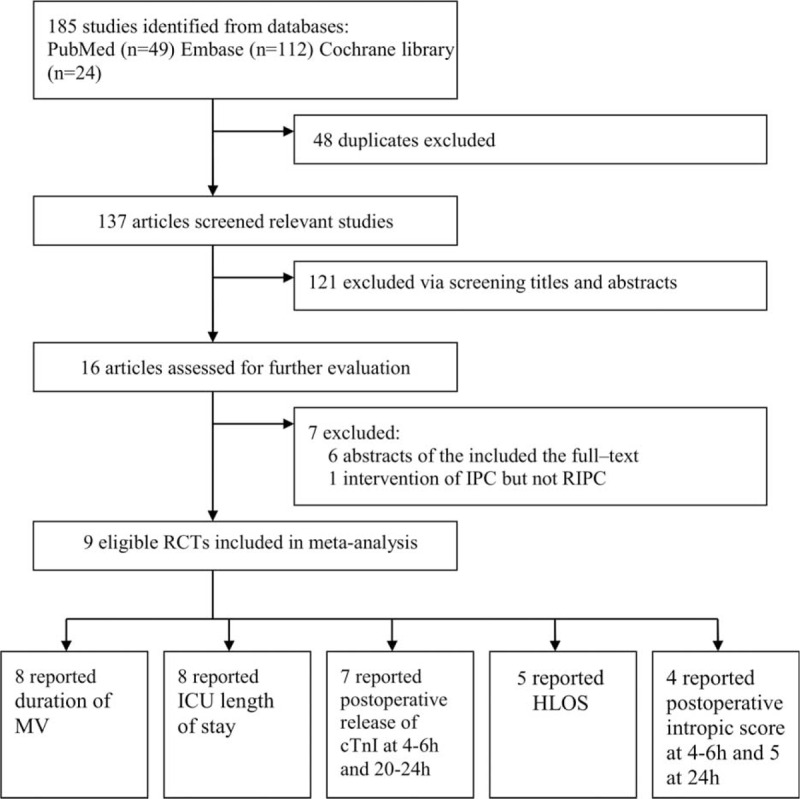
Study identification of the included RCTs. cTnI = cardiac troponin, HLOS = hospital length of stay, ICU = intensive care unit, MV = mechanical ventilation, RCT = randomized controlled trial.
Characteristics of Eligible Studies
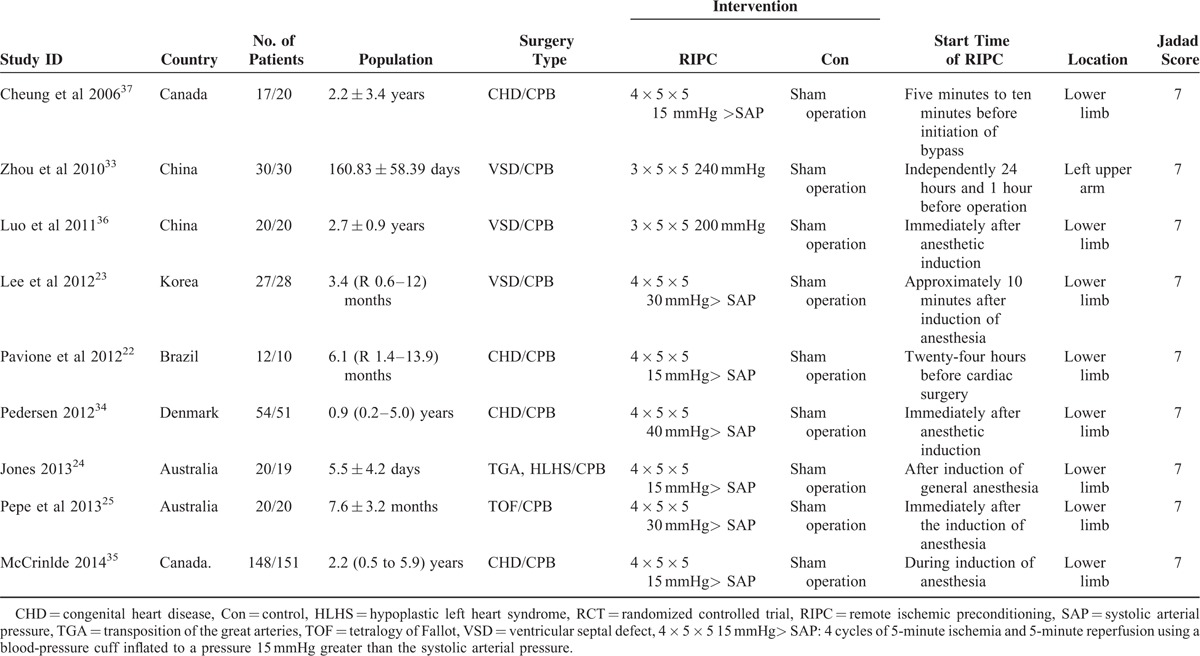
Table 1 describes the main characteristics and Table S (Additional file 2, http://links.lww.com/MD/A481) presents the outcome data of the 9 included RCTs. These studies were published between 2006 and 2014 with a total of 697 pediatric patients from 6 countries. The samples ranged from 22 to 299. All except 3 trials35–37 involved pediatric patients with an average age of less than 1 year. The types of CHD were VSD,23,33,36 tetralogy of fallot (TOF),25 transposition of the great arteries or hypoplastic left heart syndrome,24 and any form of CHD.22,34,35,37 The intervention of RIPC in all studies was induced by 3 or 4 cycles of 5-minute ischemia and 5-minute reperfusion using a blood-pressure cuff inflated to a pressure greater than the SAP, and the locations were around the lower limb in 8 trials 22–25,34–37 and the upper limb in the remaining 1.33 The intervention of RIPC was carried out after or during anesthetic induction in 6 studies,23–25,34–36 5 to 10 minutes before bypass in 1 study,37 24 hours before operation in 1 study,22 and independently 24 and 1 hour before operation in the other 1.33 Among the included studies, eight22–25,33,35–37 reported the duration of MV, eight22,23,25,33–37 reported the ICU length of stay, seven22–25,33,36,37 reported the release of cTnI at postoperative 4 to 6 and 20 to 24 hours, five22,25,34–36 reported HLOS, four23,25,33,37 reported inotropic score at postoperative 4 to 6 hours, and five23,25,33,36,37 reported inotropic score at postoperative 24 hours. All included RCTs were high-quality ones with Jadad scores ≥4.
TABLE 1.
The Baseline Characteristics of 9 Included RCTs
Duration of Mechanical Ventilation
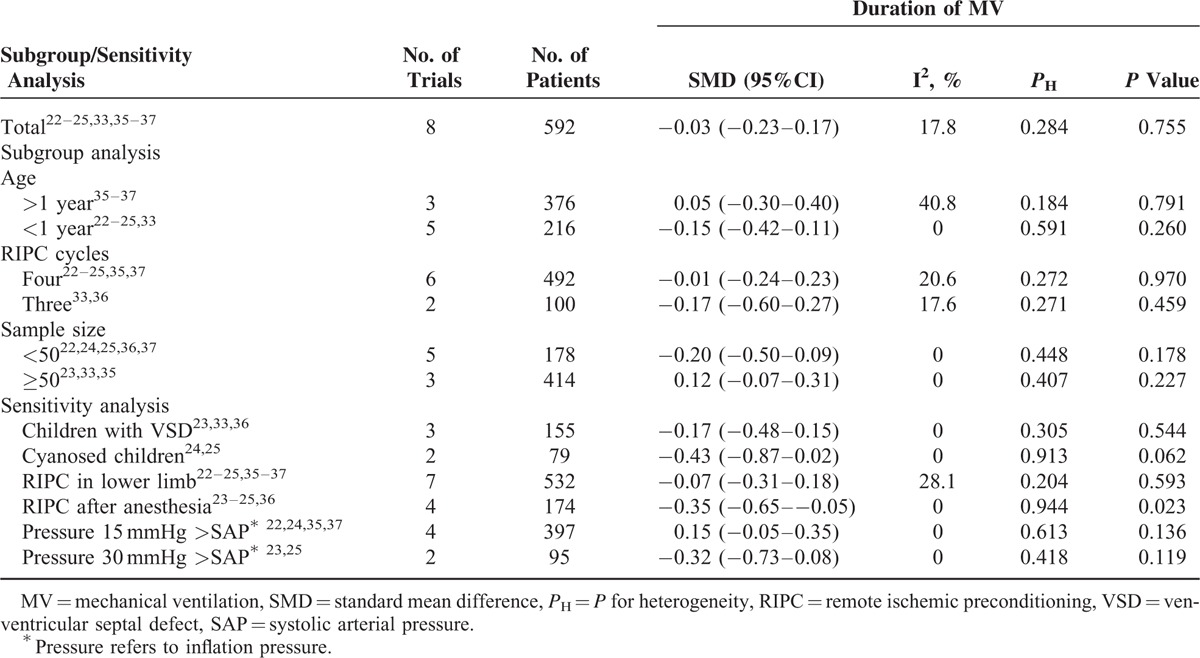
The pooled estimate of 8 studies with 592 children22–25,33,35–37 revealed that RIPC failed to shorten the duration of MV (SMD −0.03, 95% CI −0.23–0.17, I2 = 17.7%, P for heterogeneity [PH] = 0.288; P = 0.758, Fig. 2A). To explore the potential sources of heterogeneity and the impact of stratification factors on the pooled estimate, subgroup and sensitivity analysis were performed as predesigned. Table 2 shows the results of subgroup analysis and sensitivity analysis according to various inclusion criteria. Omitting one study and combining the remaining ones in each turn showed that the null association remained stable, with a range from −0.15 (95% CI −0.38–0.08) to 0.06 (95% CI −0.11–0.23).
FIGURE 2.
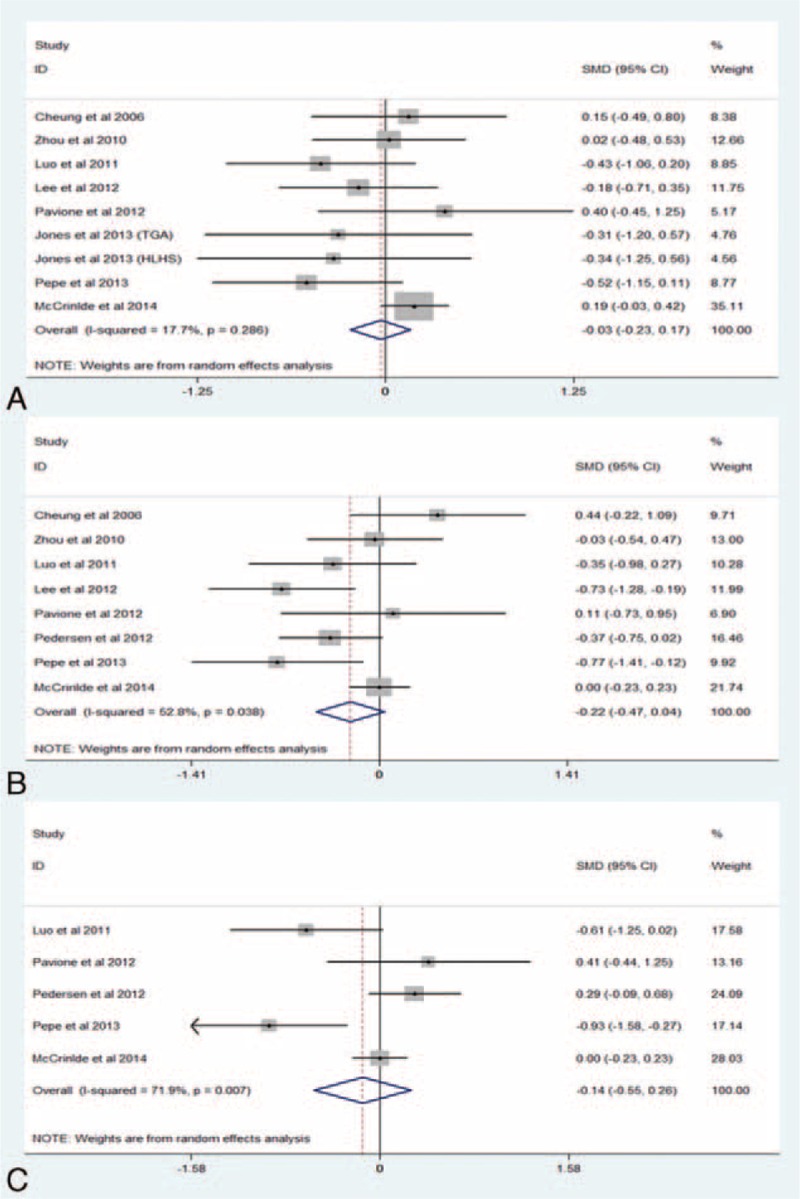
(A) Forest plots for the effect of RIPC on the duration of MV. (B) Forest plots for the effect of RIPC on ICU length of stay. (C) Forest plots for the effect of RIPC on HLOS. ICU = intensive care unit, HLOS = hospital length of stay, MV = mechanical ventilation, RIPC = remote ischemic preconditioning, SMD = standard mean difference.
TABLE 2.
Subgroup Analysis and Sensitivity Analysis According to Various Inclusion Criteria for the Duration of MV
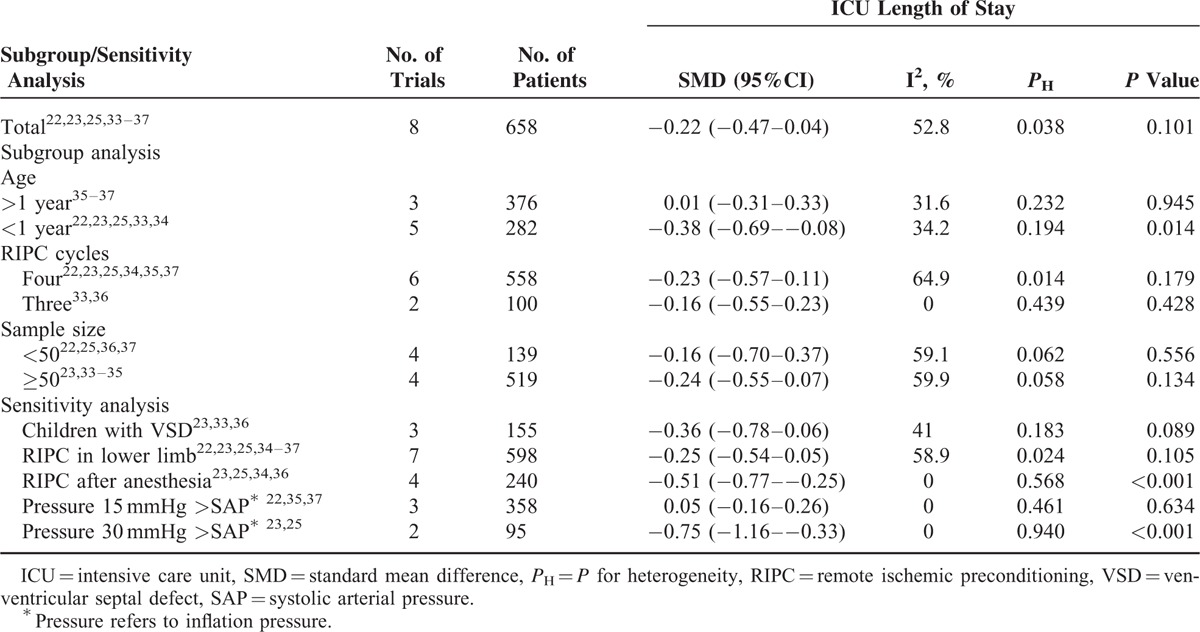
Intensive Care Unit Length of Stay
Eight studies22,23,25,33–37 with 658 patients reported the outcome of ICU length of stay, and the combined estimate showed that RIPC could not significantly reduce the ICU length of stay (SMD −0.22, 95% CI −0.47–0.04, I2 = 52.8%, PH = 0.038; P = 0.101, Figure 2B). Subgroup and sensitivity analysis are summarized in Table 3. Sensitivity analysis via omitting 1 study in each turn showed the results remained nonsignificant except for excluding the study by Cheung et al37 (SMD −0.28, 95% CI −0.53 to −0.03).
TABLE 3.
Subgroup Analysis and Sensitivity Analysis According to Various Inclusion Criteria for ICU Length of Stay
Postoperative Cardiac Troponin
Seven RCTs22–25,33,36,37 involving 293 pediatric patients were eligible for assessing the effect of RIPC on postoperative cTnI. Overall, RIPC could not decrease concentrations of cTnI at postoperative 4 to 6 hours (SMD −0.25, 95% CI −0.73–0.23, I2 = 75.2%, PH < 0.001; P = 0.311, Figure 3A) or at postoperative 20 to 24 hours (SMD 0.09, 95% CI −0.51–0.68, I2 = 83.7%, PH < 0.001; P = 0.778, Figure 3B). Table 4 summarizes the results of subgroup and sensitivity analysis. Further exclusion of any single study could not significantly alter the results with a range from −0.39 95% CI (−0.86–0.07) to −0.05 95% CI (−0.36–0.26) for cTnI at postoperative 4 to 6 hours and from −0.13 95% CI (−0.66–0.41) to 0.31 95% CI (−0.18–0.80) for cTnI at postoperative 20 to 24 hours.
FIGURE 3.
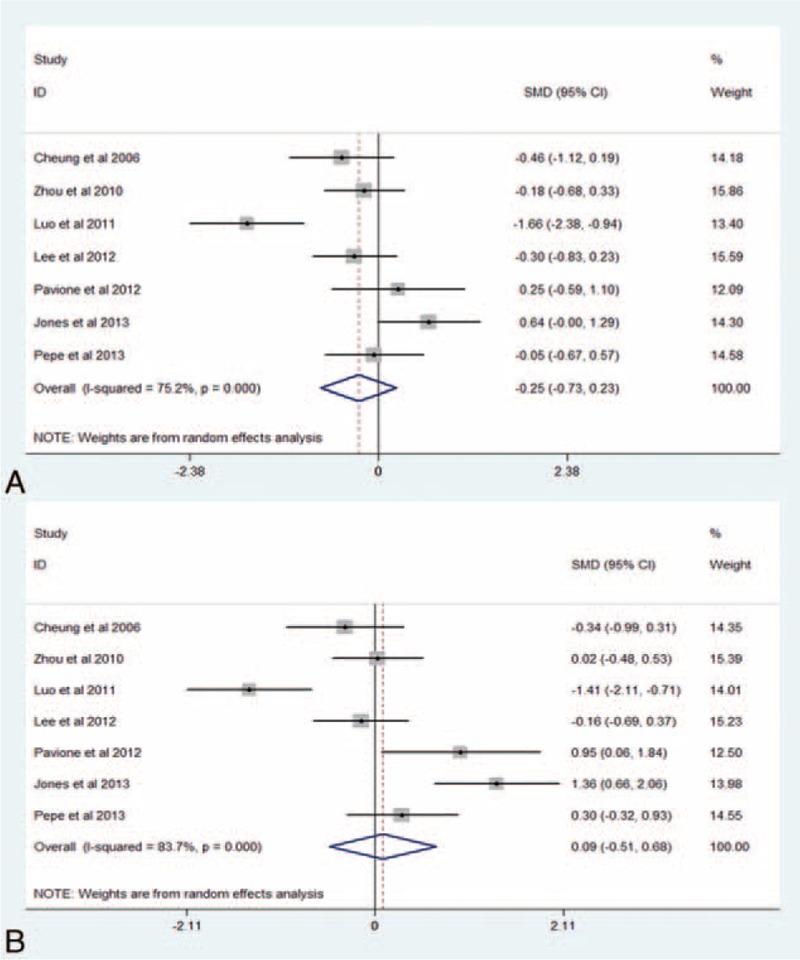
(A) Forest plots for the effect of RIPC on cTnI at postoperative 4 to 6 hours. (B) Forest plots for the effect of RIPC on cTnI at postoperative 20 to 24 hours. cTnI = cardiac troponin, RIPC = remote ischemic preconditioning, SMD = standard mean difference.
TABLE 4.
Subgroup Analysis and Sensitivity Analysis According to Various Inclusion Criteria for cTnI
Hospital Length of Stay
Five studies22,25,34–36 with 506 patients were included for the outcome of HLOS. RIPC failed to substantially alter HLOS (SMD −0.14, 95% CI −0.55–0.26, I2 = 71.9%, PH = 0.007; P = 0.493, Figure 2C). Subgroup analysis and sensitivity analysis were not performed for outcomes of HLOS and postoperative inotropic score because of the limited amount of studies.
Postoperative Inotropic Score
Four studies23,25,33,37 with 192 reported the outcome of inotropic score at postoperative 4 to 6 hours and five23,25,33,36,37 with 232 at postoperative 20 to 24 hours. Overall, the pooled estimate revealed that RIPC intervention was not associated with a reduction in the amount of hemodynamic support at postoperative 4 to 6 hours (SMD −0.19, 95% CI −0.51–0.14, I2 = 23.1%, PH = 0.272; P = 0.264, Figure 4A) or postoperative 24 hours (SMD −0.15, 95% CI −0.49–0.18, I2 = 38.2%, PH = 0.167; P = 0.365, Figure 4B).
FIGURE 4.
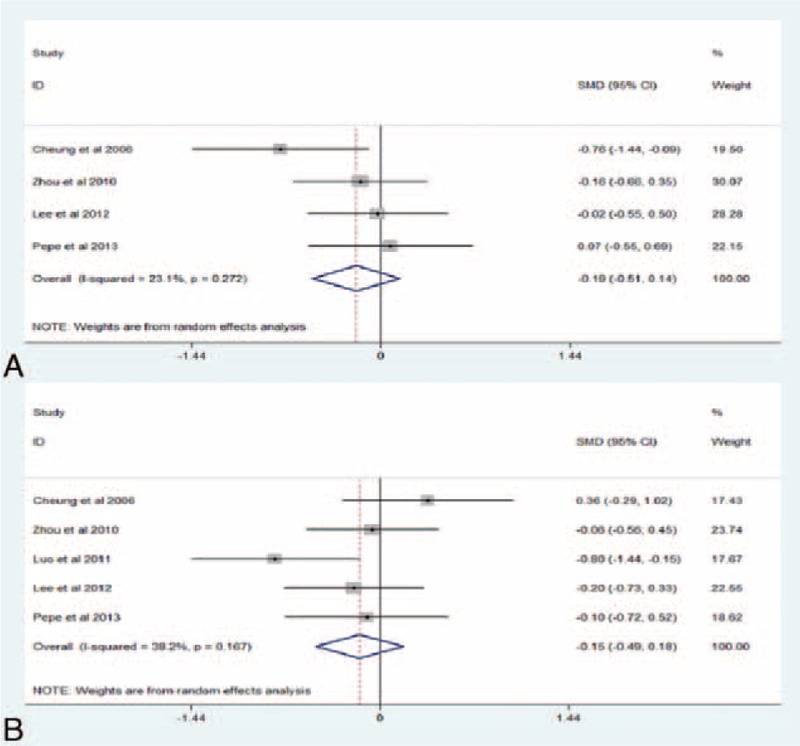
(A) Forest plots for the effect of RIPC on inotropic score at postoperative 4 to 6 hours. (B) Forest plots for the effect of RIPC on inotropic score at postoperative 24 hours. RIPC = remote ischemic preconditioning, SMD = standard mean difference.
DISCUSSION
Main Findings
Our meta-analysis suggested RIPC failed to reduce postoperative cTnI, indicating RIPC may have no benefit for cardiac protection in children undergoing CCS. The results remained stable and robust in sensitivity and subgroup analysis. Additionally, RIPC could not reduce the amount of hemodynamic support or HLOS. Moreover, overall results demonstrated that RIPC failed to shorten the duration of MV or ICU length of stay; however, the results was not consistent in subgroup or sensitivity analysis.
Comparison With Previous Studies
Our finding was inconsistent with the previous meta-analysis,20 which, involving a total of 214 subjects, suggested that RIPC could provide cardiac protection in pediatric patients undergoing CCS (postoperative cTnI: SMD −0.75, 95% CI −1.05 to −0.46). However, substantial heterogeneity among studies were observed in both our study (I2 > 75%) and the previous one (I2 = 88%), indicating that the RIPC effect was more different from each other than random error could explain. With adding 4 new RCTs of 79 patients, the controversial results might be explained by the increased statistical power. Additionally, time-point measurement data were used for cardiac protection analysis in our study, while area under the curve was used in the previous one. Nevertheless, outcome data regarding cardiac protection were estimated from the graphs in both of them if not reported directly. The estimated data might induce other potential errors, and hence both our study and the previous one should be treated with caution.
Although controversy still exists, our meta-analysis extends the previous one in several important ways. First, the increased statistical power via adding 4 RCTs with 79 patients reduced the likelihood of chance accounting for the results. Second, subgroup and sensitivity analysis were performed to test the robustness of the pooled estimate and to explore potential heterogeneity in our analysis. Although heterogeneity still remained, our findings were robust and strengthened by the subgroup and sensitivity analysis. Third, some other important clinical outcomes, such as the duration of MV, ICU length of stay, postoperative inotropic score, HLOS, and mortality, were also analyzed to give RIPC a comprehensive evaluation.
Our results demonstrated that RIPC failed to alter the amount of hemodynamic support, the duration of MV, ICU length of stay, or HLOS, which was consistent with a previous meta-analysis.38 The trial only focused on the clinical outcomes in patients undergoing coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) and also found that RIPC failed to improve these clinical outcomes. And thus there is a discrepancy between clinical outcomes and cardiac protection of RIPC in adults but not in children. We hypothesized that other concomitant diseases might overwhelm the beneficial effects of RIPC on these clinical outcomes, since adult patients undergoing cardiac surgery were almost old people and usually accompanied with other diseases, such as diabetes mellitus, hypertension, coronary heart disease, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. However, our finding was contradicted with our previous research26 which found that RIPC could only benefit ICU length of stay and we attributed the null association with other outcomes to inadequate statistical power. However, the only beneficial effect of RIPC on ICU length of stay vanished when increasing the statistical power by adding 2 studies. Therefore, we could conclude that the phenomenon that no beneficial effect of RIPC on ICU length of stay was more prone to be a verdict than happened by chance. Inconsistency existed in results of the duration of MV and ICU length of stay in the subgroup and sensitivity analysis. However, considering limitations of observational analysis and decreased statistical power, the inconsistent results should be interpreted cautiously. Seven included trials reported mortality among children undergoing CCS. However, since 6 of them reported no death in each group, quantitative analysis could not be performed. All included studies consistently demonstrated that RIPC could not alter mortality in pediatric patients after CCS, suggesting that no association between RIPC and mortality existed.
In adult patients, a mass of evidence suggested that RIPC could reduce the release of cTnI while undergoing CABG and valve replacement.39,40 The results were consistent with 2 meta-analyses despite substantial heterogeneity.19–21 Why the promising effect was not observed in pediatric patients? The contradictory effect of RIPC between adults and children might be explained by the following aspects: First, children's heart is immature and differs from adults’.37 Adults suffer more from preoperative ischemia, and the reperfusion injury is the major concern. Although pediatric patients suffer more from hypoxia, consequently, the damage derived from abrupt reintroduction of oxygen might be the main concern.41 Second, chronic myocardial hypoxia could improve the tolerance to IRI and confer direct protection to immature hearts. Children with various CHD exhibit different degrees of hypoxia and are less likely to benefit from RIPC because the protective effect of RIPC might be masked or confounded by hypoxia. Third, the long duration of ischemia during cardiac surgery might overwhelm the protective effect of RIPC;36 consequently, diverse surgery time in various CHD might be involved in the controversy. Fourth, the interval between RIPC and the initiation of cardiopulmonary bypass might be another cause for the null effect, which was confirmed by our sensitivity analysis for the duration of MV and ICU length of stay. Finally, small sample size and substantial heterogeneity might also contribute to the controversy.
Clinical Implication and Further Research
Despite well feasibility and tolerance, RIPC should not be recommended to use in children undergoing CCS according to our findings. The different intervention of RIPC, anesthetic regimens, surgery type, cyanosed or acyanotic children, and inflation pressure could contribute to the inconsistency of the results and substantial heterogeneity, thus these confounding factors should be considered in further researches. With the advances in understanding the mechanism of RIPC in cardiac surgery, several pharmacological agents have been developed to simulate IPC intervention and some have shown a promising effect in animal or human.12 The pharmacological preconditioning might be another attractive way to trigger the similar beneficial effect of RIPC in pediatric patients to adult patients, and inevitably a number of basic and clinical researches are needed.
LIMITATIONS
Several limitations should be considered in our meta-analysis. First, the original data of cTnI in several studies were estimated from the figures, which would increase some additional errors. To reduce the error to the greatest extent, the data were estimated by 2 reviewers independently and rechecked by the 3rd investigator. Second, considerable heterogeneity was observed. In order to explore the potential source of heterogeneity and the stability of pooled effects, subgroup and sensitivity analysis were conducted. Although heterogeneity still existed, the pooled effects were consistent. Third, the anesthetic regimens have been proven to influence the effect of RIPC.42 However, its impact on the pooled effect was not explored because of unavailable data. Fourth, some other interesting clinical outcomes, such as left ventricular ejection fraction, cardiac function, and renal function, were not investigated because of sparse and inconsistent reportings among studies.
CONCLUSIONS
In summary, RIPC fails to reduce the duration of MV, ICU length of stay, postoperative cTnI, amount of hemodynamic support, HLOS, or mortality, suggesting that RIPC may not benefit pediatric patients undergoing CCS. However, our findings should be interpreted with caution because of heterogeneity, and hence large-scale RCTs are still needed.
Footnotes
Abbreviations: CCS = congenital cardiac surgery, CHD = congenital heart disease, CI = confidence interval, cTnI = cardiac troponin, HLOS = hospital length of stay, ICU = intensive care unit, IPC = ischemic preconditioning, IRI = ischemia-reperfusion injury, MV = mechanical ventilation, RCT = randomized controlled trial, RIPC = remote ischemic preconditioning, SAP = systolic arterial pressure, SMD = standard mean difference.
The authors have no funding and conflicts of interest to disclose.
Supplemental digital content is available for this article. Direct URL citations appear in the printed text and are provided in the HTML and PDF versions of this article on the journal's Website (www.md-journal.com).
REFERENCES
- 1.van der Linde D, Konings EE, Slager MA, et al. Birth prevalence of congenital heart disease worldwide: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Coll Cardiol 2011; 58:2241–2247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.van der Bom T, Zomer AC, Zwinderman AH, et al. The changing epidemiology of congenital heart disease. Nat Rev Cardiol 2011; 8:50–60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Zomer AC, Verheugt CL, Vaartjes I, et al. Surgery in adults with congenital heart disease. Circulation 2011; 124:2195–2201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Pouard P, Bojan M. Neonatal cardiopulmonary bypass. Semin Thorac Cardiovasc Surg Pediatr Card Surg Annu 2013; 16:59–61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Paparella D, Yau TM, Young E. Cardiopulmonary bypass induced inflammation: pathophysiology and treatment. An update. European journal of cardio-thoracic surgery. Off J Eur Assoc Cardiothoracic Surg 2002; 21:232–244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Turer AT, Hill JA. Pathogenesis of myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury and rationale for therapy. Am J Cardiol 2010; 106:360–368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Gill RS, Pelletier JS, LaBossiere J, et al. Therapeutic strategies to protect the immature newborn myocardium during resuscitation following asphyxia. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 2012; 90:689–695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Murry CE, Jennings RB, Reimer KA. Preconditioning with ischemia: a delay of lethal cell injury in ischemic myocardium. Circulation 1986; 74:1124–1136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Toosy N, McMorris EL, Grace PA, et al. Ischaemic preconditioning protects the rat kidney from reperfusion injury. BJU Int 1999; 84:489–494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Kloner RA, Yellon D. Does ischemic preconditioning occur in patients? J Am Coll Cardiol 1994; 24:1133–1142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Hardy KJ, McClure DN, Subwongcharoen S. Ischaemic preconditioning of the liver: a preliminary study. Aust N Z J Surg 1996; 66:707–710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Bousselmi R, Lebbi MA, Ferjani M. Myocardial ischemic conditioning: physiological aspects and clinical applications in cardiac surgery. J Saudi Heart Assoc 2014; 26:93–100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Hausenloy DJ, Maddock HL, Baxter GF, et al. Inhibiting mitochondrial permeability transition pore opening: a new paradigm for myocardial preconditioning? Cardiovasc Res 2002; 55:534–543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Shinmura K, Xuan YT, Tang XL, et al. Inducible nitric oxide synthase modulates cyclooxygenase-2 activity in the heart of conscious rabbits during the late phase of ischemic preconditioning. Circ Res 2002; 90:602–608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Stein AB, Bolli R, Guo Y, et al. The late phase of ischemic preconditioning induces a prosurvival genetic program that results in marked attenuation of apoptosis. J Mol Cell Cardiol 2007; 42:1075–1085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Hausenloy DJ, Yellon DM. Remote ischaemic preconditioning: underlying mechanisms and clinical application. Cardiovasc Res 2008; 79:377–386. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Przyklenk K, Bauer B, Ovize M, et al. Regional ischemic ’preconditioning’ protects remote virgin myocardium from subsequent sustained coronary occlusion. Circulation 1993; 87:893–899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Konstantinov IE, Arab S, Kharbanda RK, et al. The remote ischemic preconditioning stimulus modifies inflammatory gene expression in humans. Physiol Genomics 2004; 19:143–150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Pilcher JM, Young P, Weatherall M, et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the cardioprotective effects of remote ischaemic preconditioning in open cardiac surgery. J R Soc Med 2012; 105:436–445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Haji Mohd Yasin NA, Herbison P, Saxena P, et al. The role of remote ischemic preconditioning in organ protection after cardiac surgery: a meta-analysis. J Surg Res 2014; 186:207–216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.D’Ascenzo F, Cavallero E, Moretti C, et al. Remote ischaemic preconditioning in coronary artery bypass surgery: a meta-analysis. Heart (British Cardiac Society) 2012; 98:1267–1271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Pavione MA, Carmona F, de Castro M, et al. Late remote ischemic preconditioning in children undergoing cardiopulmonary bypass: a randomized controlled trial. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2012; 144:178–183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Lee JH, Park YH, Byon HJ, et al. Effect of remote ischaemic preconditioning on ischaemicreperfusion injury in pulmonary hypertensive infants receiving ventricular septal defect repair. Br J Anaesth 2012; 108:223–228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Jones BO, Pepe S, Sheeran FL, et al. Remote ischemic preconditioning in cyanosed neonates undergoing cardiopulmonary bypass: a randomized controlled trial. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2013; 146:1334–1340. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Pepe S, Liaw NY, Hepponstall M, et al. Effect of remote ischemic preconditioning on phosphorylated protein signaling in children undergoing tetralogy of Fallot repair: a randomized controlled trial. J Am Heart Assoc 2013; 2:e000095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Tie HT, Luo MZ, Li ZH, et al. Remote ischemic preconditioning for pediatric patients undergoing congenital cardiac surgery: a meta-analysis. Int J Cardiol 2014; 177:551–553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, et al. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. BMJ 2009; 339:b2535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Oremus M, Wolfson C, Perrault A, et al. Interrater reliability of the modified Jadad quality scale for systematic reviews of Alzheimer's disease drug trials. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 2001; 12:232–236. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Hozo SP, Djulbegovic B, Hozo I. Estimating the mean and variance from the median, range, and the size of a sample. BMC Med Res Methodol 2005; 5:13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, et al. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ 2003; 327:557–560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Song F, Eastwood AJ, Gilbody S, et al. Publication and related biases. Health Technol Assess 2000; 4:1–115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Luo WJ. Ischemic preconditioning in children undergoing open heart operation. Ann Thorac Surg 1998; 66:2163–2164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Zhou W, Zeng D, Chen R, et al. Limb ischemic preconditioning reduces heart and lung injury after an open heart operation in infants. Pediatr Cardiol 2010; 31:22–29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Pedersen KR, Ravn HB, Povlsen JV, et al. Failure of remote ischemic preconditioning to reduce the risk of postoperative acute kidney injury in children undergoing operation for complex congenital heart disease: a randomized single-center study. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2012; 576–583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.McCrindle BW, Clarizia NA, Khaikin S, et al. Remote ischemic preconditioning in children undergoing cardiac surgery with cardiopulmonary bypass: a single-center double-blinded randomized trial. J Am Heart Assoc 2014; 3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Luo W, Zhu M, Huang R, et al. A comparison of cardiac post-conditioning and remote pre-conditioning in paediatric cardiac surgery. Cardiol Young 2011; 21:266–270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Cheung MM, Kharbanda RK, Konstantinov IE, et al. Randomized controlled trial of the effects of remote ischemic preconditioning on children undergoing cardiac surgery: first clinical application in humans. J Am Coll Cardiol 2006; 47:2277–2282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Zhang B, Zhou J, Li H, et al. Remote ischemic preconditioning does not improve the clinical outcomes in patients undergoing coronary artery bypass grafting: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Int J Cardiol 2014; 172:e36–e38. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Candilio L, Malik A, Ariti C, et al. Effect of remote ischaemic preconditioning on clinical outcomes in patients undergoing cardiac bypass surgery: a randomised controlled clinical trial. Heart 2014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Slagsvold KH, Moreira JB, Rognmo O, et al. Remote ischemic preconditioning preserves mitochondrial function and activates pro-survival protein kinase Akt in the left ventricle during cardiac surgery: a randomized trial. Int J Cardiol 2014; 177:409–417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Allen BS, Ilbawi MN. Hypoxia, reoxygenation and the role of systemic leukodepletion in pediatric heart surgery. Perfusion 2001; 16 Suppl:19–29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Malagon I, Hogenbirk K, van Pelt J, et al. Effect of three different anaesthetic agents on the postoperative production of cardiac troponin T in paediatric cardiac surgery. Br J Anaesth 2005; 94:805–809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


