Abstract
HPV types associated with genital disease are termed "high-risk" or "low-risk" viruses according to their prevalence in cancers. Two viral genes, E6 and E7, are invariably expressed in cervical carcinomas. The E7 gene product has been found to bind the retinoblastoma tumor suppressor protein and to be phosphorylated by casein kinase II. Although present in both high- and low-risk E7 proteins, these activities are diminished in the low-risk HPV-6 E7 polypeptide. To better understand the oncogenic potential of the HPV-6 E7 protein, we replaced four of its amino acids with HPV-16 E7 residues present in the analogous region of the N-terminal half of the protein. Replacement of the arginine at position 4 of the HPV-6 E7 protein with an aspartate present in HPV-16 E7 slowed the mobility of the protein when expressed in vivo. Replacement of the glycine at position 22 with an aspartate resulted in higher affinity for retinoblastoma protein binding. Replacement of valine residues at positions 30 and 37 with asparagine and aspartate, respectively, resulted in higher levels of casein kinase II phosphorylation. The substitution at position 22 was the only mutation that exhibited increased transforming activity, suggesting a correlation between the HPV E7 protein affinity for the retinoblastoma tumor suppressor protein and its ability to transform established cells. Our results show that subtle changes in sequence may result in marked differences in biological activity of HPV oncogenes.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker C. C., Phelps W. C., Lindgren V., Braun M. J., Gonda M. A., Howley P. M. Structural and transcriptional analysis of human papillomavirus type 16 sequences in cervical carcinoma cell lines. J Virol. 1987 Apr;61(4):962–971. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.4.962-971.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbosa M. S., Edmonds C., Fisher C., Schiller J. T., Lowy D. R., Vousden K. H. The region of the HPV E7 oncoprotein homologous to adenovirus E1a and Sv40 large T antigen contains separate domains for Rb binding and casein kinase II phosphorylation. EMBO J. 1990 Jan;9(1):153–160. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08091.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbosa M. S., Lowy D. R., Schiller J. T. Papillomavirus polypeptides E6 and E7 are zinc-binding proteins. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1404–1407. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1404-1407.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbosa M. S., Vass W. C., Lowy D. R., Schiller J. T. In vitro biological activities of the E6 and E7 genes vary among human papillomaviruses of different oncogenic potential. J Virol. 1991 Jan;65(1):292–298. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.1.292-298.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bedell M. A., Jones K. H., Grossman S. R., Laimins L. A. Identification of human papillomavirus type 18 transforming genes in immortalized and primary cells. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1247–1255. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1247-1255.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bedell M. A., Jones K. H., Laimins L. A. The E6-E7 region of human papillomavirus type 18 is sufficient for transformation of NIH 3T3 and rat-1 cells. J Virol. 1987 Nov;61(11):3635–3640. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.11.3635-3640.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Prediction of the secondary structure of proteins from their amino acid sequence. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1978;47:45–148. doi: 10.1002/9780470122921.ch2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeCaprio J. A., Ludlow J. W., Figge J., Shew J. Y., Huang C. M., Lee W. H., Marsilio E., Paucha E., Livingston D. M. SV40 large tumor antigen forms a specific complex with the product of the retinoblastoma susceptibility gene. Cell. 1988 Jul 15;54(2):275–283. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90559-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyson N., Howley P. M., Münger K., Harlow E. The human papilloma virus-16 E7 oncoprotein is able to bind to the retinoblastoma gene product. Science. 1989 Feb 17;243(4893):934–937. doi: 10.1126/science.2537532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dürst M., Dzarlieva-Petrusevska R. T., Boukamp P., Fusenig N. E., Gissmann L. Molecular and cytogenetic analysis of immortalized human primary keratinocytes obtained after transfection with human papillomavirus type 16 DNA. Oncogene. 1987;1(3):251–256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Firzlaff J. M., Galloway D. A., Eisenman R. N., Lüscher B. The E7 protein of human papillomavirus type 16 is phosphorylated by casein kinase II. New Biol. 1989 Oct;1(1):44–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Firzlaff J. M., Lüscher B., Eisenman R. N. Negative charge at the casein kinase II phosphorylation site is important for transformation but not for Rb protein binding by the E7 protein of human papillomavirus type 16. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 15;88(12):5187–5191. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.12.5187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gage J. R., Meyers C., Wettstein F. O. The E7 proteins of the nononcogenic human papillomavirus type 6b (HPV-6b) and of the oncogenic HPV-16 differ in retinoblastoma protein binding and other properties. J Virol. 1990 Feb;64(2):723–730. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.2.723-730.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossman S. R., Laimins L. A. E6 protein of human papillomavirus type 18 binds zinc. Oncogene. 1989 Sep;4(9):1089–1093. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halbert C. L., Demers G. W., Galloway D. A. The E6 and E7 genes of human papillomavirus type 6 have weak immortalizing activity in human epithelial cells. J Virol. 1992 Apr;66(4):2125–2134. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.4.2125-2134.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halbert C. L., Demers G. W., Galloway D. A. The E7 gene of human papillomavirus type 16 is sufficient for immortalization of human epithelial cells. J Virol. 1991 Jan;65(1):473–478. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.1.473-478.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawley-Nelson P., Vousden K. H., Hubbert N. L., Lowy D. R., Schiller J. T. HPV16 E6 and E7 proteins cooperate to immortalize human foreskin keratinocytes. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3905–3910. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08570.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemsley A., Arnheim N., Toney M. D., Cortopassi G., Galas D. J. A simple method for site-directed mutagenesis using the polymerase chain reaction. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Aug 25;17(16):6545–6551. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.16.6545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudson J. B., Bedell M. A., McCance D. J., Laiminis L. A. Immortalization and altered differentiation of human keratinocytes in vitro by the E6 and E7 open reading frames of human papillomavirus type 18. J Virol. 1990 Feb;64(2):519–526. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.2.519-526.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jewers R. J., Hildebrandt P., Ludlow J. W., Kell B., McCance D. J. Regions of human papillomavirus type 16 E7 oncoprotein required for immortalization of human keratinocytes. J Virol. 1992 Mar;66(3):1329–1335. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.3.1329-1335.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaur P., McDougall J. K. Characterization of primary human keratinocytes transformed by human papillomavirus type 18. J Virol. 1988 Jun;62(6):1917–1924. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.6.1917-1924.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuenzel E. A., Mulligan J. A., Sommercorn J., Krebs E. G. Substrate specificity determinants for casein kinase II as deduced from studies with synthetic peptides. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 5;262(19):9136–9140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matlashewski G., Schneider J., Banks L., Jones N., Murray A., Crawford L. Human papillomavirus type 16 DNA cooperates with activated ras in transforming primary cells. EMBO J. 1987 Jun;6(6):1741–1746. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02426.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Münger K., Phelps W. C., Bubb V., Howley P. M., Schlegel R. The E6 and E7 genes of the human papillomavirus type 16 together are necessary and sufficient for transformation of primary human keratinocytes. J Virol. 1989 Oct;63(10):4417–4421. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.10.4417-4421.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Münger K., Werness B. A., Dyson N., Phelps W. C., Harlow E., Howley P. M. Complex formation of human papillomavirus E7 proteins with the retinoblastoma tumor suppressor gene product. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 20;8(13):4099–4105. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08594.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
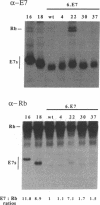
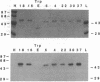
- Münger K., Yee C. L., Phelps W. C., Pietenpol J. A., Moses H. L., Howley P. M. Biochemical and biological differences between E7 oncoproteins of the high- and low-risk human papillomavirus types are determined by amino-terminal sequences. J Virol. 1991 Jul;65(7):3943–3948. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.7.3943-3948.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phelps W. C., Yee C. L., Münger K., Howley P. M. The human papillomavirus type 16 E7 gene encodes transactivation and transformation functions similar to those of adenovirus E1A. Cell. 1988 May 20;53(4):539–547. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90570-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pirisi L., Yasumoto S., Feller M., Doniger J., DiPaolo J. A. Transformation of human fibroblasts and keratinocytes with human papillomavirus type 16 DNA. J Virol. 1987 Apr;61(4):1061–1066. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.4.1061-1066.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rustgi A. K., Dyson N., Bernards R. Amino-terminal domains of c-myc and N-myc proteins mediate binding to the retinoblastoma gene product. Nature. 1991 Aug 8;352(6335):541–544. doi: 10.1038/352541a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheffner M., Münger K., Byrne J. C., Howley P. M. The state of the p53 and retinoblastoma genes in human cervical carcinoma cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 1;88(13):5523–5527. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.13.5523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlegel R., Phelps W. C., Zhang Y. L., Barbosa M. Quantitative keratinocyte assay detects two biological activities of human papillomavirus DNA and identifies viral types associated with cervical carcinoma. EMBO J. 1988 Oct;7(10):3181–3187. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03185.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider-Gädicke A., Schwarz E. Different human cervical carcinoma cell lines show similar transcription patterns of human papillomavirus type 18 early genes. EMBO J. 1986 Sep;5(9):2285–2292. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04496.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smotkin D., Wettstein F. O. Transcription of human papillomavirus type 16 early genes in a cervical cancer and a cancer-derived cell line and identification of the E7 protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4680–4684. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storey A., Osborn K., Crawford L. Co-transformation by human papillomavirus types 6 and 11. J Gen Virol. 1990 Jan;71(Pt 1):165–171. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-1-165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vousden K. H., Doniger J., DiPaolo J. A., Lowy D. R. The E7 open reading frame of human papillomavirus type 16 encodes a transforming gene. Oncogene Res. 1988 Sep;3(2):167–175. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe S., Kanda T., Sato H., Furuno A., Yoshiike K. Mutational analysis of human papillomavirus type 16 E7 functions. J Virol. 1990 Jan;64(1):207–214. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.1.207-214.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whyte P., Buchkovich K. J., Horowitz J. M., Friend S. H., Raybuck M., Weinberg R. A., Harlow E. Association between an oncogene and an anti-oncogene: the adenovirus E1A proteins bind to the retinoblastoma gene product. Nature. 1988 Jul 14;334(6178):124–129. doi: 10.1038/334124a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodworth C. D., Doniger J., DiPaolo J. A. Immortalization of human foreskin keratinocytes by various human papillomavirus DNAs corresponds to their association with cervical carcinoma. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):159–164. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.159-164.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yutsudo M., Okamoto Y., Hakura A. Functional dissociation of transforming genes of human papillomavirus type 16. Virology. 1988 Oct;166(2):594–597. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90532-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Villiers E. M. Heterogeneity of the human papillomavirus group. J Virol. 1989 Nov;63(11):4898–4903. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.11.4898-4903.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]