Abstract
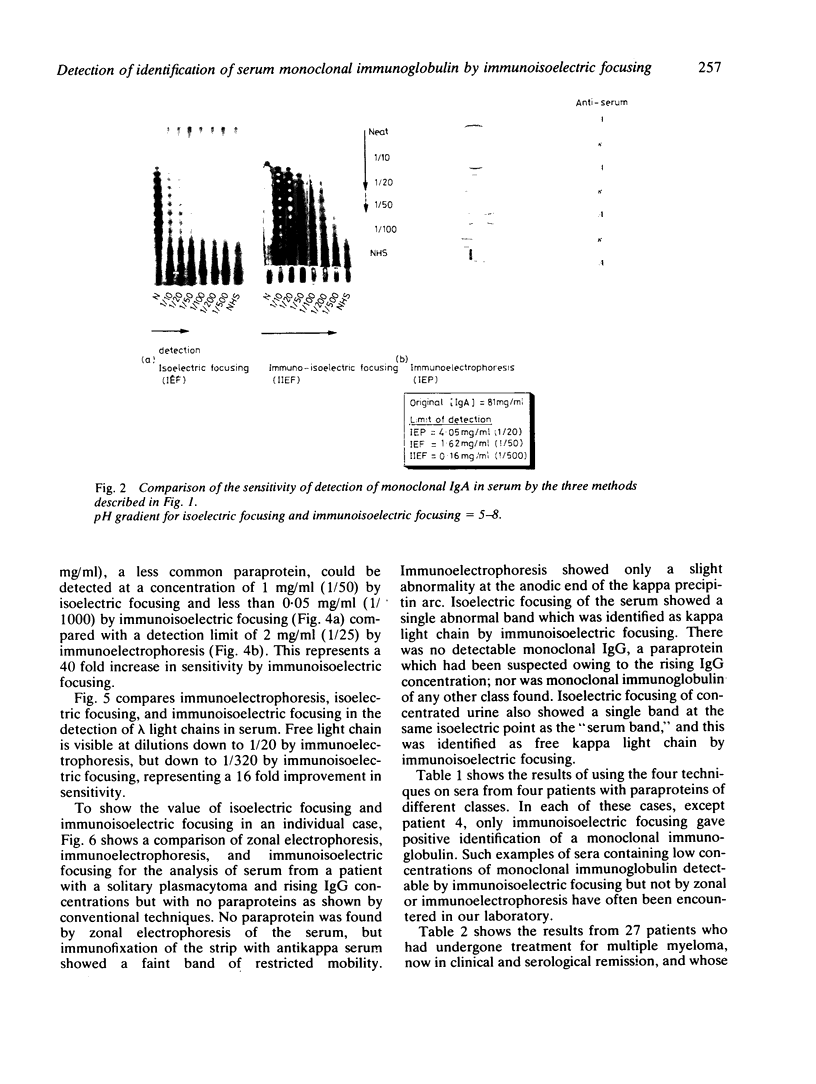
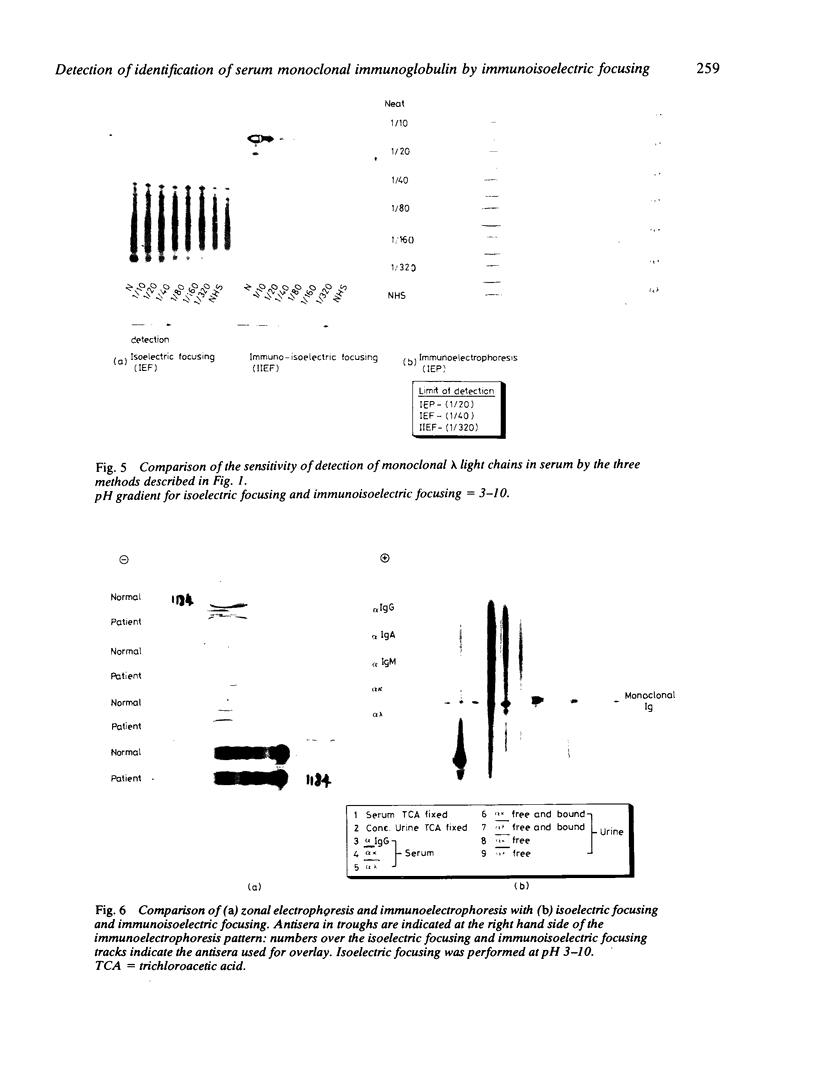
The limits of detection of four classes of monoclonal immunoglobulin and free light chain in serum by isoelectric focusing and immunoisoelectric focusing have been determined and the sensitivity of these techniques compared with that obtained using immunoelectrophoresis and zonal electrophoresis with immunofixation. Immunoisoelectric focusing was 10-40 times more sensitive than immunoelectrophoresis and could be used to detect concentrations of monoclonal immunoglobulin that were undetectable by zonal electrophoresis with immunofixation. The relevance of this work in monitoring multiple myeloma during treatment and relapse is discussed.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexanian R., Gehan E., Haut A., Saiki J., Weick J. Unmaintained remissions in multiple myeloma. Blood. 1978 Jun;51(6):1005–1011. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durie B. G., Salmon S. E. A clinical staging system for multiple myeloma. Correlation of measured myeloma cell mass with presenting clinical features, response to treatment, and survival. Cancer. 1975 Sep;36(3):842–854. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197509)36:3<842::aid-cncr2820360303>3.0.co;2-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobbs J. R. Immunocytoma o' mice an' men. Br Med J. 1971 Apr 10;2(5753):67–72. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5753.67. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyle R. A., Greipp P. R. 3. The laboratory investigation of monoclonal gammopathies. Mayo Clin Proc. 1978 Nov;53(11):719–739. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyle R. A. Monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (MGUS): a review. Clin Haematol. 1982 Feb;11(1):123–150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norfolk D., Child J. A., Cooper E. H., Kerruish S., Ward A. M. Serum beta 2-microglobulin in myelomatosis: potential value in stratification and monitoring. Br J Cancer. 1980 Oct;42(4):510–515. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1980.273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichert C. M., Everett D. F., Jr, Nadler P. I., Papadopoulos N. M. High-resolution zone electrophoresis, combined with immunofixation, in the detection of an occult myeloma paraprotein. Clin Chem. 1982 Nov;28(11):2312–2313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritchie R. F., Smith R. Immunofixation. III. Application to the study of monoclonal proteins. Clin Chem. 1976 Dec;22(12):1982–1985. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salmon S. E. Immunoglobulin synthesis and tumour cell number and the natural history of multiple myeloma. Br Med J. 1971 May 8;2(5757):321–321. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5757.321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schen R. J., Rabinowitz M. Clinical significance of abnormally shaped IgM arcs in serum immunoelectrophoresis. Clin Chim Acta. 1972 Aug;40(1):53–57. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(72)90250-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu K., Murate T., Kunii A. Circulating immunoglobulin-secreting cells in patients with plasma cell dyscrasia. Blood. 1980 Apr;55(4):590–594. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu K., Ohnishi K., Kunii A. Differentiation of benign monoclonal gammopathy and smouldering multiple myeloma from frank myeloma. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Dec;50(3):596–600. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinclair D., Kumararatne D. S., Forrester J. B., Lamont A., Stott D. I. The application of isoelectric focusing to routine screening for paraproteinaemia. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Nov 11;64(1-2):147–156. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90393-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]