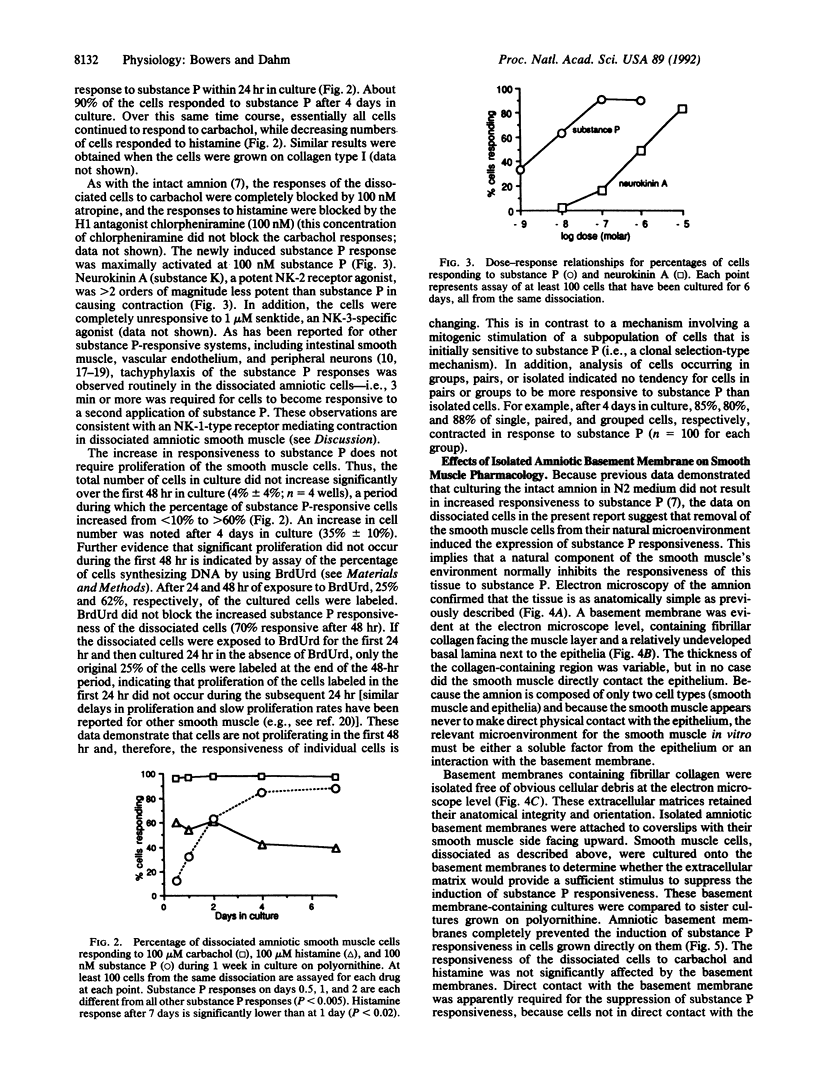
Abstract
Little is known about the extracellular factors that determine a cell's responsiveness to neurotransmitters. This is a particularly important issue for pharmacologically diverse cell types such as neurons and smooth muscle. This report demonstrates that the contractile responses of amniotic smooth muscle to a specific neuropeptide, substance P, is controlled by a molecule(s) intimately associated with the extracellular basement membrane. This molecule(s) normally represses the expression of substance P responsiveness in this tissue. When the amniotic smooth muscle is separated from the basement membrane by dissociation, normally unresponsive cells exhibit a progressive increase in responsiveness to substance P, beginning within the first 24 hr in culture. The induction of substance P responses was completely inhibited when the cells were plated onto isolated amniotic basement membrane rather than onto polyornithine or collagen I. Similar changes in the responsiveness to another agonist, histamine, did not occur. The data demonstrate that extracellular matrix exerts a major instructive influence in determining the responsiveness of avian amniotic smooth muscle to specific ligands. We suggest that similar regulatory mechanisms may operate in other tissues.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bowers C. W. Expression of functional neurotransmitter receptors in an uninnervated tissue: avian amnion. Cell Tissue Res. 1989 Nov;258(2):409–415. doi: 10.1007/BF00239462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brehm P., Henderson L. Regulation of acetylcholine receptor channel function during development of skeletal muscle. Dev Biol. 1988 Sep;129(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(88)90156-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brehm P. Resolving the structural basis for developmental changes in muscle ACh receptor function: it takes nerve. Trends Neurosci. 1989 May;12(5):174–177. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(89)90064-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodin E., Alumets J., Håkanson R., Leander S., Sundler F. Immunoreactive substance P in the chicken gut: distribution, development and possible functional significance. Cell Tissue Res. 1981;216(3):455–469. doi: 10.1007/BF00238643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burden S. J., Sargent P. B., McMahan U. J. Acetylcholine receptors in regenerating muscle accumulate at original synaptic sites in the absence of the nerve. J Cell Biol. 1979 Aug;82(2):412–425. doi: 10.1083/jcb.82.2.412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey D. J. Control of growth and differentiation of vascular cells by extracellular matrix proteins. Annu Rev Physiol. 1991;53:161–177. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.53.030191.001113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiquet-Ehrismann R., Kalla P., Pearson C. A., Beck K., Chiquet M. Tenascin interferes with fibronectin action. Cell. 1988 May 6;53(3):383–390. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90158-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Mey J. G., Vanhoutte P. M. Heterogeneous behavior of the canine arterial and venous wall. Importance of the endothelium. Circ Res. 1982 Oct;51(4):439–447. doi: 10.1161/01.res.51.4.439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dun N. J., Karczmar A. G. Actions of substance P on sympathetic neurons. Neuropharmacology. 1979 Feb;18(2):215–218. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(79)90064-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EVANS D. H., EVANS E. M. THE MEMBRANE RELATIONSHIPS OF SMOOTH MUSCLES: AN ELECTRON MICROSCOPE STUDY. J Anat. 1964 Jan;98:37–46. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fay F. S., Delise C. M. Contraction of isolated smooth-muscle cells--structural changes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Mar;70(3):641–645. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.3.641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godfrey E. W., Nitkin R. M., Wallace B. G., Rubin L. L., McMahan U. J. Components of Torpedo electric organ and muscle that cause aggregation of acetylcholine receptors on cultured muscle cells. J Cell Biol. 1984 Aug;99(2):615–627. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.2.615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman D., Carlson B. M., Staple J. Induction of adult-type nicotinic acetylcholine receptor gene expression in noninnervated regenerating muscle. Neuron. 1991 Oct;7(4):649–658. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90377-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gratzner H. G. Monoclonal antibody to 5-bromo- and 5-iododeoxyuridine: A new reagent for detection of DNA replication. Science. 1982 Oct 29;218(4571):474–475. doi: 10.1126/science.7123245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grotendorst G. R., Seppä H. E., Kleinman H. K., Martin G. R. Attachment of smooth muscle cells to collagen and their migration toward platelet-derived growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3669–3672. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay E. D. Extracellular matrix. J Cell Biol. 1981 Dec;91(3 Pt 2):205s–223s. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.3.205s. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall L. M., Sanes J. R., McMahan U. J. Reinnervation of original synaptic sites on muscle fiber basement membrane after disruption of the muscle cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jul;74(7):3073–3077. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.7.3073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinou J. C., Falls D. L., Fischbach G. D., Merlie J. P. Acetylcholine receptor-inducing activity stimulates expression of the epsilon-subunit gene of the muscle acetylcholine receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 1;88(17):7669–7673. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.17.7669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinou J. C., Merlie J. P. Nerve-dependent modulation of acetylcholine receptor epsilon-subunit gene expression. J Neurosci. 1991 May;11(5):1291–1299. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.11-05-01291.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMahan U. J., Slater C. R. The influence of basal lamina on the accumulation of acetylcholine receptors at synaptic sites in regenerating muscle. J Cell Biol. 1984 Apr;98(4):1453–1473. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.4.1453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakanishi S. Mammalian tachykinin receptors. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1991;14:123–136. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.14.030191.001011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nitkin R. M., Smith M. A., Magill C., Fallon J. R., Yao Y. M., Wallace B. G., McMahan U. J. Identification of agrin, a synaptic organizing protein from Torpedo electric organ. J Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;105(6 Pt 1):2471–2478. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.6.2471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regoli D., D'Orléans-Juste P., Escher E., Mizrahi J. Receptors for substance P. I. The pharmacological preparations. Eur J Pharmacol. 1984 Jan 27;97(3-4):161–170. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(84)90447-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regoli D., Dion S., Rhaleb N. E., Rouissi N., Tousignant C., Jukic D., D'Orleans-Juste P., Drapeau G. Selective agonists for receptors of substance P and related neurokinins. Biopolymers. 1989 Jan;28(1):81–90. doi: 10.1002/bip.360280111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichardt L. F., Tomaselli K. J. Extracellular matrix molecules and their receptors: functions in neural development. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1991;14:531–570. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.14.030191.002531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandberg B. E., Iversen L. L. Substance P. J Med Chem. 1982 Sep;25(9):1009–1015. doi: 10.1021/jm00351a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanes J. R. Extracellular matrix molecules that influence neural development. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1989;12:491–516. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.12.030189.002423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanes J. R., Marshall L. M., McMahan U. J. Reinnervation of muscle fiber basal lamina after removal of myofibers. Differentiation of regenerating axons at original synaptic sites. J Cell Biol. 1978 Jul;78(1):176–198. doi: 10.1083/jcb.78.1.176. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuger L., O'Shea K. S., Nelson B. B., Varani J. Organotypic arrangement of mouse embryonic lung cells on a basement membrane extract: involvement of laminin. Development. 1990 Dec;110(4):1091–1099. doi: 10.1242/dev.110.4.1091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Souquet J. C., Grider J. R., Bitar K. N., Makhlouf G. M. Receptors for mammalian tachykinins on isolated intestinal smooth muscle cells. Am J Physiol. 1985 Oct;249(4 Pt 1):G533–G538. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1985.249.4.G533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terranova V. P., Rohrbach D. H., Martin G. R. Role of laminin in the attachment of PAM 212 (epithelial) cells to basement membrane collagen. Cell. 1980 Dec;22(3):719–726. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90548-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thyberg J., Palmberg L., Nilsson J., Ksiazek T., Sjölund M. Phenotype modulation in primary cultures of arterial smooth muscle cells. On the role of platelet-derived growth factor. Differentiation. 1983;25(2):156–167. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1984.tb01351.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsunoo A., Konishi S., Otsuka M. Substance P as an excitatory transmitter of primary afferent neurons in guinea-pig sympathetic ganglia. Neuroscience. 1982;7(9):2025–2037. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(82)90117-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vracko R., Benditt E. P. Basal lamina: the scaffold for orderly cell replacement. Observations on regeneration of injured skeletal muscle fibers and capillaries. J Cell Biol. 1972 Nov;55(2):406–419. doi: 10.1083/jcb.55.2.406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]