Abstract
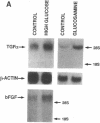
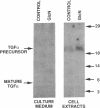
We have investigated the regulation of the expression of two growth factors found in vascular smooth muscle, transforming growth factor alpha (TGF alpha) and basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF). Cells cultured in medium containing 30 mM glucose exhibited a 2-fold increase in TGF alpha mRNA and a 3-fold increase in bFGF mRNA compared with cells grown in normal (5.5 mM) glucose. Glucosamine was more potent than glucose, leading to a 6-fold increase in TGF alpha mRNA. TGF alpha protein levels were also increased by glucosamine treatment, and the predominant species present was the membrane-bound precursor form of TGF alpha. To examine further the regulation of growth factors by sugars, cultured rat aortic smooth muscle cells were transfected with a plasmid construct consisting of a 1.2-kilobase-pair fragment of the TGF alpha promoter linked to a luciferase reporter gene. Increasing the concentration of glucose in the culture medium from 5.5 mM to 30 mM led to a rapid, 1.7-fold increase in the activity of the TGF alpha promoter. Glucosamine was much more potent than glucose in this stimulation, with 2 mM glucosamine causing a 12-fold increase in TGF alpha promoter activity. Insulin had no effect on luciferase activity in either the presence or the absence of added sugars. The glucose response element of the TGF alpha gene maps to a 130-base-pair segment that includes three potential binding sites for the transcription factor Sp1. We conclude that high glucose concentrations such as are reached in diabetes mellitus can stimulate the transcription of the genes for growth factors in vascular smooth muscle cells. This signaling pathway apparently involves the metabolism of glucose to glucosamine. This effect could be representative of nutritional regulation of a family of genes and could contribute to the toxicity of hyperglycemia and the vascular complications of diabetes.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bar R. S., Boes M., Dake B. L., Booth B. A., Henley S. A., Sandra A. Insulin, insulin-like growth factors, and vascular endothelium. Am J Med. 1988 Nov 28;85(5A):59–70. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(88)90398-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjorge J. D., Paterson A. J., Kudlow J. E. Phorbol ester or epidermal growth factor (EGF) stimulates the concurrent accumulation of mRNA for the EGF receptor and its ligand transforming growth factor-alpha in a breast cancer cell line. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 5;264(7):4021–4027. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brachmann R., Lindquist P. B., Nagashima M., Kohr W., Lipari T., Napier M., Derynck R. Transmembrane TGF-alpha precursors activate EGF/TGF-alpha receptors. Cell. 1989 Feb 24;56(4):691–700. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90591-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradbury E. M., Moss T., Hayashi H., Hjelm R. P., Suau P., Stephens R. M., Baldwin J. P., Crane-Robinson C. Nucleosomes, histone interactions, and the role of histones H3 and H4. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1978;42(Pt 1):277–286. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1978.042.01.030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang S. C., Wooden S. K., Nakaki T., Kim Y. K., Lin A. Y., Kung L., Attenello J. W., Lee A. S. Rat gene encoding the 78-kDa glucose-regulated protein GRP78: its regulatory sequences and the effect of protein glycosylation on its expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(3):680–684. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.3.680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahl-Jørgensen K., Brinchmann-Hansen O., Hanssen K. F., Sandvik L., Aagenaes O. Rapid tightening of blood glucose control leads to transient deterioration of retinopathy in insulin dependent diabetes mellitus: the Oslo study. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1985 Mar 16;290(6471):811–815. doi: 10.1136/bmj.290.6471.811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derynck R., Roberts A. B., Winkler M. E., Chen E. Y., Goeddel D. V. Human transforming growth factor-alpha: precursor structure and expression in E. coli. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):287–297. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90550-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engerman R. L., Kern T. S. Progression of incipient diabetic retinopathy during good glycemic control. Diabetes. 1987 Jul;36(7):808–812. doi: 10.2337/diab.36.7.808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukumoto H., Kayano T., Buse J. B., Edwards Y., Pilch P. F., Bell G. I., Seino S. Cloning and characterization of the major insulin-responsive glucose transporter expressed in human skeletal muscle and other insulin-responsive tissues. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 15;264(14):7776–7779. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunning P., Ponte P., Okayama H., Engel J., Blau H., Kedes L. Isolation and characterization of full-length cDNA clones for human alpha-, beta-, and gamma-actin mRNAs: skeletal but not cytoplasmic actins have an amino-terminal cysteine that is subsequently removed. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 May;3(5):787–795. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.5.787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunther S., Alexander R. W., Atkinson W. J., Gimbrone M. A., Jr Functional angiotensin II receptors in cultured vascular smooth muscle cells. J Cell Biol. 1982 Feb;92(2):289–298. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.2.289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt G. D., Hart G. W. The subcellular distribution of terminal N-acetylglucosamine moieties. Localization of a novel protein-saccharide linkage, O-linked GlcNAc. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 15;261(17):8049–8057. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson S. P., Tjian R. O-glycosylation of eukaryotic transcription factors: implications for mechanisms of transcriptional regulation. Cell. 1988 Oct 7;55(1):125–133. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90015-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadonaga J. T., Carner K. R., Masiarz F. R., Tjian R. Isolation of cDNA encoding transcription factor Sp1 and functional analysis of the DNA binding domain. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):1079–1090. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90594-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kearse K. P., Hart G. W. Lymphocyte activation induces rapid changes in nuclear and cytoplasmic glycoproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 1;88(5):1701–1705. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.5.1701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klagsbrun M., Edelman E. R. Biological and biochemical properties of fibroblast growth factors. Implications for the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. Arteriosclerosis. 1989 May-Jun;9(3):269–278. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.9.3.269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauritzen T., Frost-Larsen K., Larsen H. W., Deckert T. Two-year experience with continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion in relation to retinopathy and neuropathy. Diabetes. 1985 Aug;34 (Suppl 3):74–79. doi: 10.2337/diab.34.3.s74. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee D. C., Rose T. M., Webb N. R., Todaro G. J. Cloning and sequence analysis of a cDNA for rat transforming growth factor-alpha. Nature. 1985 Feb 7;313(6002):489–491. doi: 10.1038/313489a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee T. S., MacGregor L. C., Fluharty S. J., King G. L. Differential regulation of protein kinase C and (Na,K)-adenosine triphosphatase activities by elevated glucose levels in retinal capillary endothelial cells. J Clin Invest. 1989 Jan;83(1):90–94. doi: 10.1172/JCI113889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] [Retracted]
- Lee T. S., Saltsman K. A., Ohashi H., King G. L. Activation of protein kinase C by elevation of glucose concentration: proposal for a mechanism in the development of diabetic vascular complications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):5141–5145. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.5141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] [Research Misconduct Found]
- Lindner V., Lappi D. A., Baird A., Majack R. A., Reidy M. A. Role of basic fibroblast growth factor in vascular lesion formation. Circ Res. 1991 Jan;68(1):106–113. doi: 10.1161/01.res.68.1.106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall S., Bacote V., Traxinger R. R. Discovery of a metabolic pathway mediating glucose-induced desensitization of the glucose transport system. Role of hexosamine biosynthesis in the induction of insulin resistance. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 15;266(8):4706–4712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClain D. A., Maegawa H., Lee J., Dull T. J., Ulrich A., Olefsky J. M. A mutant insulin receptor with defective tyrosine kinase displays no biologic activity and does not undergo endocytosis. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 25;262(30):14663–14671. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller S. G., Paterson A. J., Kudlow J. E. Transforming growth factor alpha in arterioles: cell surface processing of its precursor by elastases. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;10(9):4596–4602. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.9.4596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy L. J., Ghahary A., Chakrabarti S. Insulin regulation of IGF-I expression in rat aorta. Diabetes. 1990 Jun;39(6):657–662. doi: 10.2337/diab.39.6.657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raja R. H., Paterson A. J., Shin T. H., Kudlow J. E. Transcriptional regulation of the human transforming growth factor-alpha gene. Mol Endocrinol. 1991 Apr;5(4):514–520. doi: 10.1210/mend-5-4-514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R., Glomset J. A. Atherosclerosis and the arterial smooth muscle cell: Proliferation of smooth muscle is a key event in the genesis of the lesions of atherosclerosis. Science. 1973 Jun 29;180(4093):1332–1339. doi: 10.1126/science.180.4093.1332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R., Masuda J., Raines E. W., Gown A. M., Katsuda S., Sasahara M., Malden L. T., Masuko H., Sato H. Localization of PDGF-B protein in macrophages in all phases of atherogenesis. Science. 1990 May 25;248(4958):1009–1012. doi: 10.1126/science.2343305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossi F., Grzeskowiak M., Della Bianca V., Sbarbati A. De novo synthesis of diacylglycerol from glucose. A new pathway of signal transduction in human neutrophils stimulated during phagocytosis of beta-glucan particles. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 5;266(13):8034–8038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz G. S., White M., Mitchell R., Brown G., Lynch J., Twardzik D. R., Todaro G. J. Epithelial wound healing enhanced by transforming growth factor-alpha and vaccinia growth factor. Science. 1987 Jan 16;235(4786):350–352. doi: 10.1126/science.3492044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorens B., Charron M. J., Lodish H. F. Molecular physiology of glucose transporters. Diabetes Care. 1990 Mar;13(3):209–218. doi: 10.2337/diacare.13.3.209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watzele G., Tanner W. Cloning of the glutamine:fructose-6-phosphate amidotransferase gene from yeast. Pheromonal regulation of its transcription. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):8753–8758. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]