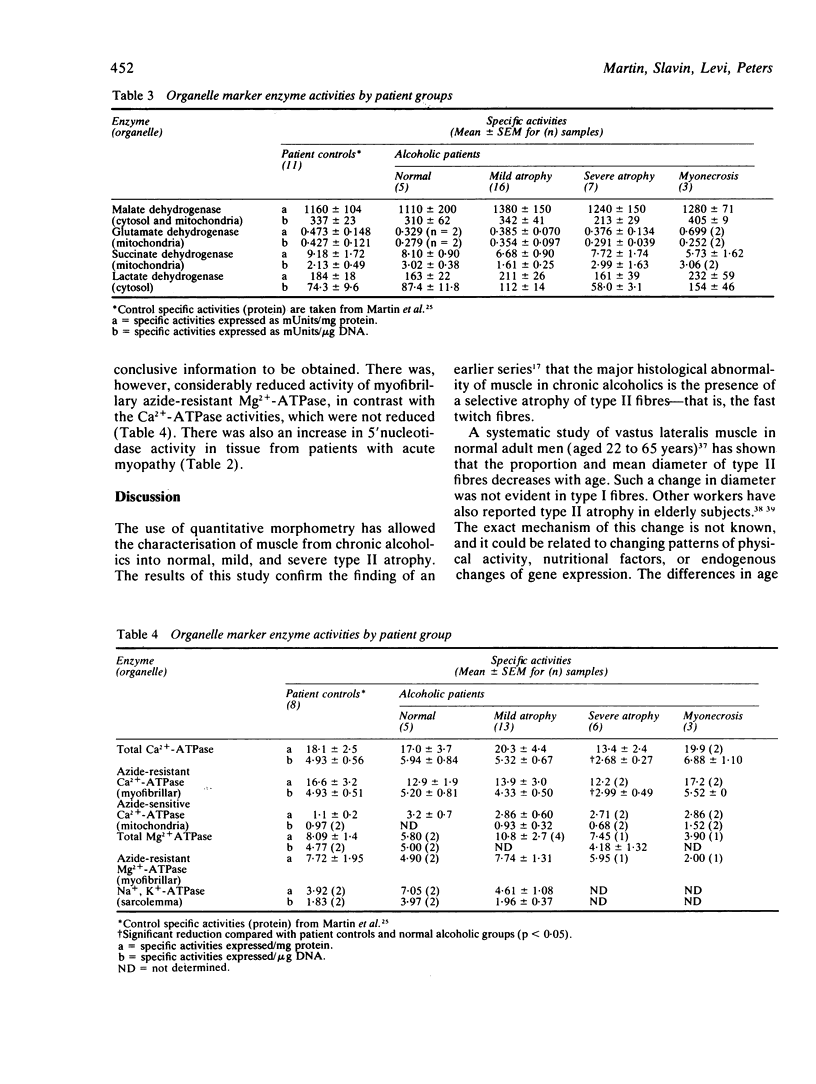
Abstract
The muscle abnormalities associated with chronic alcohol consumption were studied by applying histological and biochemical techniques to tissue obtained by percutaneous needle biopsy from the quadriceps muscles of 41 patients. Measurement of the fibre size showed atrophy of both type I (p less than 0.05) and type II (p less than 0.001) fibres. The degree of atrophy was more severe for type II fibres (33% reduction in median diameter) than type I (17%). Marker enzyme activities for the principal organelles were assayed. Compared with biopsy specimens from non-alcoholic controls, no differences were found in the activities of lysosomal, mitochondrial, peroxisomal, cytosolic, sarcolemmal, or sarcoplasmic reticulum enzymes, expressed per microgram DNA. A reduction in the protein to DNA ratio was evident in severely atrophic biopsies, and this was associated with a significant reduction of myofibrillary Ca2+-ATPase activity. These results suggest a selective loss of type II fibre myofibrillary protein and do not confirm earlier suggestions of specific mitochondrial damage.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brooke M. H., Engel W. K. The histographic analysis of human muscle biopsies with regard to fiber types. 1. Adult male and female. Neurology. 1969 Mar;19(3):221–233. doi: 10.1212/wnl.19.3.221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edström L. Selective atrophy of red muscle fibres in the quadriceps in long-standing knee-joint dysfunction. Injuries to the anterior cruciate ligament. J Neurol Sci. 1970 Dec;11(6):551–558. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(70)90105-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards R., Young A., Wiles M. Needle biopsy of skeletal muscle in the diagnosis of myopathy and the clinical study of muscle function and repair. N Engl J Med. 1980 Jan 31;302(5):261–271. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198001313020504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel W. K. Selective and nonselective susceptibility of muscle fiber types. A new approach to human neuromuscular diseases. Arch Neurol. 1970 Feb;22(2):97–117. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1970.00480200003001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitchett D. H., Scott J., Stephens H. R., Peters T. J. Myocardial subcellular fractionation studies on cardiomyopathic Syrian hamsters. Cardiovasc Res. 1979 May;13(5):260–268. doi: 10.1093/cvr/13.5.260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitchett D. H., Wells G., Peters T. J. Analytical subcellular fractionation of human heart: a comparison of left and right ventricle with hypertrophic obstructive myopathic tissue. Cardiovasc Res. 1979 Sep;13(9):532–540. doi: 10.1093/cvr/13.9.532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanid A., Slavin G., Mair W., Sowter C., Ward P., Webb J., Levi J. Fibre type changes in striated muscle of alcoholics. J Clin Pathol. 1981 Sep;34(9):991–995. doi: 10.1136/jcp.34.9.991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Häggmark T., Eriksson E. Cylinder or mobile cast brace after knee ligament surgery. A clinical analysis and morphologic and enzymatic studies of changes in the quadriceps muscle. Am J Sports Med. 1979 Jan-Feb;7(1):48–56. doi: 10.1177/036354657900700111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarman C. M., Kellett J. M. Alcoholism in the general hospital. Br Med J. 1979 Aug 25;2(6188):469–472. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6188.469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn L. B., Meyer J. S. Acute myopathy in chronic alcoholism: a study of 22 autopsy cases, with ultrastructural observations. Am J Clin Pathol. 1970 Apr;53(4):516–530. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/53.4.516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapuściński J., Skoczylas B. Simple and rapid fluorimetric method for DNA microassay. Anal Biochem. 1977 Nov;83(1):252–257. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90533-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kar N. C., Pearson C. M. Catalase, superoxide dismutase, glutathione reductase and thiobarbituric acid-reactive products in normal and dystrophic human muscle. Clin Chim Acta. 1979 Jun 15;94(3):277–280. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(79)90076-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiessling K. H., Pilström L., Bylund A. C., Piehl K., Saltin B. Effects of chronic ethanol abuse on structure and enzyme activities of skeletal muscle in man. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1975 Oct;35(6):601–607. doi: 10.1080/00365517509095786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klinkerfuss G., Bleisch V., Dioso M. M., Perkoff G. T. A spectrum of myopathy associated with alcoholism. II. Light and electron microscopic observations. Ann Intern Med. 1967 Sep;67(3):493–510. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-67-3-493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIEBER C. S., JONES D. P., DECARLI L. M. EFFECTS OF PROLONGED ETHANOL INTAKE: PRODUCTION OF FATTY LIVER DESPITE ADEQUATE DIETS. J Clin Invest. 1965 Jun;44:1009–1021. doi: 10.1172/JCI105200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin F. C., Levi A. J., Slavin G., Peters T. J. Analytical subcellular fractionation of normal human skeletal muscle by sucrose density gradient centrifugation. Eur J Clin Invest. 1983 Feb;13(1):49–56. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1983.tb00064.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin F. C., Slavin G., Levi A. J. Alcoholic muscle disease. Br Med Bull. 1982 Jan;38(1):53–56. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters T. J. Investigation of tissue organelles by a combination of analytical subcellular fractionation and enzymic microanalysis: a new approach to pathology. J Clin Pathol. 1981 Jan;34(1):1–12. doi: 10.1136/jcp.34.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters T. J., Wells G., Oakley C. M., Brooksby I. A., Jenkins B. S., Webb-Peploe M. M., Coltart D. J. Enzymic analysis of endomyocardial biopsy specimens from patients with cardiomyopathies. Br Heart J. 1977 Dec;39(12):1333–1339. doi: 10.1136/hrt.39.12.1333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollack M. S., Bird J. W. Distribution and particle properties of acid hydroase in denervated muscle. Am J Physiol. 1968 Sep;215(3):716–722. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1968.215.3.716. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin E. Alcoholic myopathy in heart and skeletal muscle. N Engl J Med. 1979 Jul 5;301(1):28–33. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197907053010107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin E., Katz A. M., Lieber C. S., Stein E. P., Puszkin S. Muscle damage produced by chronic alcohol consumption. Am J Pathol. 1976 Jun;83(3):499–516. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schacterle G. R., Pollack R. L. A simplified method for the quantitative assay of small amounts of protein in biologic material. Anal Biochem. 1973 Feb;51(2):654–655. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90523-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shafiq S. A., Milhorat A. T., Gorycki M. A. Fine structure of human muscle in neurogenic atrophy. Neurology. 1967 Oct;17(10):934–948. doi: 10.1212/wnl.17.10.934. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sirca A., Susec-Michieli M. Selective type II fibre muscular atrophy in patients with osteoarthritis of the hip. J Neurol Sci. 1980 Jan;44(2-3):149–159. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(80)90123-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slavin G., Sowter C., Ward P., Paton K. Measurement of striated muscle fibre diameters using interactive computer-aided microscopy. J Clin Pathol. 1982 Nov;35(11):1268–1271. doi: 10.1136/jcp.35.11.1268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. D., Peters T. J. Analytical subcellular fractionation of rat liver with special reference to the localisation of putative plasma membrane marker enzymes. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Feb;104(1):305–311. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04429.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stauber W. T., Bird J. W., Schottelius B. A. Catalase: an enzymatic indicator of the degree of muscle wasting. Exp Neurol. 1977 May;55(2):381–389. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(77)90008-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suominen H., Forsberg S., Heikkinen E., Osterback L. Enzyme activities and glycogen concentration in skeletal muscle in alcoholism. The effect of abstinence and physical conditioning. Acta Med Scand. 1974 Sep;196(3):199–202. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1974.tb00995.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorstensson A., Sjödin B., Tesch P., Karlsson J. Actomyosin ATPase, myokinase, CPK and LDH in human fast and slow twitch muscle fibres. Acta Physiol Scand. 1977 Feb;99(2):225–229. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1977.tb10373.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomonaga M. Histochemical and ultrastructural changes in senile human skeletal muscle. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1977 Mar;25(3):125–131. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.1977.tb00274.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]