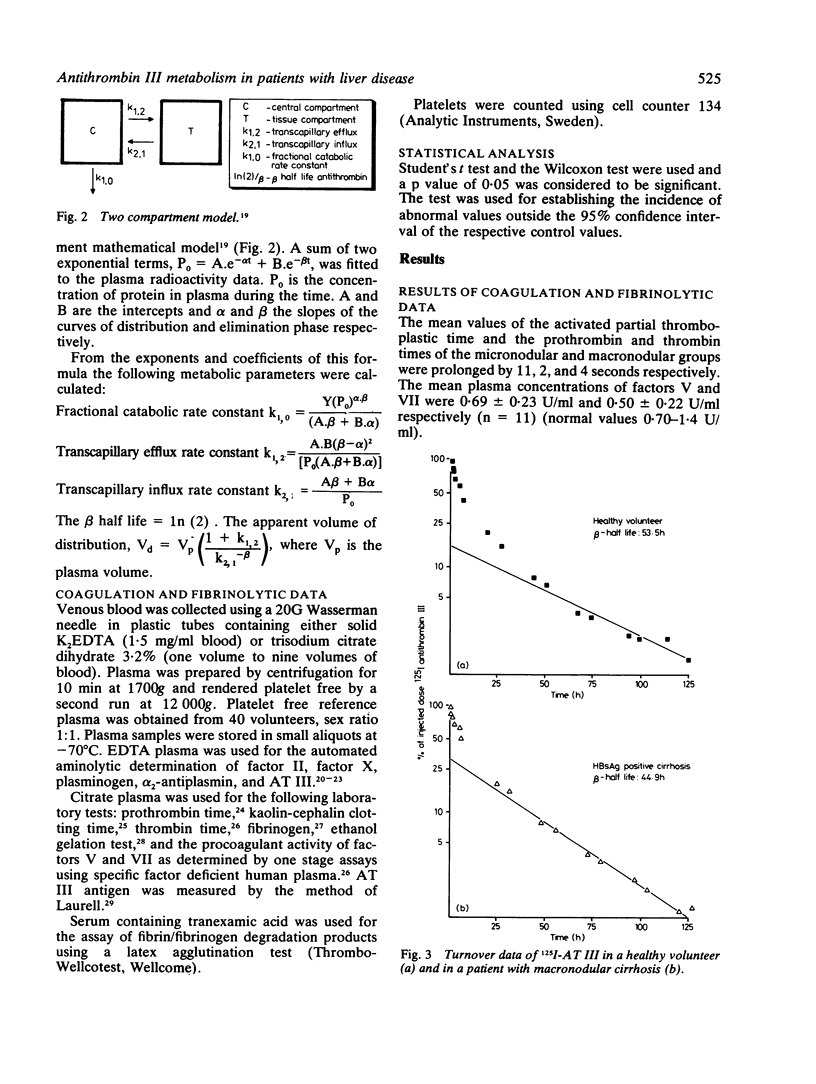
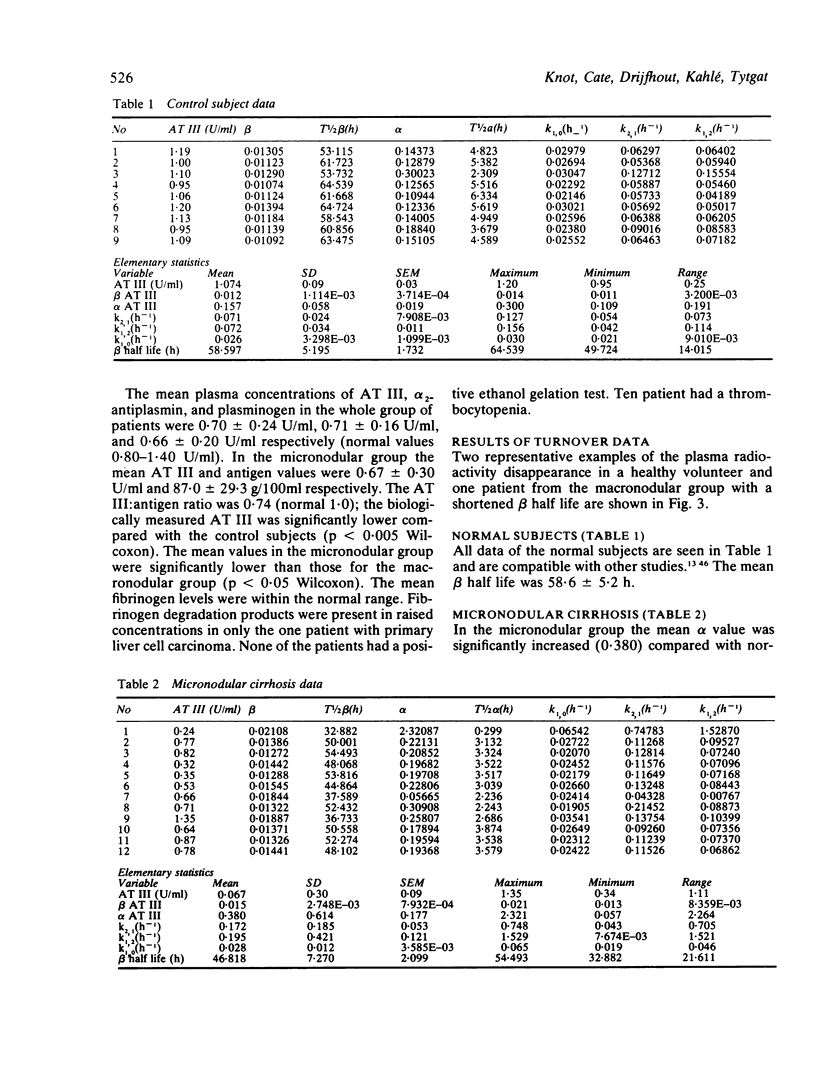
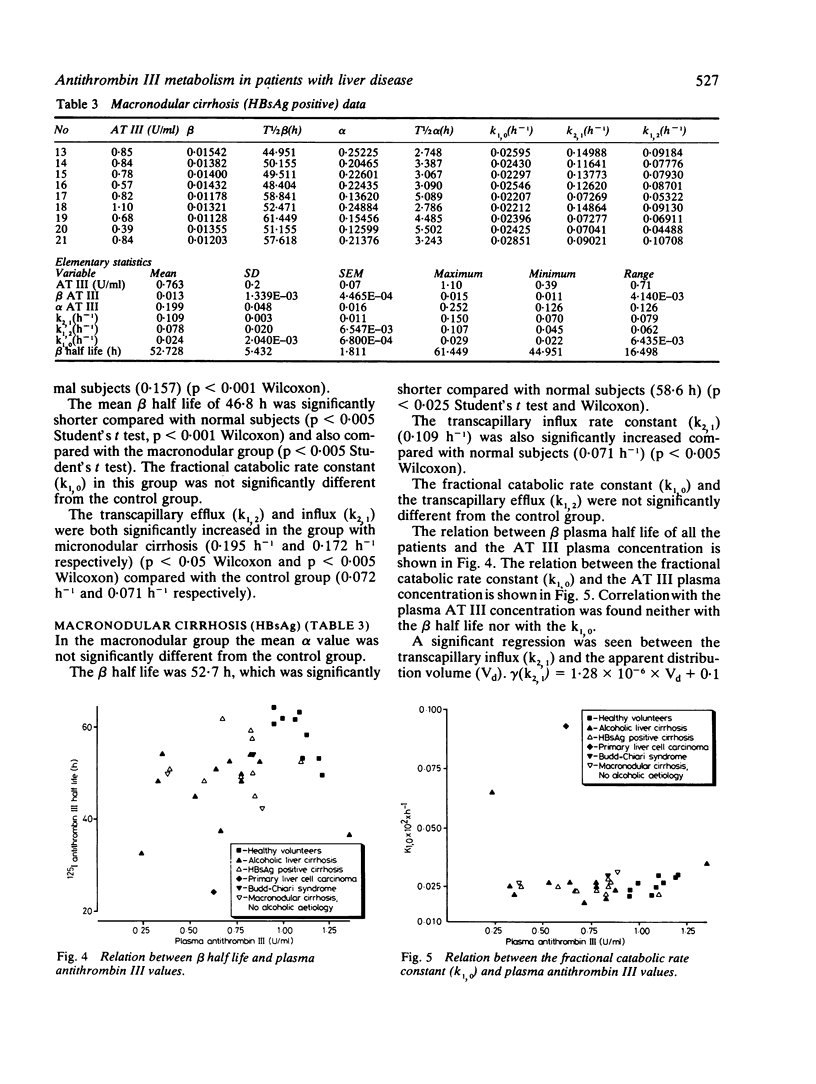
Abstract
Liver diseases are associated with complex haemostasis defects, in which platelets, coagulation, and fibrinolysis may all be affected. The low plasma concentrations of clotting factors often found can be the result of many changes such as impaired synthesis, increased catabolism due to intravascular coagulation, or alternate distribution. In this study, we investigated the metabolism of purified human antithrombin III(AT III) labelled with 125I in 25 patients with histologically established liver disease and in nine control subjects. The results showed that, in general, low plasma concentrations of AT III in liver cirrhosis are not due to consumption in the central compartment but rather to altered transcapillary flux ratio. Such altered transcapillary flux ratios may already exist even with normal plasma AT III concentrations. Altered ratios are not only found for coagulation proteins but also for albumin and thus may be a general phenomenon of liver disease. In micronodular cirrhosis the alpha phase, the transcapillary efflux (k1, 2) and influx (k2, 1) were significantly increased compared with the normal subjects.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abildgaard U., Fagerhol M. K., Egeberg O. Comparison of progressive antithrombin activity and the concentration of three thrombin inhibitors in human plasma. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1970 Dec;26(4):349–354. doi: 10.3109/00365517009046245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson L. O., Engman L., Henningsson E. Crossed immunoelectrophoresis as applied to studies on complex formation. The binding of heparin to antithrombin III and the antithrombin III--thrombin complex. J Immunol Methods. 1977;14(3-4):271–281. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(77)90138-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ansley J. D., Bethel R. A., Bowen P. A., 2nd, Warren W. D. Effect of peritoneovenous shunting with the Le Veen valve on ascites, renal function, and coagulation in six patients with intractable ascites. Surgery. 1978 Feb;83(2):181–187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom A. L. Intravascular coagulation and the liver. Br J Haematol. 1975 May;30(1):1–7. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1975.tb00511.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan V., Lai C. L., Chan T. K. Metabolism of antithrombin III in cirrhosis and carcinoma of the liver. Clin Sci (Lond) 1981 Jun;60(6):681–688. doi: 10.1042/cs0600681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R. D., Gazzard B. G., Lewis M. L., Flute P. T., Williams R. Fibrinogen metabolism in acute hepatitis and active chronic hepatitis. Br J Haematol. 1975 May;30(1):95–102. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1975.tb00522.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman M., Finlayson N., Bettigole R. E., Sadula D., Cohn M., Pasmantier M. Fibrinogen survival in cirrhosis: improvement by "low dose" heparin. Ann Intern Med. 1975 Jul;83(1):79–81. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-83-1-79. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collen D., Schetz J., de Cock F., Holmer E., Verstraete M. Metabolism of antithrombin III (heparin cofactor) in man: effects of venous thrombosis and of heparin administration. Eur J Clin Invest. 1977 Feb;7(1):27–35. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1977.tb01566.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordova C., Musca A., Violi F., Alessandri C., Vezza E. Improvement of some blood coagulation factors in cirrhotic patients treated with low doses of heparin. Scand J Haematol. 1982 Sep;29(3):235–240. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1982.tb00588.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dykes P. W. The rates of distribution and catabolism of albumin in normal subjects and in patients with cirrhosis of the liver. Clin Sci. 1968 Feb;34(1):161–183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EGEBERG O. INHERITED ANTITHROMBIN DEFICIENCY CAUSING THROMBOPHILIA. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1965 Jun 15;13:516–530. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elin R. J., Wolff S. M. Biology of endotoxin. Annu Rev Med. 1976;27:127–141. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.27.020176.001015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs H. E., Shifman M. A., Pizzo S. V. In vivo catabolism of alpha 1-proteinase inhibitor-trypsin, antithrombin III-thrombin and alpha 2-macroglobulin-methylamine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 May 27;716(2):151–157. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(82)90263-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godal H. C., Abildgaard U. Gelation of soluble fibrin in plasma by ethanol. Scand J Haematol. 1966;3(5):342–350. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1966.tb02378.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALLEN A., NILSSON I. M. COAGULATION STUDIES IN LIVER DISEASE. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1964 Apr 15;11:51–63. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
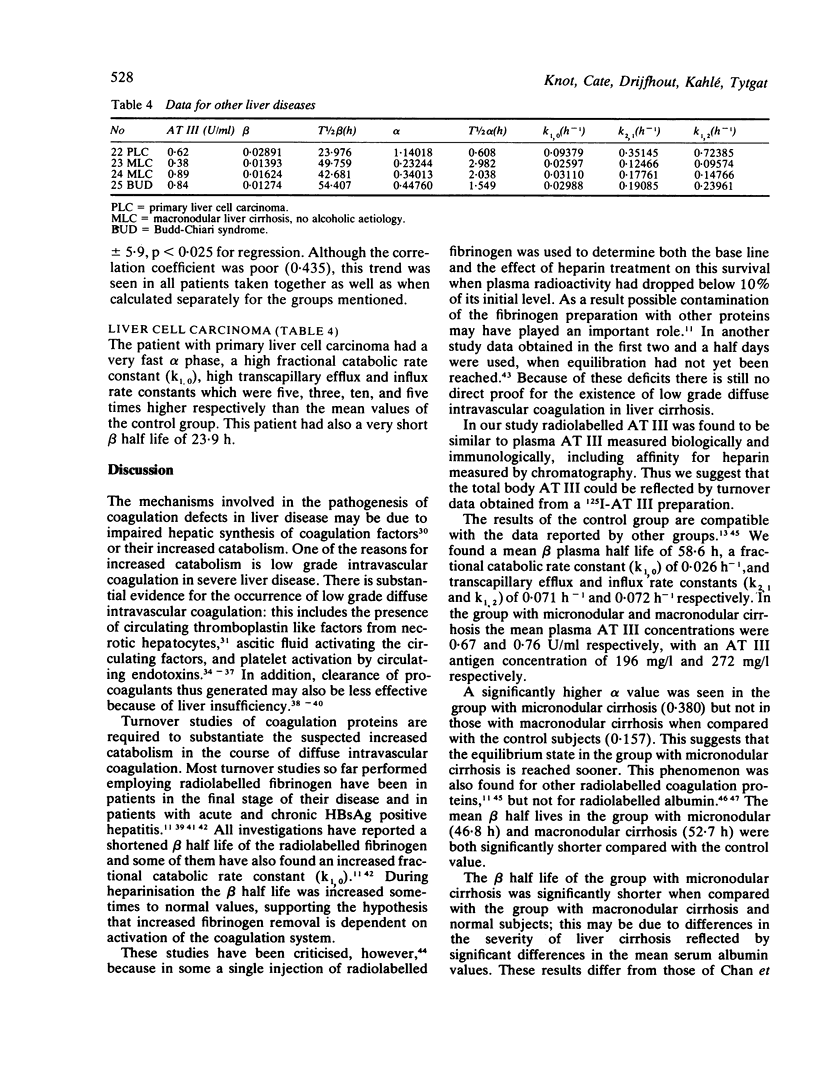
- Harpel P. C., Rosenberg R. D. Alpha 2-macroglobulin and antithrombin-heparin cofactor: modulators of hemostatic and inflammatory reactions. Alpha 2-macroglobulin. Prog Hemost Thromb. 1976;3:145–189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawiger J., Hawiger A., Steckley S., Timmons S., Cheng C. Membrane changes in human platelets induced by lipopolysaccharide endotoxin. Br J Haematol. 1977 Feb;35(2):285–299. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1977.tb00585.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahlé L. H., Schipper H. G., Jenkins C. S., ten Cate J. W. Antithrombin III. I. Evaluation of an automated antithrombin III method. Thromb Res. 1978 Jun;12(6):1003–1014. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(78)90056-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kauffmann R. H., Veltkamp J. J., Van Tilburg N. H., Van Es L. A. Acquired antithrombin III deficiency and thrombosis in the nephrotic syndrome. Am J Med. 1978 Oct;65(4):607–613. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(78)90848-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAURELL C. B. ANTIGEN-ANTIBODY CROSSED ELECTROPHORESIS. Anal Biochem. 1965 Feb;10:358–361. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(65)90278-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lévy V. G., Opolon P., Pauleau N., Caroli J. Treatment of ascites by reinfusion of concentrated peritoneal fluid--review of 318 procedures in 210 patients. Postgrad Med J. 1975 Aug;51(598):564–566. doi: 10.1136/pgmj.51.598.564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARGOLIS J. The kaolin clotting time; a rapid one-stage method for diagnosis of coagulation defects. J Clin Pathol. 1958 Sep;11(5):406–409. doi: 10.1136/jcp.11.5.406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MATTHEWS C. M. The theory of tracer experiments with 131I-labelled plasma proteins. Phys Med Biol. 1957 Jul;2(1):36–53. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/2/1/305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. C., Cochrane C. G. Direct evidence for Hageman factor (factor XII) activation by bacterial lipopolysaccharides (endotoxins). J Exp Med. 1974 Sep 1;140(3):797–811. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.3.797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rake M. O., Flute P. T., Pannell G., Williams R. Intravascular coagulation in acute hepatic necrosis. Lancet. 1970 Mar 14;1(7646):533–537. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(70)90767-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rüegg R., Straub P. W. Exchange between intravascularly and extravascularly injected radioiodinated fibrinogen and its in vivo derivatives. J Lab Clin Med. 1980 Jun;95(6):842–856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STRENGERS T., ASBERG E. G. EEN SCREENING-TEST, GEVOLGD DOOR EEN SNELLE KWANTITATIEVE MICROBEPALING VAN FIBRINOGEEN IN PLASMA. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 1963 Nov 2;107:2044–2045. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salacinski P. R., McLean C., Sykes J. E., Clement-Jones V. V., Lowry P. J. Iodination of proteins, glycoproteins, and peptides using a solid-phase oxidizing agent, 1,3,4,6-tetrachloro-3 alpha,6 alpha-diphenyl glycoluril (Iodogen). Anal Biochem. 1981 Oct;117(1):136–146. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90703-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schipper H. G., ten Cate J. W. Antithrombin III transfusion in patients with hepatic cirrhosis. Br J Haematol. 1982 Sep;52(1):25–33. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1982.tb03858.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein S. F., Harker L. A. Kinetic and functional studies of platelets, fibrinogen, and plasminogen in patients with hepatic cirrhosis. J Lab Clin Med. 1982 Feb;99(2):217–230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tytgat G. N., Collen D., Verstraete M. Metabolism of fibrinogen in cirrhosis of the liver. J Clin Invest. 1971 Aug;50(8):1690–1701. doi: 10.1172/JCI106658. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verstraete M., Vermylen J., Collen D. Intravascular coagulation in liver disease. Annu Rev Med. 1974;25:447–455. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.25.020174.002311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILKINSON P., MENDENHALL C. L. SERUM ALBUMIN TURNOVER IN NORMAL SUBJECTS AND PATIENTS WITH CIRRHOSIS MEASURED BY 131I-LABELLED HUMAN ALBUMIN. Clin Sci. 1963 Oct;25:281–292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wessler S., Yin E. T., Gaston L. W., Nicol I. A distinction between the role of precursor and activated forms of clotting factors in the genesis of stasis thrombi. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1967 Aug 15;18(1-2):12–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Wijk E. M., Kahlé L. H., ten Cate J. W. Mechanized amidolytic technique for determination of factor X and factor-X antigen, and its application to patients being treated with oral anticoagulants. Clin Chem. 1980 Jun;26(7):885–890. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Kaulla E., von Kaulla K. N. Deficiency of antithrombin 3 activity associated with hereditary thrombosis tendency. J Med. 1972;3(6):349–358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]