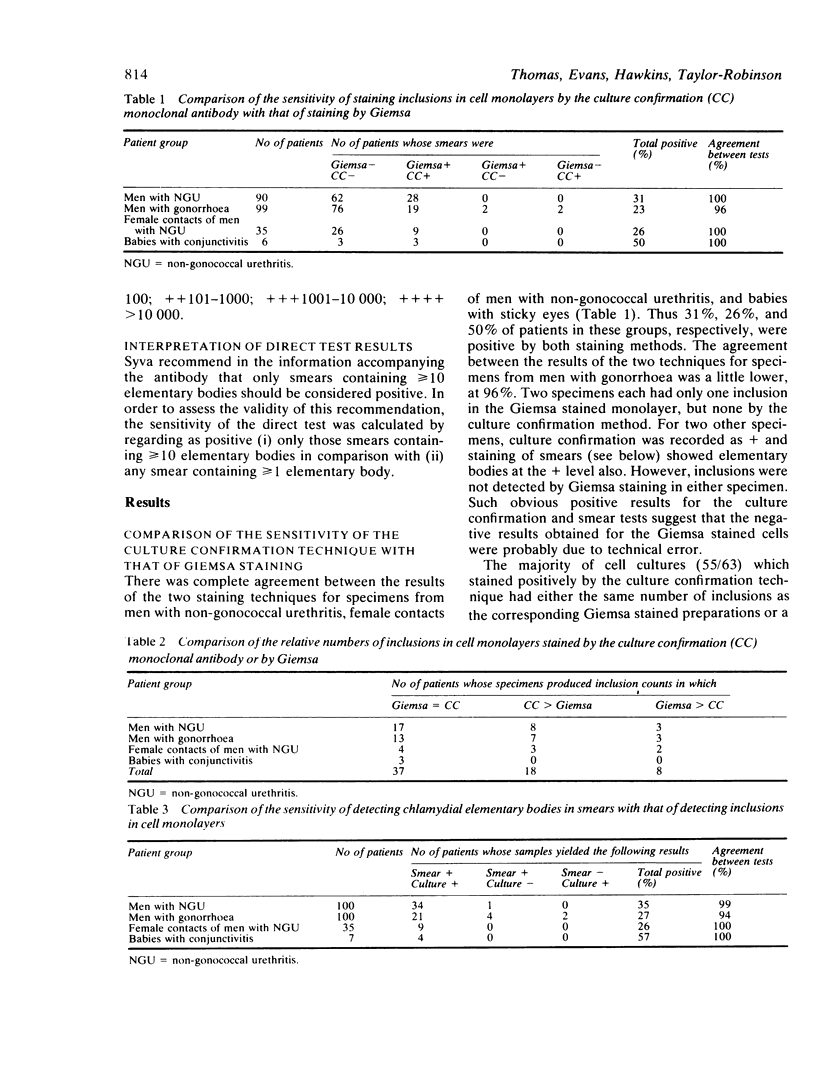
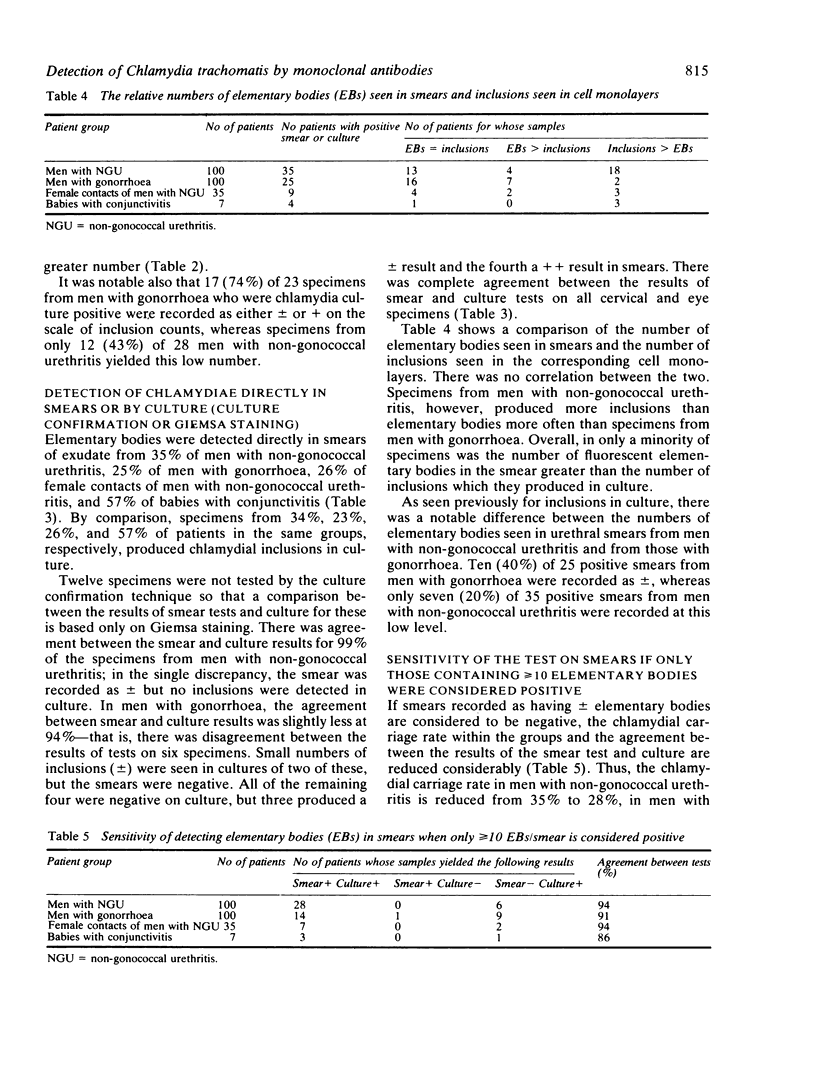
Abstract
Commercially produced fluorescein labelled monoclonal antibodies for the detection of Chlamydia trachomatis have recently become available. One is for detecting inclusions in cell culture (culture confirmation) and the other for detecting elementary bodies in smears from potentially infected sites. We have compared the two monoclonal antibodies with our routine isolation method, which utilises Giemsa staining of cycloheximide treated McCoy cell cultures. The culture confirmation system offered no advantages over Giemsa staining for the detection of inclusions in cell monolayers. By contrast, using monoclonal antibody to detect elementary bodies in smears was much quicker and simpler and slightly more sensitive than isolation of chlamydiae in cell culture. For specimens from seven babies with conjunctivitis and from 35 female contacts of men with non-gonococcal urethritis, there was complete agreement between the results of detecting inclusions in culture and those of seeking elementary bodies in smears. For samples from 100 men with non-gonococcal urethritis and from 100 men with gonorrhoea there was 99% and 94% agreement, respectively, between the results of the two tests. Other aspects and possible uses of the new detection system are discussed.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Evans R. T., Woodland R. M. Detection of chlamydiae by isolation and direct examination. Br Med Bull. 1983 Apr;39(2):181–186. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas B. J., Evans R. T., Hutchinson G. R., Taylor-Robinson D. Early detection of chlamydial inclusions combining the use of cycloheximide-treated McCoy cells and immunofluorescence staining. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Sep;6(3):285–292. doi: 10.1128/jcm.6.3.285-292.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


