Abstract
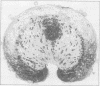
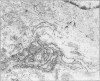
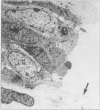
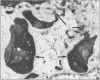
A method has been developed for rapid processing of fetal skin for prenatal diagnosis of hereditary skin diseases by light and electron microscopy. Fixation, dehydration, embedding, and polymerisation can be achieved in about 5 h. The quality of tissue preservation compares favourably with that produced by slower conventional techniques. This procedure may provoke a wider interest in the potential use of fetal skin biopsy in prenatal diagnosis, especially if identification of structural abnormalities is a feasible alternative to more time consuming biochemical analysis.
Full text
PDF

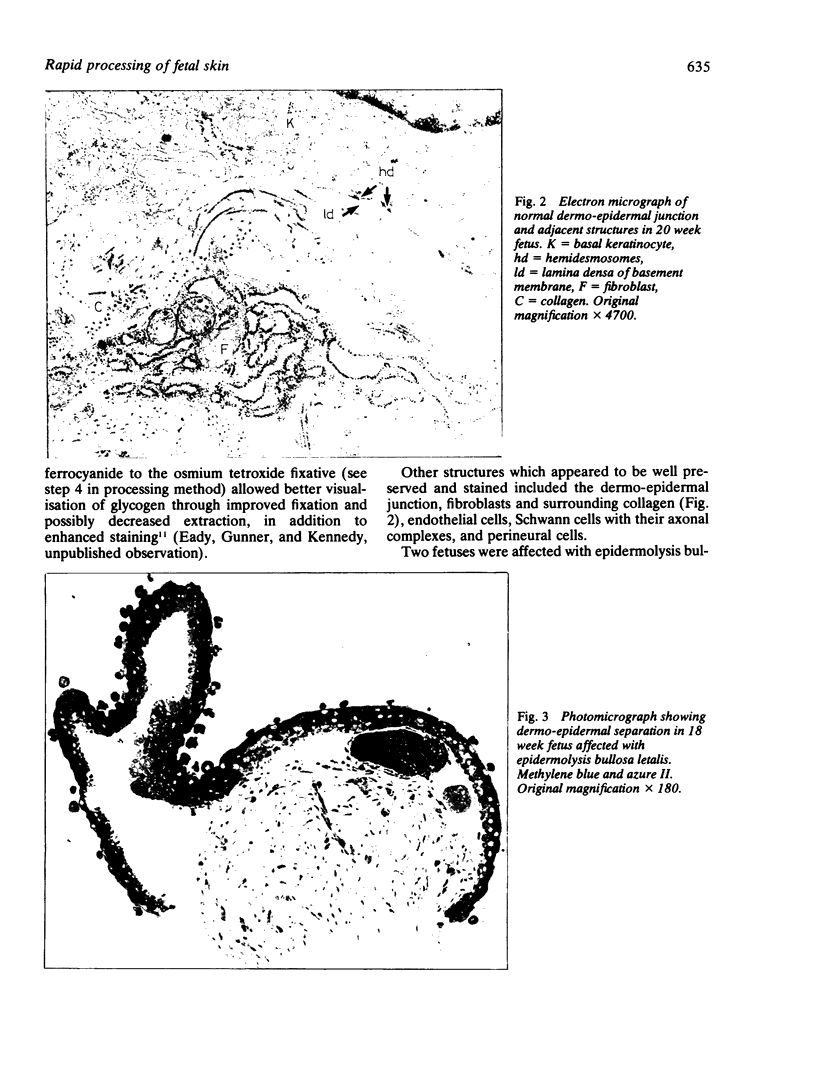
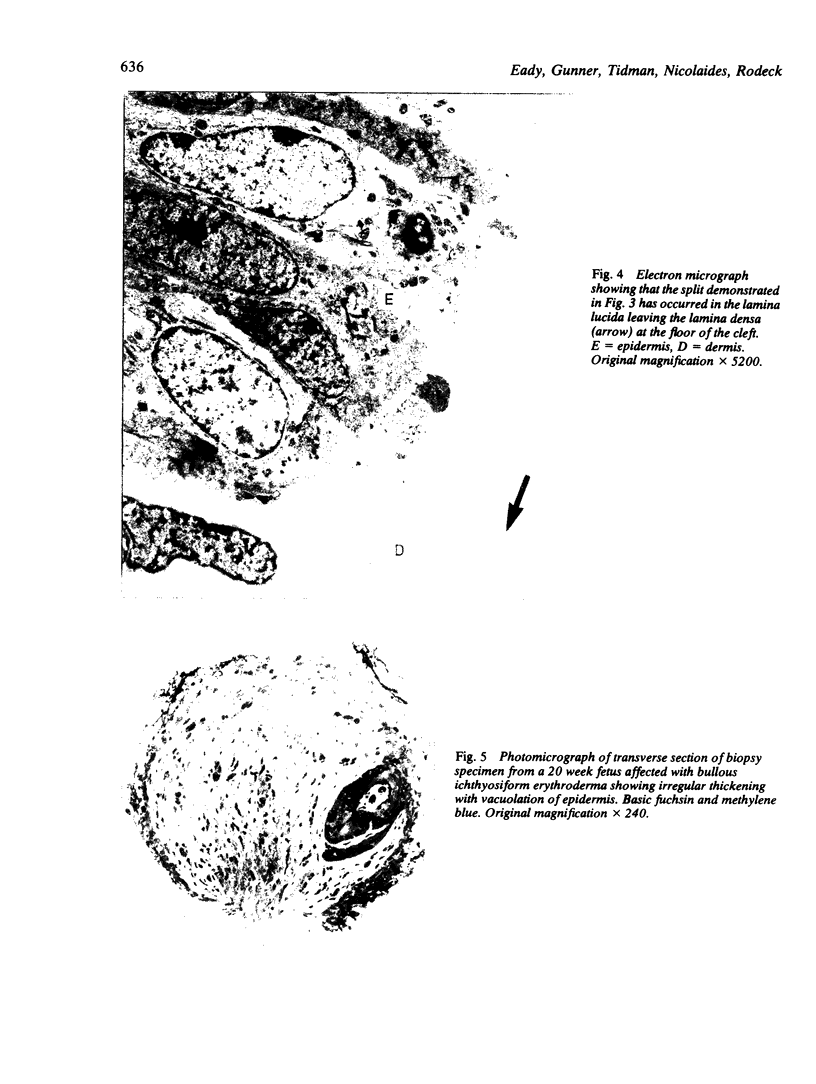


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anton-Lamprecht I., Arnold M. L., Rauskolb R., Schinzel A., Schmid W., Schnyder U. W. Prenatal diagnosis of anhydrotic ectodermal dysplasia. Hum Genet. 1982;62(2):180–180. doi: 10.1007/BF00282312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anton-Lamprecht I., Rauskolb R., Jovanovic V., Kern B., Arnold M. L., Schenck W. Prenatal diagnosis of epidermolysis bullosa dystrophica Hallopeau-Siemens with electron microscopy of fetal skin. Lancet. 1981 Nov 14;2(8255):1077–1079. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)91278-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bencosme S. A., Tsutsumi V. Fast method for processing biologic material for electron microscopy. Lab Invest. 1970 Oct;23(4):447–450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eady R. A., Gunner D. B., Garner A., Rodeck C. H. Prenatal diagnosis of oculocutaneous albinism by electron microscopy of fetal skin. J Invest Dermatol. 1983 Mar;80(3):210–212. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12534349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elias S., Mazur M., Sabbagha R., Esterly N. B., Simpson J. L. Prenatal diagnosis of harlequin ichthyosis. Clin Genet. 1980 Apr;17(4):275–280. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1980.tb00147.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estes L. W., Apicella J. V. A rapid embedding technique for electron microscopy. Lab Invest. 1969 Feb;20(2):159–163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golbus M. S., Sagebiel R. W., Filly R. A., Gindhart T. D., Hall J. G. Prenatal diagnosis of congenital bullous ichthyosiform erythroderma (epidermolytic hyperkeratosis) by fetal skin biopsy. N Engl J Med. 1980 Jan 10;302(2):93–95. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198001103020205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber J. D., Parker F., Odland G. F. A basic fuchsin and alkalinized methylene blue rapid stain for epoxy-embedded tissue. Stain Technol. 1968 Mar;43(2):83–87. doi: 10.3109/10520296809115048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johannessen J. V. Rapid processing of kidney biopsies for electron microscopy. Kidney Int. 1973 Jan;3(1):46–50. doi: 10.1038/ki.1973.7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kousseff B. G., Matsuoka L. Y., Stenn K. S., Hobbins J. C., Mahoney M. J., Hashimoto K. Prenatal diagnosis of Sjögren-Larsson syndrome. J Pediatr. 1982 Dec;101(6):998–1001. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(82)80030-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS E. S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:208–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RICHARDSON K. C., JARETT L., FINKE E. H. Embedding in epoxy resins for ultrathin sectioning in electron microscopy. Stain Technol. 1960 Nov;35:313–323. doi: 10.3109/10520296009114754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodeck C. H., Eady R. A., Gosden C. M. Prenatal diagnosis of epidermolysis bullosa letalis. Lancet. 1980 May 3;1(8175):949–952. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)91404-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodeck C. H., Nicolaides K. H. Fetoscopy and fetal tissue sampling. Br Med Bull. 1983 Oct;39(4):332–337. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071844. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowden G., Lewis M. G. Experience with a three-hour electron microscopy biopsy service. J Clin Pathol. 1974 Jun;27(6):505–510. doi: 10.1136/jcp.27.6.505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Bruijn W. C., Den Breejen P. Glycogen, its chemistry and morphological appearance in the electron microscope. III. Identification of the tissue ligands involved in the glycogen contrast staining reaction with the osmium (VI)--iron(II) complex. Histochem J. 1976 Mar;8(2):121–142. doi: 10.1007/BF01007164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]