Abstract
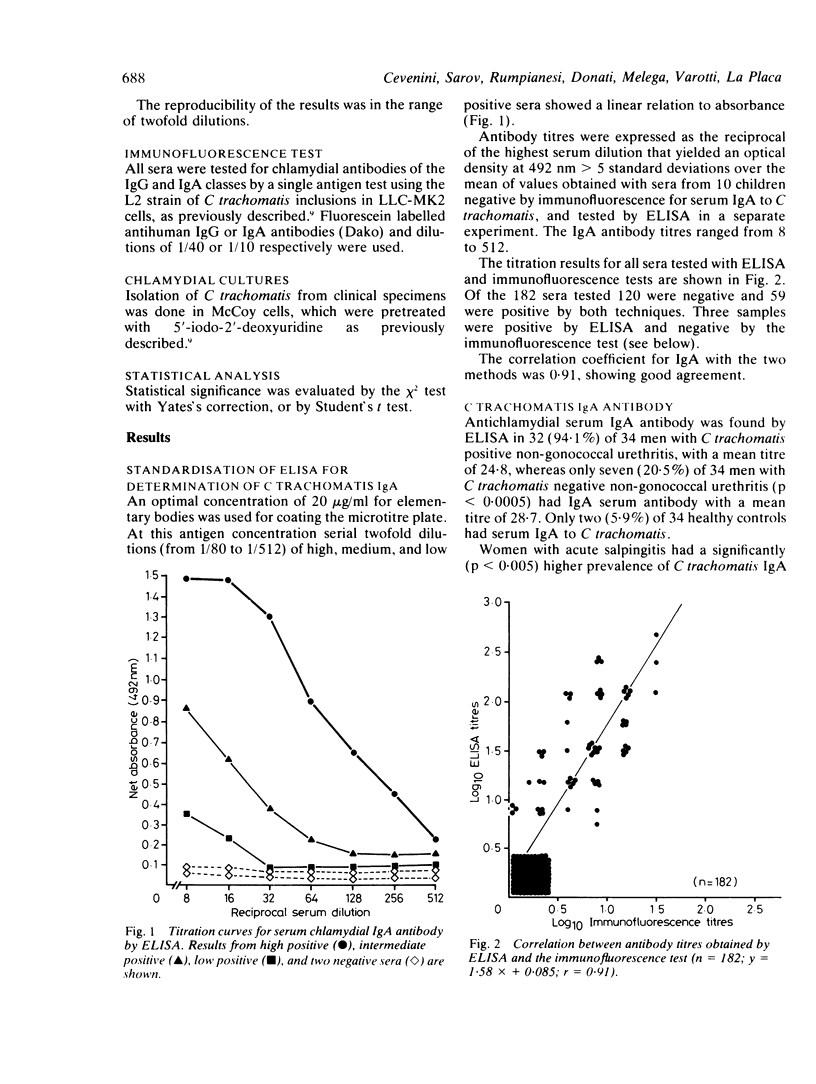
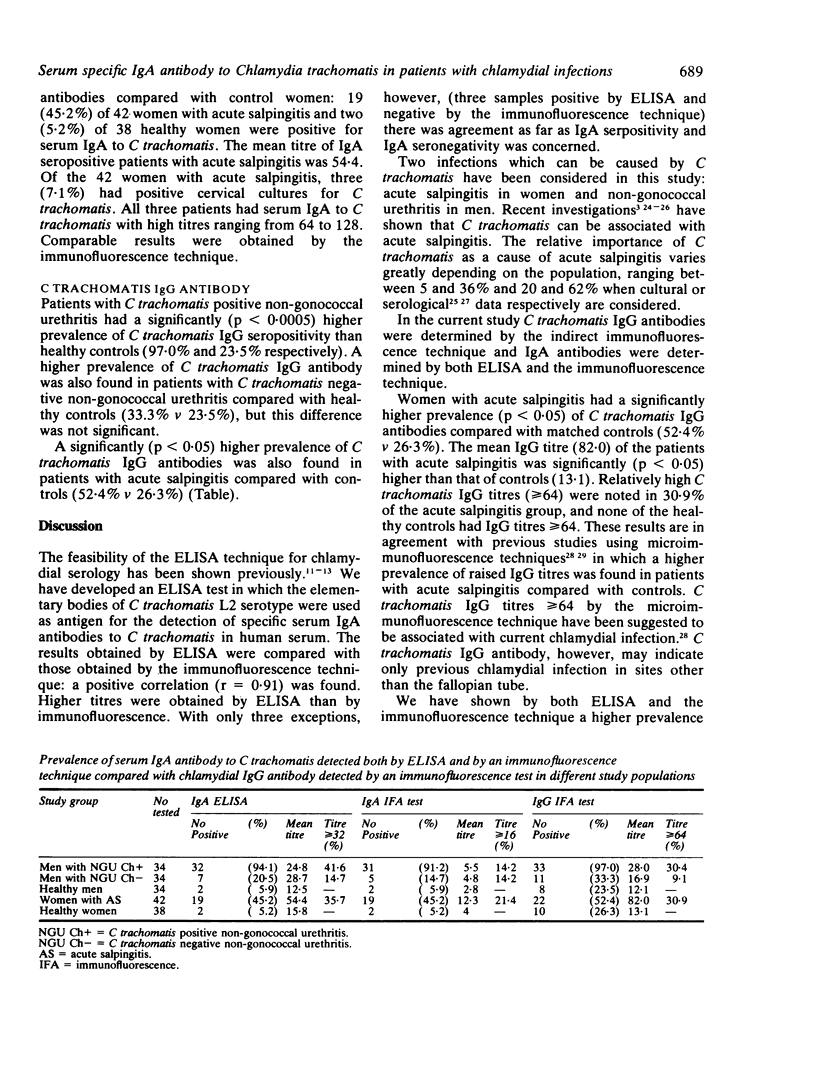
Sera obtained from 34 men with Chlamydia trachomatis positive non-gonococcal urethritis, 34 men with C trachomatis negative non-gonococcal urethritis, 42 women with acute salpingitis, 38 healthy women, and 34 healthy men were studied for the presence of specific serum C trachomatis IgA and IgG antibodies. Serological results were correlated with C trachomatis isolation in cell culture. An enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for C trachomatis specific serum IgA was employed using highly purified elementary bodies of C trachomatis serotype L2 grown in LLC-MK2 cells. Results obtained for C trachomatis IgA antibody by the ELISA test were compared with results obtained for the same sera by a single antigen immunofluorescence technique. A good correlation (r = 0.91) was found between two methods. Serum IgG antibody was also determined in the same sera by the immunofluorescence technique. Patients with C trachomatis positive non-gonococcal urethritis had a significantly (p less than 0.0005) higher prevalence (94.1%) of serum IgA antibody by ELISA compared with patients with C trachomatis negative non-gonococcal urethritis (20.5%) or healthy men (5.9%). Similarly, women with acute salpingitis had a significantly (p less than 0.005) higher prevalence of serum IgA antibody (45.2%) compared with healthy controls (5.2%). Comparable results were obtained for C trachomatis serum IgA antibody using the immunofluorescence technique. The prevalence of C trachomatis IgG antibody was significantly higher in patients with C trachomatis positive non-gonococcal urethritis (97.0%) compared with those with C trachomatis negative non-gonococcal urethritis (33.3%) and healthy controls (23.5%). The importance of using specific C trachomatis serum IgA in the identification of chlamydial infection is discussed.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Caldwell H. D., Kromhout J., Schachter J. Purification and partial characterization of the major outer membrane protein of Chlamydia trachomatis. Infect Immun. 1981 Mar;31(3):1161–1176. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.3.1161-1176.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cevenini R., La Placa M. Chlamydial infections in Italy. Sex Transm Dis. 1981 Oct-Dec;8(4 Suppl):349–352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cevenini R., Rumpianesi F., Donati M., Sarov I. A rapid immunoperoxidase assay for the detection of specific IgG antibodies to Chlamydia trachomatis. J Clin Pathol. 1983 Mar;36(3):353–356. doi: 10.1136/jcp.36.3.353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans A. S., Niederman J. C. EBV-IgA and new heterophile antibody tests in diagnosis of infectious mononucleosis. Am J Clin Pathol. 1982 May;77(5):555–560. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/77.5.555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. T., Taylor-Robinson D. Development and evaluation of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), using chlamydial group antigen, to detect antibodies, to Chlamydia trachomatis. J Clin Pathol. 1982 Oct;35(10):1122–1128. doi: 10.1136/jcp.35.10.1122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilton A. L., Richmond S. J., Milne J. D., Hindley F., Clarke S. K. Chlamydia A in the female genital tract. Br J Vener Dis. 1974 Feb;50(1):1–10. doi: 10.1136/sti.50.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho H. C., Ng M. H., Kwan H. C., Chau J. C. Epstein-Barr-virus-specific IgA and IgG serum antibodies in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 1976 Dec;34(6):655–660. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1976.228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes K. K., Handsfield H. H., Wang S. P., Wentworth B. B., Turck M., Anderson J. B., Alexander E. R. Etiology of nongonococcal urethritis. N Engl J Med. 1975 Jun 5;292(23):1199–1205. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197506052922301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hornsleth A., Leerhoy J., Grauballe P., Spanggaard H. Persistence of rubellavirus-specific immunoglobulin M and immunoglobulin A antibodies: investigation of successive serum samples with lowered immunoglobulin G concentration. Infect Immun. 1975 Apr;11(4):804–808. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.4.804-808.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. B., Ardery B. R., Hui S. L., Cleary R. E. Correlation between serum antichlamydial antibodies and tubal factor as a cause of infertility. Fertil Steril. 1982 Nov;38(5):553–558. doi: 10.1016/s0015-0282(16)46634-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. B., Bruins S. C., Newhall W. J., 5th Comparison of reticulate and elementary body antigens in detection of antibodies against Chlamydia trachomatis by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Mar;17(3):466–471. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.3.466-471.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy E., Sarov I. Detection of specific IgA antibodies in serum of patients with varicella and zoster infections. Intervirology. 1981;15(2):103–110. doi: 10.1159/000149220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore D. E., Spadoni L. R., Foy H. M., Wang S. P., Daling J. R., Kuo C. C., Grayston J. T., Eschenbach D. A. Increased frequency of serum antibodies to Chlamydia trachomatis in infertility due to distal tubal disease. Lancet. 1982 Sep 11;2(8298):574–577. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)90659-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Märdh P. A., Lind I., Svensson L., Weström L., Møller B. R. Antibodies to Chlamydia trachomatis, Mycoplasma hominis, and Neisseria gonorrhoeae in sera from patients with acute salpingitis. Br J Vener Dis. 1981 Apr;57(2):125–129. doi: 10.1136/sti.57.2.125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mårdh P. A., Ripa T., Svensson L., Weström L. Chilamydia trachomatis infection in patients with acute salpingitis. N Engl J Med. 1977 Jun 16;296(24):1377–1379. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197706162962403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees E. The treatment of pelvic inflammatory disease. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1980 Dec 1;138(7 Pt 2):1042–1047. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(80)91105-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saikku P., Paavonen J. Single-antigen immunofluorescence test for chlamydial antibodies. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Aug;8(2):119–122. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.2.119-122.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarov I., Levy E., Aymard M., Chardonnet Y., Bosshard S., Revillard J. P., Friedman M., Nord E., Greiff M., Haikin H. Detection of virus-specific IgA antibodies in serum of kidney transplant patients with recurrent cytomegalovirus infection by enzymeimmuno and radioimmunoassay techniques. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 May;48(2):321–328. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schachter J., Grossman M. Chlamydial infections. Annu Rev Med. 1981;32:45–61. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.32.020181.000401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweet R. L., Draper D. L., Schachter J., James J., Hadley W. K., Brooks G. F. Microbiology and pathogenesis of acute salpingitis as determined by laparoscopy: what is the appropriate site to sample? Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1980 Dec 1;138(7 Pt 2):985–989. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(80)91093-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terho P., Meurman O. Chlamydial serum IgG, IgA and local IgA antibodies in patients with genital-tract infections measured by solid-phase radioimmunoassay. J Med Microbiol. 1981 Feb;14(1):77–87. doi: 10.1099/00222615-14-1-77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas B. J., Reeve P., Oriel J. D. Simplified serological test for antibodies to Chlamydia trachomatis. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Jul;4(1):6–10. doi: 10.1128/jcm.4.1.6-10.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasi T. B., Grey H. M. Structure and function of immunoglobulin A. Prog Allergy. 1972;16:81–213. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treharne J. D., Ripa K. T., Mårdh P. A., Svensson L., Weström L., Darougar S. Antibodies to Chlamydia trachomatis in acute salpingitis. Br J Vener Dis. 1979 Feb;55(1):26–29. doi: 10.1136/sti.55.1.26. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang S. P., Grayston J. T. Immunologic relationship between genital TRIC, lymphogranuloma venereum, and related organisms in a new microtiter indirect immunofluorescence test. Am J Ophthalmol. 1970 Sep;70(3):367–374. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(70)90096-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


