Abstract
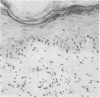
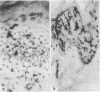
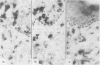
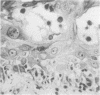
Skin biopsies from leukaemic patients undergoing allogeneic bone marrow transplantations and treated prophylactically with cyclosporin A were analysed using histological, morphometric, and immunohistological techniques. Samples from donors were used to establish normal values. Biopsies taken from recipients two days before grafting were all histologically normal, but on immunohistological staining half of them showed a reduction in the number of epidermal Langerhans' cells and 29% a reduction in T inducer lymphocytes. Thirty two biopsies were taken from patients with rashes at various times after transplantation: 14 showed lichenoid changes consistent with graft versus host disease, three eczematous tissue reactions, two vesicular lesions, and 12 no histological abnormality. One sample showed changes intermediate between the lichenoid and eczematous forms. The numbers of epidermal Langerhans' cells were low during the first few weeks after transplantation and were normal or raised later regardless of histological appearances. Unlike epidermal Langerhans' cells, significant reductions in the numbers of lymphocytes were not seen. Lesions of all histological types contained mixtures of T inducer and T suppressor/cytotoxic cells, although the eczematous and vesicular lesions contained higher proportions of T inducer cells. Epidermal infiltrates invariably contained T suppressor/cytotoxic cells but infiltration of epidermis by T inducer cells occurred only in the presence of normal numbers of epidermal Langerhans' cells. Natural killer cells were not identified. The immunological appearances of the various histological subgroups thus change with time after transplantation.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abo T., Balch C. M. A differentiation antigen of human NK and K cells identified by a monoclonal antibody (HNK-1). J Immunol. 1981 Sep;127(3):1024–1029. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhan A. K., Harrist T. J., Murphy G. F., Mihm M. C., Jr T cell subsets and Langerhans cells in lichen planus: in situ characterization using monoclonal antibodies. Br J Dermatol. 1981 Dec;105(6):617–622. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1981.tb00970.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodsky F. M., Parham P., Barnstable C. J., Crumpton M. J., Bodmer W. F. Monoclonal antibodies for analysis of the HLA system. Immunol Rev. 1979;47:3–61. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1979.tb00288.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochran R. E., Thomson J., Fleming K., McQueen A. The psoriasiform eruption induced by practolol. J Cutan Pathol. 1975;2(6):314–319. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0560.1975.tb00184.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FAN J., SCHOENFELD R. J., HUNTER R. A study of the epidermal clear cells with special reference to their relationship to the cells of Langerhans. J Invest Dermatol. 1959 Mar;32(3):445–450. doi: 10.1038/jid.1959.74. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Favrot M., Janossy G., Tidman N., Blacklock H., Lopez E., Bofill M., Lampert I., Morgenstein G., Powles R., Prentice H. G. T cell regeneration after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. Clin Exp Immunol. 1983 Oct;54(1):59–72. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gatter K. C., Pulford K. A., Vanstapel M. J., Roach B., Mortimer P., Woolston R. E., Taylor-Papadimitriou J., Lane E. B., Mason D. Y. An immunohistological study of benign and malignant skin tumours: epithelial aspects. Histopathology. 1984 Mar;8(2):209–227. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1984.tb02337.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hercend T., Ritz J., Schlossman S. F., Reinherz E. L. Comparative expression of T9, T10, and Ia antigens on activated human T cell subsets. Hum Immunol. 1981 Nov;3(3):247–259. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(81)90021-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes R. C., Jurecka W., Cooper C. B., McGibbon D. H., Black M. M. Syndrome resembling graft-versus-host disease in a patient with disseminated carcinoma. J R Soc Med. 1983 Aug;76(8):703–705. doi: 10.1177/014107688307600815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz S. I., Tamaki K., Sachs D. H. Epidermal Langerhans cells are derived from cells originating in bone marrow. Nature. 1979 Nov 15;282(5736):324–326. doi: 10.1038/282324a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampert I. A., Janossy G., Suitters A. J., Bofill M., Palmer S., Gordon-Smith E., Prentice H. G., Thomas J. A. Immunological analysis of the skin in graft versus host disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Oct;50(1):123–131. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampert I. A., Suitters A. J., Chisholm P. M. Expression of Ia antigen on epidermal keratinocytes in graft-versus-host disease. Nature. 1981 Sep 10;293(5828):149–150. doi: 10.1038/293149a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawler S. D., Baker M. C., Harris H., Morgenstern G. R. Cytogenetic studies on recipients of allogeneic bone marrow using the sex chromosomes as markers of cellular origin. Br J Haematol. 1984 Mar;56(3):431–443. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1984.tb03973.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner K. G., Kao G. F., Storb R., Buckner C. D., Clift R. A., Thomas E. D. Histopathology of graft-vs.-host reaction (GvHR) in human recipients of marrow from HL-A-matched sibling donors. Transplant Proc. 1974 Dec;6(4):367–371. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason D. W., Dallman M., Barclay A. N. Graft-versus-host disease induces expression of Ia antigen in rat epidermal cells and gut epithelium. Nature. 1981 Sep 10;293(5828):150–151. doi: 10.1038/293150a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller C., Schüch K., Pawelec G., Wilms K., Wernet P. Immunohistology of graft-versus-host disease mediated skin lesions and its correlation to a large granular lymphocyte surface phenotype and function. Blut. 1982 Feb;44(2):89–94. doi: 10.1007/BF00320095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nadler L. M., Stashenko P., Hardy R., Pesando J. M., Yunis E. J., Schlossman S. F. Monoclonal antibodies defining serologically distinct HLA-D/DR related Ia-like antigens in man. Hum Immunol. 1981 Feb;2(1):77–90. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(81)90009-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinkus H. Lichenoid tissue reactions. A speculative review of the clinical spectrum of epidermal basal cell damage with special reference to erythema dyschromicum perstans. Arch Dermatol. 1973 Jun;107(6):840–846. doi: 10.1001/archderm.107.6.840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pizzolo G., Sloane J., Beverley P., Thomas J. A., Bradstock K. F., Mattingly S., Janossy G. Differential diagnosis of malignant lymphoma and nonlymphoid tumors using monoclonal anti-leucocyte antibody. Cancer. 1980 Dec 15;46(12):2640–2647. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19801215)46:12<2640::aid-cncr2820461218>3.0.co;2-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sale G. E., Lerner K. G., Barker E. A., Shulman H. M., Thomas E. D. The skin biopsy in the diagnosis of acute graft-versus-host disease in man. Am J Pathol. 1977 Dec;89(3):621–636. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein H., Gerdes J., Mason D. Y. The normal and malignant germinal centre. Clin Haematol. 1982 Oct;11(3):531–559. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suitters A. J., Lampert I. A. The loss of Ia+ Langerhans' cells during graft-versus-host disease in rats. Transplantation. 1983 Nov;36(5):540–546. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198311000-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. A., Biggerstaff M., Sloane J. P., Easton D. F. Immunological and histochemical analysis of regional variations of epidermal Langerhans cells in normal human skin. Histochem J. 1984 May;16(5):507–519. doi: 10.1007/BF01041351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weedon D. The lichenoid tissue reaction. Int J Dermatol. 1982 May;21(4):203–206. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-4362.1982.tb02072.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodruff J. M., Eltringham J. R., Casey H. W. Early secondary disease in the Rhesus monkey. I. A comparative histopathologic study. Lab Invest. 1969 Jun;20(6):499–511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]