Abstract
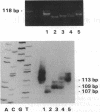
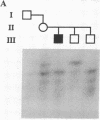
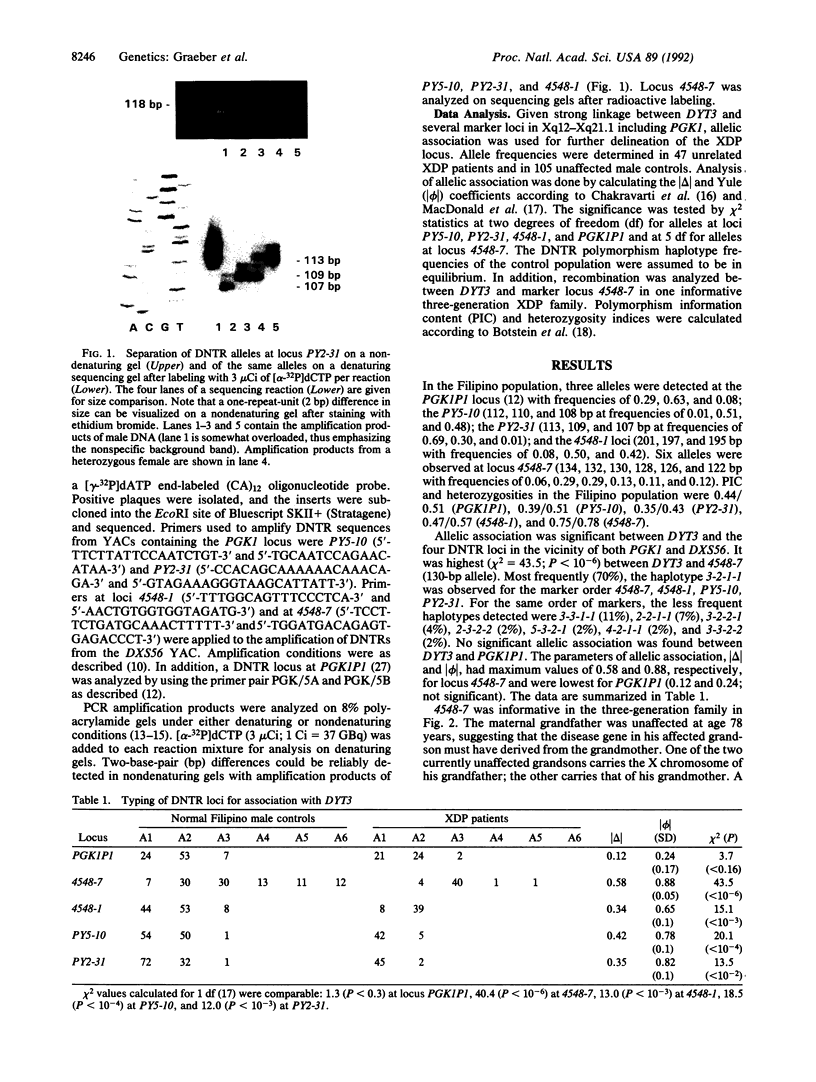
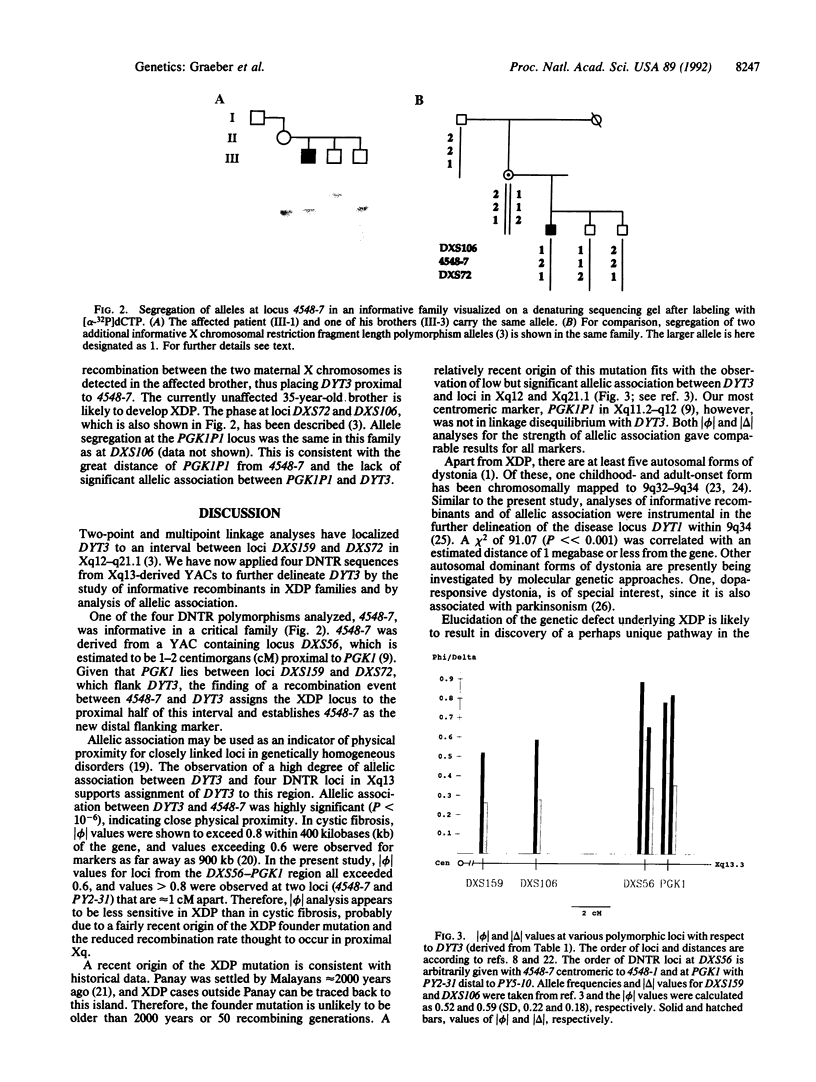
The X chromosome-linked dystonia-parkinsonism syndrome (XDP) is a severe movement disorder, characterized by both dystonia and parkinsonism. XDP is a genetically homogeneous disorder. Known ancestry of all patients has been traced back to Panay, Philippines, where the disease probably originated from a single mutation (founder effect). The gene locus, DYT3, has been previously assigned to the proximal long arm of the X chromosome (Xq12-q21.1). Using four dinucleotide tandem repeat (DNTR) sequences from Xq13-derived yeast artificial chromosomes (YACs), we further delineate DYT3 within Xq13. Observation of a recombination event between DYT3 and DNTR locus 4548-7, derived from a YAC encompassing locus DXS56, establishes 4548-7 as a distal flanking marker. Assignment of DYT3 to a region in Xq13, flanked by loci 4548-7 and DXS159, is further supported by highly significant allelic association between DYT3 and a total of four DNTR loci--PY2-31, PY5-10, 4548-1, and 4548-7--located in a region defined by PGK1 and DXS56. /phi/ and /delta/ values were 0.82/0.35, 0.78/0.42, 0.65/0.34, and 0.88/0.58 for PY2-31, PY5-10, 4548-1, and 4548-7 at P less than 10(-2), P less than 10(-4), P less than 10(-3), and P less than 10(-6).
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aldridge J., Kunkel L., Bruns G., Tantravahi U., Lalande M., Brewster T., Moreau E., Wilson M., Bromley W., Roderick T. A strategy to reveal high-frequency RFLPs along the human X chromosome. Am J Hum Genet. 1984 May;36(3):546–564. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beggs A. H., Kunkel L. M. A polymorphic CACA repeat in the 3' untranslated region of dystrophin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Apr 11;18(7):1931–1931. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.7.1931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botstein D., White R. L., Skolnick M., Davis R. W. Construction of a genetic linkage map in man using restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Am J Hum Genet. 1980 May;32(3):314–331. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Browne D. L., Zonana J., Litt M. Dinucleotide repeat polymorphism at the DXYS1X locus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Apr 11;19(7):1721–1721. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Browne D. L., Zonana J., Litt M. Dinucleotide repeat polymorphism at the PGK1P1 locus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Mar 11;20(5):1169–1169. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.5.1169-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakravarti A., Buetow K. H., Antonarakis S. E., Waber P. G., Boehm C. D., Kazazian H. H. Nonuniform recombination within the human beta-globin gene cluster. Am J Hum Genet. 1984 Nov;36(6):1239–1258. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feener C. A., Boyce F. M., Kunkel L. M. Rapid detection of CA polymorphisms in cloned DNA: application to the 5' region of the dystrophin gene. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Mar;48(3):621–627. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerem B., Rommens J. M., Buchanan J. A., Markiewicz D., Cox T. K., Chakravarti A., Buchwald M., Tsui L. C. Identification of the cystic fibrosis gene: genetic analysis. Science. 1989 Sep 8;245(4922):1073–1080. doi: 10.1126/science.2570460. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer P. L., de Leon D., Ozelius L., Risch N., Bressman S. B., Brin M. F., Schuback D. E., Burke R. E., Kwiatkowski D. J., Shale H. Dystonia gene in Ashkenazi Jewish population is located on chromosome 9q32-34. Ann Neurol. 1990 Feb;27(2):114–120. doi: 10.1002/ana.410270203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kupke K. G., Graeber M. B., Müller U. Dystonia-parkinsonism syndrome (XDP) locus: flanking markers in Xq12-q21.1. Am J Hum Genet. 1992 Apr;50(4):808–815. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larin Z., Monaco A. P., Lehrach H. Yeast artificial chromosome libraries containing large inserts from mouse and human DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 15;88(10):4123–4127. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.10.4123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee L. V., Kupke K. G., Caballar-Gonzaga F., Hebron-Ortiz M., Müller U. The phenotype of the X-linked dystonia-parkinsonism syndrome. An assessment of 42 cases in the Philippines. Medicine (Baltimore) 1991 May;70(3):179–187. doi: 10.1097/00005792-199105000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee L. V., Pascasio F. M., Fuentes F. D., Viterbo G. H. Torsion dystonia in Panay, Philippines. Adv Neurol. 1976;14:137–151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald M. E., Lin C., Srinidhi L., Bates G., Altherr M., Whaley W. L., Lehrach H., Wasmuth J., Gusella J. F. Complex patterns of linkage disequilibrium in the Huntington disease region. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Oct;49(4):723–734. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahtani M. M., Lafrenière R. G., Kruse T. A., Willard H. F. An 18-locus linkage map of the pericentromeric region of the human X chromosome: genetic framework for mapping X-linked disorders. Genomics. 1991 Aug;10(4):849–857. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90172-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeer P. L., McGeer E. G., Itagaki S., Mizukawa K. Anatomy and pathology of the basal ganglia. Can J Neurol Sci. 1987 Aug;14(3 Suppl):363–372. doi: 10.1017/s0317167100037756. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller U., Kupke K. G. The genetics of primary torsion dystonia. Hum Genet. 1990 Jan;84(2):107–115. doi: 10.1007/BF00208922. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nygaard T. G., Marsden C. D., Duvoisin R. C. Dopa-responsive dystonia. Adv Neurol. 1988;50:377–384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oudet C., Heilig R., Hanauer A., Mandel J. L. Nonradioactive assay for new microsatellite polymorphisms at the 5' end of the dystrophin gene, and estimation of intragenic recombination. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Aug;49(2):311–319. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozelius L. J., Kramer P. L., de Leon D., Risch N., Bressman S. B., Schuback D. E., Brin M. F., Kwiatkowski D. J., Burke R. E., Gusella J. F. Strong allelic association between the torsion dystonia gene (DYT1) andloci on chromosome 9q34 in Ashkenazi Jews. Am J Hum Genet. 1992 Mar;50(3):619–628. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozelius L., Kramer P. L., Moskowitz C. B., Kwiatkowski D. J., Brin M. F., Bressman S. B., Schuback D. E., Falk C. T., Risch N., de Leon D. Human gene for torsion dystonia located on chromosome 9q32-q34. Neuron. 1989 May;2(5):1427–1434. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90188-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]