Abstract
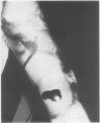
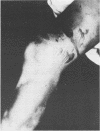
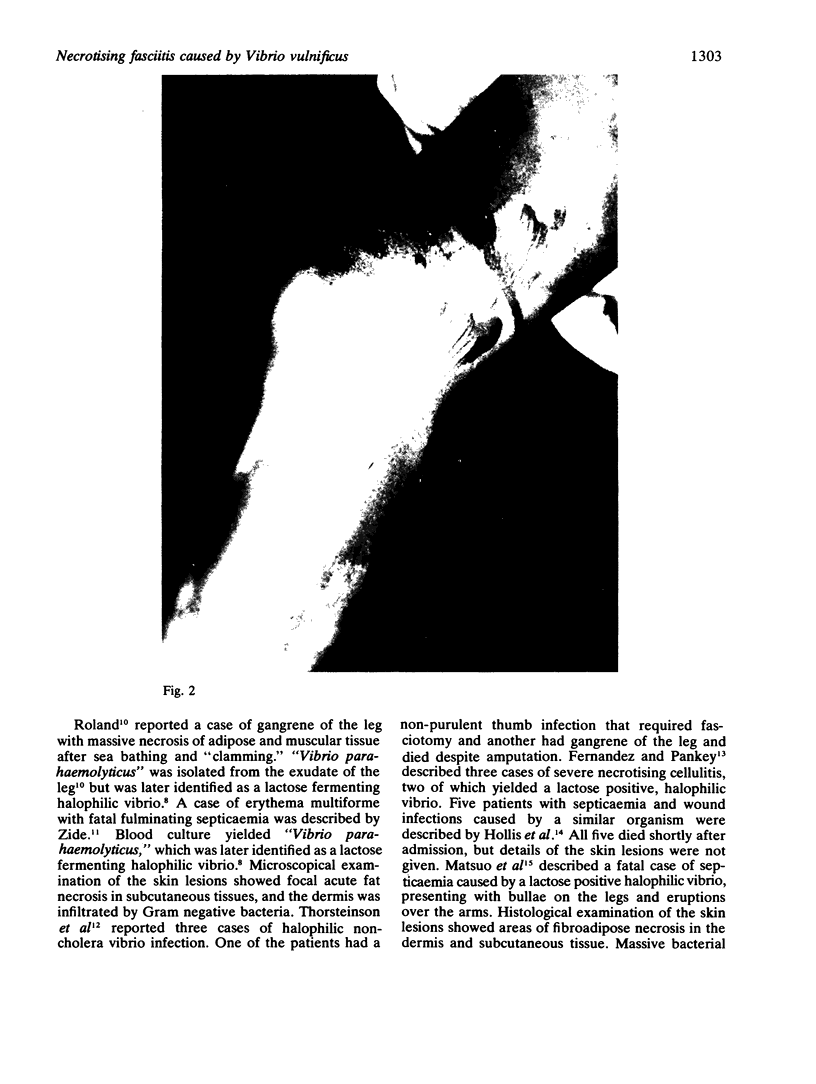
A case of necrotising fasciitis caused by Vibrio vulnificus is described. The need for early recognition and aggressive surgical treatment are highlighted, and the necrotising infections due to V vulnificus described in the published work are reviewed.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blake P. A., Merson M. H., Weaver R. E., Hollis D. G., Heublein P. C. Disease caused by a marine Vibrio. Clinical characteristics and epidemiology. N Engl J Med. 1979 Jan 4;300(1):1–5. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197901043000101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castillo L. E., Winslow D. L., Pankey G. A. Wound infection and septic shock due to Vibrio vulnificus. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1981 Jul;30(4):844–848. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1981.30.844. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmer J. J., 3rd Vibrio ("Beneckea") vulnificus, the bacterium associated with sepsis, septicaemia, and the sea. Lancet. 1979 Oct 27;2(8148):903–903. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)92715-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez C. R., Pankey G. A. Tissue invasion by unnamed marine vibrios. JAMA. 1975 Sep 15;233(11):1173–1176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giuliano A., Lewis F., Jr, Hadley K., Blaisdell F. W. Bacteriology of necrotizing fasciitis. Am J Surg. 1977 Jul;134(1):52–57. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(77)90283-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollis D. G., Weaver R. E., Baker C. N., Thornsberry C. Halophilic Vibrio species isolated from blood cultures. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Apr;3(4):425–431. doi: 10.1128/jcm.3.4.425-431.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janevicius R. V., Hann S. E., Batt M. D. Necrotizing fasciitis. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1982 Jan;154(1):97–102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly M. T., McCormick W. F. Acute bacterial myositis caused by Vibrio vulnificus. JAMA. 1981 Jul 3;246(1):72–73. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leppard B. J., Seal D. V. The value of bacteriology and serology in the diagnosis of necrotizing fasciitis. Br J Dermatol. 1983 Jul;109(1):37–44. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1983.tb03989.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuo T., Kohno S., Ikeda T., Saruwatari K., Ninomiya H. Fulminating lactose-positive Vibrio septicemia. Acta Pathol Jpn. 1978 Nov;28(6):937–948. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1827.1978.tb01282.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mertens A., Nagler J., Hansen W., Gepts-Friedenreich E. Halophilic, lactose-positive Vibrio in a case of fatal septicemia. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Feb;9(2):233–235. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.2.233-235.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poole M. D., Oliver J. D. Experimental pathogenicity and mortality in ligated ileal loop studies of the newly reported halophilic lactose-positive Vibrio sp. Infect Immun. 1978 Apr;20(1):126–129. doi: 10.1128/iai.20.1.126-129.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roland F. P. Leg gangrene and endotoxin shock due to vibrio parahaemolyticus--an infection acquired in New England coastal waters. N Engl J Med. 1970 Jun 4;282(23):1306–1306. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197006042822306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tacket C. O., Barrett T. J., Mann J. M., Roberts M. A., Blake P. A. Wound infections caused by Vibrio vulnificus, a marine vibrio, in inland areas of the United States. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Feb;19(2):197–199. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.2.197-199.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorsteinsson S. B., Minuth J. N., Musher D. M. Clinical manifestations of halophilic non-cholera Vibrio infections. Lancet. 1974 Nov 30;2(7892):1283–1284. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)90141-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver R. E., Ehrenkranz N. J. Letter: Vibrio parahaemolyticus septicemia. Arch Intern Med. 1975 Jan;135(1):197–197. doi: 10.1001/archinte.135.1.197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zide N., Davis J., Ehrenkranz N. J. Fulminating vibrio parahemolyticus septicemia. A syndrome of erythemia multiforme, hemolytic anemia, and hypotension. Arch Intern Med. 1974 Mar;133(3):479–481. doi: 10.1001/archinte.133.3.479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]