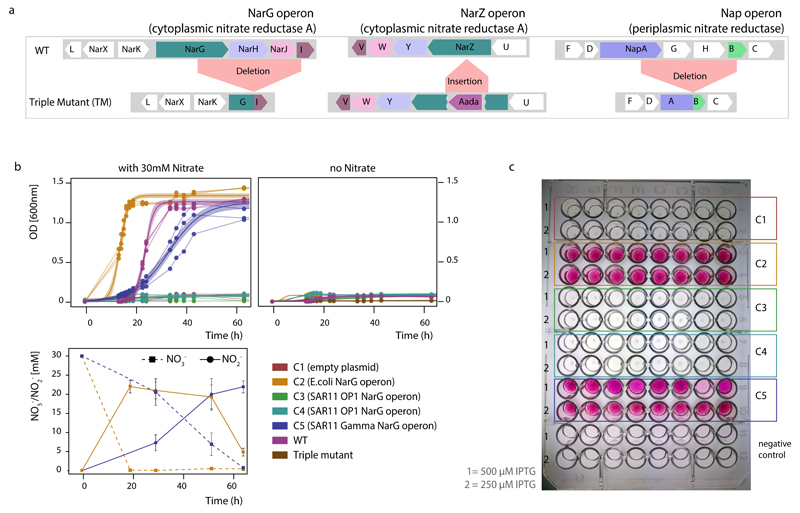
Extended Data Figure 5. Functional characterization of the SAR11 nar operons in the Escherichia coli heterologous expression system.
a, Genotype of the E. coli triple mutant confirmed by whole genome sequencing. The triple mutant lacks complete functional operons of all three NO3- reductases, and thus is incapable of NO3- reduction. b, Anaerobic growth of triple mutant clones, complemented with the SAR11 nar operons. For each strain three independent clones were monitored, and data from the replicate growth curves were fitted into a logistic model. Shaded areas represent the 95% confidence intervals of optical density readings (OD600nm) in the fitted logistic growth models. NO3- and NO2- were measured in parallel with ion chromatography. Note that the Gamma-type SAR11 operon complements the triple mutant phenotype, growing anaerobically by reducing NO3- to NO2-. E. coli encodes functional nitrite reductases, thus the accumulated NO2- can be further reduced to ammonia, accounting for the non-stoichiometric NO2- production. c, Whole cell NO2- production assays under aerobic conditions. Eight independent clones (columns A-H) of each type (C1-C5) were inoculated in LB supplemented with 30mM NO3- and different IPTG concentrations, and the well plate was incubated for 2 days at room temperature. Griess reagent was added, and development of pink color indicated NO2- production.