Abstract
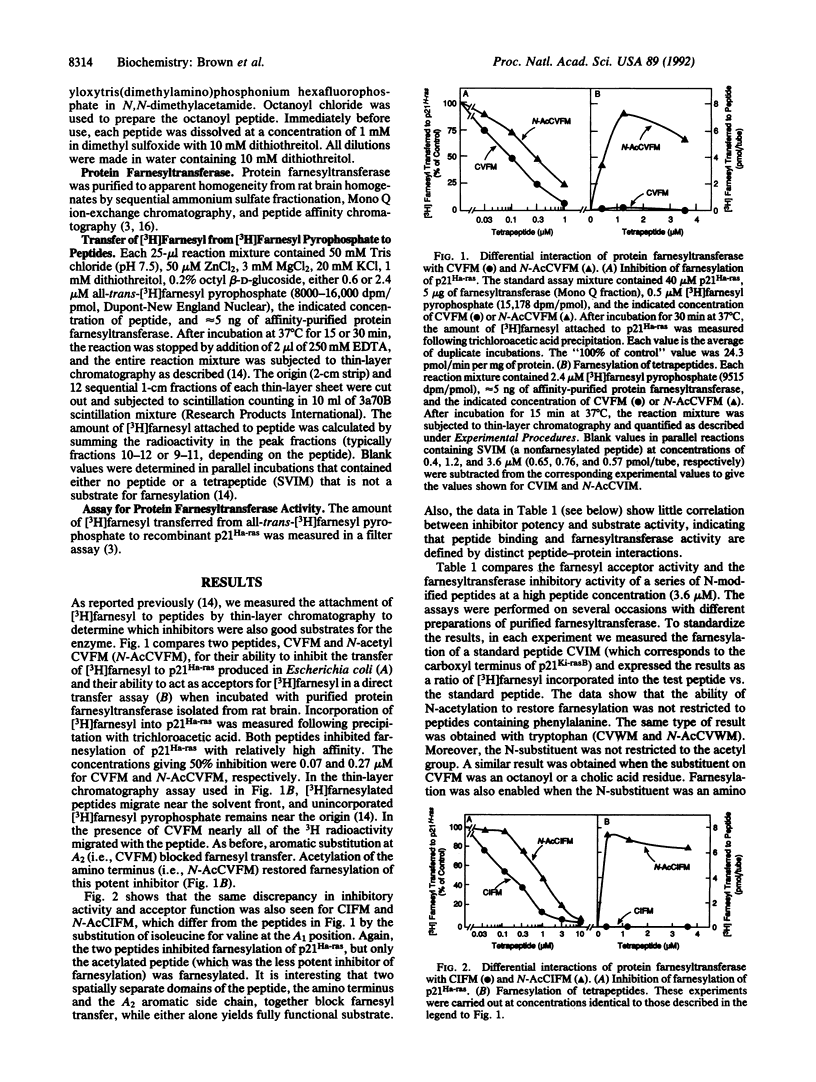
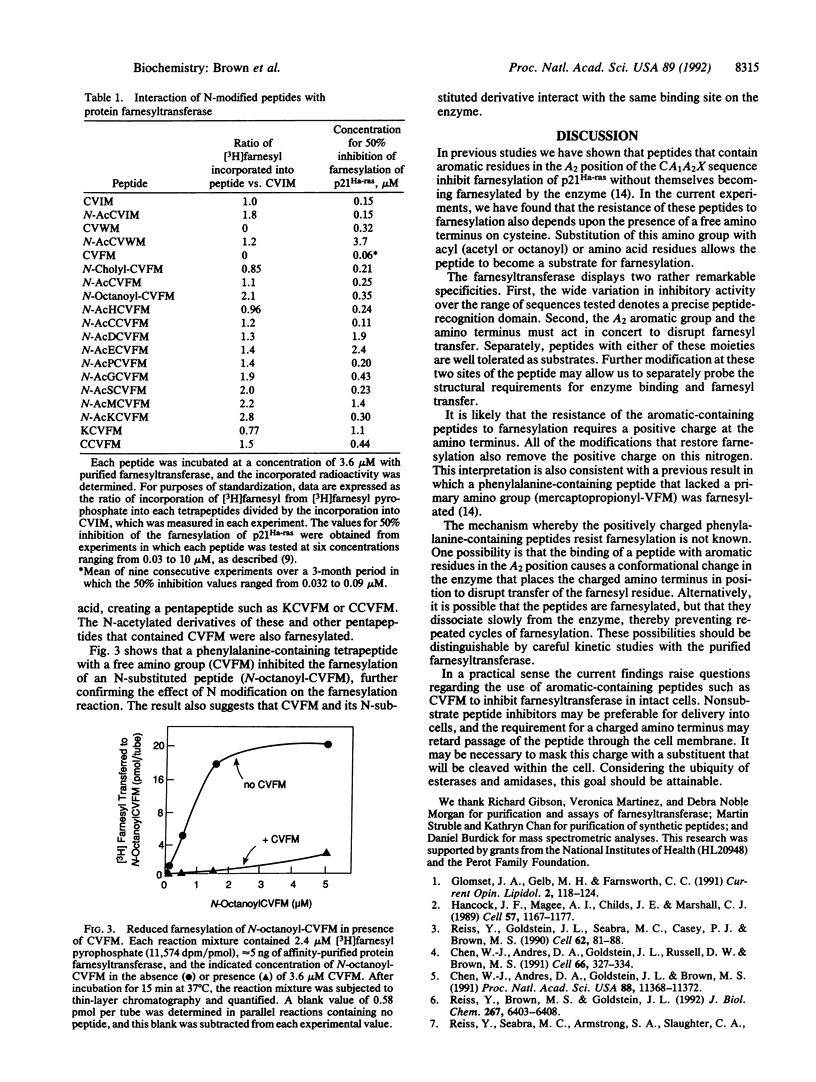
Protein farnesyltransferase from rat brain transfers farnesyl residues to cysteine residues in tetrapeptides that conform to the sequence CA1A2X, where C is cysteine, A1 and A2 are aliphatic amino acids, and X is methionine or serine. When the A2 residue is aromatic [e.g., phenylalanine as in Cys-Val-Phe-Met (CVFM)], the tetrapeptide continues to bind to the enzyme, but it can no longer accept a farnesyl group, and it becomes a pure inhibitor. The current studies show that this resistance to farnesylation also requires a positive charge on the cysteine amino group. Derivatization of this group with acetyl, octanoyl, or cholic acid residues or extension of the peptide with an additional amino acid restores the ability of phenylalanine-containing peptides to accept a farnesyl residue. The same result was obtained when the amino group of cysteine was deleted (mercaptopropionyl-VFM). These data suggest that the positive change on the cysteine amino group acts in concert with an aromatic residue in the A2 position to render peptides resistant to farnesylation by the rat brain enzyme.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Casey P. J., Thissen J. A., Moomaw J. F. Enzymatic modification of proteins with a geranylgeranyl isoprenoid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8631–8635. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen W. J., Andres D. A., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. Cloning and expression of a cDNA encoding the alpha subunit of rat p21ras protein farnesyltransferase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 15;88(24):11368–11372. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.24.11368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen W. J., Andres D. A., Goldstein J. L., Russell D. W., Brown M. S. cDNA cloning and expression of the peptide-binding beta subunit of rat p21ras farnesyltransferase, the counterpart of yeast DPR1/RAM1. Cell. 1991 Jul 26;66(2):327–334. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90622-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finegold A. A., Johnson D. I., Farnsworth C. C., Gelb M. H., Judd S. R., Glomset J. A., Tamanoi F. Protein geranylgeranyltransferase of Saccharomyces cerevisiae is specific for Cys-Xaa-Xaa-Leu motif proteins and requires the CDC43 gene product but not the DPR1 gene product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 15;88(10):4448–4452. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.10.4448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S., Stradley S. J., Reiss Y., Gierasch L. M. Nonfarnesylated tetrapeptide inhibitors of protein farnesyltransferase. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 25;266(24):15575–15578. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman L. E., Perou C. M., Fujiyama A., Tamanoi F. Structure and expression of yeast DPR1, a gene essential for the processing and intracellular localization of ras proteins. Yeast. 1988 Dec;4(4):271–281. doi: 10.1002/yea.320040405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock J. F., Magee A. I., Childs J. E., Marshall C. J. All ras proteins are polyisoprenylated but only some are palmitoylated. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1167–1177. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90054-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moores S. L., Schaber M. D., Mosser S. D., Rands E., O'Hara M. B., Garsky V. M., Marshall M. S., Pompliano D. L., Gibbs J. B. Sequence dependence of protein isoprenylation. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 5;266(22):14603–14610. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiss Y., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Divalent cation and prenyl pyrophosphate specificities of the protein farnesyltransferase from rat brain, a zinc metalloenzyme. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 25;267(9):6403–6408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiss Y., Goldstein J. L., Seabra M. C., Casey P. J., Brown M. S. Inhibition of purified p21ras farnesyl:protein transferase by Cys-AAX tetrapeptides. Cell. 1990 Jul 13;62(1):81–88. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90242-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiss Y., Seabra M. C., Armstrong S. A., Slaughter C. A., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. Nonidentical subunits of p21H-ras farnesyltransferase. Peptide binding and farnesyl pyrophosphate carrier functions. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 5;266(16):10672–10677. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiss Y., Stradley S. J., Gierasch L. M., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Sequence requirement for peptide recognition by rat brain p21ras protein farnesyltransferase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 1;88(3):732–736. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.3.732. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seabra M. C., Reiss Y., Casey P. J., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Protein farnesyltransferase and geranylgeranyltransferase share a common alpha subunit. Cell. 1991 May 3;65(3):429–434. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90460-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



