Figure 3. Cerulenin induces ROCK1 activation, Akt inactivation, and JNK activation.
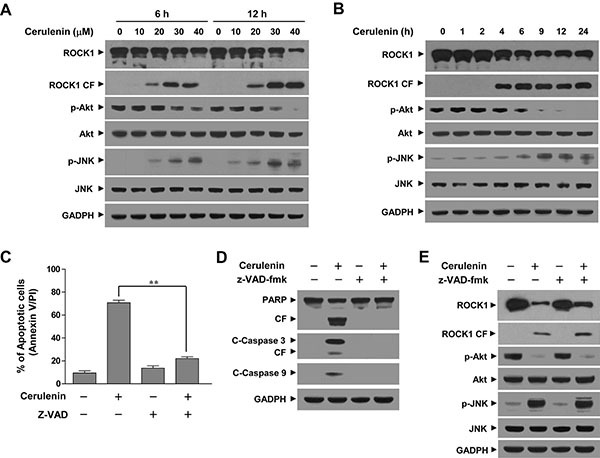
(A and B) Jurkat cells were treated with either various concentrations of cerulenin as indicated for 6 and 12 h or with 40 μM cerulenin for 1, 2, 4, 6, 9, 12, and 24 h. After treatment with cerulenin, WCLs were prepared and subjected to western blot analysis using antibodies against ROCK1, phosphorylated Akt (p-Akt), Akt, phosphorylated JNK (p-JNK), and JNK. Jurkat cells were pretreated with the caspase inhibitor z-VAD-fmk (10 μM) for 1 h, and then treated with 40 μM of cerulenin for 12 h. (C) Cells were stained with annexin V/PI, and apoptosis was evaluated using flow cytometry as described in the Materials and Methods. The values obtained from the annexin V/PI assays represent the mean ± s.d. for three separate experiments. **The values for cells treated with cerulenin and z-VAD-fmk were significantly lower that those of cells treated with cerulenin alone based on Student's t-tests; P < 0.01. (D and E) After treatment with cerulenin in the presence or absence of z-VAD-fmk, WCLs were prepared and subjected to western blot analysis using antibodies against PARP, C-Caspase 3, C-Caspase 9, ROCK1, p-Akt, Akt, p-JNK, and JNK. For western blot analyses, each lane was loaded with 30 μg of protein. The blots were subsequently stripped and reprobed with an antibody against GADPH to ensure equivalent loading. Two additional studies yielded equivalent results.
