Abstract
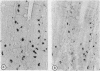
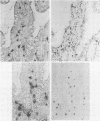
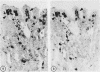
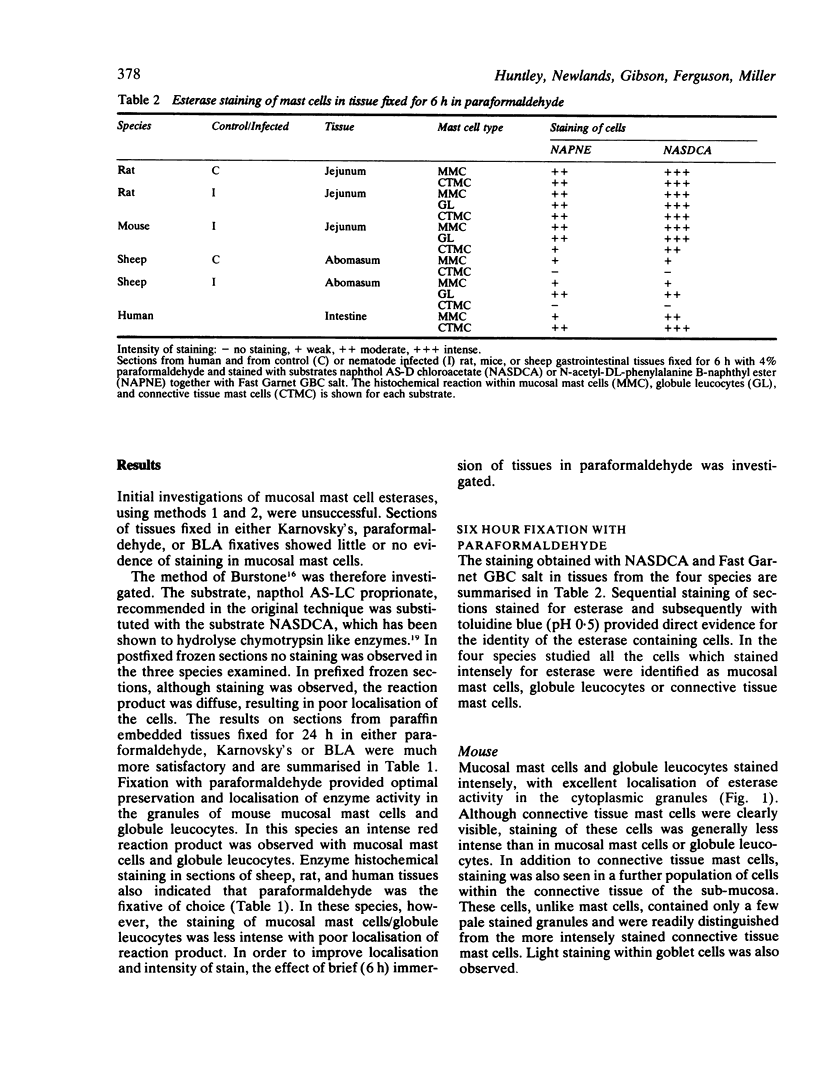
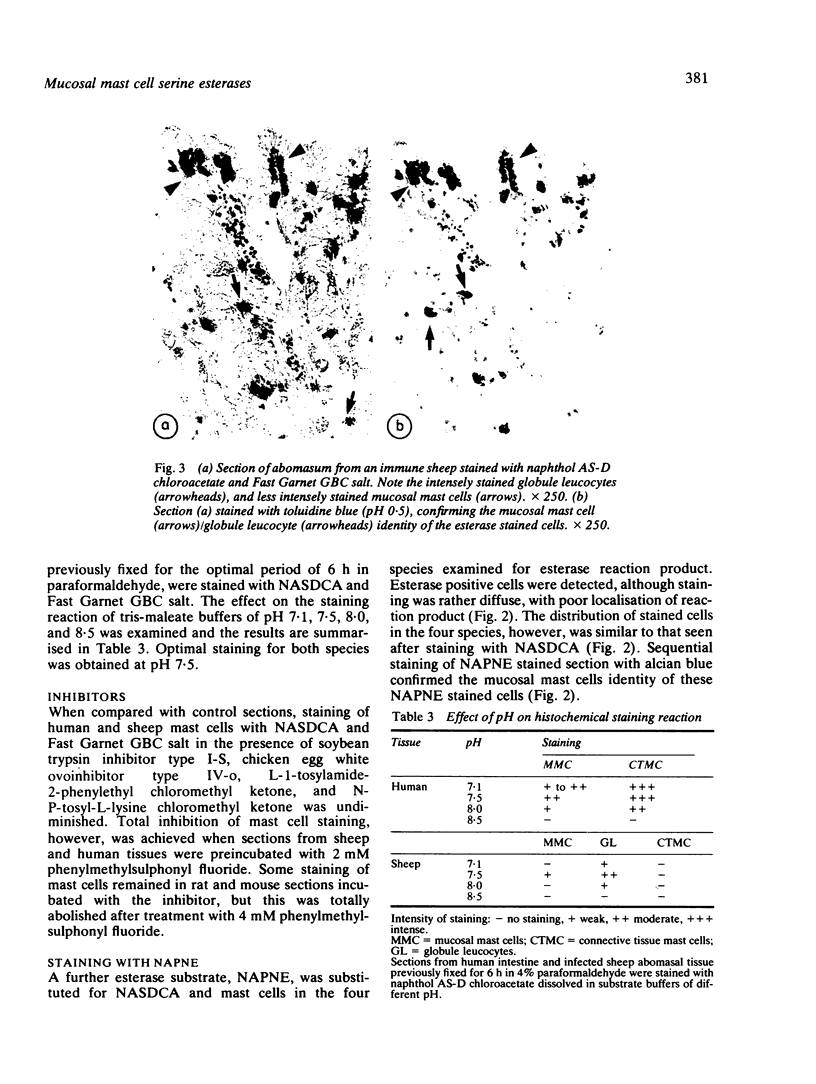
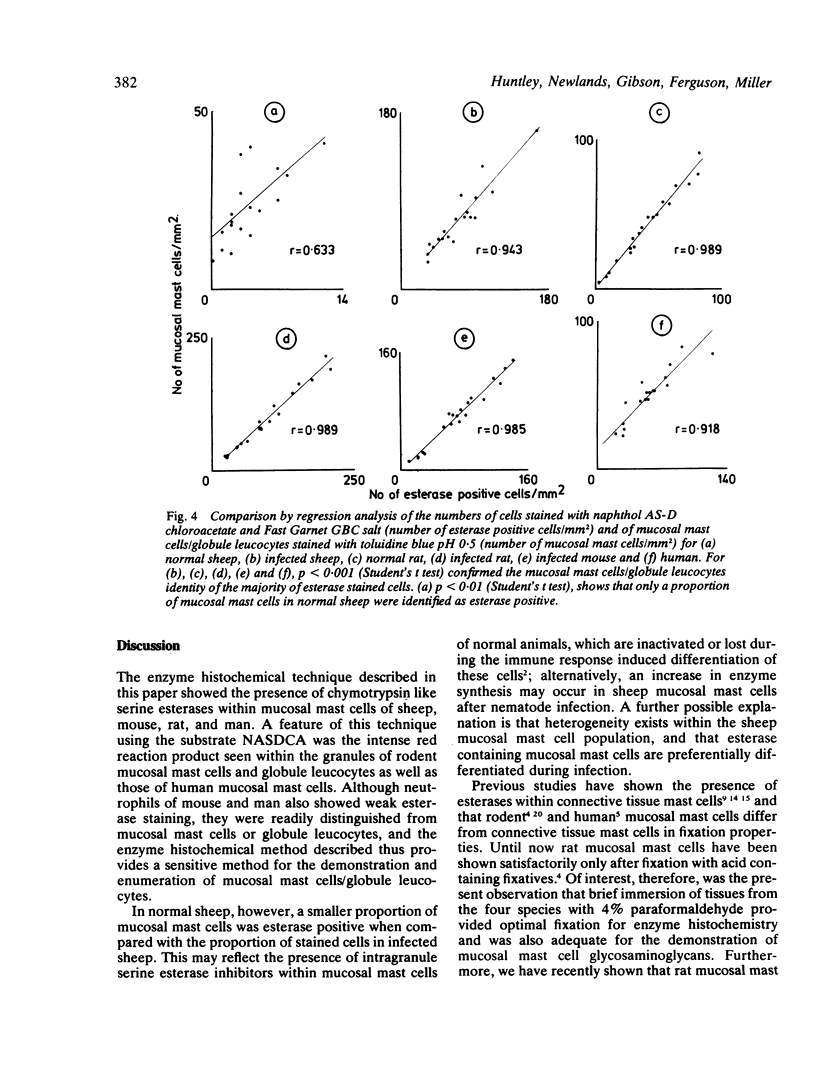
Serine esterases were detected in the granules of mucosal mast cells from rat, mouse, sheep, and man. Successful demonstration of enzyme activity required brief fixation (6 h) of tissues in 4% paraformaldehyde. Staining with naphthol AS-D chloroacetate produced an intense red reaction product in intraepithelial mucosal mast cells (globule leucocytes) and mucosal mast cells within the lamina propria of the gastrointestinal tract. The mast cell identity of cells stained for esterase was confirmed by sequential staining with toluidine blue (pH 0.5). Furthermore, the numbers of cells detected after staining for esterases or with toluidine blue were highly correlated. Esterase activity within mucosal mast cells/globule leucocytes from all species was inhibited with the serine enzyme inhibitor phenylmethylsulphonyl fluoride. Further histochemical studies with the substrate, N-acetyl-DL-phenylalanine B-naphthyl ester, indicated that mucosal mast cells and globule leucocytes contain esterases which are chymotrypsin like in substrate specificity.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BENDITT E. P., ARASE M. An enzyme in mast cells with properties like chymotrypsin. J Exp Med. 1959 Sep 1;110:451–460. doi: 10.1084/jem.110.3.451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bienenstock J., Befus A. D., Pearce F., Denburg J., Goodacre R. Mast cell heterogeneity: derivation and function, with emphasis on the intestine. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1982 Dec;70(6):407–412. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(82)90001-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowle P. K., Phillips D. E. Characteristics of mast cells in Chediak-Higashi mice: light and electron microscopic studies of connective tissue and mucosal mast cells. Exp Cell Biol. 1983;51(3):130–139. doi: 10.1159/000163183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enerbäck L. Mast cells in rat gastrointestinal mucosa. 2. Dye-binding and metachromatic properties. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1966;66(3):303–312. doi: 10.1111/apm.1966.66.3.303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enerbäck L. Mast cells in rat gastrointestinal mucosa. I. Effects of fixation. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1966;66(3):289–302. doi: 10.1111/apm.1966.66.3.289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLENNER G. G., COHEN L. A. Histochemical demonstration of a species-specific trypsin-like enzyme in mast cells. Nature. 1960 Mar 19;185:846–847. doi: 10.1038/185846a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOMORI G. Chloroacyl esters as histochemical substrates. J Histochem Cytochem. 1953 Nov;1(6):469–470. doi: 10.1177/1.6.469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huntley J. F., Newlands G., Miller H. R. The isolation and characterization of globule leucocytes: their derivation from mucosal mast cells in parasitized sheep. Parasite Immunol. 1984 Jul;6(4):371–390. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1984.tb00809.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King S. J., Miller H. R. Anaphylactic release of mucosal mast cell protease and its relationship to gut permeability in Nippostrongylus-primed rats. Immunology. 1984 Apr;51(4):653–660. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller H. R. Immune reactions in mucous membranes. II. The differentiation of intestinal mast cells during helminth expulsion in the rat. Lab Invest. 1971 May;24(5):339–347. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller H. R., Jackson F., Newlands G., Appleyard W. T. Immune exclusion, a mechanism of protection against the ovine nematode Haemonchus contortus. Res Vet Sci. 1983 Nov;35(3):357–363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller H. R., Walshaw R. Immune reactions in mucous membranes. IV. Histochemistry of intestinal mast cells during helminth expulsion in the rat. Am J Pathol. 1972 Oct;69(1):195–208. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rindler R., Hörtnagl H., Schmalzl F., Braunsteiner H. Hydrolysis of a chymotrypsin substrate and of naphthol AS-D chloroacetate by human leukocyte granules. Blut. 1973 Apr;26(4):239–249. doi: 10.1007/BF01631788. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seppä H. E. Rat skin main neutral protease: immunohistochemical localization. J Invest Dermatol. 1978 Nov;71(5):311–315. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12529791. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strobel S., Miller H. R., Ferguson A. Human intestinal mucosal mast cells: evaluation of fixation and staining techniques. J Clin Pathol. 1981 Aug;34(8):851–858. doi: 10.1136/jcp.34.8.851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vensel W. H., Komender J., Barnard E. A. Non-pancreatic proteases of the chymotrypsin family. II. Two proteases from a mouse mast cell tumor. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Nov 13;250(2):395–407. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(71)90196-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wingren U., Enerbäck L. Mucosal mast cells of the rat intestine: a re-evaluation of fixation and staining properties, with special reference to protein blocking and solubility of the granular glycosaminoglycan. Histochem J. 1983 Jun;15(6):571–582. doi: 10.1007/BF01954148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodbury R. G., Gruzenski G. M., Lagunoff D. Immunofluorescent localization of a serine protease in rat small intestine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2785–2789. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodbury R. G., Miller H. R. Quantitative analysis of mucosal mast cell protease in the intestines of Nippostrongylus-infected rats. Immunology. 1982 Jul;46(3):487–495. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodbury R. G., Neurath H. Structure, specificity and localization of the serine proteases of connective tissue. FEBS Lett. 1980 Jun 2;114(2):189–196. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)81112-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]