Abstract
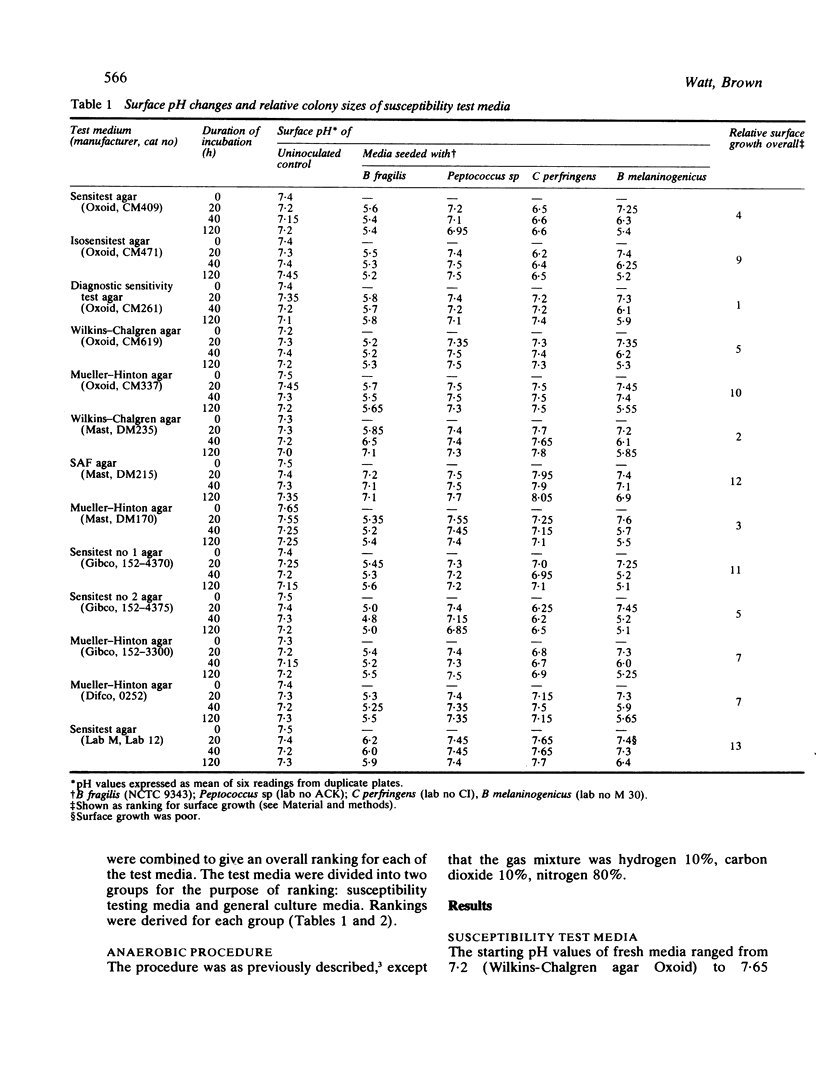
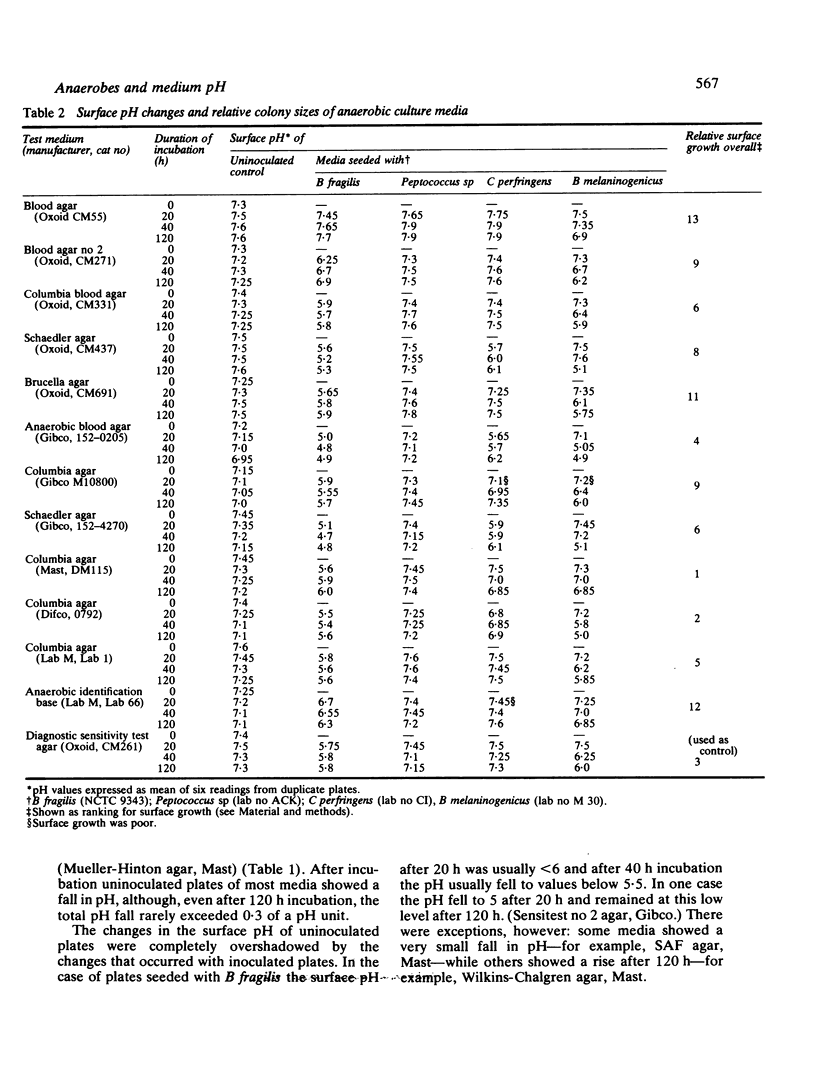
Changes in surface pH occurring after varying periods of anaerobic incubation were measured for a total of 23 test solid media. There was little change in the surface pH of uninoculated plates, but plates inoculated with Bacteriodes fragilis showed a striking fall in pH, to pH 5 in the case of some of the test media. The problems of controlling the surface pH of solid media are discussed and possible methods of control are considered.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berry P. L., Taylor E., Phillips I. The use of an anaerobic incubator for the isolation of anaerobes from clinical samples. J Clin Pathol. 1982 Oct;35(10):1158–1162. doi: 10.1136/jcp.35.10.1158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen S. L., Swomley P., Drusano G. Effect of carbon dioxide and pH on susceptibility of Bacteroides fragilis group to erythromycin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Feb;19(2):335–336. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.2.335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingham H. R., Selkon J. B., Codd A. A., Hale J. H. The effect of carbon dioxide on the sensitivity of Bacteroides fragilis to certain antibiotics in vitro. J Clin Pathol. 1970 Apr;23(3):254–258. doi: 10.1136/jcp.23.3.254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watt B., Brown F. V. The comparative activity of cefsulodin against anaerobic bacteria of clinical interest: synergy with cefoxitin. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1981 Mar;7(3):269–278. doi: 10.1093/jac/7.3.269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


