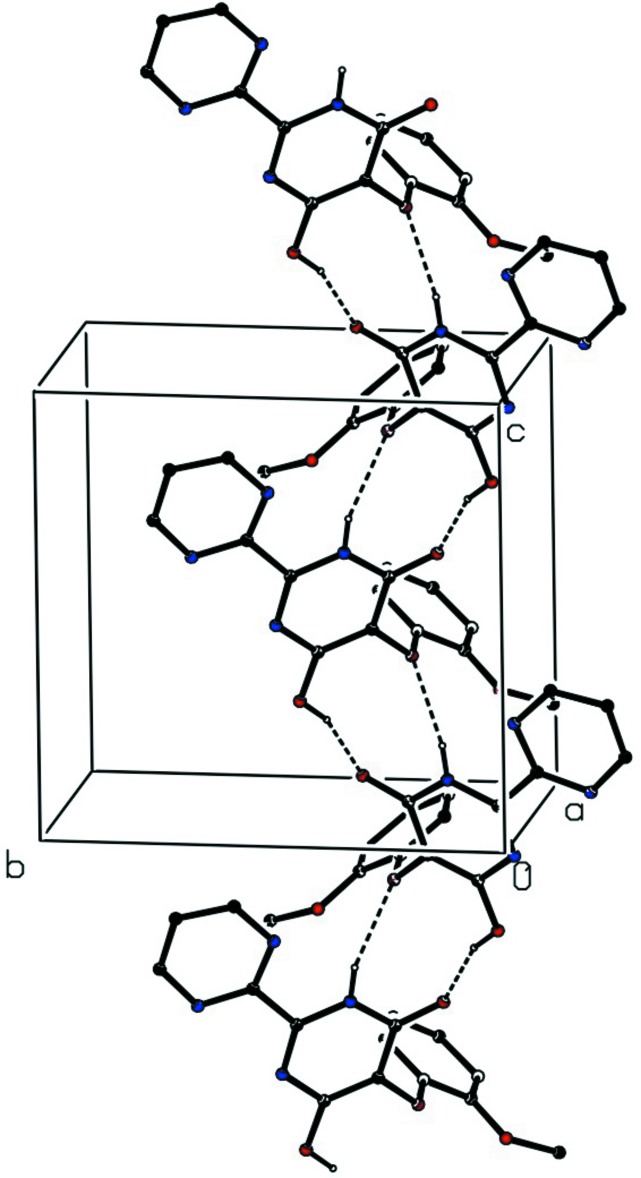
In the crystal, a combination of N—H⋯O and O—H⋯O hydrogen bonds links the molecules of the title compounds into a chain of rings.
Keywords: crystal structure, supramolecular structure, bipyrimidines, molecular conformation, hydrogen bonding
Abstract
In the title compound, C15H12N4O4, the dihedral angle between the heterocyclic rings is 12.60 (8)°, and that between the benzene ring and the adjacent heterocyclic ring is 85.14 (6)°. In the crystal, a combination of N—H⋯O and O—H⋯O hydrogen bonds link molecules related by a glide plane into a C(5) C(6)[R 2 2(9)] chain of rings, which is a distinctly different packing motif to those observed in hydrated modifications of this compound.
Chemical context
Pyrimidine derivatives exhibit a wide variety of biological actions (Önal & Yıldırım, 2007 ▸) and specific examples are of particular value in the treatment of cardiovascular diseases (Goldmann & Stoltefuss, 1991 ▸). One such derivative is bosentan, 4-tert-butyl-N-[6-(2-hydroxyethoxy)-5-(2-methoxyphenoxy)-2-(pyrimidin-2-yl)pyrimidin-4-yl]benzene-1-sulfonamide, which is used in the treatment of pulmonary artery hypertension (Pearl et al., 1999 ▸; Hoeper et al., 2003 ▸; Kenyon & Nappi, 2003 ▸).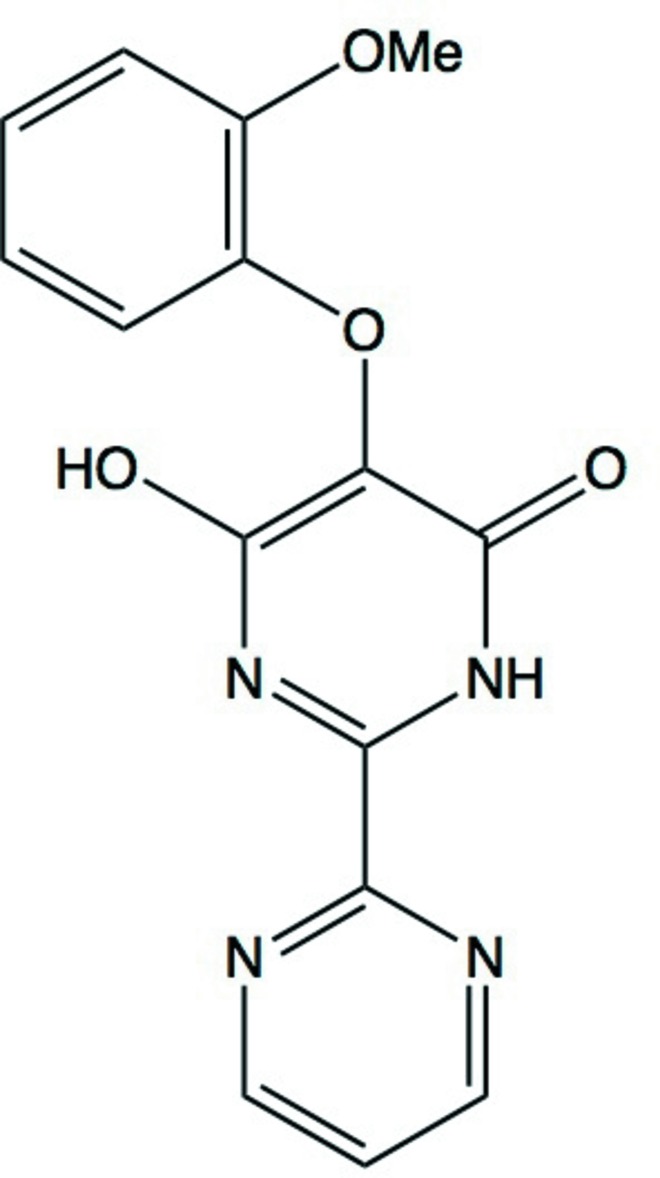
4-Hydroxy-5-(2-methoxyphenoxy)-2,2′-bipyrimidin-6(1H)-one (I) (Fig. 1 ▸) is an intermediate in the synthesis of bosentan (Rebelli et al., 2013 ▸; Kompella et al., 2014 ▸) and accordingly it is of interest to determine its crystal and molecular structure, which we report here. Crystals of the anhydrous title compound (I) were obtained from a solution of a 1:1 mixture of dimethylsulfoxide and N,N-dimethylformamide in the presence of adipic acid: by contrast, a similar crystallization regime but omitting the adipic acid yielded the corresponding dihydrate (II) (Yamuna et al., 2013 ▸), so permitting comparison of the anhydrous and hydrated forms.
Figure 1.

The molecular structure of compound (I) showing displacement ellipsoids drawn at the 30% probability level.
Structural commentary
The bond distances in the ring containing atom N11 clearly show the presence of localized double bonds in the bonds C12=N13 and C14=C15 as well as the exocyclic C16=O16, fully consistent with the location of the H atoms on atoms N11 and O14, as deduced from difference maps and confirmed by the refinement. By contrast, the bond distances in the other heterocyclic ring indicate conventional aromatic-type delocalization.
At each of the sites C14, C31 and C32, the corresponding pairs of exocyclic O—C—N (at C14) or O—C—C angles (at C31 and C32) differ by almost 10°, as generally observed in the arenes of type ArOR when the substituent R lies close to the plane of the aryl ring (Seip & Seip, 1973 ▸; Ferguson et al., 1996 ▸). Here atoms C15 and C37 (Fig. 1 ▸) are displaced from the plane of the aryl ring (C31–C36) by 0.219 (3) and 0.204 (4) Å, respectively, with both substituents displaced to the same side of the aryl ring. The C—O—C angles at atoms O15 and O32, 115.41 (12) and 117.65 (18)° respectively, and the C—O—H angle at atom O14 is 114.2 (16)°; are all significantly larger the the idealized tetrahedral value of 109.5°.
The dihedral angle between the heterocyclic rings is 12.60 (8)° and that between the ring containing N11 and the aryl ring is 85.14 (6)°. Accordingly, the molecule of (I) exhibits no internal symmetry and thus the compound is conformationally chiral: the centrosymmetric space group confirms that (I) crystallizes as a conformational racemate.
Supramolecular interactions
In the crystal, molecules of (I) are linked by a combination of O—H⋯N and N—H⋯N hydrogen bonds (Table 1 ▸) to form a C(5) C(6)[ (9)] chain of rings running parallel to the [001] direction (Fig. 2 ▸): adjacent molecules are related by glide-plane symmetry. Two chains of this type, related to one another by inversion, pass through each unit cell, but there are no direction-specific interactions between adjacent chains.
(9)] chain of rings running parallel to the [001] direction (Fig. 2 ▸): adjacent molecules are related by glide-plane symmetry. Two chains of this type, related to one another by inversion, pass through each unit cell, but there are no direction-specific interactions between adjacent chains.
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N11—H11⋯O15i | 0.855 (19) | 2.257 (19) | 2.9733 (18) | 141.4 (17) |
| O14—H14⋯O16ii | 0.85 (2) | 1.80 (2) | 2.6117 (18) | 160 (2) |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii) 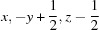 .
.
Figure 2.
Part of the crystal structure of compound (I) showing the formation of a hydrogen-bonded C(5) C(6)[ )9)] chain of rings parallel to [001]. For the sake of clarity, the H atoms bonded to C atoms have all been omitted.
)9)] chain of rings parallel to [001]. For the sake of clarity, the H atoms bonded to C atoms have all been omitted.
Database survey
In the dihydrate (II), an extensive series of hydrogen bonds, encompassing N—H⋯O, O—H⋯N and O—H⋯O types links the molecular components into a complex sheet structure (Yamuna et al., 2013 ▸), in contrast to the rather simple chains in (I) reported here. A sheet structure, built from a combination of the same three types of hydrogen bond is found also in the structure of bosentan monohydrate (Kaur et al., 2013 ▸).
Synthesis and crystallization
A sample of compound (I) was a gift from Cadila Pharmaceuticals Ltd, Ahmedabad, Gujarat, India. Colourless plates of the anhydrous compound (I) were grown by slow evaporation, at room temperature of a solution of (I) in a mixture of dimethylsulfoxide and N,N-dimethylformamide (1:1, v/v) containing an excess of adipic acid (hexane-1,6-dioic acid).
Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 2 ▸. All H atoms were located in difference maps. The H atoms bonded to C atoms were then treated as riding atoms in geometrically idealized positions with C—H distances 0.93 Å (aromatic and heteroaromatic) or 0.96 Å (CH3) and with U iso(H) = kU eq(C) where k = 1.5 for the methyl group, which was permitted to rotate but not to tilt and 1.2 for all other H atoms bonded to C atoms. For the H atoms bonded to O or N atoms, the atomic coordinates were refined with U iso(H) = 1.5U eq(O) or 1.2U eq(N), giving the O—H and N—H distances shown in Table 1 ▸.
Table 2. Experimental details.
| Crystal data | |
| Chemical formula | C15H12N4O4 |
| M r | 312.29 |
| Crystal system, space group | Monoclinic, P21/c |
| Temperature (K) | 298 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 12.1863 (9), 10.7079 (8), 11.1726 (8) |
| β (°) | 105.412 (8) |
| V (Å3) | 1405.48 (19) |
| Z | 4 |
| Radiation type | Mo Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 0.11 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.49 × 0.46 × 0.28 |
| Data collection | |
| Diffractometer | Agilent Xcalibur, Eos, Gemini CCD |
| Absorption correction | Multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 2003 ▸) |
| T min, T max | 0.812, 0.969 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2σ(I)] reflections | 7121, 3113, 2311 |
| R int | 0.037 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.650 |
| Refinement | |
| R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.051, 0.134, 1.07 |
| No. of reflections | 3113 |
| No. of parameters | 215 |
| H-atom treatment | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 0.26, −0.25 |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016009075/hb7590sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016009075/hb7590Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016009075/hb7590Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 1483503
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
BKS thanks the UGC for the award of a Rajeev Gandhi fellowship and the University of Mysore for research facilities. HSY thanks Cadila Pharmaceuticals Ltd, Ahmedabad, Gujarat, India, for a sample of compound (I). JPJ acknowledges the NSF–MRI program (grant No. 1039027) for funds to purchase the X-ray diffractometer.
supplementary crystallographic information
Crystal data
| C15H12N4O4 | F(000) = 648 |
| Mr = 312.29 | Dx = 1.476 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 12.1863 (9) Å | Cell parameters from 3266 reflections |
| b = 10.7079 (8) Å | θ = 3.5–29.2° |
| c = 11.1726 (8) Å | µ = 0.11 mm−1 |
| β = 105.412 (8)° | T = 298 K |
| V = 1405.48 (19) Å3 | Plate, colourles |
| Z = 4 | 0.49 × 0.46 × 0.28 mm |
Data collection
| Agilent Xcalibur, Eos, Gemini CCD diffractometer | 2311 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Detector resolution: 16.0416 pixels mm-1 | Rint = 0.037 |
| φ and ω scans | θmax = 27.5°, θmin = 3.5° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 2003) | h = −15→15 |
| Tmin = 0.812, Tmax = 0.969 | k = −13→10 |
| 7121 measured reflections | l = −14→14 |
| 3113 independent reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.051 | Hydrogen site location: mixed |
| wR(F2) = 0.134 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 1.07 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0582P)2 + 0.1493P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 3113 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 215 parameters | Δρmax = 0.26 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.25 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| N11 | 0.18153 (12) | 0.35790 (14) | 0.63063 (13) | 0.0295 (3) | |
| H11 | 0.1817 (15) | 0.3477 (17) | 0.7066 (18) | 0.035* | |
| C12 | 0.14803 (12) | 0.47018 (16) | 0.58084 (14) | 0.0257 (4) | |
| N13 | 0.15092 (11) | 0.50269 (13) | 0.46986 (12) | 0.0288 (3) | |
| C14 | 0.19721 (13) | 0.41910 (16) | 0.40542 (14) | 0.0259 (4) | |
| C15 | 0.23862 (13) | 0.30650 (15) | 0.45349 (14) | 0.0246 (4) | |
| C16 | 0.22954 (14) | 0.26765 (16) | 0.57208 (15) | 0.0286 (4) | |
| O14 | 0.20095 (11) | 0.45956 (12) | 0.29445 (11) | 0.0384 (3) | |
| H14 | 0.2235 (18) | 0.405 (2) | 0.251 (2) | 0.058* | |
| O15 | 0.29101 (9) | 0.22750 (11) | 0.38791 (10) | 0.0286 (3) | |
| O16 | 0.26156 (12) | 0.16663 (12) | 0.62240 (11) | 0.0435 (4) | |
| N21 | 0.10457 (13) | 0.51230 (15) | 0.77235 (13) | 0.0382 (4) | |
| C22 | 0.11108 (13) | 0.55897 (16) | 0.66440 (15) | 0.0287 (4) | |
| N23 | 0.09267 (14) | 0.67630 (15) | 0.62621 (15) | 0.0442 (4) | |
| C24 | 0.06898 (19) | 0.7543 (2) | 0.7096 (2) | 0.0534 (6) | |
| H24 | 0.0564 | 0.8380 | 0.6881 | 0.064* | |
| C25 | 0.06238 (17) | 0.7179 (2) | 0.8239 (2) | 0.0503 (6) | |
| H25 | 0.0467 | 0.7743 | 0.8805 | 0.060* | |
| C26 | 0.07998 (16) | 0.5938 (2) | 0.85148 (18) | 0.0472 (5) | |
| H26 | 0.0746 | 0.5653 | 0.9283 | 0.057* | |
| C31 | 0.41008 (14) | 0.22844 (17) | 0.42471 (15) | 0.0305 (4) | |
| C32 | 0.46353 (16) | 0.1335 (2) | 0.37687 (17) | 0.0417 (5) | |
| C33 | 0.58106 (19) | 0.1307 (3) | 0.4082 (2) | 0.0639 (7) | |
| H33 | 0.6184 | 0.0678 | 0.3771 | 0.077* | |
| C34 | 0.64289 (19) | 0.2205 (3) | 0.4850 (3) | 0.0713 (8) | |
| H34 | 0.7220 | 0.2185 | 0.5043 | 0.086* | |
| C35 | 0.59019 (18) | 0.3127 (3) | 0.5336 (2) | 0.0595 (6) | |
| H35 | 0.6330 | 0.3720 | 0.5868 | 0.071* | |
| C36 | 0.47253 (15) | 0.3169 (2) | 0.50285 (17) | 0.0414 (5) | |
| H36 | 0.4358 | 0.3795 | 0.5351 | 0.050* | |
| O32 | 0.39382 (13) | 0.05064 (15) | 0.30120 (14) | 0.0585 (5) | |
| C37 | 0.4443 (3) | −0.0572 (3) | 0.2648 (2) | 0.0755 (8) | |
| H37A | 0.4889 | −0.0336 | 0.2095 | 0.113* | |
| H37B | 0.3857 | −0.1143 | 0.2233 | 0.113* | |
| H37C | 0.4923 | −0.0968 | 0.3369 | 0.113* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| N11 | 0.0418 (8) | 0.0269 (8) | 0.0233 (7) | 0.0053 (6) | 0.0148 (6) | 0.0020 (6) |
| C12 | 0.0255 (8) | 0.0249 (9) | 0.0261 (8) | 0.0005 (7) | 0.0059 (6) | −0.0018 (7) |
| N13 | 0.0345 (7) | 0.0239 (8) | 0.0278 (7) | 0.0035 (6) | 0.0078 (6) | 0.0006 (6) |
| C14 | 0.0298 (8) | 0.0261 (9) | 0.0216 (7) | −0.0028 (7) | 0.0063 (6) | −0.0010 (7) |
| C15 | 0.0283 (8) | 0.0233 (9) | 0.0235 (7) | 0.0008 (7) | 0.0090 (6) | −0.0023 (7) |
| C16 | 0.0342 (9) | 0.0251 (10) | 0.0283 (8) | 0.0022 (7) | 0.0112 (6) | 0.0005 (7) |
| O14 | 0.0632 (8) | 0.0300 (8) | 0.0255 (6) | 0.0066 (6) | 0.0178 (6) | 0.0038 (5) |
| O15 | 0.0310 (6) | 0.0293 (7) | 0.0267 (6) | 0.0032 (5) | 0.0098 (4) | −0.0058 (5) |
| O16 | 0.0722 (9) | 0.0286 (8) | 0.0360 (7) | 0.0176 (7) | 0.0256 (6) | 0.0095 (6) |
| N21 | 0.0455 (9) | 0.0392 (10) | 0.0327 (8) | −0.0007 (7) | 0.0155 (6) | −0.0068 (7) |
| C22 | 0.0273 (8) | 0.0283 (10) | 0.0304 (8) | −0.0007 (7) | 0.0074 (6) | −0.0054 (7) |
| N23 | 0.0592 (10) | 0.0287 (9) | 0.0473 (9) | 0.0076 (8) | 0.0189 (8) | −0.0052 (7) |
| C24 | 0.0661 (14) | 0.0319 (12) | 0.0638 (14) | 0.0109 (10) | 0.0198 (11) | −0.0135 (10) |
| C25 | 0.0466 (11) | 0.0519 (14) | 0.0544 (13) | 0.0037 (10) | 0.0169 (9) | −0.0267 (11) |
| C26 | 0.0511 (11) | 0.0596 (15) | 0.0354 (10) | −0.0023 (11) | 0.0194 (9) | −0.0162 (10) |
| C31 | 0.0315 (8) | 0.0330 (10) | 0.0278 (8) | 0.0055 (7) | 0.0091 (6) | 0.0059 (7) |
| C32 | 0.0456 (11) | 0.0453 (13) | 0.0333 (9) | 0.0162 (9) | 0.0092 (8) | 0.0034 (9) |
| C33 | 0.0484 (13) | 0.085 (2) | 0.0592 (14) | 0.0317 (13) | 0.0169 (11) | 0.0048 (14) |
| C34 | 0.0340 (12) | 0.101 (2) | 0.0756 (17) | 0.0110 (13) | 0.0089 (11) | 0.0157 (17) |
| C35 | 0.0424 (12) | 0.0687 (17) | 0.0600 (14) | −0.0114 (11) | 0.0008 (10) | 0.0076 (13) |
| C36 | 0.0394 (10) | 0.0399 (12) | 0.0438 (11) | −0.0031 (9) | 0.0089 (8) | 0.0016 (9) |
| O32 | 0.0649 (9) | 0.0506 (10) | 0.0543 (9) | 0.0259 (8) | 0.0057 (7) | −0.0188 (8) |
| C37 | 0.113 (2) | 0.0547 (16) | 0.0594 (15) | 0.0433 (15) | 0.0238 (14) | −0.0059 (13) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| N11—C12 | 1.342 (2) | C26—N21 | 1.332 (2) |
| N11—H11 | 0.86 (2) | C16—O16 | 1.234 (2) |
| C12—N13 | 1.297 (2) | C26—H26 | 0.9300 |
| C12—C22 | 1.484 (2) | C31—C36 | 1.373 (3) |
| N13—C14 | 1.361 (2) | C31—C32 | 1.389 (3) |
| C14—C15 | 1.361 (2) | C32—O32 | 1.357 (2) |
| C15—C16 | 1.421 (2) | C32—C33 | 1.381 (3) |
| C16—N11 | 1.381 (2) | C33—C34 | 1.373 (4) |
| C14—O14 | 1.3255 (19) | C33—H33 | 0.9300 |
| C15—O15 | 1.3816 (18) | C34—C35 | 1.367 (4) |
| O14—H14 | 0.85 (2) | C34—H34 | 0.9300 |
| O15—C31 | 1.3990 (19) | C35—C36 | 1.384 (3) |
| N21—C22 | 1.327 (2) | C35—H35 | 0.9300 |
| C22—N23 | 1.327 (2) | C36—H36 | 0.9300 |
| N23—C24 | 1.339 (2) | O32—C37 | 1.418 (3) |
| C24—C25 | 1.358 (3) | C37—H37A | 0.9600 |
| C24—H24 | 0.9300 | C37—H37B | 0.9600 |
| C25—C26 | 1.368 (3) | C37—H37C | 0.9600 |
| C25—H25 | 0.9300 | ||
| C12—N11—C16 | 123.44 (14) | N21—C26—H26 | 118.8 |
| C12—N11—H11 | 116.5 (13) | C25—C26—H26 | 118.8 |
| C16—N11—H11 | 119.4 (13) | C36—C31—C32 | 120.81 (17) |
| N13—C12—N11 | 123.65 (15) | O15—C31—C32 | 115.95 (15) |
| N13—C12—C22 | 121.28 (15) | O15—C31—C36 | 123.24 (16) |
| N11—C12—C22 | 115.02 (14) | O32—C32—C31 | 116.00 (16) |
| C12—N13—C14 | 116.70 (14) | O32—C32—C33 | 125.34 (19) |
| O14—C14—N13 | 113.69 (14) | C15—O15—C31 | 115.41 (12) |
| O14—C14—C15 | 123.87 (15) | C32—O32—C37 | 117.65 (18) |
| C15—C14—N13 | 122.41 (14) | C33—C32—C31 | 118.7 (2) |
| C14—C15—O15 | 120.54 (13) | C34—C33—C32 | 120.2 (2) |
| C14—C15—C16 | 120.98 (15) | C34—C33—H33 | 119.9 |
| O15—C15—C16 | 118.47 (14) | C32—C33—H33 | 119.9 |
| O16—C16—N11 | 121.35 (15) | C35—C34—C33 | 121.1 (2) |
| O16—C16—C15 | 126.03 (16) | C35—C34—H34 | 119.4 |
| N11—C16—C15 | 112.61 (14) | C33—C34—H34 | 119.4 |
| C14—O14—H14 | 114.2 (16) | C34—C35—C36 | 119.4 (2) |
| C22—N21—C26 | 115.78 (17) | C34—C35—H35 | 120.3 |
| N23—C22—N21 | 127.09 (16) | C36—C35—H35 | 120.3 |
| N23—C22—C12 | 117.26 (15) | C31—C36—C35 | 119.9 (2) |
| N21—C22—C12 | 115.59 (15) | C31—C36—H36 | 120.1 |
| C22—N23—C24 | 114.59 (17) | C35—C36—H36 | 120.1 |
| N23—C24—C25 | 123.6 (2) | O32—C37—H37A | 109.5 |
| N23—C24—H24 | 118.2 | O32—C37—H37B | 109.5 |
| C25—C24—H24 | 118.2 | H37A—C37—H37B | 109.5 |
| C24—C25—C26 | 116.47 (19) | O32—C37—H37C | 109.5 |
| C24—C25—H25 | 121.8 | H37A—C37—H37C | 109.5 |
| C26—C25—H25 | 121.8 | H37B—C37—H37C | 109.5 |
| N21—C26—C25 | 122.44 (19) | ||
| C16—N11—C12—N13 | 4.3 (2) | N11—C12—C22—N21 | −6.7 (2) |
| C16—N11—C12—C22 | −173.20 (14) | N21—C22—N23—C24 | 2.4 (3) |
| N11—C12—N13—C14 | −4.0 (2) | C12—C22—N23—C24 | −174.60 (16) |
| C22—C12—N13—C14 | 173.33 (13) | C22—N23—C24—C25 | −0.9 (3) |
| C12—N13—C14—O14 | −177.94 (14) | N23—C24—C25—C26 | −0.8 (3) |
| C12—N13—C14—C15 | 0.1 (2) | C22—N21—C26—C25 | 0.0 (3) |
| O14—C14—C15—O15 | 1.7 (2) | C24—C25—C26—N21 | 1.3 (3) |
| N13—C14—C15—O15 | −176.13 (13) | C15—O15—C31—C36 | −12.1 (2) |
| O14—C14—C15—C16 | −178.56 (15) | C15—O15—C31—C32 | 168.10 (14) |
| N13—C14—C15—C16 | 3.6 (2) | C36—C31—C32—O32 | 179.61 (17) |
| C12—N11—C16—O16 | 178.32 (16) | O15—C31—C32—O32 | −0.6 (2) |
| C12—N11—C16—C15 | −0.4 (2) | C36—C31—C32—C33 | −0.8 (3) |
| C14—C15—C16—O16 | 178.06 (17) | O15—C31—C32—C33 | 178.93 (17) |
| O15—C15—C16—O16 | −2.2 (3) | O32—C32—C33—C34 | 179.5 (2) |
| C14—C15—C16—N11 | −3.2 (2) | C31—C32—C33—C34 | −0.1 (3) |
| O15—C15—C16—N11 | 176.48 (13) | C32—C33—C34—C35 | 1.1 (4) |
| C14—C15—O15—C31 | 100.24 (17) | C33—C34—C35—C36 | −1.2 (4) |
| C16—C15—O15—C31 | −79.49 (18) | C32—C31—C36—C35 | 0.7 (3) |
| C26—N21—C22—N23 | −2.0 (3) | O15—C31—C36—C35 | −179.05 (17) |
| C26—N21—C22—C12 | 175.03 (15) | C34—C35—C36—C31 | 0.3 (3) |
| N13—C12—C22—N23 | −6.9 (2) | C33—C32—O32—C37 | 9.3 (3) |
| N11—C12—C22—N23 | 170.67 (15) | C31—C32—O32—C37 | −171.21 (19) |
| N13—C12—C22—N21 | 175.73 (14) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N11—H11···O15i | 0.855 (19) | 2.257 (19) | 2.9733 (18) | 141.4 (17) |
| O14—H14···O16ii | 0.85 (2) | 1.80 (2) | 2.6117 (18) | 160 (2) |
Symmetry codes: (i) x, −y+1/2, z+1/2; (ii) x, −y+1/2, z−1/2.
References
- Agilent (2014). CrysAlis PRO. Agilent Technologies Ltd, Yarnton, England.
- Ferguson, G., Glidewell, C. & Patterson, I. L. J. (1996). Acta Cryst. C52, 420–423.
- Goldmann, S. & Stoltefuss, J. (1991). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 30, 1559–1578.
- Hoeper, M., Taha, N., Bekjarova, A., Gatzke, R. & Spiekerkoetter, E. (2003). Eur. Respir. J. 22, 330–334. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Kaur, M., Jasinski, J. P., Keeley, A. C., Yathirajan, H. S., Betz, R., Gerber, T. & Butcher, R. J. (2013). Acta Cryst. E69, o12–o13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Kenyon, K. W. & Nappi, J. M. (2003). Ann. Pharmacother. 37, 1055–1062. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Kompella, A., Kasa, S., Balina, V. S., Kusumba, S., Adibhatla, B. R. K. & Muddasani, P. R. (2014). Sci. J. Chem. 2, 9–15.
- Önal, Z. & Yıldırım, İ. (2007). Heterocycl. Commun. 13, 113–120.
- Pearl, J. M., Wellmann, S. A., McNamara, J. L., Lombardi, J. P., Wagner, C. J., Raake, J. L. & Nelson, D. P. (1999). Ann. Thorac. Surg. 68, 1714–21 discussion 1721–1714-21; discussion 1722. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Rebelli, P., Yerrabelly, J. R., Yalamanchili, B. K., Kommera, R., Ghojala, V. R. & Bairy, K. R. (2013). Org. Process Res. Dev. 17, 1021–1026.
- Seip, H. M. & Seip, R. (1973). Acta Chem. Scand. 27, 4024–4027.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2003). SADABS. University of Göttingen, Germany.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Yamuna, T. S., Jasinski, J. P., Anderson, B. J., Yathirajan, H. S. & Kaur, M. (2013). Acta Cryst. E69, o1707–o1708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016009075/hb7590sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016009075/hb7590Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016009075/hb7590Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 1483503
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report