The title isonicotinohydrazides adopt an E conformation about the C=N bonds and in each molecule there is an intramolecular O—H⋯N hydrogen bond, forming an S(6) ring motif. In the crystals of both compounds, zigzag chains are formed via N—H⋯N hydrogen bonds, in the [10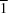 ] the first compound and [010] for the other.
] the first compound and [010] for the other.
Keywords: crystal structure, iron chelator, isonicotinohydrazide, hydrogen bonds
Abstract
Two derivatives of the well-known iron chelator, (E)-N′-(2-hydroxybenzylidene)isonicotinohydrazide (SIH), substituted in the 5-position of the 2-hydroxybenzene ring by a methyl and a fluorine group viz. (E)-N′-(2-hydroxy-5-methylbenzylidene)isonicotinohydrazide, C14H13N3O2, (I), and (E)-N′-(5-fluoro-2-hydroxybenzylidene)isonicotinohydrazide, C13H10FN3O2, (II), have been prepared and characterized by single-crystal X-ray diffraction, 1H NMR and mass spectrometry. The molecules of both compounds deviate slightly from planarity [r.m.s. deviations are 0.145 and 0.110 Å for (I) and (II), respectively] and adopt an E conformation with respect to the double bond of the hydrazone bridge. In each molecule, there is an intramolecular O—H⋯N hydrogen bond forming an S(6) ring motif. The dihedral angles between the mean planes of the isonicotinoyl ring and the cresol ring in (I) or the fluorophenol ring in (II) are 10.49 (6) and 9.43 (6)°, respectively. In the crystals of both compounds, zigzag chains are formed via N—H⋯N hydrogen bonds, in the [10-1] direction for (I) and [010] for (II). In (I), the chains are linked by weak C—H⋯π and π–π stacking interactions [centroid-to-centroid distances = 3.6783 (8) Å; inter-planar angle = 10.94 (5)°], leading to the formation of a three-dimensional supramolecular architecture. In (II), adjacent chains are connected through C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds to form sheets parallel to (100), which enclose R 4 4(30) ring motifs. The sheets are linked by weak C—H⋯π and π–π [centroid-to-centroid distance = 3.7147 (8) Å; inter-planar angle = 10.94 (5)°] interactions, forming a three-dimensional supramolecular architecture.
Chemical context
Hydrazone-based chelators for metal ions have received a significant amount of attention (Bendova et al., 2010 ▸; Hrušková et al., 2016 ▸). Compounds from this class, such as salicyl aldehyde isonicotinoyl hydrazide (SIH), have been studied as potential metal chelators in biological systems (Hrušková et al., 2011 ▸). These compounds have also been shown to be effective in protecting against metal-based oxidative stress (Jansová et al., 2014 ▸). In our research we are interested in developing probes for metal ions (Carter et al., 2014 ▸). We have therefore synthesized the title compounds, which are derivatives of the chelator SIH containing a signalling unit.
Structural commentary
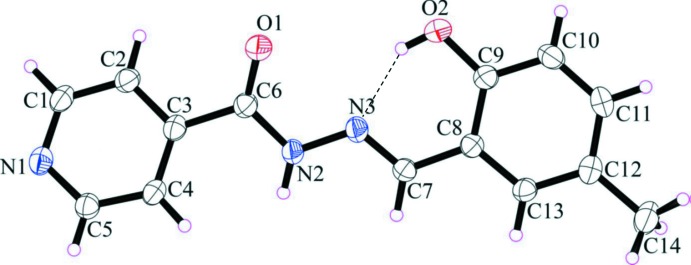
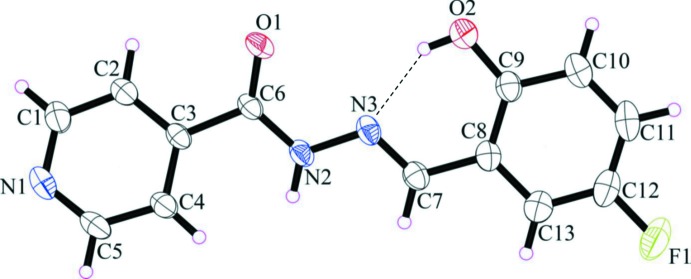
The molecular structures of the title compounds, (I) and (II), are illustrated in Figs. 1 ▸ and 2 ▸, respectively. They consist of an isonicotinoyl moiety linked by a –C7=N3–N2– linkage to a cresol unit in (I) and a fluorophenol ring in (II). The molecules deviate slightly from planarity with the r.m.s deviations for the fitted atoms being 0.145 for (I) and 0.110 Å for (II). In each molecule, there is an intramolecular O—H⋯N hydrogen bond forming an S(6) ring motif. Both compounds have an E conformation with respect to the double bond of the hydrazone bridge (C7=N3) with the C8—C7=N3—N2 torsion angles being −179.03 (12) and −177.61 (11)° for (I) and (II), respectively. The dihedral angles between the mean planes of the isonicotinoyl moiety and the cresol moiety in (I), or the fluorophenol moiety in (II) are 10.49 (6) and 9.43 (6)°, respectively. The bond lengths and angles in the title molecules agree reasonably well with those found in closely related structures (Chumakov et al., 2001 ▸; Yang, 2006a
▸,b
▸; Kargar et al., 2010 ▸; Sedaghat et al., 2014 ▸) .
.
Figure 1.
The molecular structure of compound (I), showing the atom-numbering scheme. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 40% probability level. The intramolecular O—H⋯N hydrogen bond is shown as a dashed line (see Table 1 ▸).
Figure 2.
The molecular structure of compound (II), showing the atom-numbering scheme. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 40% probability level. The intramolecular O—H⋯N hydrogen bond is shown as a dashed line (see Table 2 ▸).
Supramolecular features
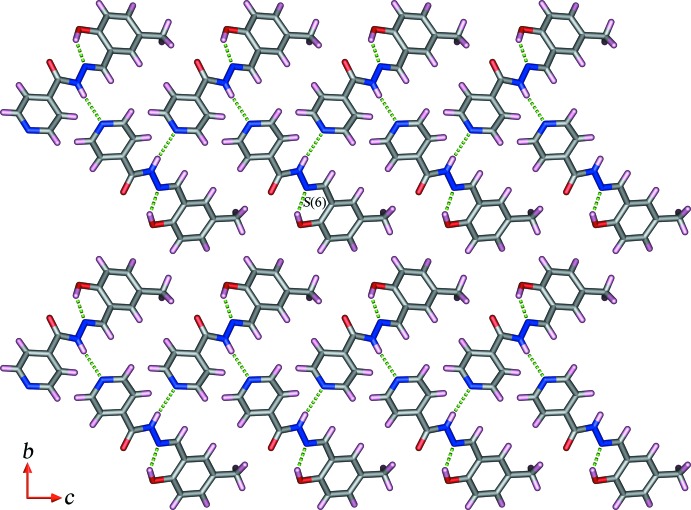
In the crystals of both compounds, zigzag chains are formed via N—H⋯N hydrogen bonds (Tables 1 ▸ and 2 ▸), in direction [10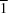 ] for (I) and [010] for (II). In (I), the chains are linked by weak C—H⋯π and π–π stacking interactions [centroid-to-centroid distances = 3.6783 (8) Å; inter-planar angle = 10.94 (5)°], leading to the formation of a three-dimensional supramolecular architecture (Fig. 3 ▸). In (II), adjacent chains are connected through C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds to form sheets parallel to (100), which enclose
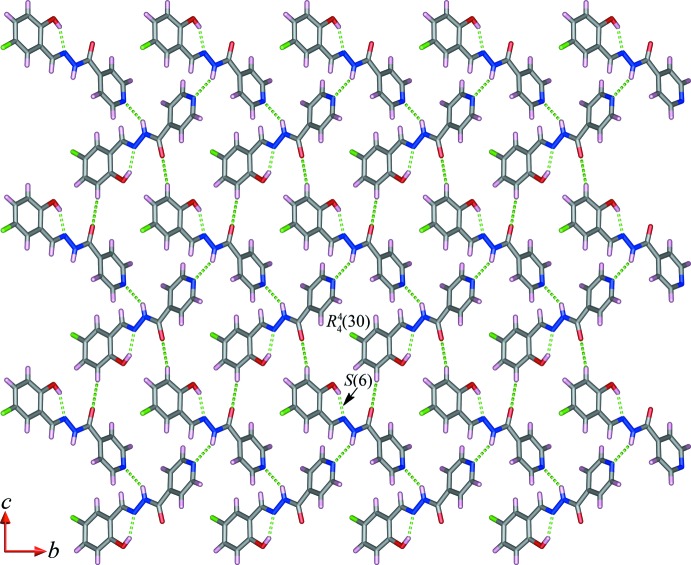
] for (I) and [010] for (II). In (I), the chains are linked by weak C—H⋯π and π–π stacking interactions [centroid-to-centroid distances = 3.6783 (8) Å; inter-planar angle = 10.94 (5)°], leading to the formation of a three-dimensional supramolecular architecture (Fig. 3 ▸). In (II), adjacent chains are connected through C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds to form sheets parallel to (100), which enclose 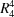 (30) ring motifs. Weak C—H⋯π and π—π [centroid-to-centroid distance = 3.7147 (8) Å, inter-planar angle = 10.94 (5)°] interactions link the sheets, forming a three-dimensional supramolecular architecture (Fig. 4 ▸).
(30) ring motifs. Weak C—H⋯π and π—π [centroid-to-centroid distance = 3.7147 (8) Å, inter-planar angle = 10.94 (5)°] interactions link the sheets, forming a three-dimensional supramolecular architecture (Fig. 4 ▸).
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °) for (I) .
Cg1 is the centroid of the N1/C1–C5 ring.
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O2—H2O⋯N3 | 0.82 | 1.87 | 2.5857 (16) | 145 |
| N2—H2N⋯N1i | 0.86 | 2.19 | 3.0232 (17) | 164 |
| C10—H10⋯Cg1ii | 0.93 | 2.85 | 3.5259 (17) | 130 |
Symmetry codes: (i) 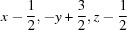 ; (ii)
; (ii) 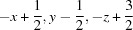 .
.
Table 2. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °) for (II) .
Cg1 is the centroid of the N1/C1–C5 ring.
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O2—H2⋯N3 | 0.82 | 1.92 | 2.6329 (15) | 145 |
| N2—H2A⋯N1i | 0.86 | 2.19 | 2.8889 (15) | 138 |
| C10—H10⋯O1ii | 0.93 | 2.51 | 3.2573 (18) | 138 |
| C11—H11⋯Cg1iii | 0.93 | 2.98 | 3.8917 (18) | 168 |
Symmetry codes: (i) 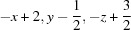 ; (ii)
; (ii) 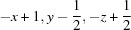 ; (iii)
; (iii) 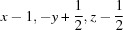 .
.
Figure 3.
Partial view along the a axis of the crystal packing of compound (I), showing the hydrogen-bonded (dashed lines; see Table 1 ▸) zigzag chains parallel to [10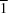 ].
].
Figure 4.
Partial view along the a axis of the crystal packing of compound (II), showing the N—H⋯N and C—H⋯O hydrogen-bonded (dashed lines; see Table 2 ▸) sheet propagating in the bc plane.
Database survey
A search of the Cambridge Structural Database (Version 5.37, last update November 2015; Groom et al., 2016 ▸) indicated the presence of 40 structures containing the (E)-N-(2-hydroxybezylydene)isonicotinohydrazide substructure. They include the isotypic crystal structures with chloride (UCAREV, Chumakov et al., 2001 ▸; UCAREV01, Yang, 2006a
▸), bromide (XENDOK, Yang, 2006b
▸; XENDOK01, Sedaghat et al., 2014 ▸) and methoxy (VACHAK, Kargar et al., 2010 ▸) groups substituted at the 5-position of the phenyl ring. In the crystals of all three compounds, the N—H⋯N hydrogen bond involving the hydrazone hydrogen and the pyridine nitrogen atoms organize the molecules into a herringbone motif, while in the crystal of the methoxy compound there are also weak N—H⋯O and C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds present forming 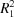 (6) ring motifs.
(6) ring motifs.
Synthesis and crystallization
A solution of isonicotinic acid hydrazide (0.184 g, 1.34 mmol) and the appropriately substituted salicyl aldehyde (1.47 mmol) in a mixture of ethanol (3 ml) and water (1 ml) containing a catalytic amount of acetic acid was heated to reflux for 5 h. The reaction mixture was allowed to cool to room temperature, resulting in the formation of a white precipitate. The reaction mixture was filtered and the isolated solid was washed with diethyl ether and dried in vacuo. The compounds were isolated as white crystalline solids in 73% and 66% yield for the methyl (I) and fluoro (II) derivatives, respectively. Single crystals suitable for X-ray diffraction were grown by slow evaporation of methanolic solutions of the title compounds.
Spectroscopic data for (I): 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d 6) d 2.25 (1H, s, CH3), 6.84 (1H, d, J = 8.4, CH—Ph), 7.12 (1H, dd, J = 2.0, J = 8.4, CH—Ph), 7.40 (1H, d, J = 1.6, CH—Ph), 7.84 (2H, d, J = 6.0, CH—Py), 8.63 (1H, s, CH=N), 8.79 (2H, d, J = 6.0, CH—Py), 10.82 (1H, s, NH), 12.26 (1H, s, OH). HR–MS (ES+) C14H14N3O2 requires 256.1086 [M+H]+; found 256.1051.
Spectroscopic data for (II): 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d 6) d 6.94 (1H, dd, J = 4.4, J = 8.8, CH—Ph), 7.16 (1H, td, J = 3.2, J = 8.8, CH—Ph), 7.46 (1H, dd, J = 3.2, J = 9.6, CH—Ph), 7.84 (2H, d, J = 6.0, CH—Py), 8.67 (1H, s, CH=N), 8.80 (2H, d, J = 6.0, CH—Py), 10.84 (1H, s, NH), 12.35 (1H, s, OH). HR–MS (ES+) C13H11FN3O2 requires 260.0835 [M+H]+; found 260.0831.
Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 3 ▸. H atoms bonded to C, N, and O atoms were placed at calculated positions and refined using a riding-model approximation: N—H = 0.86 Å, O—H = 0.82 Å, and C—H = 0.93–0.96 Å with U iso(H) = 1.5U eq(C-methyl,O) and 1.2U eq(N,C) for other H atoms.
Table 3. Experimental details.
| (I) | (II) | |
|---|---|---|
| Crystal data | ||
| Chemical formula | C14H13N3O2 | C13H10FN3O2 |
| M r | 255.27 | 259.24 |
| Crystal system, space group | Monoclinic, P21/n | Monoclinic, P21/c |
| Temperature (K) | 296 | 296 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 8.5318 (4), 15.9973 (8), 9.4637 (5) | 8.9195 (3), 10.1128 (3), 13.6254 (4) |
| β (°) | 102.738 (2) | 103.481 (1) |
| V (Å3) | 1259.87 (11) | 1195.16 (6) |
| Z | 4 | 4 |
| Radiation type | Mo Kα | Mo Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 0.09 | 0.11 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.30 × 0.22 × 0.22 | 0.32 × 0.26 × 0.26 |
| Data collection | ||
| Diffractometer | Bruker D8 QUEST CMOS | Bruker APEX2 D8 QUEST CMOS |
| Absorption correction | Multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2014 ▸) | Multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2014 ▸) |
| T min, T max | 0.685, 0.746 | 0.685, 0.746 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2σ(I)] reflections | 26052, 2996, 2111 | 31833, 2848, 2128 |
| R int | 0.045 | 0.039 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.659 | 0.658 |
| Refinement | ||
| R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.046, 0.126, 1.01 | 0.042, 0.124, 1.03 |
| No. of reflections | 2996 | 2848 |
| No. of parameters | 174 | 174 |
| H-atom treatment | H-atom parameters constrained | H-atom parameters constrained |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 0.20, −0.22 | 0.26, −0.29 |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) Global, I, II. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016009762/su5301sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016009762/su5301Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016009762/su5301Isup4.cdx
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) II. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016009762/su5301IIsup3.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016009762/su5301Isup5.cml
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016009762/su5301IIsup6.cml
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a National Research Councils of Thailand grant provided by the Naresuan University Division of Research Administration (R2558B106). The authors thank the Faculty of Science and Technology, Thammasat University, for funds to purchase the X-ray diffractometer.
supplementary crystallographic information
(I) (E)-N'-(2-Hydroxy-5-methylbenzylidene)isonicotinohydrazide . Crystal data
| C14H13N3O2 | F(000) = 536 |
| Mr = 255.27 | Dx = 1.346 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/n | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 8.5318 (4) Å | Cell parameters from 6456 reflections |
| b = 15.9973 (8) Å | θ = 2.9–27.3° |
| c = 9.4637 (5) Å | µ = 0.09 mm−1 |
| β = 102.738 (2)° | T = 296 K |
| V = 1259.87 (11) Å3 | Block, colourless |
| Z = 4 | 0.30 × 0.22 × 0.22 mm |
(I) (E)-N'-(2-Hydroxy-5-methylbenzylidene)isonicotinohydrazide . Data collection
| Bruker D8 QUEST CMOS diffractometer | 2996 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: microfocus sealed x-ray tube, Incoatec Iµus | 2111 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| GraphiteDouble Bounce Multilayer Mirror monochromator | Rint = 0.045 |
| Detector resolution: 10.5 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 27.9°, θmin = 2.9° |
| φ and ω scans | h = −11→11 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2014) | k = −21→21 |
| Tmin = 0.685, Tmax = 0.746 | l = −12→12 |
| 26052 measured reflections |
(I) (E)-N'-(2-Hydroxy-5-methylbenzylidene)isonicotinohydrazide . Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.046 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.126 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0596P)2 + 0.2954P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.01 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 2996 reflections | Δρmax = 0.20 e Å−3 |
| 174 parameters | Δρmin = −0.22 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints |
(I) (E)-N'-(2-Hydroxy-5-methylbenzylidene)isonicotinohydrazide . Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
(I) (E)-N'-(2-Hydroxy-5-methylbenzylidene)isonicotinohydrazide . Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O1 | 0.55036 (17) | 0.49610 (7) | 0.82618 (13) | 0.0710 (4) | |
| O2 | 0.21987 (15) | 0.36743 (7) | 0.62695 (11) | 0.0575 (3) | |
| H2O | 0.2779 | 0.4085 | 0.6481 | 0.086* | |
| N1 | 0.84669 (14) | 0.76238 (8) | 0.96854 (13) | 0.0422 (3) | |
| N2 | 0.43283 (14) | 0.57825 (7) | 0.63975 (12) | 0.0390 (3) | |
| H2N | 0.4281 | 0.6255 | 0.5957 | 0.047* | |
| N3 | 0.33377 (14) | 0.51301 (7) | 0.58586 (13) | 0.0392 (3) | |
| C1 | 0.81205 (18) | 0.69573 (9) | 1.04127 (15) | 0.0430 (4) | |
| H1 | 0.8580 | 0.6923 | 1.1398 | 0.052* | |
| C2 | 0.71232 (18) | 0.63196 (9) | 0.97872 (15) | 0.0418 (4) | |
| H2 | 0.6922 | 0.5868 | 1.0340 | 0.050* | |
| C3 | 0.64217 (16) | 0.63598 (8) | 0.83192 (15) | 0.0362 (3) | |
| C4 | 0.67688 (16) | 0.70444 (9) | 0.75506 (15) | 0.0377 (3) | |
| H4 | 0.6321 | 0.7096 | 0.6565 | 0.045* | |
| C5 | 0.77918 (17) | 0.76509 (9) | 0.82720 (15) | 0.0406 (3) | |
| H5 | 0.8025 | 0.8106 | 0.7741 | 0.049* | |
| C6 | 0.53873 (18) | 0.56378 (9) | 0.76673 (16) | 0.0415 (3) | |
| C7 | 0.23407 (16) | 0.51994 (8) | 0.46483 (14) | 0.0365 (3) | |
| H7 | 0.2291 | 0.5691 | 0.4116 | 0.044* | |
| C8 | 0.12838 (16) | 0.45084 (8) | 0.41038 (14) | 0.0336 (3) | |
| C9 | 0.12462 (17) | 0.37797 (9) | 0.49306 (15) | 0.0393 (3) | |
| C10 | 0.02068 (19) | 0.31395 (9) | 0.43625 (17) | 0.0463 (4) | |
| H10 | 0.0153 | 0.2664 | 0.4914 | 0.056* | |
| C11 | −0.07485 (18) | 0.31991 (10) | 0.29884 (17) | 0.0453 (4) | |
| H11 | −0.1419 | 0.2755 | 0.2622 | 0.054* | |
| C12 | −0.07365 (16) | 0.39037 (10) | 0.21364 (15) | 0.0409 (4) | |
| C13 | 0.02749 (17) | 0.45510 (9) | 0.27258 (15) | 0.0378 (3) | |
| H13 | 0.0283 | 0.5034 | 0.2182 | 0.045* | |
| C14 | −0.1769 (2) | 0.39481 (12) | 0.06279 (18) | 0.0601 (5) | |
| H14A | −0.1905 | 0.3397 | 0.0218 | 0.090* | |
| H14B | −0.1260 | 0.4299 | 0.0039 | 0.090* | |
| H14C | −0.2800 | 0.4176 | 0.0664 | 0.090* |
(I) (E)-N'-(2-Hydroxy-5-methylbenzylidene)isonicotinohydrazide . Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1 | 0.0903 (10) | 0.0412 (7) | 0.0624 (8) | −0.0114 (6) | −0.0244 (7) | 0.0126 (6) |
| O2 | 0.0751 (8) | 0.0487 (7) | 0.0403 (6) | −0.0108 (6) | −0.0055 (5) | 0.0119 (5) |
| N1 | 0.0409 (7) | 0.0425 (7) | 0.0401 (7) | 0.0010 (5) | 0.0022 (5) | −0.0074 (5) |
| N2 | 0.0408 (7) | 0.0309 (6) | 0.0400 (7) | −0.0020 (5) | −0.0022 (5) | −0.0019 (5) |
| N3 | 0.0409 (7) | 0.0332 (6) | 0.0404 (7) | −0.0023 (5) | 0.0021 (5) | −0.0041 (5) |
| C1 | 0.0457 (8) | 0.0465 (9) | 0.0320 (7) | 0.0056 (7) | −0.0018 (6) | −0.0044 (6) |
| C2 | 0.0475 (8) | 0.0376 (8) | 0.0368 (8) | 0.0037 (6) | 0.0019 (6) | 0.0009 (6) |
| C3 | 0.0341 (7) | 0.0348 (7) | 0.0368 (7) | 0.0065 (6) | 0.0018 (6) | −0.0044 (6) |
| C4 | 0.0371 (8) | 0.0406 (8) | 0.0323 (7) | 0.0043 (6) | 0.0011 (6) | −0.0025 (6) |
| C5 | 0.0419 (8) | 0.0392 (8) | 0.0391 (8) | 0.0003 (6) | 0.0057 (6) | −0.0022 (6) |
| C6 | 0.0446 (8) | 0.0357 (8) | 0.0395 (8) | 0.0018 (6) | −0.0007 (6) | −0.0010 (6) |
| C7 | 0.0411 (8) | 0.0301 (7) | 0.0368 (7) | 0.0008 (6) | 0.0053 (6) | 0.0005 (6) |
| C8 | 0.0354 (7) | 0.0314 (7) | 0.0339 (7) | 0.0027 (6) | 0.0076 (5) | −0.0027 (5) |
| C9 | 0.0439 (8) | 0.0386 (8) | 0.0350 (7) | −0.0010 (6) | 0.0076 (6) | 0.0011 (6) |
| C10 | 0.0547 (9) | 0.0361 (8) | 0.0491 (9) | −0.0080 (7) | 0.0136 (7) | 0.0034 (6) |
| C11 | 0.0411 (8) | 0.0418 (8) | 0.0531 (9) | −0.0100 (7) | 0.0107 (7) | −0.0105 (7) |
| C12 | 0.0348 (7) | 0.0454 (8) | 0.0406 (8) | 0.0022 (6) | 0.0046 (6) | −0.0080 (6) |
| C13 | 0.0408 (8) | 0.0344 (7) | 0.0362 (7) | 0.0032 (6) | 0.0041 (6) | 0.0012 (6) |
| C14 | 0.0527 (10) | 0.0672 (11) | 0.0513 (10) | −0.0003 (9) | −0.0081 (8) | −0.0085 (8) |
(I) (E)-N'-(2-Hydroxy-5-methylbenzylidene)isonicotinohydrazide . Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| O1—C6 | 1.2140 (17) | C5—H5 | 0.9300 |
| O2—H2O | 0.8200 | C7—H7 | 0.9300 |
| O2—C9 | 1.3566 (17) | C7—C8 | 1.4476 (19) |
| N1—C1 | 1.3371 (19) | C8—C9 | 1.4083 (19) |
| N1—C5 | 1.3353 (18) | C8—C13 | 1.3969 (18) |
| N2—H2N | 0.8600 | C9—C10 | 1.383 (2) |
| N2—N3 | 1.3687 (16) | C10—H10 | 0.9300 |
| N2—C6 | 1.3547 (17) | C10—C11 | 1.377 (2) |
| N3—C7 | 1.2720 (17) | C11—H11 | 0.9300 |
| C1—H1 | 0.9300 | C11—C12 | 1.387 (2) |
| C1—C2 | 1.376 (2) | C12—C13 | 1.384 (2) |
| C2—H2 | 0.9300 | C12—C14 | 1.505 (2) |
| C2—C3 | 1.3878 (19) | C13—H13 | 0.9300 |
| C3—C4 | 1.382 (2) | C14—H14A | 0.9600 |
| C3—C6 | 1.5011 (19) | C14—H14B | 0.9600 |
| C4—H4 | 0.9300 | C14—H14C | 0.9600 |
| C4—C5 | 1.3808 (19) | ||
| C9—O2—H2O | 109.5 | C8—C7—H7 | 120.2 |
| C5—N1—C1 | 116.49 (12) | C9—C8—C7 | 121.54 (12) |
| N3—N2—H2N | 122.1 | C13—C8—C7 | 120.15 (12) |
| C6—N2—H2N | 122.1 | C13—C8—C9 | 118.31 (12) |
| C6—N2—N3 | 115.88 (12) | O2—C9—C8 | 122.64 (13) |
| C7—N3—N2 | 120.30 (12) | O2—C9—C10 | 118.14 (13) |
| N1—C1—H1 | 118.1 | C10—C9—C8 | 119.21 (13) |
| N1—C1—C2 | 123.76 (13) | C9—C10—H10 | 119.6 |
| C2—C1—H1 | 118.1 | C11—C10—C9 | 120.72 (14) |
| C1—C2—H2 | 120.5 | C11—C10—H10 | 119.6 |
| C1—C2—C3 | 119.05 (14) | C10—C11—H11 | 119.1 |
| C3—C2—H2 | 120.5 | C10—C11—C12 | 121.76 (13) |
| C2—C3—C6 | 117.42 (13) | C12—C11—H11 | 119.1 |
| C4—C3—C2 | 117.92 (13) | C11—C12—C14 | 120.79 (14) |
| C4—C3—C6 | 124.62 (12) | C13—C12—C11 | 117.23 (13) |
| C3—C4—H4 | 120.6 | C13—C12—C14 | 121.98 (15) |
| C5—C4—C3 | 118.81 (13) | C8—C13—H13 | 118.6 |
| C5—C4—H4 | 120.6 | C12—C13—C8 | 122.74 (13) |
| N1—C5—C4 | 123.95 (14) | C12—C13—H13 | 118.6 |
| N1—C5—H5 | 118.0 | C12—C14—H14A | 109.5 |
| C4—C5—H5 | 118.0 | C12—C14—H14B | 109.5 |
| O1—C6—N2 | 122.27 (13) | C12—C14—H14C | 109.5 |
| O1—C6—C3 | 121.01 (13) | H14A—C14—H14B | 109.5 |
| N2—C6—C3 | 116.73 (12) | H14A—C14—H14C | 109.5 |
| N3—C7—H7 | 120.2 | H14B—C14—H14C | 109.5 |
| N3—C7—C8 | 119.63 (13) | ||
| O2—C9—C10—C11 | −177.73 (14) | C5—N1—C1—C2 | −0.3 (2) |
| N1—C1—C2—C3 | −0.2 (2) | C6—N2—N3—C7 | −177.70 (13) |
| N2—N3—C7—C8 | −179.03 (12) | C6—C3—C4—C5 | −177.39 (13) |
| N3—N2—C6—O1 | 3.1 (2) | C7—C8—C9—O2 | −0.7 (2) |
| N3—N2—C6—C3 | −176.69 (12) | C7—C8—C9—C10 | 179.63 (13) |
| N3—C7—C8—C9 | 4.8 (2) | C7—C8—C13—C12 | 178.65 (13) |
| N3—C7—C8—C13 | −174.87 (13) | C8—C7—N3—N2 | −179.03 (12) |
| C1—N1—C5—C4 | 0.7 (2) | C8—C9—C10—C11 | 1.9 (2) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 0.2 (2) | C9—C8—C13—C12 | −1.0 (2) |
| C1—C2—C3—C6 | 177.94 (13) | C9—C10—C11—C12 | −1.5 (2) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 0.1 (2) | C10—C11—C12—C13 | −0.2 (2) |
| C2—C3—C6—O1 | −19.9 (2) | C10—C11—C12—C14 | 178.89 (15) |
| C2—C3—C6—N2 | 159.99 (13) | C11—C12—C13—C8 | 1.5 (2) |
| C3—C4—C5—N1 | −0.6 (2) | C13—C8—C9—O2 | 178.91 (14) |
| C4—C3—C6—O1 | 157.69 (16) | C13—C8—C9—C10 | −0.7 (2) |
| C4—C3—C6—N2 | −22.5 (2) | C14—C12—C13—C8 | −177.64 (14) |
(I) (E)-N'-(2-Hydroxy-5-methylbenzylidene)isonicotinohydrazide . Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
Cg1 is the centroid of the N1/C1–C5 ring.
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O2—H2O···N3 | 0.82 | 1.87 | 2.5857 (16) | 145 |
| N2—H2N···N1i | 0.86 | 2.19 | 3.0232 (17) | 164 |
| C10—H10···Cg1ii | 0.93 | 2.85 | 3.5259 (17) | 130 |
Symmetry codes: (i) x−1/2, −y+3/2, z−1/2; (ii) −x+1/2, y−1/2, −z+3/2.
(II) (E)-N'-(5-Fluoro-2-hydroxybenzylidene)isonicotinohydrazide . Crystal data
| C13H10FN3O2 | F(000) = 536 |
| Mr = 259.24 | Dx = 1.441 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 8.9195 (3) Å | Cell parameters from 9934 reflections |
| b = 10.1128 (3) Å | θ = 3.1–28.5° |
| c = 13.6254 (4) Å | µ = 0.11 mm−1 |
| β = 103.481 (1)° | T = 296 K |
| V = 1195.16 (6) Å3 | Block, colourless |
| Z = 4 | 0.32 × 0.26 × 0.26 mm |
(II) (E)-N'-(5-Fluoro-2-hydroxybenzylidene)isonicotinohydrazide . Data collection
| Bruker APEX2 D8 QUEST CMOS diffractometer | 2848 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: microfocus sealed x-ray tube, Incoatec Iµus | 2128 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| GraphiteDouble Bounce Multilayer Mirror monochromator | Rint = 0.039 |
| Detector resolution: 10.5 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 27.9°, θmin = 3.1° |
| φ and ω scans | h = −11→11 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2014) | k = −13→13 |
| Tmin = 0.685, Tmax = 0.746 | l = −17→17 |
| 31833 measured reflections |
(II) (E)-N'-(5-Fluoro-2-hydroxybenzylidene)isonicotinohydrazide . Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| Least-squares matrix: full | H-atom parameters constrained |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.042 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0595P)2 + 0.282P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| wR(F2) = 0.124 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| S = 1.03 | Δρmax = 0.26 e Å−3 |
| 2848 reflections | Δρmin = −0.29 e Å−3 |
| 174 parameters | Extinction correction: SHELXL2014 (Sheldrick, 2015b), Fc*=kFc[1+0.001xFc2λ3/sin(2θ)]-1/4 |
| 0 restraints | Extinction coefficient: 0.020 (3) |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
(II) (E)-N'-(5-Fluoro-2-hydroxybenzylidene)isonicotinohydrazide . Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
(II) (E)-N'-(5-Fluoro-2-hydroxybenzylidene)isonicotinohydrazide . Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| F1 | 0.20524 (13) | −0.04313 (11) | 0.46463 (10) | 0.0868 (4) | |
| O1 | 0.82356 (13) | 0.59703 (11) | 0.44402 (7) | 0.0572 (3) | |
| O2 | 0.53778 (15) | 0.31773 (13) | 0.30688 (8) | 0.0650 (3) | |
| H2 | 0.5959 | 0.3608 | 0.3508 | 0.097* | |
| N1 | 1.11088 (14) | 0.82083 (13) | 0.75798 (9) | 0.0497 (3) | |
| N2 | 0.75299 (13) | 0.47336 (11) | 0.56431 (8) | 0.0404 (3) | |
| H2A | 0.7633 | 0.4582 | 0.6276 | 0.048* | |
| N3 | 0.65442 (13) | 0.39828 (11) | 0.49277 (8) | 0.0410 (3) | |
| C1 | 1.12858 (18) | 0.81537 (17) | 0.66408 (12) | 0.0553 (4) | |
| H1 | 1.2031 | 0.8689 | 0.6466 | 0.066* | |
| C2 | 1.04204 (17) | 0.73427 (16) | 0.59110 (11) | 0.0497 (4) | |
| H2B | 1.0577 | 0.7346 | 0.5260 | 0.060* | |
| C3 | 0.93237 (14) | 0.65288 (12) | 0.61510 (9) | 0.0355 (3) | |
| C4 | 0.91374 (17) | 0.65656 (14) | 0.71277 (10) | 0.0429 (3) | |
| H4 | 0.8417 | 0.6026 | 0.7327 | 0.052* | |
| C5 | 1.00507 (19) | 0.74261 (15) | 0.78056 (10) | 0.0502 (4) | |
| H5 | 0.9910 | 0.7455 | 0.8460 | 0.060* | |
| C6 | 0.83297 (15) | 0.57142 (13) | 0.53241 (9) | 0.0376 (3) | |
| C7 | 0.57486 (15) | 0.31041 (13) | 0.52504 (10) | 0.0413 (3) | |
| H7 | 0.5825 | 0.3020 | 0.5940 | 0.050* | |
| C8 | 0.47255 (15) | 0.22351 (13) | 0.45483 (10) | 0.0408 (3) | |
| C9 | 0.46263 (16) | 0.22688 (15) | 0.35051 (11) | 0.0457 (3) | |
| C10 | 0.37199 (18) | 0.13466 (17) | 0.28799 (13) | 0.0569 (4) | |
| H10 | 0.3694 | 0.1346 | 0.2194 | 0.068* | |
| C11 | 0.28665 (18) | 0.04408 (16) | 0.32564 (14) | 0.0597 (4) | |
| H11 | 0.2260 | −0.0174 | 0.2834 | 0.072* | |
| C12 | 0.29224 (18) | 0.04568 (15) | 0.42667 (15) | 0.0567 (4) | |
| C13 | 0.38397 (17) | 0.13144 (15) | 0.49236 (12) | 0.0499 (4) | |
| H13 | 0.3870 | 0.1282 | 0.5610 | 0.060* |
(II) (E)-N'-(5-Fluoro-2-hydroxybenzylidene)isonicotinohydrazide . Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| F1 | 0.0769 (7) | 0.0678 (7) | 0.1118 (9) | −0.0293 (6) | 0.0143 (7) | 0.0139 (6) |
| O1 | 0.0767 (7) | 0.0616 (7) | 0.0271 (5) | −0.0163 (6) | −0.0006 (5) | −0.0004 (4) |
| O2 | 0.0697 (8) | 0.0754 (8) | 0.0453 (6) | −0.0252 (6) | 0.0041 (5) | −0.0007 (6) |
| N1 | 0.0495 (7) | 0.0494 (7) | 0.0426 (7) | 0.0033 (6) | −0.0048 (5) | −0.0125 (5) |
| N2 | 0.0452 (6) | 0.0399 (6) | 0.0297 (5) | −0.0020 (5) | −0.0040 (4) | −0.0007 (4) |
| N3 | 0.0404 (6) | 0.0380 (6) | 0.0379 (6) | 0.0007 (5) | −0.0044 (5) | −0.0031 (5) |
| C1 | 0.0519 (9) | 0.0616 (10) | 0.0502 (9) | −0.0136 (8) | 0.0077 (7) | −0.0123 (7) |
| C2 | 0.0530 (8) | 0.0598 (9) | 0.0356 (7) | −0.0099 (7) | 0.0092 (6) | −0.0088 (6) |
| C3 | 0.0382 (7) | 0.0351 (6) | 0.0291 (6) | 0.0058 (5) | −0.0007 (5) | −0.0021 (5) |
| C4 | 0.0532 (8) | 0.0409 (7) | 0.0324 (6) | 0.0015 (6) | 0.0051 (6) | −0.0022 (5) |
| C5 | 0.0662 (9) | 0.0509 (8) | 0.0294 (6) | 0.0075 (8) | 0.0026 (6) | −0.0066 (6) |
| C6 | 0.0418 (7) | 0.0377 (7) | 0.0285 (6) | 0.0027 (6) | −0.0011 (5) | −0.0016 (5) |
| C7 | 0.0413 (7) | 0.0394 (7) | 0.0393 (7) | 0.0042 (6) | 0.0013 (6) | −0.0011 (6) |
| C8 | 0.0348 (7) | 0.0358 (7) | 0.0475 (7) | 0.0039 (5) | 0.0008 (5) | −0.0004 (6) |
| C9 | 0.0396 (7) | 0.0462 (8) | 0.0469 (8) | −0.0005 (6) | 0.0016 (6) | −0.0020 (6) |
| C10 | 0.0514 (9) | 0.0605 (10) | 0.0525 (9) | −0.0037 (8) | −0.0006 (7) | −0.0119 (7) |
| C11 | 0.0464 (8) | 0.0472 (9) | 0.0759 (12) | −0.0042 (7) | −0.0051 (8) | −0.0132 (8) |
| C12 | 0.0435 (8) | 0.0398 (8) | 0.0824 (12) | −0.0038 (6) | 0.0060 (8) | 0.0060 (7) |
| C13 | 0.0452 (8) | 0.0445 (8) | 0.0572 (9) | 0.0022 (6) | 0.0060 (7) | 0.0051 (7) |
(II) (E)-N'-(5-Fluoro-2-hydroxybenzylidene)isonicotinohydrazide . Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| F1—C12 | 1.3651 (19) | C3—C6 | 1.5061 (17) |
| O1—C6 | 1.2154 (15) | C4—H4 | 0.9300 |
| O2—H2 | 0.8200 | C4—C5 | 1.387 (2) |
| O2—C9 | 1.3537 (18) | C5—H5 | 0.9300 |
| N1—C1 | 1.3263 (19) | C7—H7 | 0.9300 |
| N1—C5 | 1.322 (2) | C7—C8 | 1.4537 (18) |
| N2—H2A | 0.8600 | C8—C9 | 1.404 (2) |
| N2—N3 | 1.3783 (15) | C8—C13 | 1.393 (2) |
| N2—C6 | 1.3513 (17) | C9—C10 | 1.388 (2) |
| N3—C7 | 1.2775 (18) | C10—H10 | 0.9300 |
| C1—H1 | 0.9300 | C10—C11 | 1.365 (2) |
| C1—C2 | 1.378 (2) | C11—H11 | 0.9300 |
| C2—H2B | 0.9300 | C11—C12 | 1.366 (2) |
| C2—C3 | 1.375 (2) | C12—C13 | 1.372 (2) |
| C3—C4 | 1.3796 (18) | C13—H13 | 0.9300 |
| C9—O2—H2 | 109.5 | N2—C6—C3 | 115.07 (11) |
| C5—N1—C1 | 116.85 (12) | N3—C7—H7 | 119.7 |
| N3—N2—H2A | 120.8 | N3—C7—C8 | 120.53 (13) |
| C6—N2—H2A | 120.8 | C8—C7—H7 | 119.7 |
| C6—N2—N3 | 118.31 (11) | C9—C8—C7 | 122.23 (13) |
| C7—N3—N2 | 116.98 (11) | C13—C8—C7 | 119.03 (13) |
| N1—C1—H1 | 118.4 | C13—C8—C9 | 118.72 (13) |
| N1—C1—C2 | 123.25 (15) | O2—C9—C8 | 122.70 (13) |
| C2—C1—H1 | 118.4 | O2—C9—C10 | 117.61 (14) |
| C1—C2—H2B | 120.2 | C10—C9—C8 | 119.68 (14) |
| C3—C2—C1 | 119.64 (13) | C9—C10—H10 | 119.5 |
| C3—C2—H2B | 120.2 | C11—C10—C9 | 121.06 (15) |
| C2—C3—C4 | 117.76 (12) | C11—C10—H10 | 119.5 |
| C2—C3—C6 | 118.48 (11) | C10—C11—H11 | 120.7 |
| C4—C3—C6 | 123.65 (12) | C10—C11—C12 | 118.57 (14) |
| C3—C4—H4 | 120.8 | C12—C11—H11 | 120.7 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 118.37 (14) | F1—C12—C11 | 118.92 (15) |
| C5—C4—H4 | 120.8 | F1—C12—C13 | 118.30 (16) |
| N1—C5—C4 | 124.13 (13) | C11—C12—C13 | 122.77 (15) |
| N1—C5—H5 | 117.9 | C8—C13—H13 | 120.5 |
| C4—C5—H5 | 117.9 | C12—C13—C8 | 119.09 (15) |
| O1—C6—N2 | 123.74 (12) | C12—C13—H13 | 120.5 |
| O1—C6—C3 | 121.15 (12) | ||
| F1—C12—C13—C8 | −179.45 (13) | C4—C3—C6—N2 | −18.13 (18) |
| O2—C9—C10—C11 | −176.72 (15) | C5—N1—C1—C2 | 0.6 (2) |
| N1—C1—C2—C3 | −0.8 (3) | C6—N2—N3—C7 | −176.78 (12) |
| N2—N3—C7—C8 | −177.61 (11) | C6—C3—C4—C5 | −175.40 (12) |
| N3—N2—C6—O1 | −0.3 (2) | C7—C8—C9—O2 | −5.4 (2) |
| N3—N2—C6—C3 | 177.26 (10) | C7—C8—C9—C10 | 174.98 (13) |
| N3—C7—C8—C9 | 3.5 (2) | C7—C8—C13—C12 | −177.30 (13) |
| N3—C7—C8—C13 | −178.08 (12) | C8—C7—N3—N2 | −177.61 (11) |
| C1—N1—C5—C4 | 0.2 (2) | C8—C9—C10—C11 | 2.9 (2) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 0.1 (2) | C9—C8—C13—C12 | 1.1 (2) |
| C1—C2—C3—C6 | 176.36 (13) | C9—C10—C11—C12 | −0.1 (2) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 0.6 (2) | C10—C11—C12—F1 | 178.91 (14) |
| C2—C3—C6—O1 | −16.5 (2) | C10—C11—C12—C13 | −2.3 (2) |
| C2—C3—C6—N2 | 165.85 (12) | C11—C12—C13—C8 | 1.7 (2) |
| C3—C4—C5—N1 | −0.8 (2) | C13—C8—C9—O2 | 176.21 (13) |
| C4—C3—C6—O1 | 159.53 (14) | C13—C8—C9—C10 | −3.4 (2) |
(II) (E)-N'-(5-Fluoro-2-hydroxybenzylidene)isonicotinohydrazide . Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
Cg1 is the centroid of the N1/C1–C5 ring.
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O2—H2···N3 | 0.82 | 1.92 | 2.6329 (15) | 145 |
| N2—H2A···N1i | 0.86 | 2.19 | 2.8889 (15) | 138 |
| C10—H10···O1ii | 0.93 | 2.51 | 3.2573 (18) | 138 |
| C11—H11···Cg1iii | 0.93 | 2.98 | 3.8917 (18) | 168 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+2, y−1/2, −z+3/2; (ii) −x+1, y−1/2, −z+1/2; (iii) x−1, −y+1/2, z−1/2.
References
- Allen, F. H., Johnson, O., Shields, G. P., Smith, B. R. & Towler, M. (2004). J. Appl. Cryst. 37, 335–338.
- Bendova, P., Mackova, E., Haskova, P., Vavrova, A., Jirkovsky, E., Sterba, M., Popelova, O., Kalinowski, D. S., Kovarikova, P., Vavrova, K., Richardson, D. R. & Simunek, T. (2010). Chem. Res. Toxicol. 23, 1105–1114. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Brandenburg, K. (2006). DIAMOND. Crystal Impact GbR, Bonn, Germany.
- Bruker (2014). APEX2, SADABS and SAINT. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Carter, K. P., Young, A. M. & Palmer, A. E. (2014). Chem. Rev. 114, 4564–4601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Chumakov, Y. M., Antosyak, B. Y., Tsapkov, V. I. & Samus, N. M. (2001). J. Struct. Chem. 42, 335–339.
- Dolomanov, O. V., Bourhis, L. J., Gildea, R. J., Howard, J. A. K. & Puschmann, H. (2009). J. Appl. Cryst. 42, 339–341.
- Farrugia, L. J. (2012). J. Appl. Cryst. 45, 849–854.
- Groom, C. R., Bruno, I. J., Lightfoot, M. P. & Ward, S. C. (2016). Acta Cryst. B72, 171–179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Hrušková, K., Kovaříková, P., Bendová, P., Hašková, P., Macková, E., Stariat, J., Vávrová, A., Vávrová, K. & Šimůnek, T. (2011). Chem. Res. Toxicol. 24, 290–302. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Hrušková, K., Potůčková, E., Hergeselová, T., Liptáková, L., Hašková, P., Mingas, P., Kovaříková, P., Šimůnek, T. & Vávrová, K. (2016). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 120, 97–110. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Jansová, H., Macháček, M., Wang, Q., Hašková, P., Jirkovská, A., Potůčková, E., Kielar, F., Franz, K. J. & Šimůnek, T. (2014). Free Radical Biol. Med. 74, 210–221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Kargar, H., Kia, R., Akkurt, M. & Büyükgüngör, O. (2010). Acta Cryst. E66, o2982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Sedaghat, T., Yousefi, M., Bruno, G., Rudbari, H. A., Motamedi, H. & Nobakht, V. (2014). Polyhedron, 79, 88–96.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015a). Acta Cryst. A71, 3–8.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015b). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
- Westrip, S. P. (2010). J. Appl. Cryst. 43, 920–925.
- Yang, D.-S. (2006a). Acta Cryst. E62, o3755–o3756.
- Yang, D.-S. (2006b). Acta Cryst. E62, o3792–o3793.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) Global, I, II. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016009762/su5301sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016009762/su5301Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016009762/su5301Isup4.cdx
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) II. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016009762/su5301IIsup3.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016009762/su5301Isup5.cml
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016009762/su5301IIsup6.cml
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report