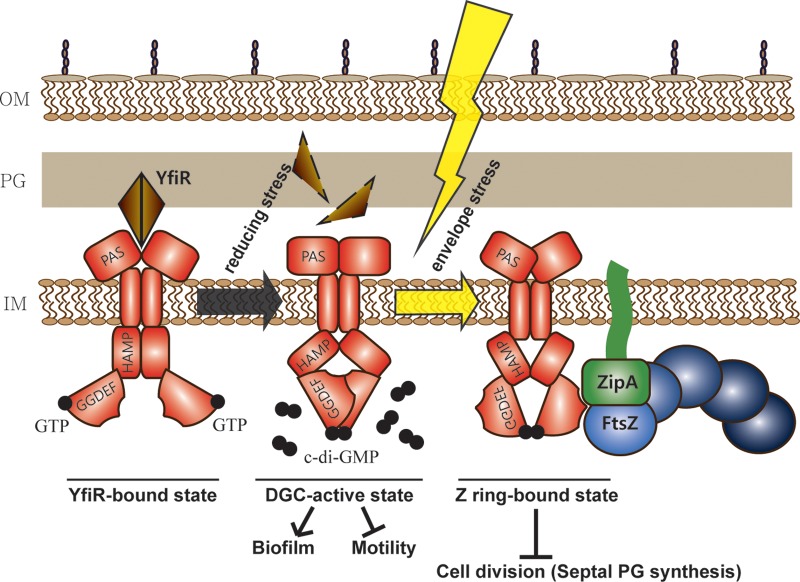
FIG 8 .
Model for YfiN as a cell division inhibitor. EYfiN is a bifunctional protein that responds to two different environmental stresses—reductive and envelope stress. The DGC function is known to be activated when reductive stress inactivates the periplasmic repressor EYfiR. The c-di-GMP thus produced inhibits motility and activates biofilm formation. The second function of EYfiN as a cell division inhibitor, as revealed in this study, requires an additional envelope stress after the DGC function is activated. The envelope stress-induced conformation of EYfiN, which is likely in a c-di-GMP-bound state, exposes binding sites for division proteins FtsZ and ZipA, directing EYfiN to the future division site, where it halts division by preventing the initiation of septal peptidoglycan synthesis.