Abstract
Background:
Orthodontic therapy has oral ecological changes causing increased numbers of mutans streptococci in saliva and plaque. The purpose of this study was to estimate counts and colonization pattern of Streptococcus mutans after application of fixed orthodontic appliances.
Materials and Methods:
Plaque samples of randomly selected sixty patients were collected before placement of orthodontic appliances from buccal and labial aspects of the anterior teeth and four first molars and readings were recorded as T0. After placement of appliances (0.22 MBT preadjusted Gemini), i.e., 2nd and 3rd month, the plaque samples were collected again from same site and readings were recorded as T1 and T2, respectively. Counts of S. mutans in these patients were determined by using DM Strips (Orion Diagnostic, Espoo, Finland). Kruskal–Wallis test and Mann–Whitney U-test were used to find out significant differences between different time interval for Dentocult score for S. mutans in orthodontic patients (P < 0.001).
Results:
Prior to the treatment, 46 patients (76%) showed mild and 14 patients (24%) showed moderate colonization of S. mutans. After treatment, the severity of colonization increased showing fifty patients (84%) moderate and six patients (10%) showing severe colonization of S. mutans at T1, which further increased in severity at T2 with 54 patients (90%) showing severe colonization with S. mutans.
Conclusion:
Results showed that fixed orthodontic appliance increases colonization of S. mutans during orthodontic treatment.
Key Words: Toothbrushing, oral hygiene, streptococcus mutans
INTRODUCTION
Streptococcus mutans is a Gram-positive cocci, commonly found in the mouth from where it can spread to cause dental caries or endocarditis in individuals with risk factors. Bacteremia of odontogenic origin following tooth brushing has been reported in 25% of subjects wearing orthodontic appliances.[1]
Patients undergoing orthodontic therapy have oral ecological changes that lead to increased numbers of mutans streptococci in the saliva and dental plaque of these patients.[1] The placement of fixed orthodontic appliances on teeth results in iatrogenic side effects. There is an increase in the volume of dental plaque as well as an increase in the number of bacteria and the concentration of carbohydrate in each milligram of plaque.[2]
According to Chang et al.,[2] the increase in S. mutans following placement of orthodontic devices can be explained by the irregular nature of their surfaces, which promote the growth of these aciduric and acidogenic bacteria that prefer hard surfaces to grow on. The fixed installation of retained elements that remain in the mouth for at least 1 or 2 years results in a multiplication of cariogenic microorganisms.
The accumulation of dental plaque at gingival margins is most important etiologic factor in periodontal disease. Fixed or removable orthodontic appliances also impede the maintenance of oral hygiene, resulting in plaque accumulation.[3,4] Thus, the combination of orthodontic therapy and poor oral hygiene can cause serious damage to the periodontium.[1]
S. mutans is a part of normal flora of oral cavity. They become pathogenic only under circumstances that lead to frequent and prolonged acidification of the dental plaque.[5] S. mutans adapt to low pH of this environment and thus, increase their rate of acid production and derive the pH still lower resulting in a cariogenic plaque which results in dental caries.[6] Patients undergoing orthodontic therapy have oral ecological changes that lead to increased numbers of mutans streptococci in saliva and plaque.
Extensive banding favors the local growth of S. mutans which in turn increases the general infection level of the organism.[5] S. mutans colonizes 40–85% of patients with orthodontic appliances. In a study, the number of subjects harboring mutans streptococci in their dental plaque was significantly higher in groups of orthodontic children without caries incidence in comparison with caries-free children of the control group (83.3% vs. 34%).[3] In a study by Scheie et al., the numbers of commensal bacteria and transient bacteria in anaerobic culture medium were examined in salivary level, to investigate the alternation of microflora during orthodontic therapy. The number of mutans streptococci and lactobacilli decreased after 1-month of treatment and then increased to reach the initial level in 3 months.[7]
Though various studies had been designed to determine the influence of orthodontic brackets on the relative number of S. mutans in dental plaque associated with affected surface but there is a scarcity of literature on the same topic among Indian orthodontic patients. The purpose of this study was to estimate the counts and colonization pattern of S. mutans after application of fixed orthodontic appliances in homogenous Indian population.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
After complete oral examination, thorough oral hygiene instructions and plaque control measures a total number of sixty patients scheduled for orthodontic treatment age group of 15–25 years were selected randomly from the Department of Orthodontics, Peoples College of Dental Science and Research C enter, Bhopal, India. Careful Sampling was done considering following inclusion criteria, i.e., patients with permanent dentition, no clinical sign of peridontitis. No history of any systemic illness and no antibiotic administration at least 3 months prior to treatment. Exclusion criteria were smoking, pregnancy, poor general health, history of periodontal treatment, antibiotic administration, and socioeconomic status, which was found via a detailed questionnaire.
Plaque samples were collected before placement of appliance from buccal and labial aspects of the anterior teeth and four first molars [Figure 1a and b] to determine oral carriage of S. mutans of these patients, and reading were recorded as T0. After that the placement of appliances (0.22 MBT preadjusted Gemini stainless steel, 3M Unitek, CA, USA) were done by only one operator to avoid inter-operator bias. After 2nd and 3rd month, the plaque samples were collected again from the same site and reading were recorded as T1 and T2, respectively [Figure 2a and b]. Intervals was chosen in assumption to allow sufficient colonization of bacteria after placement of orthodontic appliance. All patients had been taught and demonstrated modified bass technique of brushing and were motivated to reinforce and follow throughout treatment period. Counts of S. mutans in these patients were determined using DM Strips (Orion Diagnostic, Espoo, Finland) [Figure 3a].
Figure 1.
(a) Plaque sample collected from sterile cotton swab before starting treatment from incisors area. (b) Plaque sample collected from sterile cotton swab before starting treatment from molars area.
Figure 2.
(a) Plaque sample collected from sterile cotton swab after starting treatment from Incisors area (b) Plaque sample collected from sterile cotton swab after starting treatment from molar area.
Figure 3.
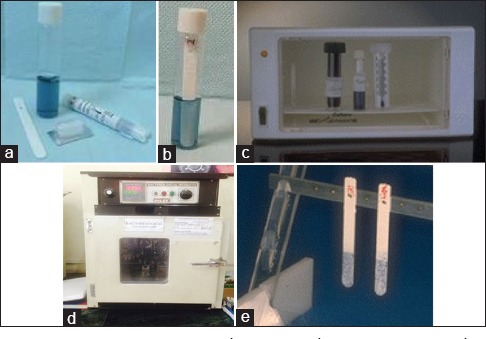
(a) Dentocult SM strip mutans kit. (b) Inoculated strips placed in the selective culture broth with the smooth surface attached to the cap and vial is labelled with the patient's name, age, sex, date and duration of fixed orthodontic appliances. (c) Vials containing inoculated strips are incubated in an upright position at 37°C for 48 h. (d) Bacteriological incubator. (e) Results were interpreted by comparing the strip with the manufacturer's model chart scores for Streptococcus mutans in CFU/ml.
Sample processing for Streptococcus mutans
Counts of S. mutans were determined by using Dentocult SM kit (Orion Diagnostica, Espoo, Finland).
Dentocult SM kit (Orion Diagnostica, Espoo, Finland)
Dentocult SM strip mutans is used to detect mutans streptococci in saliva and plaque [Figure 3a].
Principle
This method is based on the use of a selective culture broth and the adherence and growth of mutans streptococcus bacteria on the test strip.
Preparation
Bacitracin disc was placed in the selective culture broth provided in the kit about 15 min before sampling using a needle or forceps, cap was closed, and the medium was shaked gently for even distribution of bacitracin.
Processing
First, plaque sample collected from sterile cotton swab was spread thoroughly but gently on the four rough surface of the strip [Figure 3b]
Inoculated strips were then placed in the selective culture broth with the smooth surface attached to the cap and vial is labelled with the patient's name, age, sex, date, and duration of fixed orthodontic appliances [Figure 3c]
Vials containing inoculated strips are incubated in an upright position at 37°C for 48 h with cap opened one-quarter of the turn to allow growth of the organisms [Figure 3d].
Interpretation of results
The presence of mutans streptococci was evidenced by light blue to dark blue raised colonies on the inoculated surface of the strip. Results were interpreted by comparing the strip with the manufacturer's model chart scores [Figure 3e].[8]
Score 0: <10,000 Colony forming units (CFU)/ml
Score 1: <100,000 CFU/ml
Score 2: 100,000–1,000,000 CFU/ml
Score 3: >1,000,000 CFU/ml.
RESULTS
A total number of sixty patients with orthodontic appliances of age group 15–25 years were taken. The counts of S. mutans were evaluated using Dentocult SM kit and the results were interpreted according to the model chart as Class 0, Class 1, Class 2, and Class 3. Patients with Class 3=>106 CFU/ml were considered heavy colonizers of S. mutans.
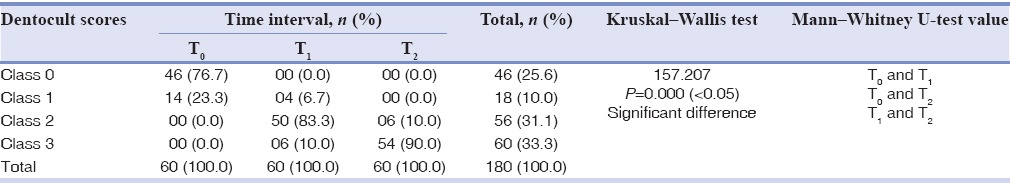
The study showed that of the sixty patients, before starting orthodontic treatment 46 patients (76%) showed mild and 14 patients (24%) showed moderate colonization of S. mutans. This could be due to the low levels of hygiene, improper brushing habits, and visible plaque accumulation. After orthodontic treatment, the severity of colonization increased dramatically showing fifty patients (84%) moderate and six patients (10%) showing severe colonization of S. mutans at T1, which further increased in severity at T2 with 54 patients (90%) showing severe colonization with S. mutans. Kruskal–Wallis Test showed a significant difference between different time interval for Dentocult score for S. mutans in orthodontic patients (P = 0.000). Mann–Whitney U-test showed a significant difference between T0 and T1; T0 and T2; and T1 and T2 during pairwise comparison (P = 0.000) [Table 1].
Table 1.
Comparison of Dentocult score for Streptococcus mutans in orthodontic patients
DISCUSSION
Fixed orthodontic appliances are considered to jeopardize dental health due to the accumulation of microorganisms that may cause enamel demineralization, clinically visible as white spot lesions.[9] Biofilm formation on dentures results from complex interactions among yeast, bacteria, nutrients, and saliva or even serum proeins.[4]
S. mutans is isolated in 50–80% of orthodontic patients as a common cause of decalcification due to the accumulation of cariogenic plaque around the brackets progressing into carious lesions in such patients.[10]
In the present study, although the sample size was relatively small, the crossover design enabled meaningful statistical results to be achieved. A total number of sixty patients of age group 15–25 years, undergoing fixed orthodontic therapy from 3 to 4 months were selected. Plaque samples were collected from all sixty patients and evaluated for the presence of S. mutans in their first visit.
Findings of increased S. mutans colonization in present study correlates with a similar study by Papaioannou et al.[11] in a cross-sectional study, suggested that in addition to a quantitative change, metal banding resulted in a qualitative change characterized by an increase in percentage of S. mutans. The present study showed that counts of S. mutans were higher in plaque samples of patient with orthodontic appliances as compared to patients without orthodontic appliances. Its finding also correlates with an investigation by Attin et al.,[12] which revealed that mutans streptococci colonization was higher in teeth with fixed orthodontic appliances compared with the control teeth without appliances. Recent studies have reported that demineralization of dental surfaces during treatment can be found in 50–75% of all patients with fixed orthodontic appliances.[13,14,15]
Isolation of S. mutans from dental plaque or saliva samples involves culturing samples on selective media or chair side cultural assays. Traditional selective culture-based media are culture-based media techniques generally involve the plating of sonicated and serially diluted samples onto selective agar media, incubation under anaerobic conditions, and enumeration with the aid of a stereomicroscope.[16]
Different agar media used in various studies are mitis salivarius with bacitracin, tripticase soy with sucrose and bacitracin, and mitis salivarius with bacitracin and kanyamycin.
Different chairside cultural tests generally used in various studies are: Caries screen SM® (John O. Butler Co., Chicago, IL, USA), Mucount® (Showa Yakuhin Kako Co., Tokyo, Japan), and Dentocult SM strip mutans® (Orion Diagnostica, Helsinki, Finland). In our study also, counts of S. mutans were determined by a chair side assay Dentocult SM strips. Chairside cultural tests (rapid assays) for the enumeration of S. mutans had been used which lowered the cost, reduced the amount of equipment needed, and simplified the enumeration process.[8]
Peros et al.[8] showed the success of antimicrobial preventive measures for orthodontic patients may be improved by proper timing. Such measures should be applied between weeks 6 and 12 of orthodontic therapy, when the number of S. mutans and Lactobacillus spp., increase in the saliva.
According to Topaloglu-Ak et al.,[17] long-term utilization of orthodontic appliances may have a negative effect on microbial flora and increase the risk of new carious lesions. In our study, the follow-up lasted 3 months. It would be interesting to evaluate the evolution of these microbial parameters until the end of the orthodontic treatment. Preventive measures should continue until the removal of the orthodontic appliances.
Maret et al.[18] showed that oral microflora changed with time in the orthodontic group compared to the control group, with S. mutans and Lactobacillus spp., numbers increased during the 6 months of follow-up in their study. Results concur present study findings positively.
CONCLUSION
From the study, it concludes that before starting orthodontic treatment, 46 patients (76%) showed mild and 14 patients (24%) showed moderate colonization of S. mutans later severity of colonization increased dramatically showing fifty patients (84%) moderate and six patients (10%) severe colonization of S. mutans at T1, which further increased in severity at T2 with 54 patients (90%) showing severe colonization with S. mutans. Results clearly showed that an orthodontic appliance increases colonization of S. mutan in oral cavity during orthodontic treatment.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
Conflicts of interest
The authors of this manuscript declare that they have no conflicts of interest, real or perceived, financial or non-financial in this article.
REFERENCES
- 1.Parahitiyawa NB, Jin LJ, Leung WK, Yam WC, Samaranayake LP. Microbiology of odontogenic bacteremia: Beyond endocarditis. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2009;22:46–64. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00028-08. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Chang HS, Walsh LJ, Freer TJ. The effect of orthodontic treatment on salivary flow, pH, buffer capacity, and levels of mutans streptococci and lactobacilli. Aust Orthod J. 1999;15:229–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Glans R, Larsson E, Øgaard B. Longitudinal changes in gingival condition in crowded and noncrowded dentitions subjected to fixed orthodontic treatment. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2003;124:679–82. doi: 10.1016/j.ajodo.2003.05.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Batoni G, Pardini M, Giannotti A, Ota F, Giuca MR, Gabriele M, et al. Effect of removable orthodontic appliances on oral colonisation by mutans streptococci in children. Eur J Oral Sci. 2001;109:388–92. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0722.2001.00089.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Jordan C, LeBlanc DJ. Influences of orthodontic appliances on oral populations of mutans streptococci. Oral Microbiol Immunol. 2002;17:65–71. doi: 10.1046/j.0902-0055.2001.00083.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Jeevarathan J, Deepti A, Muthu MS, Rathna Prabhu V, Chamundeeswari GS. Effect of fluoride varnish on Streptococcus mutans counts in plaque of caries-free children using Dentocult SM strip mutans test: A randomized controlled triple blind study. J Indian Soc Pedod Prev Dent. 2007;25:157–63. doi: 10.4103/0970-4388.37010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Scheie AA, Arneberg P, Krogstand O. Effect of orthodontic treatment on prevalence of Streptococcus mutans in plaque and saliva. Eur J Oral Sci. 2007;92:102–6. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0722.1984.tb00881.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Peros K, Mestrovic S, Anic-Milosevic S, Slaj M. Salivary microbial and nonmicrobial parameters in children with fixed orthodontic appliances. Angle Orthod. 2011;81:901–6. doi: 10.2319/012111-44.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Zero DT. Dental caries process. Dent Clin North Am. 1999;43:653–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Costa MR, Silva VC, Miqui MN, Sakima T, Spolidorio DM, Cirelli JA. Efficacy of ultrasonic, electric and manual toothbrushes in patients with fixed orthodontic appliances. Angle Orthod. 2007;77:361–6. doi: 10.2319/0003-3219(2007)077[0361:EOUEAM]2.0.CO;2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Papaioannou W, Gizani S, Nassika M, Kontou E, Nakou M. Adhesion of Streptococcus mutans to different types of brackets. Angle Orthod. 2007;77:1090–5. doi: 10.2319/091706-375.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Attin R, Thon C, Schlagenhauf U, Werner C, Wiegand A, Hannig C, et al. Recolonization of mutans steptococci on teeth with orthodontic appliances after antimicrobial therapy. Eur J Orthod. 2005;27:489–93. doi: 10.1093/ejo/cji018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Collee JG, Fraser AG, Marmion BP, Simmons A. Practical Medical Microbiology. 14th ed. New York: Churchill Livingstone; 1996. Mackey & McCartney; pp. 796–9. [Google Scholar]
- 14.Nikawa H, Nishimura H, Hamada T, Kumagai H, Samaranayake LP. Effects of dietary sugars and, saliva and serum on Candida bioflim formation on acrylic surfaces. Mycopathologia. 1997;139:87–91. doi: 10.1023/a:1006851418963. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Ogaard B, Arends J, Helseth H, Dijkman G, van der Kuijl M. Fluoride level in saliva after bonding orthodontic brackets with a fluoride containing adhesive. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 1997;111:199–202. doi: 10.1016/s0889-5406(97)70216-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Davenport ES, Day S, Hardie JM, Smith JM. A comparison between commercial kits and conventional methods for enumeration of salivary mutans streptococci and lactobacilli. Community Dent Health. 1992;9:261–71. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Topaloglu-Ak A, Ertugrul F, Eden E, Ates M, Bulut H. Effect of orthodontic appliances on oral microbiota-6 month follow-up. J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2011;35:433–6. doi: 10.17796/jcpd.35.4.61114412637mt661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Maret D, Marchal-Sixou C, Vergnes JN, Hamel O, Georgelin-Gurgel M, Van Der Sluis L, et al. Effect of fixed orthodontic appliances on salivary microbial parameters at 6 months: A controlled observational study. J Appl Oral Sci. 2014;22:38–43. doi: 10.1590/1678-775720130318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


