Abstract
A double staining immunofluorescence method was developed that allowed the reliable differential counting of cells containing cytoplasmic immunoglobulin in human bone marrow. These cells were stained with a polyspecific antihuman immunoglobulin serum conjugated with rhodamine. In separate preparations subpopulations of cells containing each heavy chain class and light chain type were identified by prior staining with isotype specific fluorescein conjugated antihuman immunoglobulin sera. A standardised counting procedure was adopted to indicate the degree of plasma cell infiltration and to establish the percentage of cells containing each type of immunoglobulin. A series of 122 patients requiring haematological investigation of the bone marrow for various disorders but without evidence of paraproteinaemia was tested to provide results for a nonmyelomatous reference group. These results were compared with those from 40 patients with paraproteins of various classes in their serum. The procedure described here clearly differentiated the two groups. When combined with serum paraprotein assays and conventional haematological cytology of bone marrow these counts provided useful additional information in cases of diagnostic difficulty and in the assessment of individual patients before, during, and after treatment.
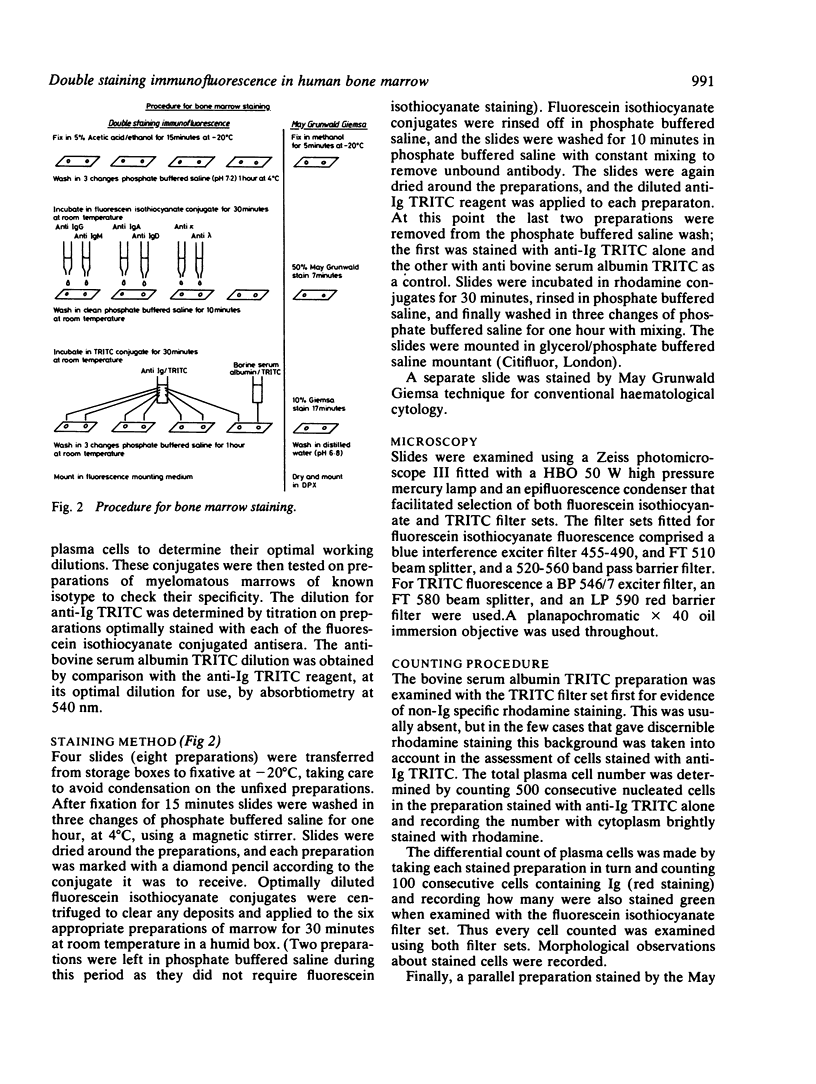
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ameis A., Ko H. S., Pruzanski W. M components-a review of 1242 cases. Can Med Assoc J. 1976 May 22;114(10):889-92, 895. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benner R., Meima F., van der Meulen G. M., van Muiswinkel W. B. Antibody formation in mouse bone marrow. I. Evidence for the development of plaque-forming cells in situ. Immunology. 1974 Feb;26(2):247–255. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordell J. L., Falini B., Erber W. N., Ghosh A. K., Abdulaziz Z., MacDonald S., Pulford K. A., Stein H., Mason D. Y. Immunoenzymatic labeling of monoclonal antibodies using immune complexes of alkaline phosphatase and monoclonal anti-alkaline phosphatase (APAAP complexes). J Histochem Cytochem. 1984 Feb;32(2):219–229. doi: 10.1177/32.2.6198355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hijmans W., Schuit H. R., Hulsing-Hesselink E. An immunofluorescence study on intracellular immunoglobulins in human bone marrow cells. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1971 Jun 21;177:290–305. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1971.tb35059.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hijmans W., Schuit H. R., Klein F. An immunofluorescence procedure for the detection of intracellular immunoglobulins. Clin Exp Immunol. 1969 Apr;4(4):457–472. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VAZQUEZ J. J. Antibody- or gamma globulin--forming cells, as observed by the fluorescent antibody technic. Lab Invest. 1961 Nov-Dec;10:1110–1125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


