Abstract
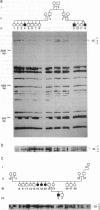
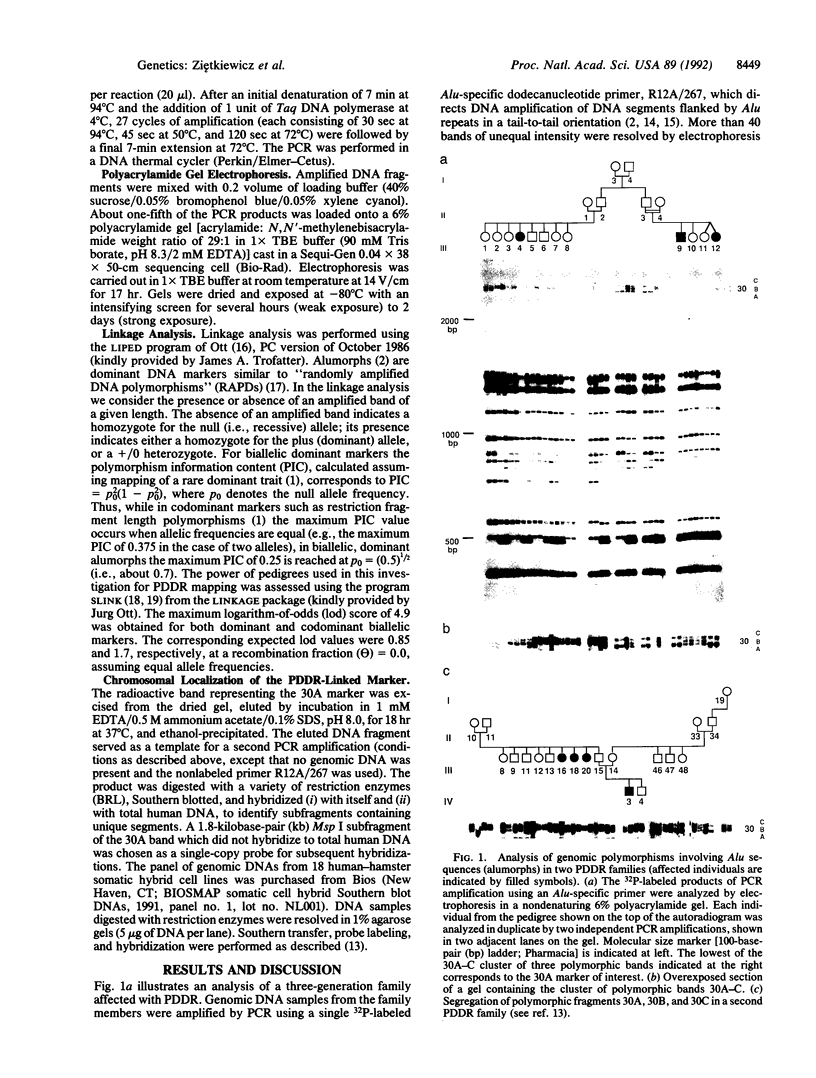
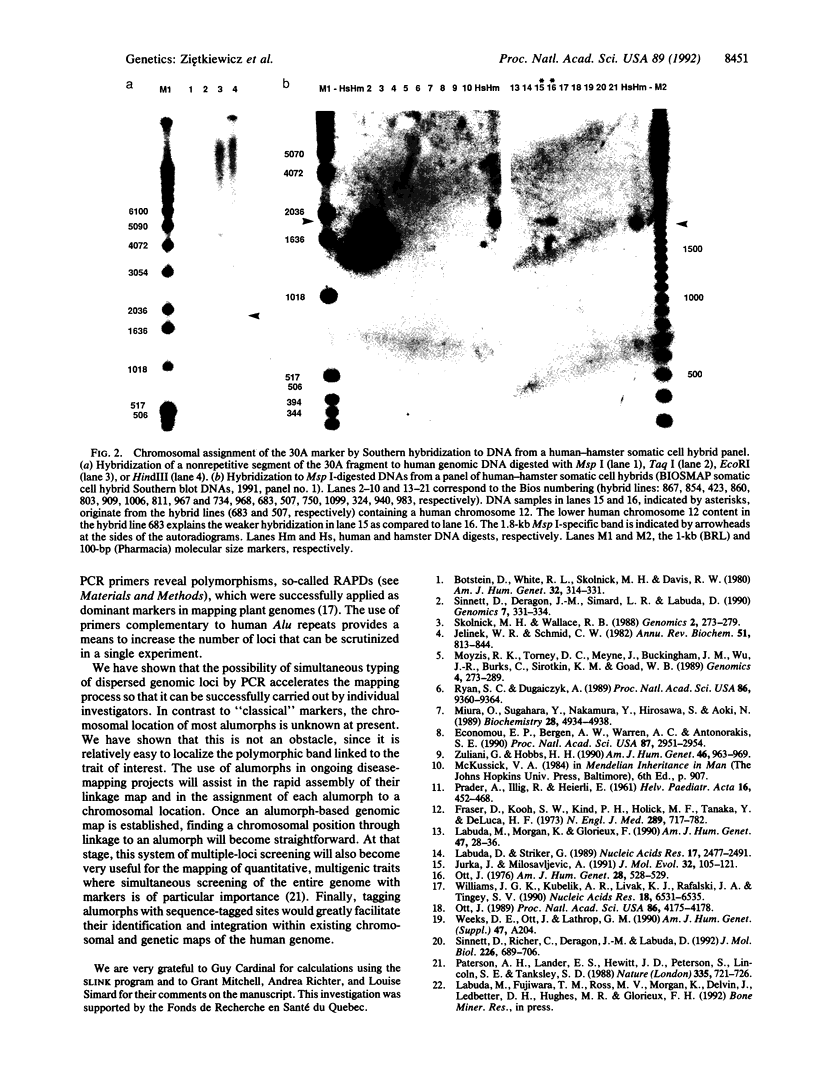
We present the use of our recently described multiple-loci polymorphic DNA markers ("alumorphs") for linkage mapping of the human genome. By using the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) with an Alu-specific primer we could reveal, in a single experiment, up to 20 genomic polymorphisms seen as the presence or absence of amplified DNA fragments originating from genomic segments flanked by Alu repeats. Using this approach we examined genomic DNA samples from two families with a history of pseudovitamin D-deficiency rickets (PDDR), an autosomal recessive disorder. An indication of linkage with the PDDR phenotype was found for one of the polymorphic bands, denoted 30A. A significant linkage [logarithm-of-odds (lod) score greater than 3.0] was obtained between this polymorphism and a number of chromosome 12q markers tightly linked to PDDR. The 30A band specifically hybridized to DNA digests from hybrid cell lines carrying a human chromosome 12, thus independently assigning the 30A marker to this chromosome. Since Alu elements are ubiquitous in human DNA, the use of alternative Alu-specific primers, which reveal different sets of Alu-flanked loci, should provide an efficient and rapid approach to human genetic mapping.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Botstein D., White R. L., Skolnick M., Davis R. W. Construction of a genetic linkage map in man using restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Am J Hum Genet. 1980 May;32(3):314–331. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Economou E. P., Bergen A. W., Warren A. C., Antonarakis S. E. The polydeoxyadenylate tract of Alu repetitive elements is polymorphic in the human genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(8):2951–2954. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.8.2951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jelinek W. R., Schmid C. W. Repetitive sequences in eukaryotic DNA and their expression. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:813–844. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.004121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jurka J., Milosavljevic A. Reconstruction and analysis of human Alu genes. J Mol Evol. 1991 Feb;32(2):105–121. doi: 10.1007/BF02515383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labuda D., Striker G. Sequence conservation in Alu evolution. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Apr 11;17(7):2477–2491. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.7.2477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labuda M., Morgan K., Glorieux F. H. Mapping autosomal recessive vitamin D dependency type I to chromosome 12q14 by linkage analysis. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Jul;47(1):28–36. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miura O., Sugahara Y., Nakamura Y., Hirosawa S., Aoki N. Restriction fragment length polymorphism caused by a deletion involving Alu sequences within the human alpha 2-plasmin inhibitor gene. Biochemistry. 1989 Jun 13;28(12):4934–4938. doi: 10.1021/bi00438a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moyzis R. K., Torney D. C., Meyne J., Buckingham J. M., Wu J. R., Burks C., Sirotkin K. M., Goad W. B. The distribution of interspersed repetitive DNA sequences in the human genome. Genomics. 1989 Apr;4(3):273–289. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90331-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ott J. A computer program for linkage analysis of general human pedigrees. Am J Hum Genet. 1976 Sep;28(5):528–529. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ott J. Computer-simulation methods in human linkage analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(11):4175–4178. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.11.4175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PRADER A., ILLIG R., HEIERLI E. [An unusual form of primary vitamin D-resistant rickets with hypocalcemia and autosomal-dominant hereditary transmission: hereditary pseudo-deficiency rickets]. Helv Paediatr Acta. 1961 Dec;16:452–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson A. H., Lander E. S., Hewitt J. D., Peterson S., Lincoln S. E., Tanksley S. D. Resolution of quantitative traits into Mendelian factors by using a complete linkage map of restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Nature. 1988 Oct 20;335(6192):721–726. doi: 10.1038/335721a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan S. C., Dugaiczyk A. Newly arisen DNA repeats in primate phylogeny. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9360–9364. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinnett D., Deragon J. M., Simard L. R., Labuda D. Alumorphs--human DNA polymorphisms detected by polymerase chain reaction using Alu-specific primers. Genomics. 1990 Jul;7(3):331–334. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90166-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinnett D., Richer C., Deragon J. M., Labuda D. Alu RNA transcripts in human embryonal carcinoma cells. Model of post-transcriptional selection of master sequences. J Mol Biol. 1992 Aug 5;226(3):689–706. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90626-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skolnick M. H., Wallace R. B. Simultaneous analysis of multiple polymorphic loci using amplified sequence polymorphisms (ASPs). Genomics. 1988 May;2(4):273–279. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(88)90014-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. G., Kubelik A. R., Livak K. J., Rafalski J. A., Tingey S. V. DNA polymorphisms amplified by arbitrary primers are useful as genetic markers. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Nov 25;18(22):6531–6535. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.22.6531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuliani G., Hobbs H. H. A high frequency of length polymorphisms in repeated sequences adjacent to Alu sequences. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 May;46(5):963–969. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]