Abstract
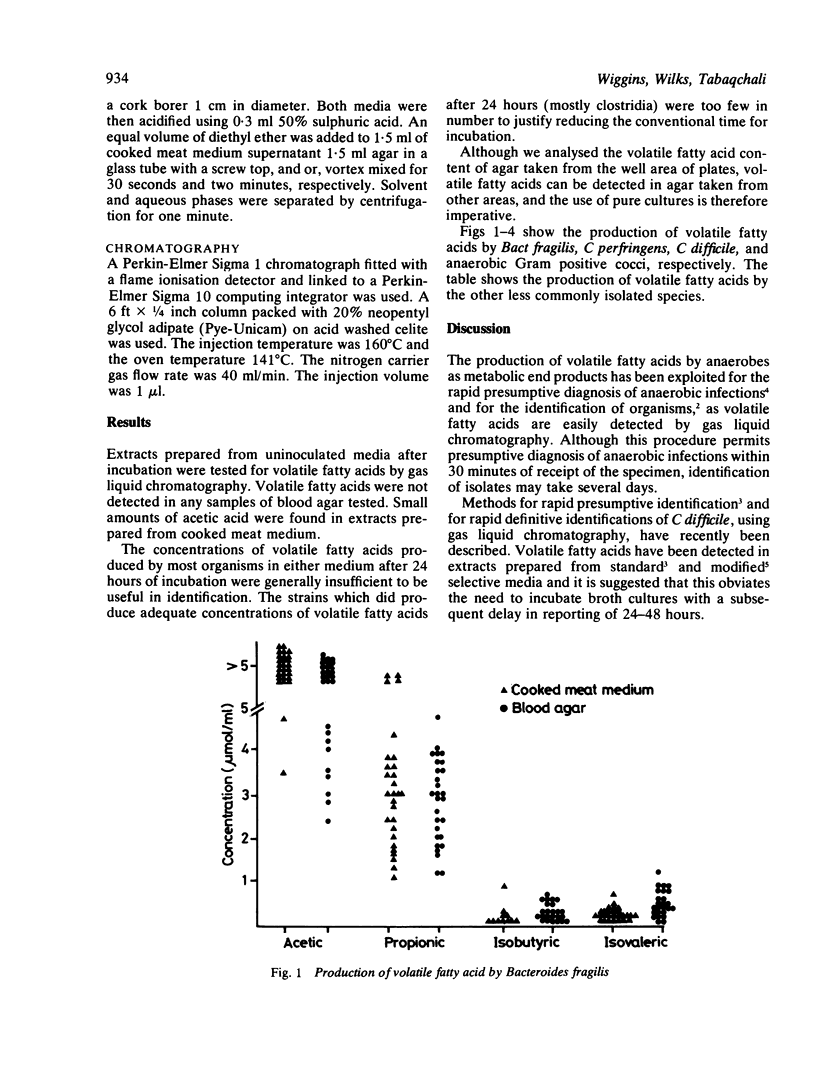
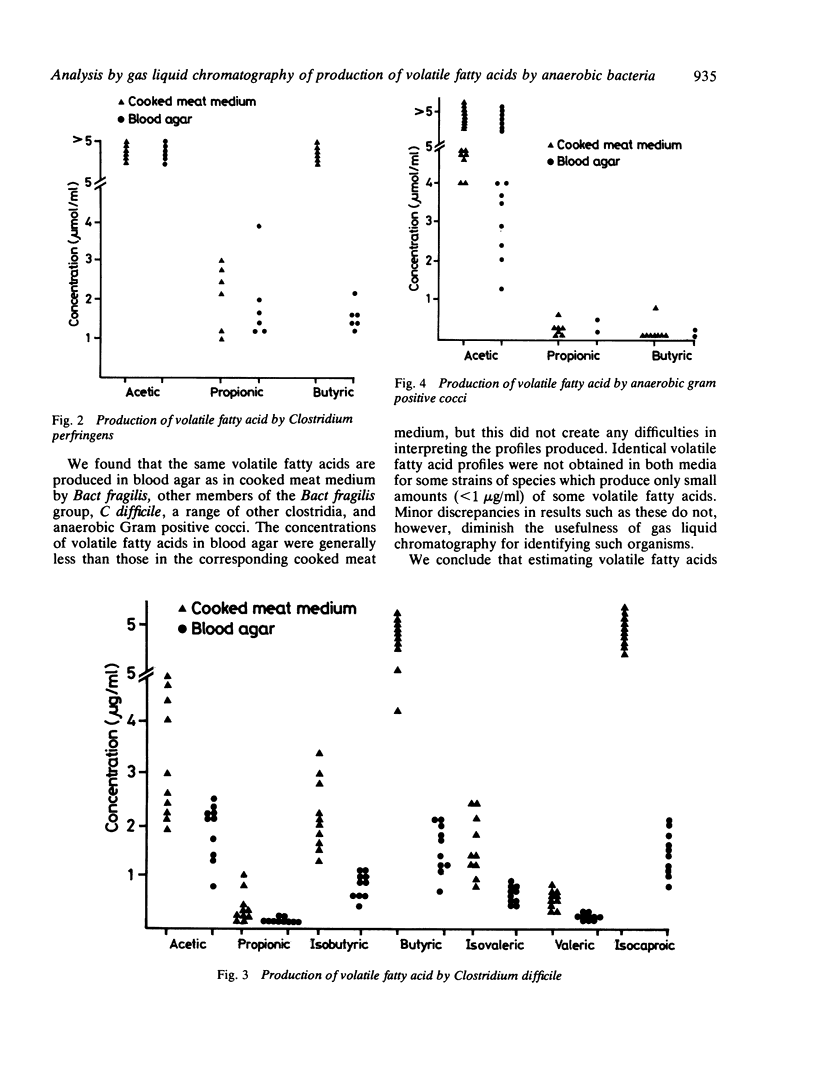
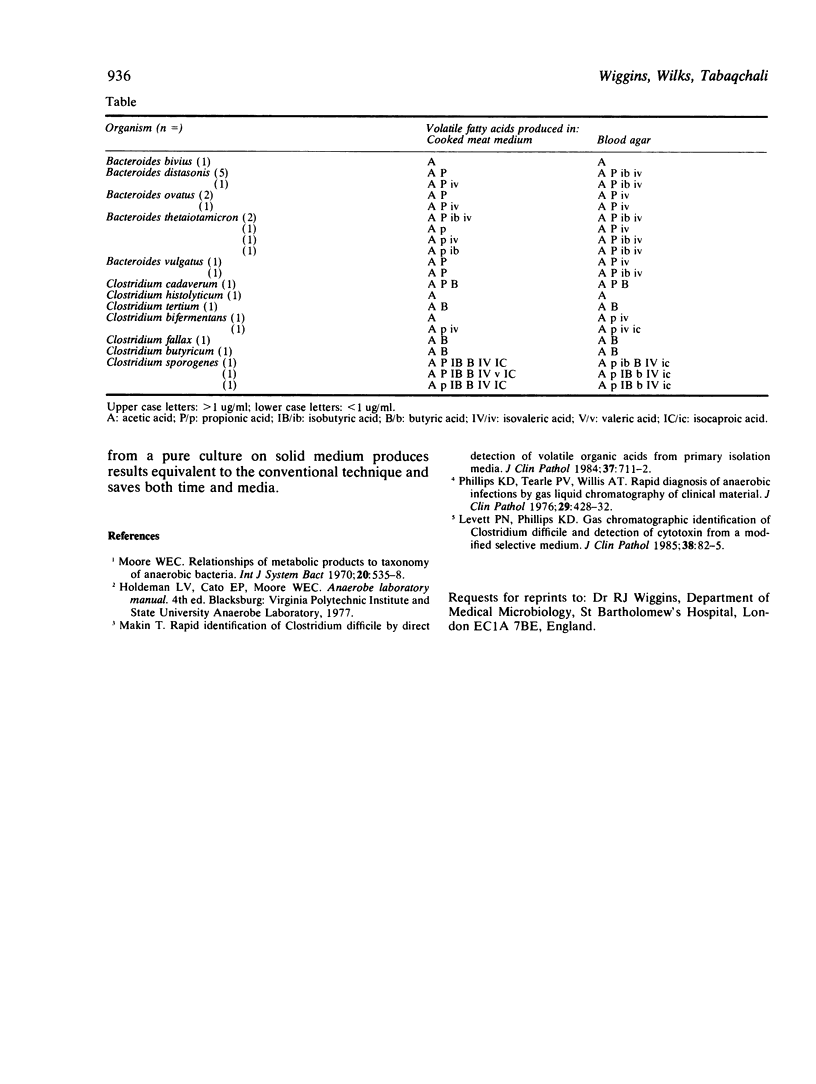
Volatile fatty acids produced in Robertson's cooked meat medium by a range of clinically relevant anaerobes were compared by gas liquid chromatography with those produced in blood agar. The same volatile fatty acid profiles were obtained in both media, although the concentration of acids was lower in blood agar. We conclude that detection of volatile fatty acids from a pure culture of an organism on solid medium is practicable and offers advantages over the conventional technique.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Levett P. N., Phillips K. D. Gas chromatographic identification of Clostridium difficile and detection of cytotoxin from a modified selective medium. J Clin Pathol. 1985 Jan;38(1):82–85. doi: 10.1136/jcp.38.1.82. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makin T. Rapid identification of Clostridium difficile by direct detection of volatile organic acids from primary isolation media. J Clin Pathol. 1984 Jun;37(6):711–712. doi: 10.1136/jcp.37.6.711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips K. D., Tearle P. V., Willis A. T. Rapid diagnosis of anaerobic infections by gas-liquid chromatography of clinical material. J Clin Pathol. 1976 May;29(5):428–432. doi: 10.1136/jcp.29.5.428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



