Abstract
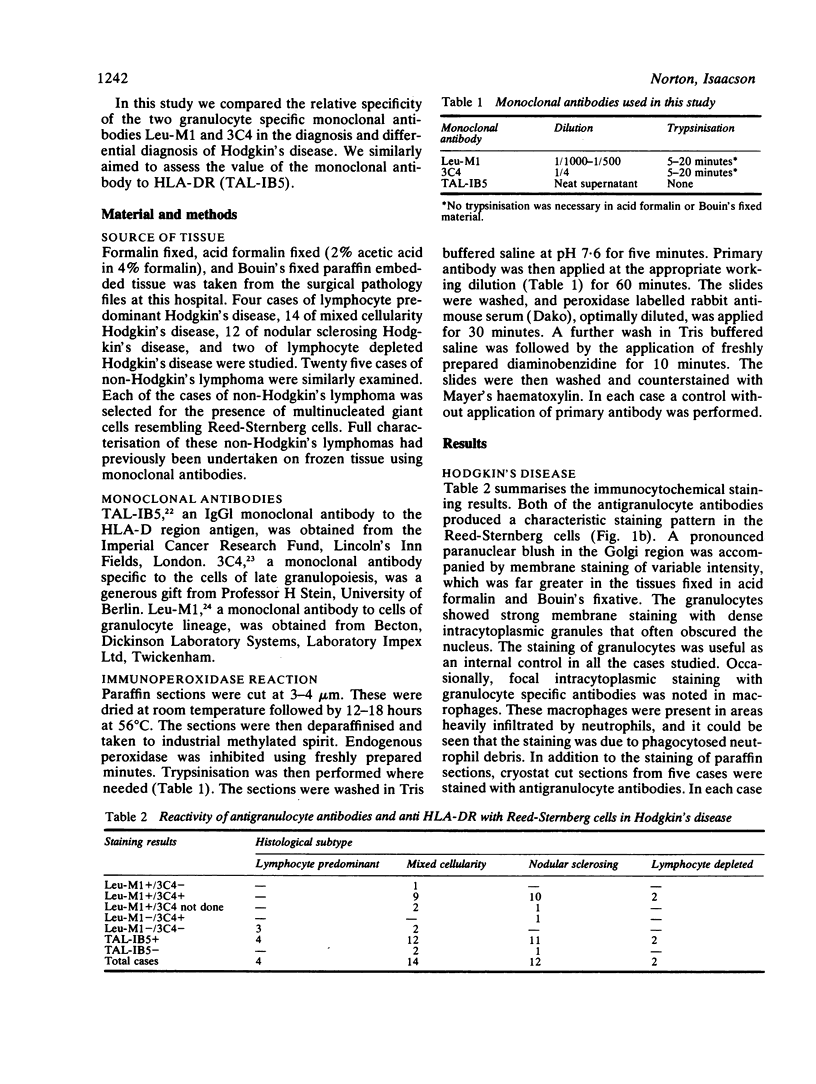
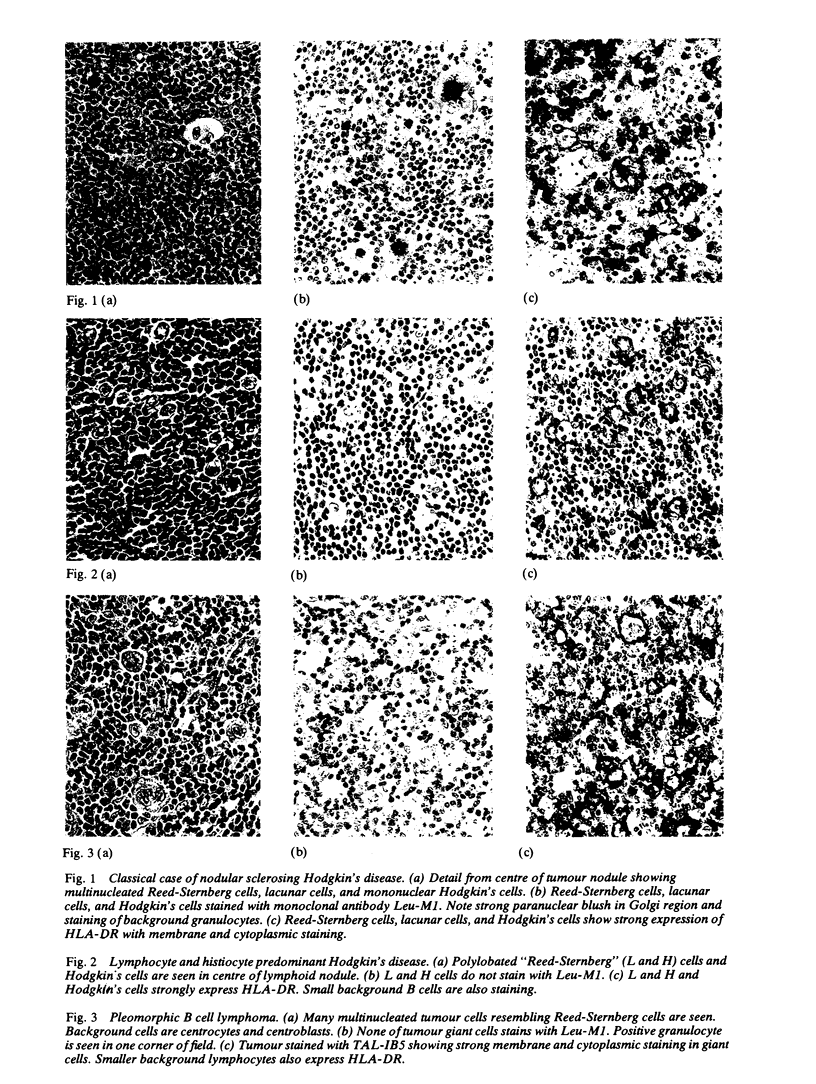
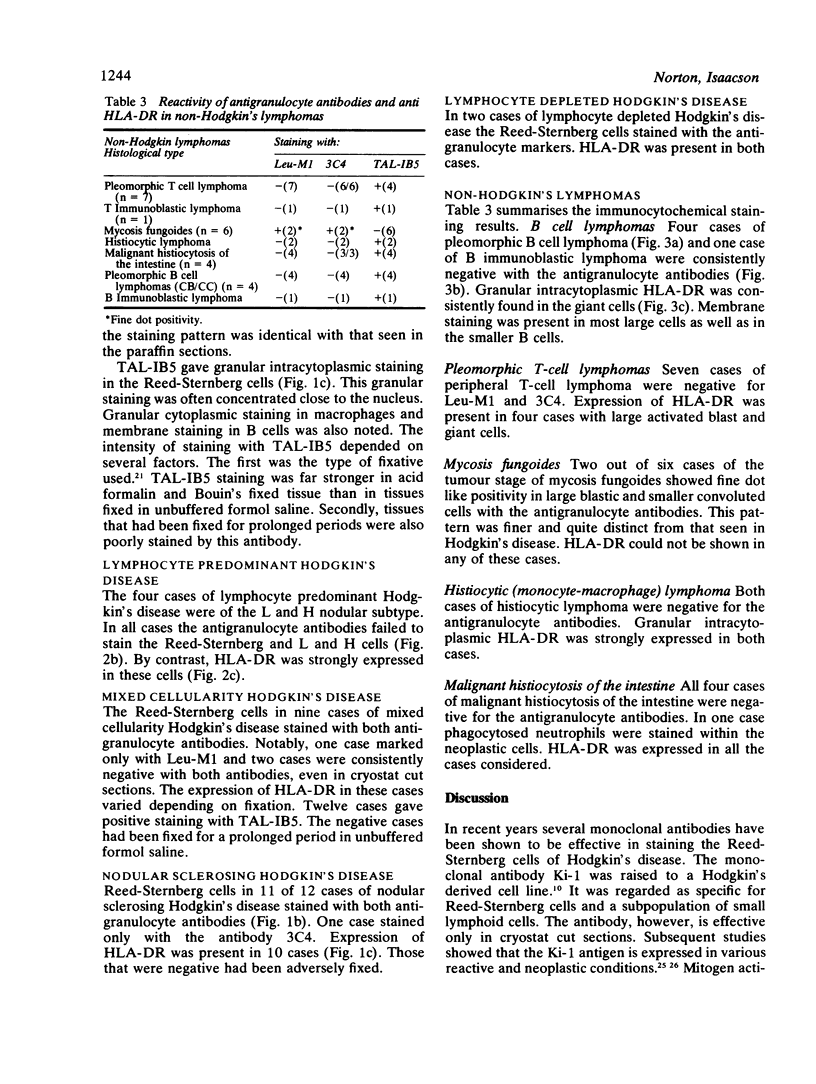
Tissue sections embedded in paraffin and fixed in formalin from 32 patients with Hodgkin's disease, representing the major histological subtypes, were studied using two granulocyte specific monoclonal antibodies (Leu-M1 and 3C4) and an HLA-D region specific monoclonal antibody (TAL-IB5). Reed-Sternberg cells were stained with one or other of the antigranulocyte antibodies in the nodular sclerosing and lymphocyte depleted subtypes. Reed-Sternberg cells in all but three cases of mixed cellularity Hodgkin's disease were positive with both Leu-M1 and 3C4. One case stained with only Leu-M1, and two cases were consistently negative with both antibodies. HLA-DR was widely expressed in the Reed-Sternberg cells of all three subtypes. In the four cases of lymphocyte predominant Hodgkin's disease the multinucleated Reed-Sternberg cells did not stain with either antigranulocyte antibody but were strongly positive with anti-HLA-DR. Twenty five cases of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, in which there were multinucleated giant cells resembling Reed-Sternberg cells, were studied in a similar way. These cases included pleomorphic T cell and B cell lymphomas, histiocytic lymphomas, and malignant histiocytosis of the intestine. In none of these did the multinucleated cells stain with either antigranulocyte antibody, but in most cases the multinucleated cells stained with anti-HLA-DR. In two cases of the tumour stage of mycosis fungoides dot like intracytoplasmic staining was shown in the tumour cells with both antigranulocyte markers. The monoclonal antigranulocyte antibodies Leu-M1 and 3C4 are of considerable value in both the diagnosis and the differential diagnosis of Hodgkin's disease and are particularly valuable in that they can be applied to tissue fixed in formalin and embedded in paraffin. Antibody to HLA-DR, while useful, is of less value.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abdalla S., Helmy N., el Essaily M., Nasser S., Hirschhorn N. Sodium balance in low birthweight babies after oral rehydration. Lancet. 1985 Mar 30;1(8431):757–757. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)91297-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andreesen R., Osterholz J., Löhr G. W., Bross K. J. A Hodgkin cell-specific antigen is expressed on a subset of auto- and alloactivated T (helper) lymphoblasts. Blood. 1984 Jun;63(6):1299–1302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borowitz M. J., Croker B. P., Metzgar R. S. Immunohistochemical analysis of the distribution of lymphocyte subpopulations in Hodgkin's disease. Cancer Treat Rep. 1982 Apr;66(4):667–674. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorreen M. S., Habeshaw J. A., Stansfeld A. G., Wrigley P. F., Lister T. A. Characteristics of Sternberg-Reed, and related cells in Hodgkin's disease: an immunohistological study. Br J Cancer. 1984 Apr;49(4):465–476. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1984.74. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epenetos A. A., Bobrow L. G., Adams T. E., Collins C. M., Isaacson P. G., Bodmer W. F. A monoclonal antibody that detects HLA-D region antigen in routinely fixed, wax embedded sections of normal and neoplastic lymphoid tissues. J Clin Pathol. 1985 Jan;38(1):12–17. doi: 10.1136/jcp.38.1.12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forni M., Hofman F. M., Parker J. W., Lukes R. J., Taylor C. R. B- and T-lymphocytes in Hodgkin's disease. An immunohistochemical study utilizing heterologous and monoclonal antibodies. Cancer. 1985 Feb 15;55(4):728–737. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19850215)55:4<728::aid-cncr2820550409>3.0.co;2-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanjan S. N., Kearney J. F., Cooper M. D. A monoclonal antibody (MMA) that identifies a differentiation antigen on human myelomonocytic cells. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1982 May;23(2):172–188. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(82)90106-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Jaffe E. S. Leu M1 and peanut agglutinin stain the neoplastic cells of Hodgkin's disease. Am J Clin Pathol. 1984 Jul;82(1):29–32. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/82.1.29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Yang K., Jaffe E. S. Phenotypic expression of Hodgkin's and Reed-Sternberg cells in Hodgkin's disease. Am J Pathol. 1985 Feb;118(2):209–217. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadin M. E., Billing R. J. B lymphocyte antigens in the differential diagnosis of human neoplasia. Blood. 1978 May;51(5):813–823. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lukes R. J., Tindle B. H., Parker J. W. Reed-Sternberg-like cells in infectious mononucleosis. Lancet. 1969 Nov 8;2(7628):1003–1004. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)90552-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinkus G. S., Said J. W., Hargreaves H. Malignant lymphoma, T-cell type. A distinct morphologic variant with large multilobated nuclei, with a report of four cases. Am J Clin Pathol. 1979 Oct;72(4):540–550. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/72.4.540. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinkus G. S., Said J. W. Hodgkin's disease, lymphocyte predominance type, nodular--a distinct entity? Unique staining profile for L&H variants of Reed-Sternberg cells defined by monoclonal antibodies to leukocyte common antigen, granulocyte-specific antigen, and B-cell-specific antigen. Am J Pathol. 1985 Jan;118(1):1–6. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poppema S., Bhan A. K., Reinherz E. L., Posner M. R., Schlossman S. F. In situ immunologic characterization of cellular constituents in lymph nodes and spleens involved by Hodgkin's disease. Blood. 1982 Feb;59(2):226–232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schienle H. W., Stein N., Müller-Ruchholtz W. Neutrophil granulocytic cell antigen defined by a monoclonal antibody--its distribution within normal haemic and non-haemic tissue. J Clin Pathol. 1982 Sep;35(9):959–966. doi: 10.1136/jcp.35.9.959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein H., Gerdes J., Kirchner H., Schaadt M., Diehl V. Hodgkin and sternberg-reed cell antigen(s) detected by an antiserum to a cell line (L428) derived from Hodgkin's disease. Int J Cancer. 1981 Oct 15;28(4):425–429. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910280406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein H., Uchánska-Ziegler B., Gerdes J., Ziegler A., Wernet P. Hodgkin and Sternberg-Reed cells contain antigens specific to late cells of granulopoiesis. Int J Cancer. 1982 Mar 15;29(3):283–290. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910290310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strum S. B., Park J. K., Rappaport H. Observation of cells resembling Sternberg-Reed cells in conditions other than Hodgkin's disease. Cancer. 1970 Jul;26(1):176–190. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197007)26:1<176::aid-cncr2820260123>3.0.co;2-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart A. E., Jackson E., Morris C. S. The reaction of xenogeneic and monoclonal antisera with Reed-Sternberg cells. J Pathol. 1982 Jun;137(2):129–138. doi: 10.1002/path.1711370206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart A. E., Volsen S. G., Zola H. The reactivity of Reed-Sternberg cells with monoclonal antisera at thin section and ultrastructural levels. J Pathol. 1983 Sep;141(1):71–82. doi: 10.1002/path.1711410108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tindle B. H., Parker J. W., Lukes R. J. "Reed-Sternberg cells" in infectious mononucleosis? Am J Clin Pathol. 1972 Dec;58(6):607–617. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/58.6.607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg D. S., Pinkus G. S. Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma of large multilobated cell type. A clinicopathologic study of ten cases. Am J Clin Pathol. 1981 Aug;76(2):190–196. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/76.2.190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





