Abstract
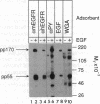
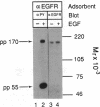
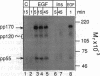
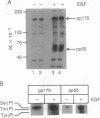
Administration of epidermal growth factor (EGF) to neonatal mice resulted in rapid tyrosine phosphorylation of a number of specific substrates in liver, kidney, lung, bladder, skin, and brain as detected by Western blot analysis of tissue homogenates with anti-phosphotyrosine antibodies. In the liver, three prominent EGF-dependent substrates of M(r) approximately 170,000, 120,000, and 55,000 were detected. A number of less prominent EGF-dependent substrates also were noted. Maximal tyrosine phosphorylation of pp170, pp120, and pp55 occurred within 5 min of subcutaneous injection and the levels of these phosphoproteins remained elevated for at least 45 min. Direct hepatic injection of EGF resulted in the tyrosine phosphorylation of these substrates within 60 sec of treatment. Tyrosine-phosphorylated pp170 was identified as the EGF receptor (EGFR). The tyrosine-phosphorylated pp55 substrate appeared to be associated with EGFR; both pp55 and EGFR were adsorbed to EGF-Affi-Gel, wheat germ lectin-Sepharose, and anti-EGFR antibodies bound to protein A-Sepharose. pp55 was not immunoreactive with anti-EGFR antiserum by Western blot analysis, indicating that it was not a fragment of the receptor. These results were confirmed by repeating the liver experiments using 32P-labeled neonatal mice. Increased amounts of 32P-labeled pp170 and pp55 were detected in anti-EGFR immunoprecipitates from liver extracts of EGF-treated animals as compared with controls. Phospho amino acid analysis of the 32P-labeled phosphoproteins revealed that EGF stimulated both serine and tyrosine phosphorylation in pp55 as well as in EGFR. The neonatal mouse may be a useful model for the study of signal transduction mediated by a variety of growth factors.
Full text
PDF
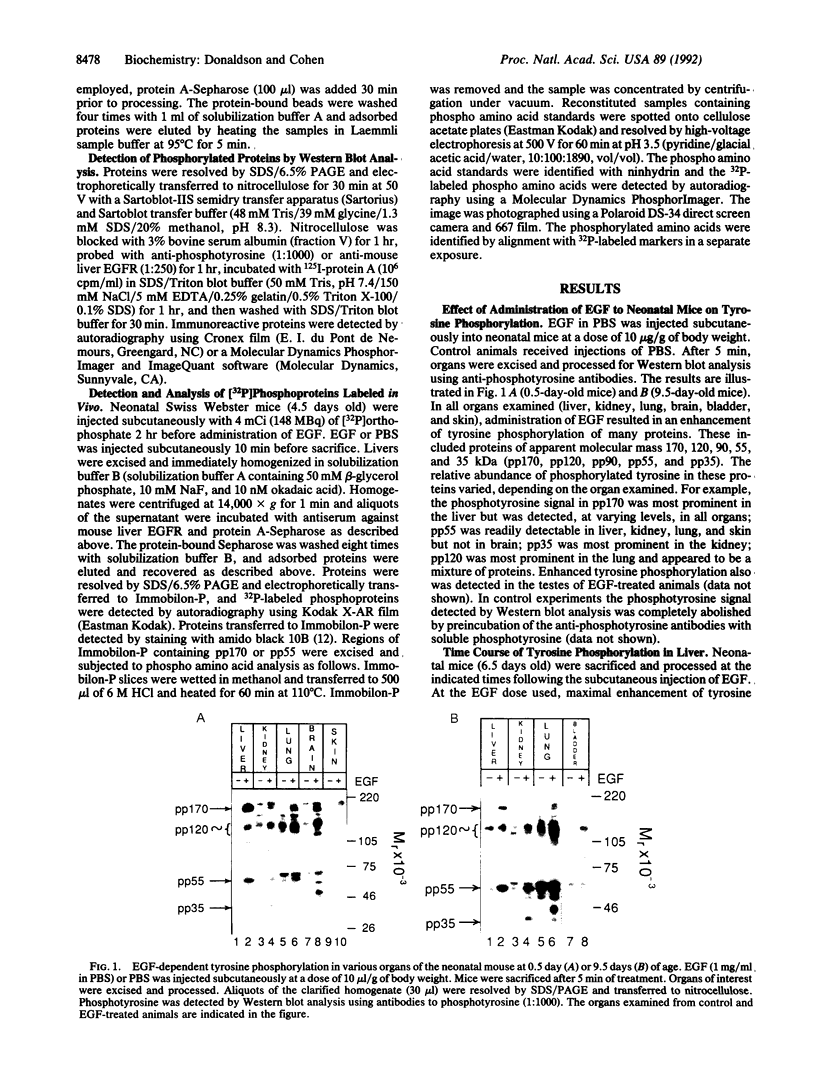
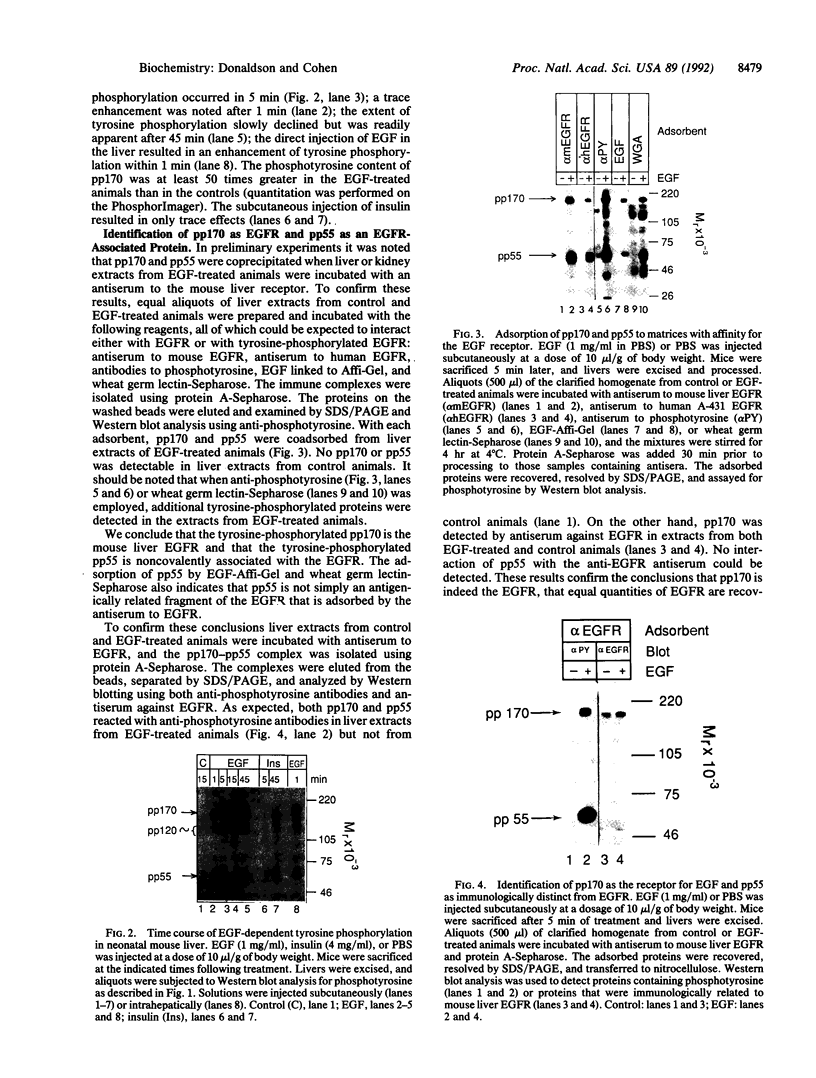


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baribault H., Blouin R., Bourgon L., Marceau N. Epidermal growth factor-induced selective phosphorylation of cultured rat hepatocyte 55-kD cytokeratin before filament reorganization and DNA synthesis. J Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;109(4 Pt 1):1665–1676. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.4.1665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter G., Cohen S. Epidermal growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 15;265(14):7709–7712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter G. Receptors for epidermal growth factor and other polypeptide mitogens. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:881–914. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.004313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochet C., Filhol O., Payrastre B., Hunter T., Gill G. N. Interaction between the epidermal growth factor receptor and phosphoinositide kinases. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 5;266(1):637–644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S., Fava R. A., Sawyer S. T. Purification and characterization of epidermal growth factor receptor/protein kinase from normal mouse liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(20):6237–6241. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.20.6237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fazioli F., Bottaro D. P., Minichiello L., Auricchio A., Wong W. T., Segatto O., Di Fiore P. P. Identification and biochemical characterization of novel putative substrates for the epidermal growth factor receptor kinase. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 15;267(8):5155–5161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher D. A., Lakshmanan J. Metabolism and effects of epidermal growth factor and related growth factors in mammals. Endocr Rev. 1990 Aug;11(3):418–442. doi: 10.1210/edrv-11-3-418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T. Protein modification: phosphorylation on tyrosine residues. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;1(6):1168–1181. doi: 10.1016/s0955-0674(89)80068-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurence D. J., Gusterson B. A. The epidermal growth factor. A review of structural and functional relationships in the normal organism and in cancer cells. Tumour Biol. 1990;11(5):229–261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCune B. K., Earp H. S. The epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase in liver epithelial cells. The effect of ligand-dependent changes in cellular location. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 15;264(26):15501–15507. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nave K. A., Probstmeier R., Schachner M. Epidermal growth factor does not cross the blood-brain barrier. Cell Tissue Res. 1985;241(2):453–457. doi: 10.1007/BF00217193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto M., Karasik A., White M. F., Kahn C. R. Epidermal growth factor stimulated phosphorylation of a 120-kilodalton endogenous substrate protein in rat hepatocytes. Biochemistry. 1990 Oct 9;29(40):9489–9494. doi: 10.1021/bi00492a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stastny M., Cohen S. Epidermal growth factor. IV. The induction of ornithine decarboxylase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Apr 15;204(2):578–589. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stastny M., Cohen S. The stimulation of ornithine decarboxylase activity in testes of the neonatal mouse. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jan 28;261(1):177–180. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(72)90327-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Signal transduction by receptors with tyrosine kinase activity. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):203–212. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90801-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wada I., Lai W. H., Posner B. I., Bergeron J. J. Association of the tyrosine phosphorylated epidermal growth factor receptor with a 55-kD tyrosine phosphorylated protein at the cell surface and in endosomes. J Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;116(2):321–330. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.2.321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarden Y., Ullrich A. Growth factor receptor tyrosine kinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:443–478. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.002303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]