Abstract
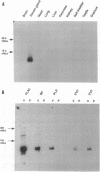
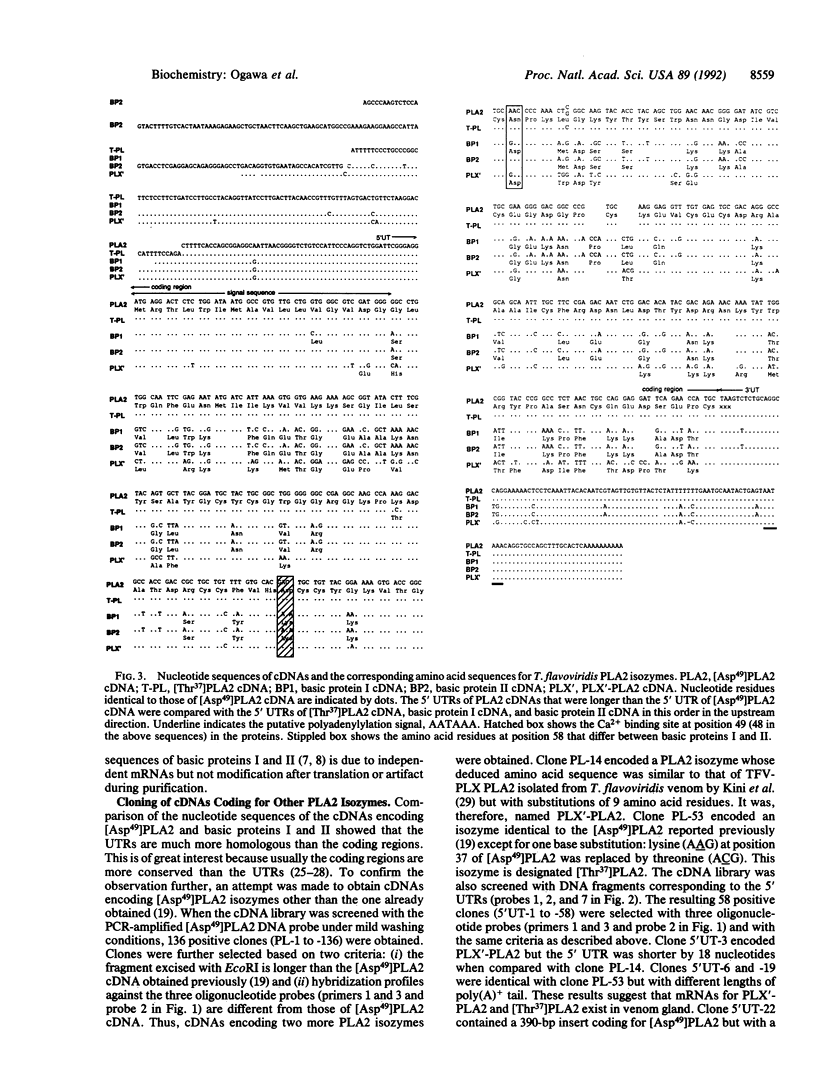
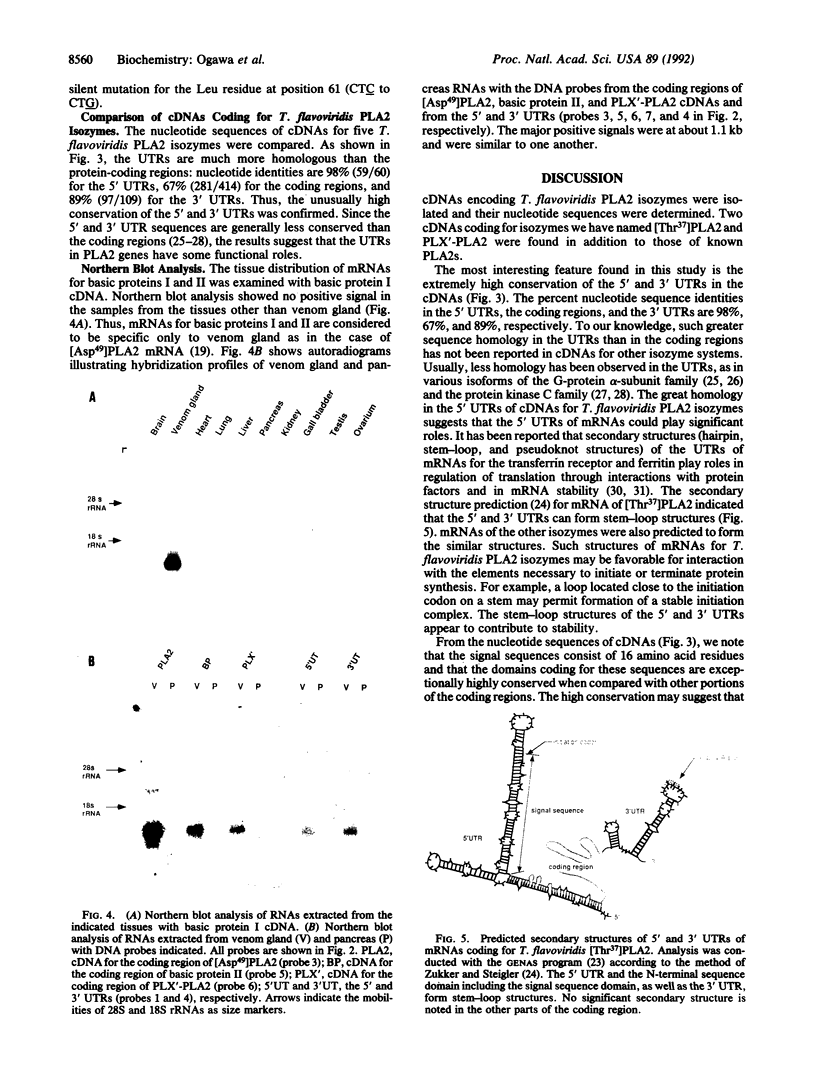
As a step toward understanding the structure and function of phospholipases A2 (PLA2s), we isolated and sequenced several cDNAs encoding Trimeresurus flavoviridis venom PLA2 isozymes including two [Lys49]PLA2s called basic proteins I and II, [Thr37]PLA2, and PLX'-PLA2. Comparison of the nucleotide sequences of these cDNAs with the previously isolated [Asp49]PLA2 cDNA revealed some interesting findings from the viewpoint of evolution. First, the homologies of the 5' and 3' untranslated regions (98% and 89%, respectively) were much higher than that of the protein-coding regions (67%). The predicted secondary structure showed the characteristic stem-loop structures for both the untranslated regions of the mRNAs, suggesting that these regions play some functional role(s) in translation or stability of mRNAs. Second, base substitutions appeared to have occurred at similar rates for the three positions of codons among these PLA2s. The results are discussed in terms of evolution of PLA2s. Northern blot analysis showed that these PLA2s are specific to venom gland.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barrington P. L., Condrea E., Soons K. R., Yang C. C., Rosenberg P. Effect of carboxylate group modification on enzymatic and cardiotoxic properties of snake venom phospholipases A2. Toxicon. 1984;22(5):743–758. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(84)90157-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson F. F., Dennis E. A. Evolutionary relationships and implications for the regulation of phospholipase A2 from snake venom to human secreted forms. J Mol Evol. 1990 Sep;31(3):228–238. doi: 10.1007/BF02109500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dijkstra B. W., Drenth J., Kalk K. H., Vandermaelen P. J. Three-dimensional structure and disulfide bond connections in bovine pancreatic phospholipase A2. J Mol Biol. 1978 Sep 5;124(1):53–60. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90146-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dufton M. J., Eaker D., Hider R. C. Conformational properties of phospholipases A2. Secondary-structure prediction, circular dichroism and relative interface hydrophobicity. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Dec 15;137(3):537–544. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07859.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomez F., Vandermeers A., Vandermeers-Piret M. C., Herzog R., Rathe J., Stievenart M., Winand J., Christophe J. Purification and characterization of five variants of phospholipase A2 and complete primary structure of the main phospholipase A2 variant in Heloderma suspectum (Gila monster) venom. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Dec 8;186(1-2):23–33. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb15172.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori M., Sakaki Y. Dideoxy sequencing method using denatured plasmid templates. Anal Biochem. 1986 Feb 1;152(2):232–238. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90403-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinrikson R. L., Krueger E. T., Keim P. S. Amino acid sequence of phospholipase A2-alpha from the venom of Crotalus adamanteus. A new classification of phospholipases A2 based upon structural determinants. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jul 25;252(14):4913–4921. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hentze M. W., Caughman S. W., Rouault T. A., Barriocanal J. G., Dancis A., Harford J. B., Klausner R. D. Identification of the iron-responsive element for the translational regulation of human ferritin mRNA. Science. 1987 Dec 11;238(4833):1570–1573. doi: 10.1126/science.3685996. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kini R. M., Kawabata S. I., Iwanaga S. Comparison of amino terminal region of three isoenzymes of phospholipases A2 (TFV PL-Ia, TFV PL-Ib, TFV PL-X) from Trimeresurus flavoviridis (habu snake) venom and the complete amino acid sequence of the basic phospholipase, TFV PL-X. Toxicon. 1986;24(11-12):1117–1129. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(86)90138-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer R. M., Hession C., Johansen B., Hayes G., McGray P., Chow E. P., Tizard R., Pepinsky R. B. Structure and properties of a human non-pancreatic phospholipase A2. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 5;264(10):5768–5775. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubo K., Ohno S., Suzuki K. Primary structures of human protein kinase C beta I and beta II differ only in their C-terminal sequences. FEBS Lett. 1987 Oct 19;223(1):138–142. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80524-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhara S., Matsuo F., Futamura S., Fujita A., Shinohara T., Takagi T., Sakaki Y. GENAS: a database system for nucleic acid sequence analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):89–99. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.89. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leibold E. A., Laudano A., Yu Y. Structural requirements of iron-responsive elements for binding of the protein involved in both transferrin receptor and ferritin mRNA post-transcriptional regulation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Apr 11;18(7):1819–1824. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.7.1819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu S. Y., Yoshizumi K., Oda N., Ohno M., Tokunaga F., Iwanaga S., Kihara H. Purification and amino acid sequence of basic protein II, a lysine-49-phospholipase A2 with low activity, from Trimeresurus flavoviridis venom. J Biochem. 1990 Mar;107(3):400–408. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maraganore J. M., Merutka G., Cho W., Welches W., Kézdy F. J., Heinrikson R. L. A new class of phospholipases A2 with lysine in place of aspartate 49. Functional consequences for calcium and substrate binding. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):13839–13843. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuoka M., Itoh H., Kozasa T., Kaziro Y. Sequence analysis of cDNA and genomic DNA for a putative pertussis toxin-insensitive guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory protein alpha subunit. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5384–5388. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMaster G. K., Carmichael G. G. Analysis of single- and double-stranded nucleic acids on polyacrylamide and agarose gels by using glyoxal and acridine orange. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4835–4838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oda N., Nakamura H., Sakamoto S., Liu S. Y., Kihara H., Chang C. C., Ohno M. Amino acid sequence of a phospholipase A2 from the venom of Trimeresurus gramineus (green habu snake). Toxicon. 1991;29(2):157–166. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(91)90100-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oda N., Ogawa T., Ohno M., Sasaki H., Sakaki Y., Kihara H. Cloning and sequence analysis of cDNA for Trimeresurus flavoviridis phospholipase A2, and consequent revision of the amino acid sequence. J Biochem. 1990 Nov;108(5):816–821. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno S., Kawasaki H., Imajoh S., Suzuki K., Inagaki M., Yokokura H., Sakoh T., Hidaka H. Tissue-specific expression of three distinct types of rabbit protein kinase C. Nature. 1987 Jan 8;325(7000):161–166. doi: 10.1038/325161a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pungercar J., Kordis D., Strukelj B., Liang N. S., Gubensek F. Cloning and nucleotide sequence of a cDNA encoding ammodytoxin A, the most toxic phospholipase A2 from the venom of long-nosed viper (Vipera ammodytes). Toxicon. 1991;29(2):269–273. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(91)90112-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt J. J., Middlebrook J. L. Purification, sequencing and characterization of pseudexin phospholipases A2 from Pseudechis porphyriacus (Australian red-bellied black snake). Toxicon. 1989;27(7):805–818. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(89)90048-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seilhamer J. J., Pruzanski W., Vadas P., Plant S., Miller J. A., Kloss J., Johnson L. K. Cloning and recombinant expression of phospholipase A2 present in rheumatoid arthritic synovial fluid. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 5;264(10):5335–5338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strathmann M., Simon M. I. G protein diversity: a distinct class of alpha subunits is present in vertebrates and invertebrates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(23):9113–9117. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.23.9113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suwa Y., Kudo I., Imaizumi A., Okada M., Kamimura T., Suzuki Y., Chang H. W., Hara S., Inoue K. Proteinaceous inhibitors of phospholipase A2 purified from inflammatory sites in rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(7):2395–2399. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.7.2395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takasaki C., Yutani F., Kajiyashiki T. Amino acid sequences of eight phospholipases A2 from the venom of Australian king brown snake, Pseudechis australis. Toxicon. 1990;28(3):329–339. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(90)90068-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verheij H. M., Boffa M. C., Rothen C., Bryckaert M. C., Verger R., de Haas G. H. Correlation of enzymatic activity and anticoagulant properties of phospholipase A2. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Nov;112(1):25–32. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04982.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang C. C., King K., Sun T. P. Chemical modification of lysine and histidine residues in phospholipase A2 from the venom of Naja naja atra (Taiwan cobra). Toxicon. 1981;19(5):645–659. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(81)90102-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshizumi K., Liu S. Y., Miyata T., Saita S., Ohno M., Iwanaga S., Kihara H. Purification and amino acid sequence of basic protein I, a lysine-49-phospholipase A2 with low activity, from the venom of Trimeresurus flavoviridis (Habu snake). Toxicon. 1990;28(1):43–54. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(90)90005-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuker M., Stiegler P. Optimal computer folding of large RNA sequences using thermodynamics and auxiliary information. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 10;9(1):133–148. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.1.133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]