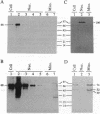
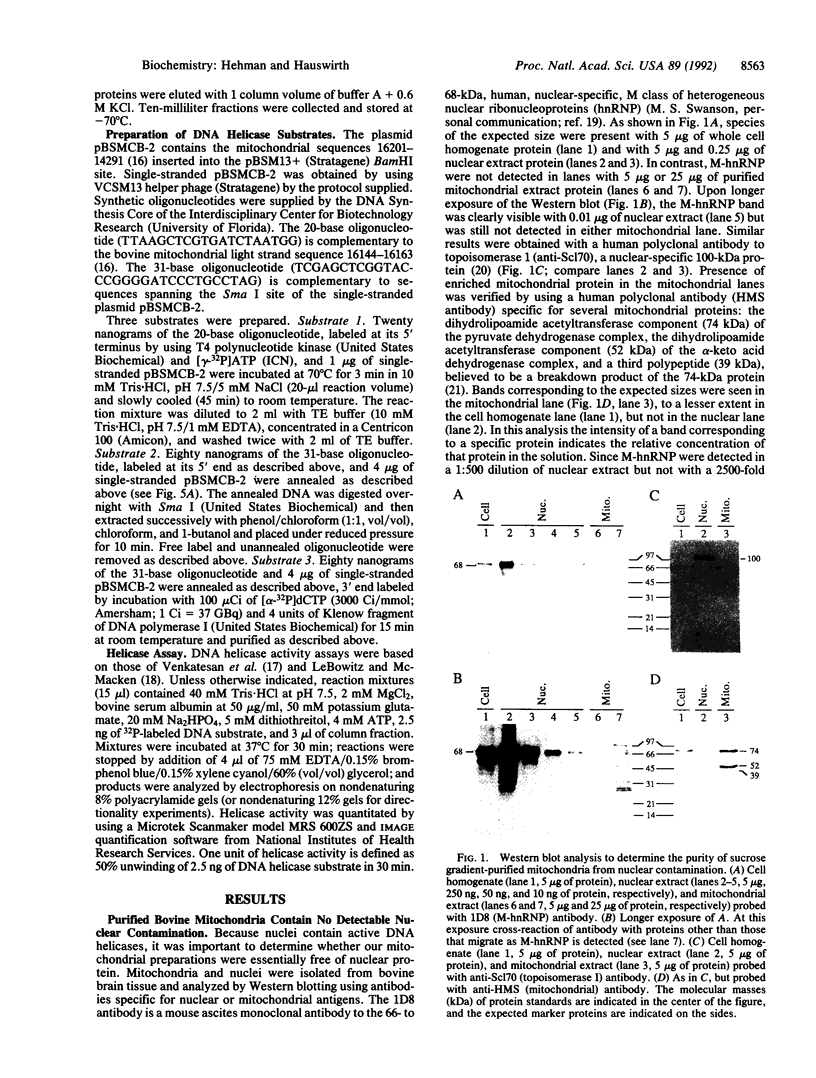
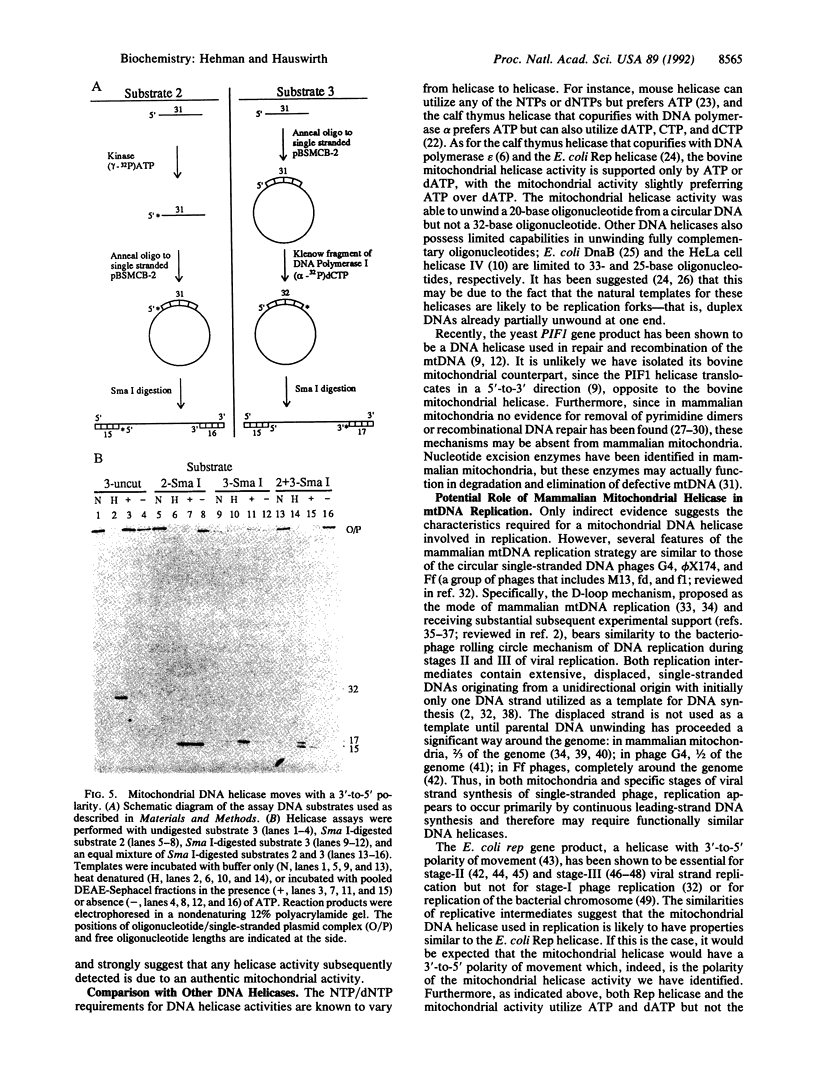
Abstract
In spite of the fact that a DNA helicase is clearly required for the predominantly leading-strand synthesis occurring during mammalian mtDNA replication, no such activity has heretofore been identified. We report the characterization of a mammalian mitochondrial DNA helicase isolated from bovine brain tissue. The sucrose gradient-purified mitochondria in which the activity was detected had less than 1 part in 2500 nuclear contamination according to Western blot analysis using nuclear- and mitochondrial-specific probes. Mitochondrial protein fractionation by DEAE-Sephacel chromatography yielded a DNA helicase activity dependent upon hydrolysis of ATP or dATP but not other NTPs or dNTPs. The mitochondrial helicase unwound 15- and 20-base oligonucleotides but was unable to unwind 32-base or longer oligonucleotides, and the polarity of the unwinding is 3'-to-5' with respect to the single-stranded portion of the partial duplex DNA substrate. This direction of unwinding would place the bovine mitochondrial helicase on the template strand ahead of DNA polymerase gamma during mtDNA replication, a situation analogous to that of the Rep helicase of Escherichia coli during leading-strand DNA synthesis of certain bacteriophages.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson S., de Bruijn M. H., Coulson A. R., Eperon I. C., Sanger F., Young I. G. Complete sequence of bovine mitochondrial DNA. Conserved features of the mammalian mitochondrial genome. J Mol Biol. 1982 Apr 25;156(4):683–717. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90137-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Annex B. H., Williams R. S. Mitochondrial DNA structure and expression in specialized subtypes of mammalian striated muscle. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Nov;10(11):5671–5678. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.11.5671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aoyama A., Hamatake R. K., Hayashi M. In vitro synthesis of bacteriophage phi X174 by purified components. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4195–4199. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Attardi G., Schatz G. Biogenesis of mitochondria. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1988;4:289–333. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.04.110188.001445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Clayton D. A. Mechanism of mitochondrial DNA replication in mouse L-cells: asynchronous replication of strands, segregation of circular daughter molecules, aspects of topology and turnover of an initiation sequence. J Mol Biol. 1974 Jul 15;86(4):801–824. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90355-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogenhagen D., Gillum A. M., Martens P. A., Clayton D. A. Replication of mouse L-cell mitochondrial DNA. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 1):253–262. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cann R. L., Wilson A. C. Length mutations in human mitochondrial DNA. Genetics. 1983 Aug;104(4):699–711. doi: 10.1093/genetics/104.4.699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmo-Fonseca M., Pepperkok R., Sproat B. S., Ansorge W., Swanson M. S., Lamond A. I. In vivo detection of snRNP-rich organelles in the nuclei of mammalian cells. EMBO J. 1991 Jul;10(7):1863–1873. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07712.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi Y. D., Dreyfuss G. Monoclonal antibody characterization of the C proteins of heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein complexes in vertebrate cells. J Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;99(6):1997–1204. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.6.1997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayton D. A., Doda J. N., Friedberg E. C. The absence of a pyrimidine dimer repair mechanism in mammalian mitochondria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jul;71(7):2777–2781. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.7.2777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayton D. A. Replication and transcription of vertebrate mitochondrial DNA. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1991;7:453–478. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.07.110191.002321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colasanti J., Denhardt D. T. The Escherichia coli rep mutation. X. Consequences of increased and decreased Rep protein levels. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Sep;209(2):382–390. doi: 10.1007/BF00329669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croizat B., Attardi G. Selective in vivo damage by "visible" light of BrdU-containing mitochondrial DNA in a thymidine kinase-deficient mouse cell line with persistent mitochondrial enzyme activity. J Cell Sci. 1975 Oct;19(1):69–84. doi: 10.1242/jcs.19.1.69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg S., Scott J. F., Kornberg A. An enzyme system for replication of duplex circular DNA: the replicative form of phage phi X174. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 May;73(5):1594–1597. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.5.1594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foury F., Kolodynski J. pif mutation blocks recombination between mitochondrial rho+ and rho- genomes having tandemly arrayed repeat units in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(17):5345–5349. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.17.5345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geider K., Bäumel I., Meyer T. F. Intermediate stages in enzymatic replication of bacteriophage fd duplex DNA. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 10;257(11):6488–6493. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godson G. N. G4 DNA replication. III. Synthesis of replicative form. J Mol Biol. 1977 Dec 5;117(2):353–367. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90132-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goetz G. S., Dean F. B., Hurwitz J., Matson S. W. The unwinding of duplex regions in DNA by the simian virus 40 large tumor antigen-associated DNA helicase activity. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 5;263(1):383–392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorski K., Carneiro M., Schibler U. Tissue-specific in vitro transcription from the mouse albumin promoter. Cell. 1986 Dec 5;47(5):767–776. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90519-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi J., Tagashira Y., Yoshida M. C. Absence of extensive recombination between inter- and intraspecies mitochondrial DNA in mammalian cells. Exp Cell Res. 1985 Oct;160(2):387–395. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(85)90185-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasamatsu H., Robberson D. L., Vinograd J. A novel closed-circular mitochondrial DNA with properties of a replicating intermediate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Sep;68(9):2252–2257. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.9.2252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khatri G. S., MacAllister T., Sista P. R., Bastia D. The replication terminator protein of E. coli is a DNA sequence-specific contra-helicase. Cell. 1989 Nov 17;59(4):667–674. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90012-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kodaira K. I., Taketo A. Conversion of bacteriophage G4 single-stranded viral DNA to double-stranded replicative form in dna mutants of Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 May 17;476(2):149–155. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(77)90091-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornberg A., Scott J. F., Bertsch L. L. ATP utilization by rep protein in the catalytic separation of DNA strands at a replicating fork. J Biol Chem. 1978 May 10;253(9):3298–3304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lahaye A., Stahl H., Thines-Sempoux D., Foury F. PIF1: a DNA helicase in yeast mitochondria. EMBO J. 1991 Apr;10(4):997–1007. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08034.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeBowitz J. H., McMacken R. The Escherichia coli dnaB replication protein is a DNA helicase. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 5;261(10):4738–4748. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martens P. A., Clayton D. A. Mechanism of mitochondrial DNA replication in mouse L-cells: localization and sequence of the light-strand origin of replication. J Mol Biol. 1979 Dec 5;135(2):327–351. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90440-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin D. M., Godson G. N. G4 DNA replication. I. Origin of synthesis of the viral and complementary DNA strands. J Mol Biol. 1977 Dec 5;117(2):321–335. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90130-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matson S. W., Kaiser-Rogers K. A. DNA helicases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:289–329. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.001445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matson S. W., Tabor S., Richardson C. C. The gene 4 protein of bacteriophage T7. Characterization of helicase activity. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 25;258(22):14017–14024. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer T. F., Geider K. Enzymatic synthesis of bacteriophage fd viral DNA. Nature. 1982 Apr 29;296(5860):828–832. doi: 10.1038/296828a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robberson D. L., Clayton D. A., Morrow J. F. Cleavage of replicating forms of mitochondrial DNA by EcoRI endonuclease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Nov;71(11):4447–4451. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.11.4447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robberson D. L., Clayton D. A. Replication of mitochondrial DNA in mouse L cells and their thymidine kinase - derivatives: displacement replication on a covalently-closed circular template. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Dec;69(12):3810–3814. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.12.3810. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robberson D. L., Kasamatsu H., Vinograd J. Replication of mitochondrial DNA. Circular replicative intermediates in mouse L cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Mar;69(3):737–741. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.3.737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J. F., Eisenberg S., Bertsch L. L., Kornberg A. A mechanism of duplex DNA replication revealed by enzymatic studies of phage phi X174: catalytic strand separation in advance of replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jan;74(1):193–197. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.1.193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seki M., Enomoto T., Eki T., Miyajima A., Murakami Y., Hanaoka F., Ui M. DNA helicase and nucleoside-5'-triphosphatase activities of polyoma virus large tumor antigen. Biochemistry. 1990 Jan 30;29(4):1003–1009. doi: 10.1021/bi00456a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seki M., Enomoto T., Hanaoka F., Yamada M. DNA-dependent adenosinetriphosphatase B from mouse FM3A cells has DNA helicase activity. Biochemistry. 1987 May 19;26(10):2924–2928. doi: 10.1021/bi00384a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shero J. H., Bordwell B., Rothfield N. F., Earnshaw W. C. High titers of autoantibodies to topoisomerase I (Scl-70) in sera from scleroderma patients. Science. 1986 Feb 14;231(4739):737–740. doi: 10.1126/science.3003910. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl H., Dröge P., Knippers R. DNA helicase activity of SV40 large tumor antigen. EMBO J. 1986 Aug;5(8):1939–1944. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04447.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thömmes P., Hübscher U. DNA helicase from calf thymus. Purification to apparent homogeneity and biochemical characterization of the enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 25;265(24):14347–14354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thömmes P., Hübscher U. Eukaryotic DNA helicases. FEBS Lett. 1990 Aug 1;268(2):325–328. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81279-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomkinson A. E., Bonk R. T., Kim J., Bartfeld N., Linn S. Mammalian mitochondrial endonuclease activities specific for ultraviolet-irradiated DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Feb 25;18(4):929–935. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.4.929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuteja N., Rahman K., Tuteja R., Falaschi A. DNA helicase IV from HeLa cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jul 11;19(13):3613–3618. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.13.3613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuteja N., Tuteja R., Rahman K., Kang L. Y., Falaschi A. A DNA helicase from human cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 11;18(23):6785–6792. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.23.6785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umezu K., Nakayama K., Nakayama H. Escherichia coli RecQ protein is a DNA helicase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(14):5363–5367. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.14.5363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van de Water J., Cooper A., Surh C. D., Coppel R., Danner D., Ansari A., Dickson R., Gershwin M. E. Detection of autoantibodies to recombinant mitochondrial proteins in patients with primary biliary cirrhosis. N Engl J Med. 1989 May 25;320(21):1377–1380. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198905253202104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venkatesan M., Silver L. L., Nossal N. G. Bacteriophage T4 gene 41 protein, required for the synthesis of RNA primers, is also a DNA helicase. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 25;257(20):12426–12434. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiekowski M., Schwarz M. W., Stahl H. Simian virus 40 large T antigen DNA helicase. Characterization of the ATPase-dependent DNA unwinding activity and its substrate requirements. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 5;263(1):436–442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. S. Mitochondrial gene expression in mammalian striated muscle. Evidence that variation in gene dosage is the major regulatory event. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 15;261(26):12390–12394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarranton G. T., Gefter M. L. Enzyme-catalyzed DNA unwinding: studies on Escherichia coli rep protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1658–1662. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1658. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]