Abstract
Background
The diagnosis of drug-resistant tuberculosis (DR-TB) in children is challenging and treatment is associated with many adverse effects.
Objective
We aimed to assess if careful observation, without initiation of second-line treatment, is safe in asymptomatic children referred with “culture-confirmed” DR-TB.
Setting
KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa - an area with high burdens of HIV, TB and DR-TB.
Design, Intervention, Main outcome measures
We performed an outcome review of children with “culture-confirmed” DR-TB who were not initiated on second-line TB treatment, as they were asymptomatic with normal chest radiographs on examination at our specialist referral hospital. Children were followed up every other month for the first year, with a final outcome assessment at the end of the study.
Results
In total, 43 asymptomatic children with normal chest radiographs were reviewed. The median length of follow-up until final evaluation was 549 days (IQR 259-722 days); most (34; 83%) children were HIV-uninfected. Resistance patterns included 9 (21%) mono-resistant and 34 (79%) multidrug-resistant (MDR) strains. Fifteen children (35%) had been treated with first-line TB treatment, prior to presentation at our referral hospital. At the final evaluation 34 (80%) children were well, 7 (16%) were lost to follow up, 1 (2%) received MDR-TB treatment and 1 (2%) died of unknown causes. The child who received MDR-TB treatment developed new symptoms at the 12 month review and responded well to second-line treatment.
Conclusion
Bacteriological evaluation should not be performed in the absence of any clinical indication. If drug-resistant M. tuberculosis is detected in an asymptomatic child with a normal chest radiograph close observation may be an appropriate strategy, especially in settings where potential laboratory error and poor record keeping are constant challenges.
Keywords: DR-TB, children, asymptomatic, management, HIV
Introduction
South Africa has a high burden of drug-resistant tuberculosis (DR-TB; resistance to one or more first-line TB drugs), which includes many children.1,2 Diagnosing DR-TB in young children is challenging, particularly in those co-infected with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), as the signs and symptoms are non-specific and the disease usually paucibacillary.2,3 DR-TB treatment requires the use of second-line drugs, which are less potent and more toxic than first-line medications. The treatment also includes a daily intramuscular injection for the first 4-8 months of therapy and lasts approximately two years. DR-TB treatment can have a significant negative physical, psychological and academic impact on children due to its duration, complexity and associated adverse effects.4 In addition, treatment places a significant financial burden on the child’s family and the health system in general.4-6
DR-TB is a laboratory diagnosis based on culture and drug-susceptibility testing (DST) or, more recently, rapid genotypic testing with Xpert MTB/RIF®. However, false-positive DR-TB tests can occur due to specimen contamination and laboratory error.7,8 In addition, transient Mycobacterium tuberculosis (M.tb) excretion, detectable by culture or other sensitive tests, is not uncommon following recent primary infection, even in the absence of active disease.9,10 Given the high risk of irreversible hearing loss and other adverse effects associated with the use of second-line injectable drugs,11 the clinical significance of a positive DR-TB test should be carefully considered. This has particular relevance in asymptomatic children with normal chest radiographs, in whom some practitioners may defer therapy and monitor closely for any suspicious symptoms or signs. The outcome and advisability of this practice, however, has not been evaluated. We aimed to assess if careful observation, without initiation of second-line treatment, is safe in asymptomatic children with “culture-confirmed” DR-TB, under programmatic conditions.
Methodology
Study population and setting
King Dinuzulu Hospital (KDH) is the specialist referral hospital for DR-TB in KwaZulu-Natal Province, South Africa. Between January 2010 and December 2011 a number of children (≤14 years) were referred to KDH for initiation of MDR-TB therapy. These children were referred by primary-level facilities, either clinics or district hospitals. At clinics they would have been assessed and treated by a professional nurse and at district hospitals by a doctor. First-line TB drugs and antiretroviral therapy (ART) are available at both clinic and hospital level, but laboratories are usually hospital based. On presentation at KDH, despite having “culture-confirmed” DR-TB, these children were clinically well with a normal chest radiograph and no signs or symptoms suggestive of active disease. Instead of being started on DR-TB treatment, a collective decision was taken at the weekly doctors meeting to enrol these children in an observation programme with monitoring every other month for a year.
Agreed criteria included a normal chest radiograph with no current signs or symptoms suggestive of intra-or extra-thoracic TB. Children who had commenced first-line TB treatment prior to enrolment continued until their course of treatment was complete. At follow-up visits, children were monitored for any suggestive TB signs or symptoms, a chest radiograph was performed, and each child’s weight checked. If children remained well after one year, they were discharged from the programme. The duration of follow-up was measured in days from the date of entry into the observation programme to any of the following outcomes: death, initiation of MDR-TB treatment, or date of last contact with the programme. Between July 2012 and June 2013, as a final outcome assessment, all children enrolled in the observation programme were contacted and asked to return to KDH for a final evaluation, irrespective of the time since enrolment.
Laboratory procedures
This study was undertaken before the introduction of the Xpert MTB/RIF® assay (Cepheid, Sunnyvale, CA, USA), in South Africa. Routine samples submitted to the centralised provincial diagnostic mycobacteriology laboratory in Durban included gastric aspirates collected from young children and sputum from older children who could expectorate. Smear microscopy for acid-fast bacilli was done using an auramine stain. Initial culture was performed in liquid media using mycobacteria growth indicator tubes MGIT 960 Mycobacteria Culture System (Becton, Dickinson and Co., Franklin Lakes, NJ) and all positive cultures underwent line probe assay testing (Hain MTBDRplus®, Hain Lifescience, Nehren, Germany ). Isolates demonstrating genotypic resistance to either isoniazid (INH) or rifampicin (RIF) then underwent first and second-line phenotypic DST using the 1% proportion method on Middlebrook 7H10 agar. Isolates were tested for susceptibility to INH (1mg/L), RIF (2 mg/L), ethambutol (EMB) (5mg/L), streptomycin (2 mg/L), kanamycin (16 mg/L) and ciprofloxacin (2mg/L).
Data collection and analysis
We retrospectively reviewed hospital medical records and extracted the following information: baseline demographic and clinical characteristics, TB history, HIV status and treatment, laboratory data and chest radiographs. Unfortunately we were unable to access clinical information at the referring facilities to assess the initial signs and symptoms that triggered the microbiological evaluation. Weight was plotted on the USA Centers for Disease Control and Prevention weight-for-age percentile charts.12 Malnutrition at baseline was classified as weight less than the third percentile for a given age in months.13 Data were double-entered and checked for errors. Baseline characteristics and outcomes are presented as proportions, means or medians where appropriate.
Ethical approval
The study protocol was approved by the ethics committee of the South African Medical Research Council, the KwaZulu-Natal Department of Health and KDH (Ref: EC011-7/2013).
Results
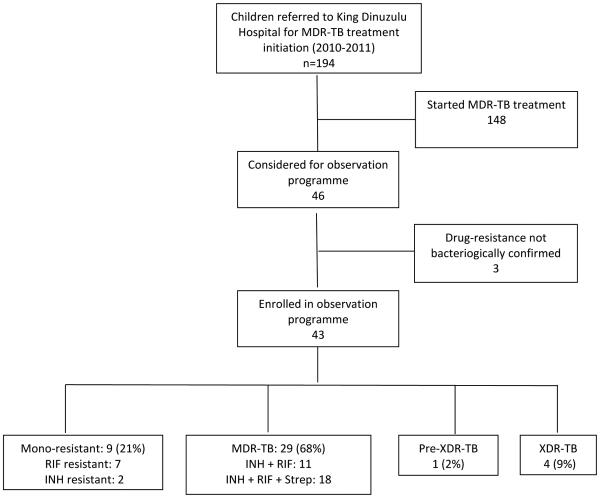
Between January 2010 and December 2011 194 children with DR-TB, were referred to KDH for initiation of DR-TB therapy. Of these children, 148 were initiated on second-line therapy; 46 (24%) asymptomatic children were enrolled in the observation programme. Three of the 46 children were excluded as they did not have “culture-confirmed” DR-TB; 43 children were included in the outcome assessment (Figure 1). Resistance patterns varied. Nine (21%) children had mono-resistant M.tb bacilli; 7 with RIF and 2 with INH mono-resistance. The majority of the children (29/43; 68%) had multi-drug resistant TB (MDR-TB; resistant to INH and RIF) with 62% (18/29) of the MDR isolates also displaying streptomycin resistance. Four children (9%) had extensively drug-resistant (XDR)-TB (MDR-TB with additional resistance to a fluoroquinolone and an aminoglycoside). One child (2%) had pre-XDR-TB (MDR-TB with added resistance to either the fluoroquinolones or a second-line injectable agent).
Figure 1. Schema of enrolment and drug susceptibility patterns identified in asymptomatic children with culture confirmed drug-resistant tuberculosis, Durban, South Africa.
INH – isoniazid; RIF – rifampicin; Strep - streptomycin
* Pre-XDR-TB: MDR-TB with resistance to either a fluoroquinolone or an aminoglycoside, but not both.
**XDR-TB: MDR-TB with resistance to both a fluoroquinolone and an aminoglycoside.
Table 1 shows the baseline characteristics of children enrolled in the observation programme; the median age at enrolment was 3 years (inter-quartile range [IQR] 1.5-6.5 years). The majority (34/41; 83% tested) were HIV-uninfected and 57% (4/7) of the HIV-infected children were on ART. The median length of time between referral and examination at KDH was 80 days (60-117 days). The positive fine needle aspiration biopsy (FNAB) was collected from a right axillary node that resolved by the time the patient was examined at KDH. Because the child was asymptomatic, MDR-TB treatment was not commenced and he was included in the observation programme. On presentation 15 (35%) were on first-line TB treatment – an initial 2 month intensive phase of isoniazid (INH), rifampicin (RIF), pyrazinamide (PZA) and ethambutol (EMB), followed by 4 months continuation phase of INH and RIF. (Children <8 years did not receive EMB). Eight of the children presently on TB treatment had previously been treated for TB.
Table 1.
Baseline characteristics of asymptomatic children with “culture-confirmed” drug-resistant tuberculosis in Durban, South Africa
| Characteristic | Number (%) N=43 |
|---|---|
| Referred from primary clinic | 5 (12) |
| Referred from district hospital | 38 (88) |
| Female | 17 (40) |
| Median age; years (IQR) | 3 (1.5 - 6.5) |
| Children ≤ 1 year. | 4 (16) |
| Weight <3rd percentile for age | 9 (21) |
| Days from DR-TB diagnosis to KDH examination; median (IQR) | 80 (60-117) |
| TB-related findings | |
| Signs or symptoms suggestive of TB | 0 |
| Abnormal chest radiograph | 0 |
| Previous TB treatment* | 18 (42) |
| Presently on TB treatment | 15 (35) |
| Previous TB treatment and presently on TB treatment | 8 (19) |
| Reported contact with infectious MDR-TB source case | 3 (7) |
| Respiratory specimen M. tuberculosis positive | 42 (98) |
| Extrapulmonary specimen (FNAB) M. tuberculosis positive | 1 (2) |
| HIV status | |
| HIV unknown | 2 (5) |
| HIV-infected | 7/41 (17) |
| On antiretroviral therapy | 4/7 (57) |
| Drug-resistance profile | |
| Mono-resistant | 9 (21) |
| Isoniazid mono-resistant | 2 (5) |
| Rifampicin mono-resistant | 7 (16) |
| MDR | 29 (68) |
| Pre-XDR | 1 (2) |
| XDR | 4 (9) |
IQR - Interquartile range; TB - tuberculosis; HIV - human immunodeficiency virus; KDH: King Dinuzulu Hospital (specialist TB hospital); FNAB: Fine needle aspiration biopsy; MDR: Multi-drug resistance; resistance to isoniazid and rifampicin; Pre-XDR-TB: MDR-TB with resistance to either a fluoroquinolone or an aminoglycoside, but not both; XDR-TB: MDR-TB with resistance to both a fluoroquinolone and an aminoglycoside.
Previous TB treatment - refers to any TB episode for which the child received treatment during the course of their life (excluding the current episode)
The median length of follow-up after evaluation was 549 days (IQR 259-722 days), with a minimum observation period of 109 days (Table 2). At the final evaluation, 34 (80%) children were well, 7 (16%) had been lost to follow up, 1 (2%) had been started on DR-TB treatment and 1 (2%) had died. The child started on treatment was 7 years old at the time of enrolment into the observation programme, was HIV-negative with no known close contact with a DR-TB source case. She was well up until the 10-month follow-up visit, but at the 12-month visit the chest radiograph, which had been clear, showed evidence of disease (infiltrates in the right lower lobe). In addition, she was coughing, complained of fatigue and had lost weight. Although sputum taken at this time was smear-and culture-negative she was started on standard MDR-TB therapy - an initial 6 month regimen of kanamycin, PZA, EMB, ethionamide (Eth), ofloxacin (Ofx) and terizidone (TRD), followed by an 18 month continuation phase of PZA, EMB, Eth, Ofx and TRD. She responded well to treatment; completing a full 24 month course. The child who died was 12 months old and had severe cerebral palsy. No DR-TB contact was reported, and her isolate showed resistance to INH, RIF and streptomycin. She was HIV-infected and not on ART until shortly before her death. She died from new onset seizures within 9 months of enrolment in the observation programme. No autopsy was performed and the possibility of central nervous system TB could not be ruled out.
Table 2.
Clinical course and final outcome of asymptomatic children with “culture-confirmed” drug-resistant tuberculosis in Durban, South Africa
| Clinical course / Outcome | Number (%) N=43 |
|---|---|
| Management | |
| Length of follow up in days; median (IQR) | 549 (259-722) |
| Minimum period of follow up (days) | 109 |
| Change in weight | |
| Crossed centile line/s upwards | 21 (49) |
| Same centile line | 10 (23) |
| Crossed centile line/s downwards | 4 (9) |
| No follow up weight recorded as lost to follow up or died | 8 (19) |
| Outcome* | |
| Well | 34 (80) |
| Lost to follow up | 7 (16) |
| Doing well at 365 days, subsequently lost to follow up | 4 (9) |
| Started on MDR-TB treatment | 1 (2) |
| Died | 1 (2) |
IQR – Interquartile range;
Outcome at final evaluation
Discussion
In this observational study, the vast majority of children with “culture-confirmed” DR-TB who were asymptomatic on presentation at our specialist referral hospital remained well and did not require TB treatment during follow up. Two points require emphasis. Firstly, the study findings apply to asymptomatic children without any physical or radiological signs suggestive of TB. Secondly, if a watchful waiting approach is adopted then careful follow up for a period of at least 12 months should be ensured, and caregivers must be informed that onset of any suspicious symptoms require urgent re-evaluation.
We are uncertain as to why TB culture specimens were collected in these children, as they had no signs or symptoms suggestive of TB on presentation to the specialist hospital. Investigation at the referring facility may have been triggered by another infection such as acute viral or bacterial pneumonia, symptoms associated with recent primary M. tuberculosis infection (not disease), documented TB exposure or other risk factors.10,14 Although routine TB screening is advocated in children with close TB contact and in HIV-infected children, specimens should only be collected in the presence of signs or symptoms suggestive of possible active disease, even if these are of acute onset.15 On presentation at KDH more than a third of children were already on first-line TB treatment and, the possibility of mixed drug-susceptible and drug-resistant M. tuberculosis strains should be considered. However, mixed infections are highly unlikely in children given the paucibacillary nature of their disease, especially in the absence of visible chest radiograph abnormalities.16 Given the median delay of more than 2 months, those with mono-resistant TB may have responded to first-line TB treatment as could MDR-TB cases with low level INH resistance and susceptibility to EMB and PZA. Although this delay seems extremely long, delays of this length were not unusual prior to the introduction of Xpert MTB/RIF® in South Africa, due to the slow culture process (4-8 weeks), as well as transport and laboratory reporting inefficiencies.17,18
The possibility of inaccurate laboratory results arising from poor specimen labelling, administrative mistakes or specimen contamination should always be considered.7,8 Chances of specimen contamination increase in countries with high DR-TB disease burdens, due to the large number and high infectivity of specimens that laboratories process on a daily basis.19 The laboratory where these samples were processed serves as the provincial reference laboratory and has strict infection control measures. However, no specific protocols were in place to limit contamination of paediatric specimens, such as processing them in a separate room, use of a dedicated paucibacillary safety cabinet or workflow re-arrangement to ensure paediatric specimens are processed early in the morning before working with highly infectious adult specimens.
Detection of M. tuberculosis in respiratory specimens from asymptomatic children could have different explanations. Firstly, it could be explained by the natural history of infection, since children may transiently excrete live bacilli in the absence of active disease following recent primary infection. This phenomena was first documented in the 1930s when Wallgren recovered M. tuberculosis from recently infected children who were not clinically diseased.10,20 Secondly, current evidence suggests that latent TB infection is not a single state, but encompasses a spectrum ranging from inactive (latent) M. tuberculosis infection to periods of subclinical growth that is insufficient to cause lung damage.21,22 Thirdly, spontaneous cure is a remote possibility and has been well documented in the pre-chemotherapy era. A recent study from Cape Town, traced 17 children with “culture-confirmed” TB who were discharged from the hospital without TB treatment initiation.14 Eight of these children were found in good health, 4 were lost to follow up, 1 died of likely TB bronchopneumonia and 2 were subsequently started on TB preventive therapy by their local clinic. Whether a completely asymptomatic person with “culture-confirmed TB,” who has no clinical or radiological signs suggestive of active disease, represents a true case of TB, remains open for debate.23 We believe such children (if laboratory contamination has been ruled out) should be categorized as latent TB infection, rather than TB disease, as has been suggested in a consensus statement on research definitions for DR-TB in children.24 In TB endemic areas where both primary infection and reinfection are common,25 a reappraisal of TB case definitions seems warranted.23 The INH mono-resistant isolate collected from an axillary lymph node probably was M. bovis BCG, only partially identified as M. tuberculosis complex. Some BCG strains exhibit INH resistance and BCG vaccination is commonly associated with transient lymph adenitis.
Potential adverse effects should be carefully considered as part of the risk:benefit analysis before second-line TB therapy is commenced in an asymptomatic individual.23,26 One of the main reasons for enrolling study participants in an observation programme was the reluctance to use toxic second-line drugs without adequate justification. Serious drug-related adverse effects associated with DR-TB therapy include irreversible hearing loss, hypokalaemia, renal damage, hypothyroidism, depression and psychosis, while unpleasant effects include tinnitus, nausea and vomiting, joint pain, vertigo, peripheral neuropathy, anxiety and confusion.27 In patients with HIV-co-infection, adverse events do not appear to be more common, but can be more difficult to diagnose and manage, due to overlapping drug-toxicities with ART.26,28 While adverse effects associated with DR-TB therapy have been well-documented in adults,27 they have been under-investigated in young children,29-31 although treatment appears to be better tolerated than in adults. TB-associated stigma,32 prolonged hospitalization and repeated painful injections may also leave psychological scars. Additionally, because most MDR-TB medications do not have adequate paediatric formulations, adult pills have to be split, crushed or ground up resulting in inaccurate dosing with potentially sub-therapeutic or toxic drug levels.31,33 Finally, the pill burden in a MDR-TB/HIV co-infected child is excessive and children often experience vomiting and/or diarrhoea, leading to further uncertainty about the actual ingested dose and potentially detrimental impacts on HIV care.34
Few studies have assessed the management of asymptomatic DR-TB child contacts.29 South African guidelines recommend high-dose isoniazid preventive therapy for DR-TB child contacts ≤5 years, however, the value of this intervention is uncertain29 and adherence to unsupervised preventive therapy is poor.35,36 International guidelines and practices vary greatly, from advocating follow-up without medication,37,38 to the provision of two drugs to which the source case’s strain is susceptible.39 Although preventive therapy based on the likely source case’s susceptibility pattern seems logical and its value has been demonstrated in observational studies,40,41 the efficacy of MDR-TB prophylaxis has not been confirmed in any randomised control trial.30 Guidelines unanimously advise against the provision of preventive therapy until active disease has been ruled out, which is why we elected to closely monitor these children instead of providing preventive therapy. We acknowledge that preventive therapy may have been appropriate in children with proven M. tuberculosis infection once active disease was ruled out with certainty.
Our study was limited by its small size and the fact that it was implemented as a pragmatic observational trial in the public sector, a sector with human resource constraints. Although the intention was to monitor children every other month, follow up was at times inadequate and parents/caregivers were not contacted if a child failed to attend his or her appointment. We used data routinely collected by health workers, which was, at times, incomplete. In addition to the 1 child who died, 3 (7%) children were lost to follow-up before 1-year and we were unable to verify if these children had developed DR-TB or died. Nevertheless, a major strength of the study is that it reflects “real-life” dilemmas, which may not be apparent in a carefully controlled trial setting. We could not secure access to records from referring facilities and were unable to compare specimens collected at the referring centre to those collected at KDH. Only 3 children were known contacts of MDR-TB cases, but unknown expsosure to DR-TB is common in this high burden setting. Detailed assessment of potential laboratory cross-contamination was impossible, due to the time delay and large numbers of samples handled daily at the reference laboratory. The study highlights the importance of meticulous infection and quality control procedures in all TB laboratories, especially in high volume reference laboratories in TB endemic areas.
Conclusion
Our findings suggest that careful clinical assessment and close observation is a justifiable option in completely asymptomatic children with a bacteriological diagnosis of DR-TB. They also highlight the need for accurate disease description in the referral letter. It is critically important that practitioners and policy makers remain aware that a laboratory diagnosis in the absence of a consistent clinical picture may reflect laboratory error, cross-contamination or recent infection (primary or re-infection) in the absence of active disease. In such cases, the risk and cost of unnecessary treatment should be taken into consideration.
What is already known on this topic.
Diagnosing drug-resistant tuberculosis in children is challenging.
Most clinicians regard culture-confirmation as an indication for treatment, irrespective of clinical presentation or potential treatment-related adverse effects.
What This Study Adds.
Diagnostic certainty should be critically reviewed in children with “culture-confirmed” drug-resistant tuberculosis.
Asymptomatic children with "culture confirmed" drug-resistant tuberculosis with a normal chest radiograph may be carefully monitored without treatment.
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the KwaZulu-Natal Department of Health, Pietermartizburg, South Africa and thank all staff of the paediatric ward at King Dinuzulu Hospital Durban. We gratefully acknowledge the participants in the study.
Funding: This study was funded by a United Way Worldwide grant made possible by the Lilly Foundation on behalf of the Lilly MDR-TB Partnership.
Footnotes
Contributors’ Statements:
Marian Loveday: Dr. Loveday conceptualized and designed the study, analysed the data, drafted the initial manuscript, and approved the final manuscript as submitted.
Babu Sunkari: Dr. Sunkari conceptualized and designed the study, as the clinician saw all the children, collected the data, reviewed the manuscript, and approved the final manuscript as submitted.
Iqbal Master: Dr. Master conceptualized and designed the study reviewed the manuscript, and approved the final manuscript as submitted.
Ben Marais: Dr. Marais assisted with the analysis, critically reviewed and revised the manuscript, and approved the final manuscript as submitted.
James Brust: Dr. Brust assisted with the analysis, critically reviewed and revised the manuscript, and approved the final manuscript as submitted.
All authors approved the final manuscript as submitted and agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Competing interests None.
Ethics approval South African Medical Research Council Ethics Committee No: EC011-7/2013.
Contributor Information
Marian Loveday, Health Systems Research Unit, South African Medical Research Council, PO Box 19070, Tygerberg, 7505, South Africa.
Babu Sunkari, Drug-resistant TB Unit, King Dinuzulu Hospital, KwaZulu-Natal Department of Health, Durban, South Africa. babu.sunkari@kznhealth.gov.za.
Ben J Marais, Clinical School, Children’s Hospital at Westmead, University of Sydney, Australia. ben.marais@health.nsw.gov.au.
Iqbal Master, Drug-resistant TB Unit, King Dinuzulu Hospital, KwaZulu-Natal Department of Health, Durban, South Africa. iqbal.master@gmail.com.
James CM Brust, Department of Medicine, Montefiore Medical Center & Albert Einstein College of Medicine, Bronx, New York, USA. jcmbrust@gmail.com.
REFERENCES
- 1.World Health Organization . WHO/HTM/TB/2015.22. World Health Organisation; Geneva, Switzerland: 2015. Global tuberculosis report 2015. (http://www.who.int/tb/publications/global_report/en/) [Google Scholar]
- 2.Seddon J, Hesseling A, Willemse M, et al. Culture-confirmed multidrug-resistant tuberculosis in children: clinical features, treatment, and outcome. Clin Infect Dis. 2012;54:157–66. doi: 10.1093/cid/cir772. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Beyers N, Gie R, Schaaf H, et al. Delay in the diagnosis, notification and initiation of treatment and compliance in children with tuberculosis. Tubercle and Lung Disease. 1994;75:260–5. doi: 10.1016/0962-8479(94)90130-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Franck C, Seddon J, Hesseling A, et al. Assessing the impact of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis in children: an exploratory qualitative study. BMC Infectious Diseases. 2014;14(1):426. doi: 10.1186/1471-2334-14-426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Resch S, Salomon J, Murray M, et al. Cost-effectiveness of treating multidrug-resistant tuberculosis. PLoS medicine. 2006;3:e241. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.0030241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Tupasi T, Gupta R, Quelapio M, et al. Feasibility and cost effectiveness of treating multidrug-resistant tuberculosis: A cohort study in the Philippines. PLoS medicine. 2006;3(9):e352. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.0030352. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pmed.0030352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Van Rie A, Warren R, Richardson M, et al. Exogenous reinfection as a cause of recurrent tuberculosis after curative treatment. N Engl J Med. 1999;341:1174–9. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199910143411602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Demers A-M, Boulle A, Warren R, et al. Use of simulated sputum specimens to estimate the specificity of laboratory-diagnosed tuberculosis. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2010;14:1016–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Marais B, Gie R, Schaaf H, et al. Childhood pulmonary tuberculosis: old wisdom and new challenges. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2006;173:1078–90. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200511-1809SO. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Marais B, Gie R, Schaaf H, et al. The natural history of childhood intrathoracic tuberculosis: a critical review of literature from the pre-chemotherapy era. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2004;8:392–402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Seddon J, Thee S, Jacobs K, et al. Hearing loss in children treated for multidrug-resistant tuberculosis. J Infect Dis. 2013;66:320–29. doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2012.09.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Centers for Disease Control and Prevention . Growth charts. CDC; Atlanta, GA, USA: 2010. http://www.cdc.gov/growthcharts/. (Last accessed 28-03-2015) [Google Scholar]
- 13.Seddon J, Hesseling A, Willemse M, et al. Culture-Confirmed Multidrug-Resistant Tuberculosis in Children: Clinical Features, Treatment, and Outcome. Clinical Infectious Diseases. 2012;54:157–66. doi: 10.1093/cid/cir772. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Engelbrecht A, Marais B, Donald P, et al. A critical look at the diagnostic value of culture-confirmation in childhood tuberculosis. Journal of Infection. 2005;53(6):364–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2005.12.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Chihota V. Health care worker TB investigation practices: did Xpert MTB/RIF change testing practice?; 45th Union World Conference on Lung Health Barcelona; Spain. 2014. pp. 651–30. [Google Scholar]
- 16.Perez-Velez C, Marais B. Tuberculosis in children. N Engl J Med. 2012;367(4):348–61. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra1008049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Narasimooloo R, Ross A. Delay in commencing treatment for MDR TB at a specialised TB treatment centre in KwaZulu-Natal. S Afr Med J. 2012;102(6):6–360. doi: 10.7196/samj.5361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Loveday M, Wallengren K, Brust J, et al. Community-based care vs. centralised hospitilisation for MDR-TB patients KwaZulu-Natal. South Africa Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2015;19(2):163–71. doi: 10.5588/ijtld.14.0369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.van Kampen S, Anthony R, Klatser P. The realistic performance achievable with mycobacterial automated culture systems in high and low prevalence settings. BMC Infectious Diseases. 2010;10(1):93. doi: 10.1186/1471-2334-10-93. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Wallgren A. Primary pulmonary tuberculosis in childhood. Am J Dis Child. 1935;49:1105–36. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Barry CE, 3rd, Boshoff H, Dartois V, et al. The spectrum of latent tuberculosis: rethinking the biology and intervention strategies. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2009;7(12):12–845. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Cardona P. Revisiting the natural history of tuberculosis. The inclusion of constant reinfection, host tolerance, and damage-response frameworks leads to a better understanding of latent infection and its evolution towards active disease. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz) 2010 Feb;58(1):1–7. doi: 10.1007/s00005-009-0062-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Marais B. Does finding M. tuberculosis in sputum always equal tuberculosis disease? Am J Resp Crit Care. 2010;181:195–6. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.181.2.195a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Seddon J, Perex-Velez C, Schaaf H, et al. Consensus statement on research definitions for drug-resistant tuberculosis in children. J Ped Infect Dis Soc. 2013;2(2):2–100. doi: 10.1093/jpids/pit012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Verver S, Warren R, Beyers N, et al. Rate of reinfection tuberculosis after successful treatment is higher than rate of new tuberculosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2005;171:1430–35. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200409-1200OC. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Brust J, Shah S, van der Merwe T, et al. Adverse events in an integrated, home-based treatment program for MDR-TB and HIV in KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. J Acq Immune Def Syndr. 2013;62:436–40. doi: 10.1097/QAI.0b013e31828175ed. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Wu S, Zhang Y, Sun F, et al. Adverse Events Associated With the Treatment of Multidrug-Resistant Tuberculosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Am J Therapeutics. 2013:10. doi: 10.1097/01.mjt.0000433951.09030.5a. 1097/01.mjt.0000433951.09030.5a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Isaakidis P, Varghese B, Mansoor H, et al. Adverse events among HIV/MDR-TB co-infected patients receiving antiretroviral and second line anti-TB treatment in Mumbai, India. PLoS One. 2012 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0040781. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0040781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Seddon J, Godfrey-Faussett P, Hesseling A, et al. Management of children exposed to multidrug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Lancet Infect Dis. 2012;12(6):6–469. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(11)70366-8. doi: 10.1016/S473-3099(11)70366-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Schaaf H, Garcia-Prats A, Hesseling A, et al. Managing multidrug-resistant tuberculosis in children: review of recent developments. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2014;27:211–19. doi: 10.1097/QCO.0000000000000062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Seddon J, Hesseling A, Marais B, et al. Paediatric use of second-line anti-tuberculosis agents: a review. Tuberculosis. 2012;92:9–17. doi: 10.1016/j.tube.2011.11.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Murray EJ, Bond VA, Marais BJ, et al. High levels of vulnerability and anticipated stigma reduce the impetus for tuberculosis diagnosis in Cape Town, South Africa. Health Policy and Planning. 2012 Sep;2:1–9. doi: 10.1093/heapol/czs072. DOI 10.1093/heapol/czs072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Marais B, Schaaf H. Childhood tuberculosis: an emerging and previously neglected problem. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2010;24:727–49. doi: 10.1016/j.idc.2010.04.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Marais B, Rabie H, Cotton M. TB and HIV in children – advances in prevention and management. Paediatr Respir Rev. 2011;12:39–45. doi: 10.1016/j.prrv.2010.09.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.van Zyl S, Marais B, Hesseling A, et al. Adherence to anti-tuberculosis chemoprophylaxis and treatment in children. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2006;10:13–18. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Marais B, van Zyl S, Schaaf H, et al. Adherence to isoniazid preventive chemotherapy: a prospective community based study. Arch Dis Child. 2006;91(9):762–65. doi: 10.1136/adc.2006.097220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.World Health Organization Stop TB Partnership Childhood TB Subgroup. Chapter 4: childhood contact screening and management. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2007;11:12–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.NICE. CG117 . Clinical diagnosis and management of tuberculosis, and measures for its prevention and control. National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence; London: 2011. Tuberculosis. https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/cg117/chapter/guidance (last accessed 11-08-2015) [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Centers for Disease Control A, Georgia, USA, Management of persons exposed to multidrug-resistant tuberculosis. MMWR Recomm Rep; 1992. pp. 61–71. www.cdc.gov/mmwr/preview/mmwrhtml/00031296.htm (last accessed 11-08-2015) [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Schaaf H, Gie RP, Kennedy M, et al. Evaluation of young children in contact with adult multidrug-resistant pulmonary tuberculosis: a 30-month follow-up. Pediatrics. 2002;109:765–71. doi: 10.1542/peds.109.5.765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Kritski A, Marques M, Rabahi M, et al. Transmission of tuberculosis to close contacts of patients with multidrug-resistant tuberculosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1996;153:331–35. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.153.1.8542139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]