Abstract
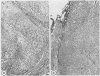
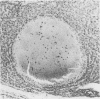
In a consecutive medicolegal necropsy series benign hepatic tumours and tumour like conditions occurred in 52% of the 95 men aged 35-69 years. The incidence increased with age, mainly due to small bile duct tumours (n = 26; mean age 56.7 years; p less than 0.01; mean size 1.3 mm). The next most common tumours were cavernous hemangiomas (n = 19; mean age 53.9 years; mean size 5.2 mm) that were not related to age. Focal nodular hyperplasia (n = 3; mean size 8.0 mm) tended to occur in a younger age group (mean age 40.3 years; p less than 0.001). Multiple bile duct tumours were present in 46% and hemangiomas in 50% of the men studied. Liver cell adenoma, nodular regenerative hyperplasia, and peliosis hepatis were incidental findings (one case of each). Nodular regenerative hyperplasia was associated with the consumption of alcohol and a total dose of 21.5 g of testosterone. These results indicate that benign hepatic tumours and tumour like conditions are not rare in men but may remain undetected because of their small size.
Full text
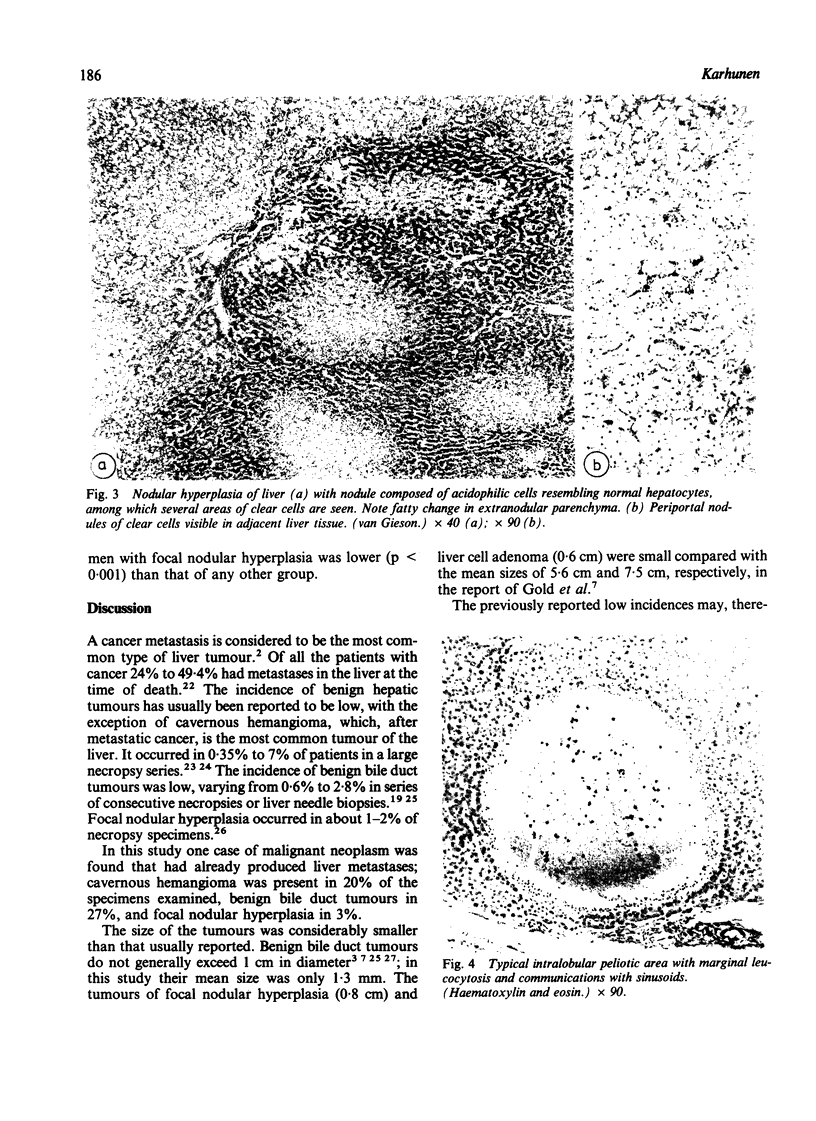
PDF
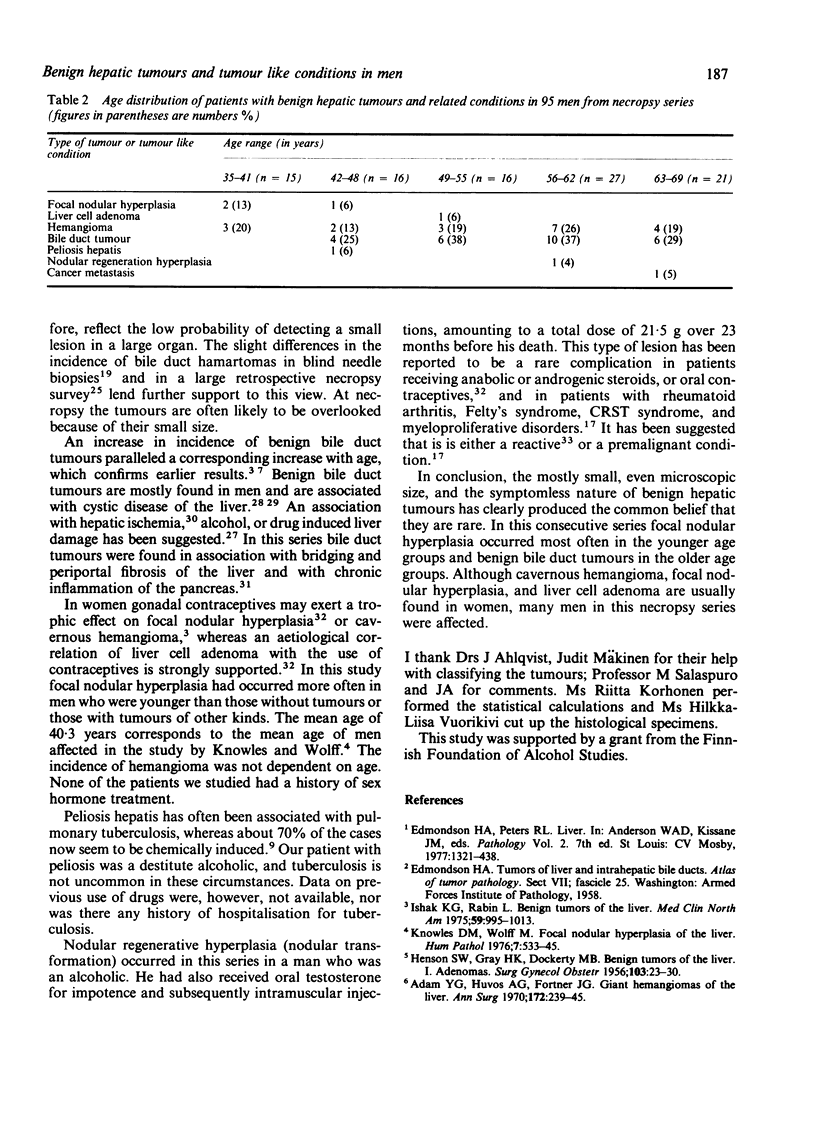

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ABRAMS H. L., SPIRO R., GOLDSTEIN N. Metastases in carcinoma; analysis of 1000 autopsied cases. Cancer. 1950 Jan;3(1):74–85. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(1950)3:1<74::aid-cncr2820030111>3.0.co;2-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adam Y. G., Huvos A. G., Fortner J. G. Giant hemangiomas of the liver. Ann Surg. 1970 Aug;172(2):239–245. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197008000-00010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang W. W., Agha F. P., Morgan W. S. Primary sarcoma of the liver in the adult. Cancer. 1983 Apr 15;51(8):1510–1517. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19830415)51:8<1510::aid-cncr2820510826>3.0.co;2-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christopherson W. M., Mays E. T., Barrows G. A clinicopathologic study of steroid-related liver tumors. Am J Surg Pathol. 1977 Mar;1(1):31–41. doi: 10.1097/00000478-197701010-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung E. B. Multiple bile-duct hamartomas. Cancer. 1970 Aug;26(2):287–296. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197008)26:2<287::aid-cncr2820260207>3.0.co;2-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FELDMAN M. Hemangioma of the liver; special reference to its association with cysts of the liver and pancreas. Am J Clin Pathol. 1958 Feb;29(2):160–162. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/29.2.160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold J. H., Guzman I. J., Rosai J. Benign tumors of the liver. Pathologic examination of 45 cases. Am J Clin Pathol. 1978 Jul;70(1):6–17. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/70.1.6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HENSON S. W., Jr, GRAY H. K., DOCKERTY M. B. Benign tumors of the liver. I. Adenomas. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1956 Jul;103(1):23–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henning H., Friedrich K., Lüders C. J. Laparoskopischer Aspekt und klinische Relevanz von Cholangiofibromen. Z Gastroenterol. 1982 Dec;20(12):744–751. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homer L. W., White H. J., Read R. C. Neoplastic transformation of v. Meyenburg complexes of the liver. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1968 Oct;96(2):499–502. doi: 10.1002/path.1700960231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishak K. G., Rabin L. Benign tumors of the liver. Med Clin North Am. 1975 Jul;59(4):995–1013. doi: 10.1016/s0025-7125(16)31998-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato M., Sugawara I., Okada A., Kuwata K., Satani M. Hemangioma of the liver. Diagnosis with combined use of laparoscopy and hepatic arteriography. Am J Surg. 1975 Jun;129(6):698–703. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(75)90350-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles D. M., Wolff M. Focal nodular hyperplasia of the liver: a clinicopathologic study and review of the literature. Hum Pathol. 1976 Sep;7(5):533–545. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(76)80101-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MELNICK P. J. Polycystic liver; analysis of seventy cases. AMA Arch Pathol. 1955 Feb;59(2):162–172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madayag M. A., Bosniak M. A., Kinkhabwala M., Becker J. A. Hemangiomas of the liver in patients with renal cell carcinoma. Radiology. 1978 Feb;126(2):391–394. doi: 10.1148/126.2.391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyai K., Bonin M. L. Nodular regenerative hyperplasia of the liver. Report of three cases and review of the literature. Am J Clin Pathol. 1980 Feb;73(2):267–271. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/73.2.267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OCHSNER J. L., HALPERT B. Cavernous hemangioma of the liver. Surgery. 1958 Apr;43(4):577–582. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popovsky M. A., Costa J. C., Doppman J. L. Meyenburg complexes of the liver and bile cysts as a consequence of hepatic ischemia. Hum Pathol. 1979 Jul;10(4):425–432. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(79)80048-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spech H. J., Liehr H. Peliosis hepatis. Eine klinische Bestandsaufnahme. Z Gastroenterol. 1982 Dec;20(12):710–721. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stromeyer F. W., Ishak K. G. Nodular transformation (nodular "regenerative" hyperplasia) of the liver. A clinicopathologic study of 30 cases. Hum Pathol. 1981 Jan;12(1):60–71. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(81)80242-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas D. B. Role of exogenous female hormones in altering the risk of benign and malignant neoplasms in humans. Cancer Res. 1978 Nov;38(11 Pt 2):3991–4000. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thommesen N. Biliary hamartomas (von Meyenburg complexes) in liver needle biopsies. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand A. 1978 Mar;86(2):93–99. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1978.tb02019.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wetzel W. J., Alexander R. W. Focal nodular hyperplasia of the liver with alcoholic hyalin bodies and cytologic atypia. Cancer. 1979 Oct;44(4):1322–1326. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197910)44:4<1322::aid-cncr2820440424>3.0.co;2-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]