Abstract
Background
Pseudomonas syringae infects diverse plant species and is widely used in the study of effector function and the molecular basis of disease. Although the relationship between bacterial metabolism, nutrient acquisition and virulence has attracted increasing attention in bacterial pathology, there is limited knowledge regarding these studies in Pseudomonas syringae. The aim of this study was to investigate the function of the carA gene and the small RNA P32, and characterize the regulation of these transcripts.
Results
Disruption of the carA gene (ΔcarA) which encodes the predicted small chain of carbamoylphosphate synthetase, resulted in arginine and pyrimidine auxotrophy in Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato DC3000. Complementation with the wild type carA gene was able to restore growth to wild-type levels in minimal medium. Deletion of the small RNA P32, which resides immediately upstream of carA, did not result in arginine or pyrimidine auxotrophy. The expression of carA was influenced by the concentrations of both arginine and uracil in the medium. When tested for pathogenicity, ΔcarA showed reduced fitness in tomato as well as Arabidopsis when compared to the wild-type strain. In contrast, mutation of the region encoding P32 had minimal effect in planta. ΔcarA also exhibited reduced motility and increased biofilm formation, whereas disruption of P32 had no impact on motility or biofilm formation.
Conclusions
Our data show that carA plays an important role in providing arginine and uracil for growth of the bacteria and also influences other factors that are potentially important for growth and survival during infection. Although we find that the small RNA P32 and carA are co-transcribed, P32 does not play a role in the phenotypes that carA is required for, such as motility, cell attachment, and virulence. Additionally, our data suggests that pyrimidines may be limited in the apoplastic space of the plant host tomato.
Electronic supplementary material
The online version of this article (doi:10.1186/s12866-016-0819-z) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
Keywords: Pseudomonas syringae pv tomato, CarAB, P32, Virulence, Swarming, Biofilm formation
Background
The model plant pathogen Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato DC3000 (DC3000) infects tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) and Arabidopsis thaliana (reviewed in [1]). DC3000 enters the apoplastic space through wounds or natural openings in the leaf, like stomata, and grows in intercellular spaces. As the infection progresses, the pathogen releases virulence factors such as the phytotoxin coronatine and injects effector proteins into host cells through the type III secretions system (T3SS). In a susceptible host, chlorosis (yellowing) of the leaves occurs and necrotic lesions develop. Alternatively in a non-host, such as Nicotiana benthamiana, a defense-associated hypersensitive response (HR) is elicited.
Most investigations of pathogenicity in P. syringae have focused on identifying and characterizing components of the T3SS [2], non-ribosomal peptides [3] and toxins [4, 5]. While these are clearly important, pathogenic bacteria must also compete successfully for limited nutrients within the host, with iron as a well-known example [6]. Unfortunately, it is not well-understood how metabolic processes in plant pathogens contribute to virulence, although experiments using IVET (in vivo expression technology) have identified a variety of bacterial genes expressed during plant-pathogen interactions as well as during host colonization [7–15]. These studies revealed the importance of genes involved in metabolism to the infection process.
Several lines of evidence suggest links between bacterial pathogenicity and metabolism. The disruption of genes involved in acquisition of nutrients such as carbon result in reduced virulence in human and animal pathogens [16–21]. As for plant pathogens, a number of metabolically related genes were identified as required for infection of shoots of apple trees by Erwinia amylovora [22] and it was shown that P. savastanoi pv savastanoi requires genes directly involved in metabolism in order to survive in olive knots [23]. Arginine metabolism and regulation are associated with the virulence of several pathogenic bacteria such as Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Listeria monocytogenes, Legionella pneumophila, and Mycobacterium bovis [24–27]. Recently Ramos et al. showed that an argD mutant in the plant pathogen Erwinia amylovora was non-pathogenic [28].
Our laboratory is interested in the identification and characterization of small RNAs in P. syringae. Livny et al. reported a Pseudomonas-specific small RNA (named P32) transcribed from an orthologous region upstream from the carABgreA operon in Pseudomonas aeruginosa [29]. The expression of P32 was confirmed by Northern blot and a transcript of about 80 bases was detected in rich medium during exponential growth and stationary phase cultures. No other function has been described for this regulatory RNA. This region is also present in the genome of DC3000. While conducting a genome-wide mapping of mRNA 5′ends in DC3000, we identified a potential transcriptional start site 118 bases upstream of carA [30]. The carAB genes encode the enzyme carbamoylphosphate synthetase (CPSase), which catalyzes the synthesis of carbamoylphosphate, a precursor of arginine and pyrimidines. Further analysis revealed a putative RpoD promoter a short distance upstream from the start site, as well as a potential rho-independent terminator located between the start site and the first codon of carA. The promoter may be associated with two overlapping transcripts, a shorter one utilizing the Rho-independent terminator, and a longer one that includes carA, carB, and greA (pseudomonas.com). Consistent with this model, we observed expression in the region encompassing the 5′UTR, carA, carB, and greA in a transcriptome analysis of the DC3000 genome [31] and detected transcriptional activity in the same region during a search for small RNAs using RNA-Seq (unpublished). Regulation of the carABgreA operon in P. aeruginosa is controlled both by arginine at the transcriptional level and also by pyrimidines, possibly through an attenuation mechanism [32, 33]. carAB mutants of Pseudomonas spp. strain G are auxotrophic for arginine as well as pyrimidines [34]. In addition, these mutants are deficient in extracellular polysaccharide production. The function of carbamoyl-phosphate synthase and P32 has not been well characterized in plant pathogenic bacteria. Just recently it was demonstrated that disruption of carB in Xanthomonas citri, resulted in loss of pathogenicity and inability to elicit a hypersensitive reaction in non-hosts, whereas disruption of carA did not affect these phenotypes [35]. However, disruption of carB resulted in reduced swimming and reduced ability to form biofilms [36].
The regulation of P32 as well as carAB and their potential contribution to virulence has not been investigated in P. syringae. In this study, we investigated P32 and its involvement in the regulation of carA in P. syringae. We found that carA is important for growth and fitness in planta and demonstrated the likely importance of uracil during infection. In contrast, P32 appears to be involved in carA regulation and does not have an obvious role in planta, although P32 is part of the same transcriptional unit as carA.
Results
Effect of P32 and carA deletions on growth of DC3000
In previous work, a MEME analysis of DC3000 genomic regions immediately upstream from captured RNA 5′ ends revealed a candidate RpoD promoter adjacent to the putative small RNA P32 [30]. P32 is located immediately upstream of PSPTO_4502 (carA) (Fig. 1). In other organisms the products of carA and carB are involved in the biosynthesis of arginine and pyrimidines [37] and carA mutants have been shown to require arginine for optimal growth [38–41]. We hypothesized that P32 may also be involved in these pathways since it closely neighbors carA. To test the involvement of P32 and CarA in arginine and pyrimidine biosynthesis we constructed two deletion mutants, one in which P32 was deleted and another in which carA was deleted. Deletions were confirmed by PCR and sequencing (data not shown). The transcript for carA could still be detected in the P32 deletion mutant indicating transcription of carA can occur in the absence of the genomic region containing P32 (Additional file 1: Figure S1). Growth of the P32 deletion mutant was comparable to that of the wild-type strain DC3000 in rich medium KB, minimal medium MG, and minimal medium VBMM (Fig. 2). In contrast, the carA mutant displayed a growth defect when grown in rich medium, and minimal media MG and VBMM. The growth defect was abolished by the simultaneous addition of arginine and uracil to VBMM. Also, complementation of the carA mutant by expressing the coding region of carA on a plasmid, restored growth to wild type levels (Additional file 1: Figure S2), indicating that the carA gene was solely responsible for the phenotype observed. Overall the data suggests that P32 is not required for expression of carA and that carA is involved in metabolism of arginine and uracil.
Fig. 1.

Genomic sequence of the genomic region containing P32. The transcriptional start site (reported in Filiatrault et al., 2011) is denoted with an arrow and marked as +1. The putative RpoD-dependent promoter sequence (MEME motif 1;[30]) is underlined. Boxed areas represent the −35 and −10 sites. The ArgR binding sites reported for Pseudomonas aeruginosa [42] consisting of two half sites in direct repeat arrangement, is indicated by brackets. A predicted terminator and inverted repeat is denoted by the convergent arrows. The mapped 3' end is denoted by the asterisk. The “M” represents the methionine start codon for CarA and “T” is the symbol for the amino acid threonine. 42 bp denotes the base pairs between the end of the coding region of DapB and the putative ArgR binding site. 45 bp denotes the base pairs from the mapped 3′end of P32 to the translational start site of CarA
Fig. 2.
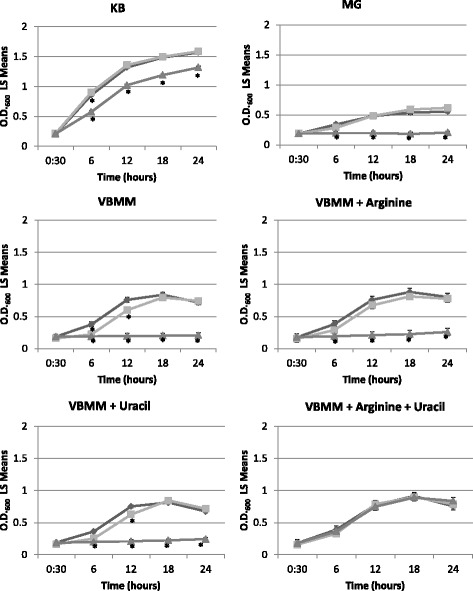
CarA influences growth in minimal medium. Growth of wild type DC3000 (dark gray diamonds), ΔP32 (light gray squares) and ΔcarA (light grey triangles) in KB, MG, VBMM, VBMM supplemented with 40 mM arginine or with 10 mM uracil, and VBMM supplemented with 40 mM arginine and 10 mM uracil. Growth is represented as least squares means with standard error of O.D.600 over time. The data shown represent three biological replicates per strain, each with three technical replicates. Post hoc comparisons were performed using Tukey HSD (α = 0.05). For each time point, the values which are significantly different from the wild type are shown with an asterisk. Statistical analyses were performed using JMP Pro 11
Expression of P32 and carA in DC3000
In P. aeruginosa, the expression of carA is controlled by both pyrimidines and arginine [32, 33]. To investigate if P32 influences the expression of carA in P. syringae, we performed a series of transcriptional analyses. First, to confirm transcriptional activity and to verify the 3′ end of P32 we performed 3′ RACE. A 3′ end was identified at nucleotide position 5073275c, immediately downstream from the predicted Rho-independent terminator (Fig. 1). The presence of a 3′end in this region could occur as a result of several events. One possibility is that distinct promoters produce two separate transcripts, one containing P32 and another containing carA, carB, and greA. Alternatively a transcript could arise from a single transcriptional start site, but under certain conditions termination or cleavage/processing could result in the generation of a small transcript containing P32 alone. Our 5′end mapping data did not detect another transcriptional start site for carA [30] although our transciptome survey detected expression through the entire P32-carA-carB-greA operon [31]. A second 5′ mapping experiment using fluorescently labeled oligonucleotide extension (FLOE) detected a single transcriptional start site using RNA isolated from cells grown in VBMM and VBMM supplemented with arginine and uracil (data not shown). This suggests that expression of the entire P32 –carA region may be under the control of a single promoter, as is the case in P. aeruginosa [32, 33].
To investigate if P32 is co-transcribed with carA, RNA was isolated from cells grown under rich or growth-limiting conditions. cDNA synthesis was performed and used for bridging PCR with different primer pairs to identify RNA that consists of both P32 and carA (see Fig. 3a). Products were obtained with each primer set using RNA from bacteria grown with or without arginine and uracil (Fig. 3b). This suggests that P32 and carA are co-transcribed under the conditions tested. These data also indicate that carA is transcribed even in the presence of arginine and uracil.
Fig. 3.
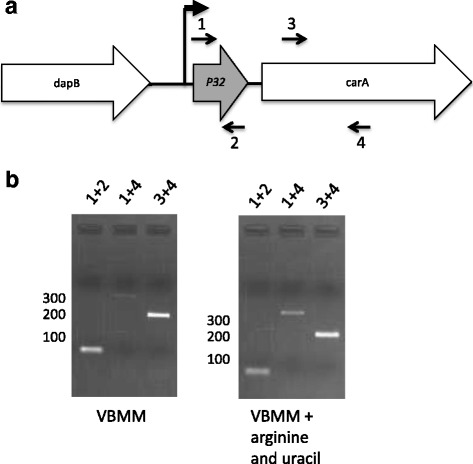
Co-transcription of P32 and carA. a Map of the genomic region containing dapB, P32 and carA in DC3000. The locations and orientations of RT- and PCR primers are indicated. b Agarose gel electrophoresis result of the RT-PCR experiments using the primers pairs indicated. The expected length of the PCR products for the primer pairs are as follows: Primer pair 1 and 2, ~54 bps; primer pair 1 and 4, ~370 bps; and primer pair 3 and 4, ~209 bps. Control reactions in which reverse transcriptase was omitted were performed for each primer set and RNA sample
To further investigate the regulation of P32 and carA we created promoter fusions and evaluated their expression in the wild-type strain (Fig. 4, top panel). The promoter fusions consisted of either the entire intergenic region between dapB (PSPTO_4503) and carA, including P32 (referred to as P1), the region from the 3′ end of dapB to the first half of the Rho-independent terminator, which therefore lacks ½ of the stem-loop (referred to as P3), the region from the 3′end of dapB to the beginning of the stem-loop (lacks the entire stem-loop and all sequence downstream; referred to as P4), P32 and downstream sequences up to carA (lacks putative promoter sequence; referred to as P5), or the region between the 3′ end of P32 and carA (lacks putative promoter region and P32; P6). Fusions lacking the putative promoter region (P5 and P6) were expressed at background levels in VBMM or VBMM supplemented with arginine or uracil (Fig. 4). This is consistent with the single mapped transcriptional start site for carA and P32 and the co-expression data that indicates P32 and carA are transcribed together from a single promoter under these conditions. In addition, we observed an increase in expression when the stem-loop structure was disrupted (P3) or completely removed (P4) compared to the full-length fusion P1. We conclude that this feature is important in modulating the expression of carA.
Fig. 4.

Expression of P32 and carA. a Regions of varying lengths upstream to the carA coding region were cloned into lux reporter constructs; the regions they span are shown graphically. The inverted arrows represent the predicted stem-loop of the Rho-independent terminator. (b) Expression from lux promoter fusions were evaluated in VBMM medium (black squares), VBMM supplemented with 40 mM arginine (dark gray triangles), VBMM supplemented with 10 mM uracil (light gray circles), and VBMM supplemented with 40 mM arginine and 10 mM uracil (dark gray diamonds). Data shown are the least squares means (LS Means) with standard error of normalized luminescence (lux) values over time, derived from at least 3 independent biological replicates for each promoter fusion-medium combination, each containing 2–3 technical replicates. Note that the scales for each panel are different in order to clearly show statistically different data points. For each time point, the values which are significantly different from VBMM are shown with an asterisk (using Tukey HSD, α = 0.05). Normalized luminescence (lux) is the ratio of luminescence to OD600. Statistical analysis was performed using the program JMP Pro11
Interestingly, when arginine was added to the medium we observed an increase in expression from promoter fusions P1, P3 and P4 (Fig. 4). The addition of uracil resulted in a decrease in expression of lux from the promoter fusions P1. The addition of both arginine and uracil had little effect on the expression of the promoter fusions.
To further investigate the expression of P32 and carA, qRT-PCR was performed with RNA isolated from wild-type cells grown in VBMM and VBMM supplemented with 40 mM arginine and 10 mM uracil. Although transcripts for P32 and carA were detected in both growth conditions, no difference in expression was observed between cells grown in VBMM or VBMM supplemented with arginine and uracil (data not shown). This is consistent with the promoter fusion data.
ArgR regulates expression of P32 and carA
ArgR binds to a region upstream of carA in P. aeruginosa [33, 42]. Although ArgR can act as a repressor or activator, in P. aeruginosa it has been shown to act as a repressor of carA expression [42]. Because the predicted binding site for ArgR, TGTCGCN8AAN5 appears to be conserved in P. syringae (Fig. 1), we hypothesized that ArgR would also regulate P32 and/or carA in P. syringae. We analyzed the expression levels of P32 and carA in the ΔargR mutant and wild-type DC3000 using qRT-PCR. Our results show that expression of P32 is increased in the ΔargR mutant compared to the wild-type strain at mid-log and stationary phases, while carA expression is increased during mid-log phase (Fig. 5). These observations indicate that ArgR likely acts as a repressor of P32 and carA in DC3000.
Fig. 5.
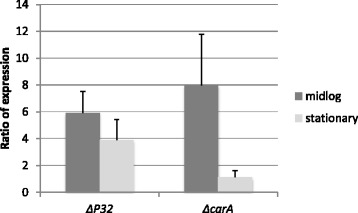
Expression of P32 and carA in wild-type DC3000 compared to ΔargR mutant using qRT-PCR. The dark gray bars represent the ratios of the transcripts comparing ΔargR mutant to the WT at mid-log phase, and the light gray bars represent the ratios of the transcripts comparing ΔargR mutant to the WT at stationary phase. RNA samples were normalized using gap1. The ΔargR mutant shows increased levels of P32 and carA transcript compared to the WT at mid-log phase. The levels of P32 and carA transcripts were analyzed by calculating the fold difference of transcript levels between WT and ΔargR mutant using the Δ Ct method. Data shown are the average and standard deviation of three independent biological replicates
Examining the contribution of P32 and carA to virulence
To test the involvement of P32 and CarA in virulence, tomato plants were dipped in suspensions of wild-type, ΔP32 mutant, and the ΔcarA mutant. The ΔcarA mutant displayed less intense disease symptoms and reduced bacterial growth on days 5 and 7 post-inoculation compared to the wild type (Fig. 6). Although ΔP32 growth was similar to wild- type, it displayed reduced symptoms (Fig. 6). However, the symptoms caused by the ΔP32 mutant were more intense than ΔcarA mutant.
Fig. 6.
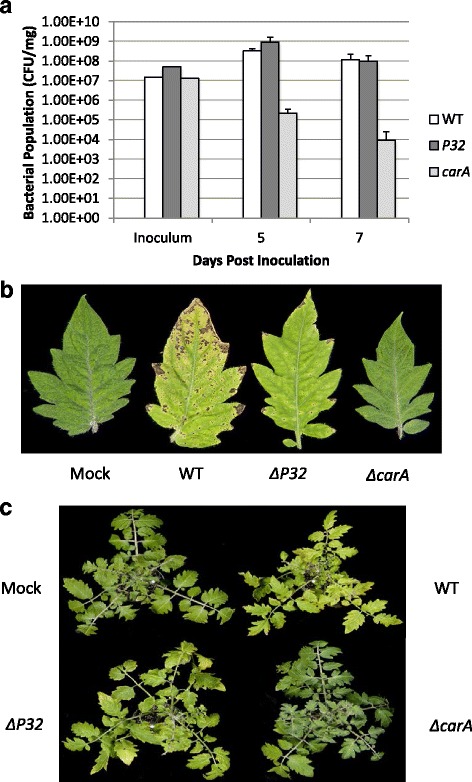
carA contributes to fitness in tomato. a Four-week-old Tomato cv. MoneyMaker tomato plants were dipped in suspensions containing 1 × 107 CFU ml−1 of WT, ΔP32, or ΔcarA. At the time points indicated, bacteria were extracted from leaves and plated on KB containing rifampicin for enumeration. The values shown are the average CFU/mg with standard deviation from three plants per strain. Similar results were obtained in two repetitions of the experiment. b Tomato leaves photographed at 7 dpi (c) Whole tomato plants photographed at 7 dpi
Since the ΔcarA mutant had reduced virulence in tomato, we tested the ability of this mutant and ΔP32 to cause disease in A. thaliana seedlings. ΔP32 grew to similar levels as the wild type (Fig. 7a). In addition, the chlorotic symptoms caused by ΔP32 were also similar to wild type (Fig. 7b). Based on these data, it is unlikely that ΔP32 plays a substantial role in virulence in DC3000. However, the ΔcarA mutant displayed reduced growth and was not able to cause the same necrotic symptoms as the WT (Fig. 7a and b), suggesting that carA is necessary for growth and fitness in planta.
Fig. 7.
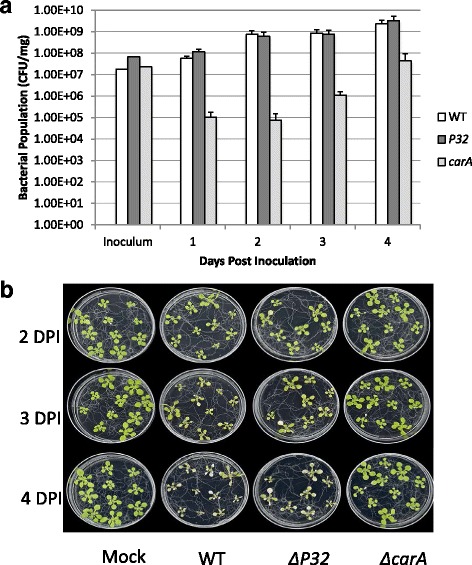
carA contributes to fitness in Arabidopsis seedlings. a Arabidopsis seedlings were inoculated with suspensions containing 1 × 107 CFU ml−1 of WT, ΔP32, or ΔcarA. At the time points shown, bacteria were extracted from leaves and plated on KB containing rifampicin for enumeration. The values shown are the average CFU/mg with standard deviation of three seedlings per strain. The experiment was repeated twice with similar results. b Disease phenotype of Arabidopsis seedlings flood-inoculated with a bacterial suspension of WT, ΔP32, or ΔcarA. Mock-inoculated seedlings were flooded with sterile distilled H2O containing 0.025 % Silwet L-77. Photographs were taken 2, 3, and 4 dpi
Growth of ΔP32 and ΔcarA in apoplastic fluid
During infection, P. syringae obtains its nutrients from the apoplast. Therefore to investigate whether the observed reduction in growth in planta was due to nutrient limitation, we compared the growth of wild-type DC3000, ΔP32, and ΔcarA in apoplastic fluid extracts. The wild-type strain and the ΔP32 mutant demonstrated similar growth. However, growth of ΔcarA was lower than the wild-type at earlier time points in apoplastic fluid with or without arginine. However, ΔcarA was able to achieve growth levels similar to wild type at later time points (Fig. 8). In apoplastic fluid supplemented with uracil or both arginine and uracil, ΔcarA and ΔP32 growth characteristics were similar to wild type, with no significant differences detected between the strains at all time points (Fig. 8).
Fig. 8.
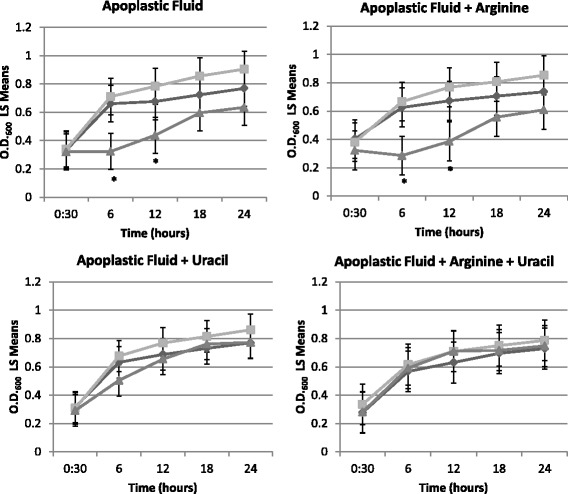
CarA contributes to growth in apoplastic fluid. Growth of wild type DC3000 (dark gray diamonds), ΔP32 (light gray squares) and ΔcarA (light grey triangles) in apoplastic fluid, apoplastic fluid supplemented with 40 mM arginine or 10 mM uracil, and apoplastic fluid supplemented with 40 mM arginine and 10 mM uracil. Growth is represented as least squares means (LS Means) with standard error of O.D.600 over time. The data shown represent 3 biological replicates per strain, each with 3 technical replicates. Post hoc comparisons were performed using Tukey HSD (α = 0.05). For each time point, the values which are significantly different from wild-type are shown with an asterisk. Statistical analyses were performed using JMP Pro 11
ΔcarA is reduced in motility
The reduced virulence observed with the ΔcarA mutant could be solely due to the inability to grow in vivo or the inability to produce other factors related to virulence. Because carA is induced in Salmonella cells that are swarming compared to cells that are in a vegetative state, and has been implicated in motility [43], we tested the ability of the ΔcarA mutant to swarm. Since the ΔcarA mutant does not grow as efficiently as the wild-type strain in minimal media, the assay was conducted in nutrient agar, a rich medium that is used to test swarming of P. aeruginosa. All strains grew equally in this medium (data not shown). As shown in Fig. 9a, the wild-type strain, ΔargR mutant and ΔP32 mutant swarmed equally (Fig. 9a) in this medium while the ΔcarA mutant exhibited reduced swarming (ANOVA, P-value <0.004 and Tukey HSD, P-values <0.01) (Fig. 9a). Motility was also examined using a soft agar to test for functional flagella. The ΔcarA mutant showed reduced swimming compared to the wild-type, ΔargR mutant and ΔP32 mutant (ANOVA P-value < 0.002; Tukey HSD P-value <0.05) (Fig. 9b).
Fig. 9.
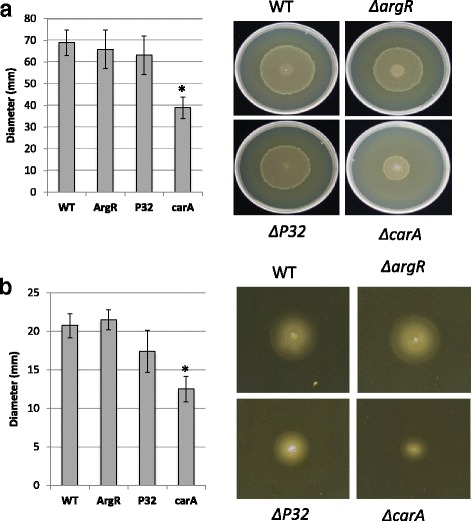
Disruption of carA impairs motility. a Swarming of Pseudomonas syringae DC3000, ΔargR, ΔP32, and ΔcarA after 24 h. b Diameter of swimming colonies of Pseudomonas syringae DC3000, ΔargR, ΔP32, and ΔcarA after 24 h. The error bars represent the standard deviation of the mean. Data were analyzed by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Tukey HSD for pair-wise comparisons. Asterisks indicates significant difference for swarming (ANOVA, P-value <0.004 and Tukey HSD, P-values <0.01) and swimming (P-value < 0.002 using ANOVA; P-values <0.05 using Tukey HSD)
Deletion of carA affects cell attachment
Since motility plays an important role in the ability of the bacteria to colonize different environments and attach to surfaces, we examined the ΔcarA mutant using the microtiter dish assay that has become a standard tool for the study of the early stages in biofilm formation [44]. The ΔcarA mutant showed a statistically significant (P < 0.003 by ANOVA; P < 0.01 using Tukey HSD) increase in biofilm formation in comparison to the wild type (Fig. 10). No observable growth differences were observed when the OD600 of planktonic cells was measured as a function of time during the period of growth in the microtiter wells.
Fig. 10.
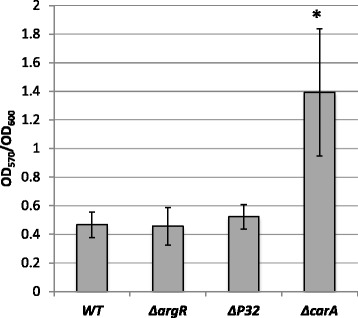
Disruption of carA enhances biofilm formation. Biofilm formation by P. syringae DC3000, ΔargR, ΔP32, and ΔcarA. Cells were grown for 72 h at 28 °C in 96-well microtiter plates containing nutrient broth, and surface-associated biofilm formation was analyzed by crystal violet staining of the adherent biofilm, extraction of the crystal violet with acetic acid, and measurement of the absorbance (OD570). All experiments were done in triplicate with at minimum of three technical repeats. Data were analyzed by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Tukey HSD for pair-wise comparisons. Asterisks indicate statistically significant difference (P < 0.003 by ANOVA; P < 0.01 using Tukey HSD)
Discussion
Although the carAB operon is conserved in many bacteria, its regulation is surprisingly variable. [37]. The well-characterized carAB operon in E. coli (reviewed by [45]) is regulated by several mechanisms. This operon makes use of two tandem promoters that are separately regulated by pyrimidines and arginine. The more distal or upstream promoter is regulated by numerous factors including integration host factor (IHF), the purine repressor (PurR), the pyrimidine ultilization regulator (RutR) as well as PepA, an aminopeptidase and a UMP-kinase PyrH. Additional regulation occurs through reiterative transcription (or RNA polymerase stuttering) when dUTP is available at high concentration, nascent transcripts originating at this promoter are released prematurely due to RNA polymerase stuttering at a T-rich region immediately downstream from the transcriptional start site. The second (proximal) promoter is negatively regulated by the transcriptional regulator ArgR which consists of two trimers that are stabilized by the binding of arginine.
In contrast to E.coli, carAB in P. aeruginosa is transcribed from a single promoter [32]. carAB expression increases in response to limitation of either arginine or pyrimidine. The carAB transcript includes an upstream untranslated region (UTR) that contains a potential stem-loop structure [32]. The pyrimidine response is reduced when a portion of the right arm of the stem-loop structure is deleted, and it is abolished when the stem-loop structure is completely removed. Since carAB expression continues to be responsive to arginine levels in these experiments, the stem-loop structure appears to be required specifically for pyrimidine regulation of carAB.
Our data shows that regulation of carAB in DC3000 resembles the regulation reported in P. aeruginosa. However there are some novel features. Although the qRT-PCR data suggests that ArgR represses the expression of P32 and carA, unexpectedly our promoter fusion data shows that addition of arginine to the medium increases the expression of P32 and carA in contrast to the repression observed in P. aeruginosa. However the regulation of the pyrimidine pathway in Pseudomonas is strongly influenced by pyrimidine and purine nucleotide effectors [46]. For example, the activity of the carbamoyl-phosphate synthase is inhibited by UMP and activated by ornithine and N-acetylornithine [47] and carAB expression is subject to pyrimidine control via an attenuation mechanism. Therefore it is possible, that under the conditions we examined expression, the DC3000 cells are experiencing a high requirement for pyrimidines and expression of P32 and carA is not repressed upon supplementation of arginine. Additionally, the CPase of previously studied pseudomonads shows in most cases only limited repression by arginine and the ability of arginine to repress genes involved in arginine biosynthesis is sometimes influenced by carbon source [37]. Taken together our data indicates that the regulation of P32 and carA is complex in P. syringae and differs from the regulation observed in P. aeruginosa. More extensive analyses are needed to determine direct regulation by ArgR and further characterize possible post-transcriptional regulation that may be occurring in these pathways in P. syringae.
Another difference we observed when compared to the P. aeruginosa is in the 5′UTR of carA. Our unpublished data of sRNAs found in P. syringae along with the mapping of the 3′ end in this study supports the notion that a small transcript is produced from the 5′UTR of carA. Interestingly, in P. aeruginosa a leader peptide is produced from the carA promoter region [32]. Inspection of the P. syringae DC3000 carA promoter region did not reveal a possible start codon that could give rise to a small peptide in this region (data not shown). Recently it was predicted that in P. syringae pv. phaseolicola 1448A carA is regulated by attenuation [48]. We hypothesize that in DC3000 P32 is generated by transcription attenuation. A sRNA derived from the 5′UTR of carA might act in trans to regulate expression of other genes. This concept was first described in E. coli [49]. Recent studies have shown that 5′UTRs of pathogenic bacteria can accumulate as stable RNA molecules [50] and are capable of acting in trans. Work in L. monocytogenes showed that several cis-acting riboswitches located in the 5′ UTRs of mRNAs produce small transcripts as the result of premature transcription and these target and regulate the expression of other mRNAs in trans [51]. The possibility that P32 may act in trans is intriguing. Since this sRNA is conserved among the Pseudomonads, this could add a new complexity to the regulation of arginine biosynthesis in the Pseudomonads and could identify regulatory links between arginine and other regulatory pathways in these bacteria.
We found that in P. syringae a carA mutant displays reduced growth in apoloplastic fluid and reduced fitness in planta. During a screen for DC3000 mutants that displayed reduced virulence, Brooks, D.M. et al. discovered that a mutant with a Tn5 insertion in the carA gene showed reduced virulence in A. thaliana [52]. Although the authors suggested that the inability of the mutant to multiply to high levels in A. thaliana leaves was likely because of limited nutrients in the apoplast of A. thaliana leaves, no further studies were performed. Interestingly our studies have shown that the growth defect of ΔcarA could not be restored at 6 or 12 h with addition of arginine to apoplastic fluid. Surprisingly, growth of ΔcarA at the earlier time points could be restored to wild-type levels with the sole addition of uracil suggesting the supply of pyrimidines may be a limiting growth factor in apoplastic fluid. These data imply that there maybe sufficient arginine concentrations in planta but pyrimidines may be limiting thus resulting in reduced fitness in planta. Studies have shown that of the 20 protein amino acids, arginine was the only amino acid that could not be detected in apoplastic fluid [53]. To our knowledge the concentrations of pyrimidines in the tomato hosts have not been reported. It has been reported that Erwinia amylovora can obtain sufficient pyrimidines from host tissue to support growth and cause disease [54]. The situation we observe with P. syringae is more similar to the findings reported for some human bacterial pathogens, where de novo pyrimidine synthesis is required for growth in host-derived material [55].
The P32 mutant was able to grow to wild type levels in planta and in apoplastic fluid extracts. However, it caused reduced disease symptoms in tomato. Previous studies using DC3000 mutants have shown that reduced symptom formation is not always associated with reduced growth in planta [56]. The precise role of P32 in as yet undefined regulatory pathways that may lead to symptom production needs to be examined further.
The carA mutant formed better biofilms but was also compromised in its ability to swarm. Several mutants with insertions within genes involved in the pyrimidine nucleotide biosynthetic pathway and arginine metabolism displayed reduced biofilm formation [57, 58]. In Vibrio parahaemolyticus [59] a carA transposon mutant forms only thin pellicles at the air–medium interface. The involvement of carA in biofilm formation and swarming of P. syringae suggests that the reduced fitness in planta may be the result of multiple factors.
carAB mutants of Pseudomonas spp. strain G are auxotrophic for arginine as well as pyrimidines but also deficient in several traits [34] such as extracellular polysaccharide production. Interestingly, the carAB genes from Pseudomonas sp. strain G are required for the degradation of diffusible signal factor (DSF), a fatty acid signal molecule involved in regulation of virulence in several Xanthomonas species as well as Xylella fastidiosa [34]. Interestingly, a carAB mutant strain of Halomonas eurihalina is also deficient in exopolysaccharide production [41]. This deficiency is thought to be a result of a decrease in the UDP-sugar pool. These compounds are essential to the synthesis of nucleotide di-phospho-sugar precursors such as UDP glucose and UDP galactose. UDP sugar is utilized in the synthesis not only of extracellular polysaccharides but also of lipopolysaccharides and the glycosylation of lipids and fatty acids. It is possible that the carA mutant of P. syringae displays altered production of extracellular polysaccharides. At least three exopolysaccharides (Psl, Pel, and alginate) contribute to biofilm formation in P. aeruginosa [60]. P. syringae DC3000 is able to produce Psl and alginate but does not encode for genes for the polysaccharide Pel [61]. Alterations in production of Psl can influence biofilm formation and swarming motility of P. aeruginosa [62]. Our future studies will explore if there is an involvement of carA in exopolysaccharide production in P. syringae.
Conclusions
In this study we found that carA of P. syringae plays an important role in providing arginine and uracil for growth of the bacterium and also influences other factors that are potentially important for growth and survival during infection. In conclusion, our data also show that carA is important for growth and survival of P. syringae in planta.
Methods
Bacterial strains and growth conditions
The bacterial strains and plasmids used in this study can be found in Additional file 2: Table S1. Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato DC3000 (DC3000) was cultured at 28 °C or at room temperature on King’s B (KB) agar [63]. Where noted, the minimal media used were MG Mannitol-Glutamate (MG) medium (10 g/L of mannitol, 2 g/L of L-glutamic acid, 0.5 g/L of KH2PO4, 0.2 g/L of NaCl, 0.2 g/L of MgSO4, final pH of 7) [64] and VBMM [65]. When desired arginine and uracil were used at final concentrations of 40 mM and 10 mM, respectively.
Bacterial growth assays
For evaluating growth, overnight cultures of each strain were prepared in liquid KB and incubated at 28 ° C with shaking. The next morning cultures were centrifuged and the pellets re-suspended in 1 mL of sterile water. The pellets were washed two more times and then re-suspended in 1 mL of sterile water. Following re-suspension, the OD600 of the cultures was measured, suspensions were diluted to OD600 = 2.0 in 1 mL of water, and the OD600 was measured again. The wells of a 96-well plate were filled with 200 μL of appropriate medium and then inoculated with 20 μL of bacterial suspension. Plates were incubated at 28.0 °C with shaking in a Biotek Synergy 2 microplate reader (Biotek, Winooski, VT). OD600 was measured every 30 min for 24 h. Three wells were measured for each bacterial strain/medium. When necessary, medium was supplemented with arginine (final concentration of 40 mM) and/or uracil (final concentration of 10 mM). Growth curves were repeated three times. Growth at time points 6, 12, 18 and 24 h was used for post-hoc statistical analysis. Statistical significance was assessed using Tukey HSD for pair-wise comparisons (α = 0.05).
Apoplastic fluid extraction and growth
Apoplastic fluid was extracted from four-week old Solanum lycopersicum cv. MoneyMaker tomato plants following the protocol described in [53] with the following modifications. Whole leaves were removed and submerged in a container of DI water. The container was placed in a bell jar and a series of vacuum-pressure cycles were applied to the leaves at approximately 24 psi until the leaves were fully infiltrated. The leaves were removed, blotted dry, and carefully rolled into a 5-mL syringe barrel. The syringe was placed in a 15-mL conical vial and centrifuged at 2,000 rpm for 5 min at 4 °C to collect apoplastic fluid. Fluid was aliquoted into 1.5 mL microcentrifuge tubes and centrifuged again at 3,000 rpm for 10 min at 4 °C. The supernatant was removed and placed into a 1.5 mL microcentrifuge tube and stored at −80 °C. To test for cytoplasmic contamination, a fraction of the extracted apoplastic fluid was evaluated for Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase (G6PDH) activity and compared to a leaf homogenate using a G6PDH Asssy Kit (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Only apoplastic fluid that had little to no cytoplasmic contamination was used in growth analysis. Growth was evaluated using the protocol described above for bacterial growth assays. Three biological replicates were performed per strain, each with three technical replicates. Statistical significance was assessed using Tukey HSD (α = 0.05).
Creation of reporter constructs
Genomic regions upstream of carA (PSPTO_4502) were amplified via PCR using chromosomal DNA isolated from wild-type DC3000. Primers 94 and 95 were designed to amplify the entire region between dapB (PSPTO_4503) and carA (PSPTO_4502) for a total product length of 228 bp. Primers 94 and 97 yielded a product of 187 bp in length that disrupted the putative stem loop region. Primers 94 and 98 amplified a region upstream of P32 (143 bp). The 117 bp product obtained using primers 99 and 95 lacks the putative promoter upstream of P32. Primers 100 and 95 amplified a region of 51 bases upstream of carA that does not include P32. These amplified regions were cloned by PCR and TOPO cloning using the pENTR/D-TOPO vector (Invitrogen, Carlsbad CA). Positive clones were selected by plating on LB supplemented with 50 μg/ml of kanamycin. Inserts were then sequenced (Biotechnology Resource Center (BRC) at Cornell University) to identify correct clones. LR cloning and the Gateway® LR Clonase® II Enzyme mix (Invitrogen) were used to move the promoter regions into the destination vector pBS58, which contains a promoterless lux operon [66, 67]. The LR mixture was transformed into One Shot Omni-Mach 2 T1 cells (Invitrogen). Positive clones were selected by plating on LB supplemented with 50 μg/ml of kanamycin and 10 μg/ml of tetracycline and subsequently confirmed by sequencing.
Promoter fusion assays
Promoter fusion constructs were introduced into the appropriate P. syringae strains using electroporation and plating transformants on KB plates containing kanamycin. Overnight cultures were prepared in KB medium supplemented with kanamycin and incubated at 28.0 °C with shaking then diluted the next day to an OD600 = 0.1 in VBMM or VBMM supplemented with 40 mM arginine and/or 10 mM uracil. 200 μL of the culture was dispensed into individual wells of a 96 well plate in a Biotek Syngery 2 microplate reader. The cultures were incubated at 28.0 °C with shaking. OD600 and relative luminescence were measured every 2 h and relative luminescence calculated as luminescence/OD600. The experiment was performed at least three times. Statistical significance was assessed using Tukey HSD (α = 0.05).
RNA isolation
Total RNA was prepared using Trizol (Invitrogen) following the manufacturer’s instructions. Once isolated, RNA was treated with DNAse (Ambion, Austin, TX) to remove residual DNA. RNA was extracted using phenol:chloroform: IAA (isoamyl alcohol) then cleaned and concentrated using RNA Clean-up & Concentrator kit (Zymo Research, Irvine, CA). Removal of DNA was verified by quantitative real-time PCR with primers to the normalizing genes gap 1 (PSPTO_1287) or gyrA (PSPTO_1745) [68].
Reverse transcription-PCR (RT-PCR)
Total RNA (100 ng) was reverse transcribed using Superscript III (Invitrogen) and primers listed in Additional file 2: Table S1 according to the manufacturer’s instructions. PCR reactions were performed for 30 cycles. The PCR products were separated by agarose gel electrophoresis.
3′ rapid amplification of cDNA ends (RACE)
3′ RACE was performed as described by Moll et al. [69]. This protocol was adapted from Argaman et al. [70].
Quantitative real-time PCR (qPCR)
qPCR was performed as described by Park et al. [71]. Extracted RNA was synthesized into cDNA using the qScript cDNA Supermix (Quanta Biosciences, Gaithersburg, MD) and qPCR was performed using IQ SYBR green Supermix (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA) on a iQ5 multicolor real-time detection system (BioRad). The production of nonspecific products was determined by the dissociation protocol included in the software provided with the machine. All primer pairs were found to yield unique products using the dissociation protocol (data not shown). The PCR assay was carried out as previously described [71]. Gene expression fold-change was calculated using the ΔΔ Ct method. Ct values of each gene tested were normalized to the Ct values of the housekeeping gene gap1 (PSPTO_1287). Primers used for qRT-PCR are listed in Additional file 2: Table S1.
Construction of mutant strains
Primers used for the construction of mutant strains are listed in Additional file 2: Table S1. Unmarked deletion strains were constructed using pK18mobsacB plasmid [72]. DNA fragments of approximately 1.0 kb upstream and downstream of P32, carA, and argR were amplified by PCR, gel purified and then joined by splicing by overlap extension PCR. The P32, carA, and argR genes were then deleted from DC3000 using the deletion constructs and marker exchange mutagenesis [71]. Mutant clones (those containing the deletion) were confirmed by DNA sequencing.
Complementation of ΔcarA
The coding region of carA along with its native Shine Dalgarno sequence was amplified from DC3000 genomic DNA using oligos SCMF3 F and SCMF4 R and the Expand High Fidelity PCR System from Roche. The primers contained the restriction enzyme site XbaI at their 5′ ends. The XbaI-digested PCR product was cloned into the XbaI site of broad host range vector pUCP22 containing the lac promoter [73], and sequenced to confirm the presence of carA. The resulting plasmid was designated as pUCP22::carA.pUCP22::carA was electroporated into DC3000ΔcarA to generate the complementation strain of ΔcarA. For controls, pUCP22 was electroporated into DC3000 and ΔcarA. The strains were selected on gentamycin at 5 μg/ml. Bacterial growth assays were performed as described above.
Evaluating virulence in Arabidopsis plant seedlings
To assess virulence, the Arabidopsis seedling flood-inoculation assay was used [74] following the modifications described in Park et al. [71].
Tomato Dip-inoculation
Tomato dip inoculations were performed as described by Park et al. [71].
Motility assays
P. syringae strains were grown overnight at 28 °C in KB. Overnight cultures were diluted to OD600 of ~0.3 and 5 μl were used to spot onto swarming plates or stab onto swimming plates. Swarming plates consisted of nutrient broth (8 g/L) and 0.5 % (wt/vol) agar. Swimming assays were performed using nutrient broth (8 g/L) and 0.3 % (wt/vol) agar. Swarm and swim zones were measured after plates were incubated for 24 h at room temperature. Three technical replicates were performed for each experiment and each experiment was performed three times. Data were analyzed by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Tukey HSD for pair-wise comparisons.
Biofilm formation
P. syringae strains were grown overnight at 28 °C in KB. Overnight cultures were washed three times with nutrient broth and diluted to OD600 of 1.0. Cultures were added to 96-well plates pre-filled with media to final OD600 of 0.1 and allowed to incubate at 28 °C for 72 h under static conditions. After 72 h of incubation the OD600 was measured and media was removed from each well. Biofilm formation was assessed based on protocols described by Merritt et al. [75] and O’Toole et al. [76]. Approximately 250 μl of 0.1 % crystal violet stain was added to each well and allowed to incubate for 5 min. The stain was removed and wells were washed three times with ddH20. The stained biofilms were resuspended in 30 % acetic acid and OD570 was recorded for each well. Four replicates of each strain were normalized using the final OD600, averaged, and standard deviation was computed. Statistical significance was assessed using a one-way ANOVA test followed by Tukey HSD for pair-wise comparisons.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Samuel Cartinhour for helpful discussions and editorial suggestions. We would also like to thank Zhongmeng Bao for contributing to the design of the P32 mutant and performing the 3′RACE, Zoe Anderson for preliminary qRT-PCR results, and Janet Wilson for preliminary analysis of the mutants in the plant seedling assay. We thank Lynn Johnson, Cornell Statistical Consulting Unit, for help with post-hoc analysis of data.
The U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) is an equal opportunity provider and employer. Mention of trade names or commercial products in this publication is solely for the purposes of providing specific information and does not imply recommendation or endorsement by the USDA.
Funding
This work was supported by the USDA-ARS CRIS project 8062-2100-035-00D, “Pseudomonas Systems Biology”.
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article and its supplementary information files.
Authors’ contributions
BB and MF conceived the project. BB, SC, KD, KS, MF designed and performed the experiments. BB, SC and MF contributed to the experimental design and data analyses. BB, SC, KD, and MF wrote the manuscript. Statistical analyses were performed by SC. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- CFU
Colony forming units
- CPSase
Carbamoylphosphate synthetase
- FLOE
Fluorescently labeled oligonucleotide extension
- G6PDH
Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase
- HR
Hypersensitive response
- IVET
In vivo expression technology
- KB
King’s B
- MG
Mannitol-glutamate
- qPCR
Quantitative real-time PCR
- RACE
Rapid amplification of cDNA ends
- T3SS
The type III secretions system
- VBMM
Vogel-bonner minimal medium
Additional files
Expression of carA in the P32 mutant. Figure S2 Growth of the complemented mutant of ΔcarA is comparable to wild type DC3000. (PDF 167 kb)
List of plasmids, strains, and primers. (PDF 96 kb)
Contributor Information
Bronwyn G. Butcher, Email: bgb27@cornell.edu
Suma Chakravarthy, Email: sc289@cornell.edu.
Katherine D’Amico, Email: kmd255@cornell.edu.
Kari Brossard Stoos, Email: kstoos@ithaca.edu.
Melanie J. Filiatrault, Email: Melanie.filiatrault@ars.usda.gov
References
- 1.Xin XF, He SY. Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato DC3000: a model pathogen for probing disease susceptibility and hormone signaling in plants. Annu Rev Phytopathol. 2013;51:473–498. doi: 10.1146/annurev-phyto-082712-102321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Lindeberg M, Cunnac S, Collmer A. Pseudomonas syringae type III effector repertoires: last words in endless arguments. Trends Microbiol. 2012;20(4):199–208. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2012.01.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.de Bruijn I, de Kock MJ, Yang M, de Waard P, van Beek TA, Raaijmakers JM. Genome-based discovery, structure prediction and functional analysis of cyclic lipopeptide antibiotics in Pseudomonas species. Mol Microbiol. 2007;63(2):417–428. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2006.05525.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Arrebola E, Cazorla FM, Perez-Garcia A, de Vicente A. Chemical and metabolic aspects of antimetabolite toxins produced by Pseudomonas syringae pathovars. Toxins (Basel) 2011;3(9):1089–1110. doi: 10.3390/toxins3091089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Gutierrez-Barranquero JA, Carrion VJ, Murillo J, Arrebola E, Arnold DL, Cazorla FM, de Vicente A. A Pseudomonas syringae diversity survey reveals a differentiated phylotype of the pathovar syringae associated with the mango host and mangotoxin production. Phytopathology. 2013;103(11):1115–1129. doi: 10.1094/PHYTO-04-13-0093-R. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Payne SM. Iron acquisition in microbial pathogenesis. Trends Microbiol. 1993;1(2):66–69. doi: 10.1016/0966-842X(93)90036-Q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Boch J, Joardar V, Gao L, Robertson TL, Lim M, Kunkel BN. Identification of Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato genes induced during infection of Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol Microbiol. 2002;44(1):73–88. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2002.02877.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Brown DG, Allen C. Ralstonia solanacearum genes induced during growth in tomato: an inside view of bacterial wilt. Mol Microbiol. 2004;53(6):1641–1660. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2004.04237.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Marco ML, Legac J, Lindow SE. Conditional survival as a selection strategy to identify plant-inducible genes of Pseudomonas syringae. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2003;69(10):5793–5801. doi: 10.1128/AEM.69.10.5793-5801.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Marco ML, Legac J, Lindow SE. Pseudomonas syringae genes induced during colonization of leaf surfaces. Environ Microbiol. 2005;7(9):1379–1391. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2005.00825.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Osbourn AE, Barber CE, Daniels MJ. Identification of plant-induced genes of the bacterial pathogen Xanthomonas campestris pathovar campestris using a promoter-probe plasmid. EMBO J. 1987;6(1):23–28. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04713.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Ramos-Gonzalez MI, Campos MJ, Ramos JL. Analysis of Pseudomonas putida KT2440 gene expression in the maize rhizosphere: in vivo [corrected] expression technology capture and identification of root-activated promoters. J Bacteriol. 2005;187(12):4033–4041. doi: 10.1128/JB.187.12.4033-4041.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Silby MW, Levy SB. Use of in vivo expression technology to identify genes important in growth and survival of Pseudomonas fluorescens Pf0-1 in soil: discovery of expressed sequences with novel genetic organization. J Bacteriol. 2004;186(21):7411–7419. doi: 10.1128/JB.186.21.7411-7419.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Yang S, Perna NT, Cooksey DA, Okinaka Y, Lindow SE, Ibekwe AM, Keen NT, Yang CH. Genome-wide identification of plant-upregulated genes of Erwinia chrysanthemi 3937 using a GFP-based IVET leaf array. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2004;17(9):999–1008. doi: 10.1094/MPMI.2004.17.9.999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Zhao Y, Blumer SE, Sundin GW. Identification of Erwinia amylovora genes induced during infection of immature pear tissue. J Bacteriol. 2005;187(23):8088–8103. doi: 10.1128/JB.187.23.8088-8103.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Hartmann T, Baronian G, Nippe N, Voss M, Schulthess B, Wolz C, Eisenbeis J, Schmidt-Hohagen K, Gaupp R, Sunderkotter C, et al. The catabolite control protein E (CcpE) affects virulence determinant production and pathogenesis of Staphylococcus aureus. J Biol Chem. 2014;289:29701–29711. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.584979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Palace SG, Proulx MK, Lu S, Baker RE, Goguen JD. Genome-Wide Mutant Fitness Profiling Identifies Nutritional Requirements for Optimal Growth of Yersinia pestis in Deep Tissue. MBio. 2014;5(4). doi:10.1128/mBio.01385-14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 18.Schoen C, Kischkies L, Elias J, Ampattu BJ. Metabolism and virulence in Neisseria meningitidis. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2014;4:114. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2014.00114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Bucker R, Heroven AK, Becker J, Dersch P, Wittmann C. The pyruvate - tricarboxylic acid cycle node: a focal point of virulence control in the enteric pathogen Yersinia pseudotuberculosis. J Biol Chem. 2014;289:30114–30132. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.581348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Papenfort K, Vogel J. Small RNA functions in carbon metabolism and virulence of enteric pathogens. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2014;4:91. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2014.00091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Lucchetti-Miganeh C, Burrowes E, Baysse C, Ermel G. The post-transcriptional regulator CsrA plays a central role in the adaptation of bacterial pathogens to different stages of infection in animal hosts. Microbiology. 2008;154(Pt 1):16–29. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.2007/012286-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Wang L, Beer SV. Application of signature-tagged mutagenesis to the study of virulence of Erwinia amylovora. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2006;265(2):164–171. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2006.00476.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Matas IM, Lambertsen L, Rodriguez-Moreno L, Ramos C. Identification of novel virulence genes and metabolic pathways required for full fitness of Pseudomonas savastanoi pv. savastanoi in olive (Olea europaea) knots. New Phytol. 2012;196(4):1182–1196. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2012.04357.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Hovel-Miner G, Faucher SP, Charpentier X, Shuman HA. ArgR-regulated genes are derepressed in the Legionella-containing vacuole. J Bacteriol. 2010;192(17):4504–4516. doi: 10.1128/JB.00465-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Ryan S, Begley M, Gahan CG, Hill C. Molecular characterization of the arginine deiminase system in Listeria monocytogenes: regulation and role in acid tolerance. Environ Microbiol. 2009;11(2):432–445. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2008.01782.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Sassetti CM, Rubin EJ. Genetic requirements for mycobacterial survival during infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003;100(22):12989–12994. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2134250100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Talaue MT, Venketaraman V, Hazbon MH, Peteroy-Kelly M, Seth A, Colangeli R, Alland D, Connell ND. Arginine homeostasis in J774.1 macrophages in the context of Mycobacterium bovis BCG infection. J Bacteriol. 2006;188(13):4830–4840. doi: 10.1128/JB.01687-05. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Ramos LS, Lehman BL, Peter KA, McNellis TW. Mutation of the Erwinia amylovora argD gene causes arginine auxotrophy, non-pathogenicity in apple and reduced virulence in pear. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2014;80:6739–6749. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02404-14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Livny J, Brencic A, Lory S, Waldor MK. Identification of 17 Pseudomonas aeruginosa sRNAs and prediction of sRNA-encoding genes in 10 diverse pathogens using the bioinformatic tool sRNAPredict2. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006;34(12):3484–3493. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkl453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Filiatrault MJ, Stodghill PV, Myers CR, Bronstein PA, Butcher BG, Lam H, Grills G, Schweitzer P, Wang W, Schneider DJ, et al. Genome-wide identification of transcriptional start sites in the plant pathogen Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato str. DC3000. PLoS One. 2011;6(12):e29335. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0029335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Filiatrault MJ, Stodghill PV, Bronstein PA, Moll S, Lindeberg M, Grills G, Schweitzer P, Wang W, Schroth GP, Luo S, et al. Transcriptome analysis of Pseudomonas syringae identifies new genes, noncoding RNAs, and antisense activity. J Bacteriol. 2010;192(9):2359–2372. doi: 10.1128/JB.01445-09. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Kwon DH, Lu CD, Walthall DA, Brown TM, Houghton JE, Abdelal AT. Structure and regulation of the carAB operon in Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Pseudomonas stutzeri: no untranslated region exists. J Bacteriol. 1994;176(9):2532–2542. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.9.2532-2542.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Park SM, Lu CD, Abdelal AT. Purification and characterization of an arginine regulatory protein, ArgR, from Pseudomonas aeruginosa and its interactions with the control regions for the car, argF, and aru operons. J Bacteriol. 1997;179(17):5309–5317. doi: 10.1128/jb.179.17.5309-5317.1997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Newman KL, Chatterjee S, Ho KA, Lindow SE. Virulence of plant pathogenic bacteria attenuated by degradation of fatty acid cell-to-cell signaling factors. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2008;21(3):326–334. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-21-3-0326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Guo J, Song X, Zou L-f, Zou H-s, Chen G-y. The small and large subunits of carbamoyl-phosphate synthase exhibit diverse contributions to pathogenicity in Xanthomonas citri subsp. citri. J Integr Agric. 2015;14(7):1338–1347. doi: 10.1016/S2095-3119(14)60965-5. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Zhuo T, Rou W, Song X, Guo J, Fan X, Kamau GG, Zou H. Molecular study on the carAB operon reveals that carB gene is required for swimming and biofilm formation in Xanthomonas citri subsp. citri. BMC Microbiol. 2015;15:225. doi: 10.1186/s12866-015-0555-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Cunin R, Glansdorff N, Pierard A, Stalon V. Biosynthesis and metabolism of arginine in bacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1986;50(3):314–352. doi: 10.1128/mr.50.3.314-352.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Arioli S, Monnet C, Guglielmetti S, Mora D. Carbamoylphosphate synthetase activity is essential for the optimal growth of Streptococcus thermophilus in milk. J Appl Microbiol. 2009;107(1):348–354. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.2009.04213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Vaishnav P, Randev S, Jatiani S, Aggarwal S, Keharia H, Vyas PR, Nareshkumar G, Archana G. Characterization of carbamoyl phosphate synthetase of Streptomyces spp. Indian J Exp Biol. 2000;38(9):931–935. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Haas D, Holloway BW, Schambock A, Leisinger T. The genetic organization of arginine biosynthesis in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Mol Gen Genet. 1977;154(1):7–22. doi: 10.1007/BF00265571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Llamas I, Suarez A, Quesada E, Bejar V, del Moral A. Identification and characterization of the carAB genes responsible for encoding carbamoylphosphate synthetase in Halomonas eurihalina. Extremophiles. 2003;7(3):205–211. doi: 10.1007/s00792-002-0311-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Lu CD, Yang Z, Li W. Transcriptome analysis of the ArgR regulon in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 2004;186(12):3855–3861. doi: 10.1128/JB.186.12.3855-3861.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Kim W, Surette MG. Metabolic differentiation in actively swarming salmonella. Mol Microbiol. 2004;54(3):702–714. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2004.04295.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.O’Toole GA. Microtiter dish biofilm formation assay. J Vis Exp. 2011;(47). doi:10.3791/2437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 45.Turnbough CL, Jr, Switzer RL. Regulation of pyrimidine biosynthetic gene expression in bacteria: repression without repressors. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2008;72(2):266–300. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00001-08. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Chu CP, West TP. Pyrimidine biosynthetic pathway of Pseudomonas fluorescens. J Gen Microbiol. 1990;136(5):875–880. doi: 10.1099/00221287-136-5-875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Abdelal AT, Bussey L, Vickers L. Carbamoylphosphate synthetase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Subunit composition, kinetic analysis and regulation. Eur J Biochem. 1983;129(3):697–702. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07105.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Naville M, Gautheret D. Premature terminator analysis sheds light on a hidden world of bacterial transcriptional attenuation. Genome Biol. 2010;11(9):R97. doi: 10.1186/gb-2010-11-9-r97. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Vogel J, Bartels V, Tang TH, Churakov G, Slagter-Jager JG, Huttenhofer A, Wagner EG. RNomics in Escherichia coli detects new sRNA species and indicates parallel transcriptional output in bacteria. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003;31(22):6435–6443. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkg867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Sharma CM, Hoffmann S, Darfeuille F, Reignier J, Findeiss S, Sittka A, Chabas S, Reiche K, Hackermuller J, Reinhardt R, et al. The primary transcriptome of the major human pathogen Helicobacter pylori. Nature. 2010;464(7286):250–255. doi: 10.1038/nature08756. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Loh E, Dussurget O, Gripenland J, Vaitkevicius K, Tiensuu T, Mandin P, Repoila F, Buchrieser C, Cossart P, Johansson J. A trans-acting riboswitch controls expression of the virulence regulator PrfA in Listeria monocytogenes. Cell. 2009;139(4):770–779. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.08.046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Brooks DM, Hernandez-Guzman G, Kloek AP, Alarcon-Chaidez F, Sreedharan A, Rangaswamy V, Penaloza-Vazquez A, Bender CL, Kunkel BN. Identification and characterization of a well-defined series of coronatine biosynthetic mutants of Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato DC3000. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2004;17(2):162–174. doi: 10.1094/MPMI.2004.17.2.162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Rico A, Preston GM. Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato DC3000 uses constitutive and apoplast-induced nutrient assimilation pathways to catabolize nutrients that are abundant in the tomato apoplast. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2008;21(2):269–282. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-21-2-0269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Ramos LS, Sinn JP, Lehman BL, Pfeufer EE, Peter KA, McNellis TW. Erwinia amylovora pyrC mutant causes fire blight despite pyrimidine auxotrophy. Lett Appl Microbiol. 2015;60(6):572–579. doi: 10.1111/lam.12417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Samant S, Lee H, Ghassemi M, Chen J, Cook JL, Mankin AS, Neyfakh AA. Nucleotide biosynthesis is critical for growth of bacteria in human blood. PLoS Pathog. 2008;4(2):e37. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.0040037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Munkvold KR, Russell AB, Kvitko BH, Collmer A. Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato DC3000 type III effector HopAA1-1 functions redundantly with chlorosis-promoting factor PSPTO4723 to produce bacterial speck lesions in host tomato. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2009;22(11):1341–1355. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-22-11-1341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Musken M, Di Fiore S, Dotsch A, Fischer R, Haussler S. Genetic determinants of Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm establishment. Microbiology. 2010;156(Pt 2):431–441. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.033290-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Ueda A, Attila C, Whiteley M, Wood TK. Uracil influences quorum sensing and biofilm formation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa and fluorouracil is an antagonist. Microb Biotechnol. 2009;2(1):62–74. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-7915.2008.00060.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Enos-Berlage JL, Guvener ZT, Keenan CE, McCarter LL. Genetic determinants of biofilm development of opaque and translucent Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Mol Microbiol. 2005;55(4):1160–1182. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2004.04453.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Wei Q, Ma LZ. Biofilm matrix and its regulation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Int J Mol Sci. 2013;14(10):20983–21005. doi: 10.3390/ijms141020983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Buell CR, Joardar V, Lindeberg M, Selengut J, Paulsen IT, Gwinn ML, Dodson RJ, Deboy RT, Durkin AS, Kolonay JF, et al. The complete genome sequence of the Arabidopsis and tomato pathogen Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato DC3000. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003;100(18):10181–10186. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1731982100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Wang S, Yu S, Zhang Z, Wei Q, Yan L, Ai G, Liu H, Ma LZ. Coordination of swarming motility, biosurfactant synthesis, and biofilm matrix exopolysaccharide production in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2014;80(21):6724–6732. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01237-14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.King EO, Ward MK, Raney DE. Two simple media for the demonstration of pyocyanin and fluorescin. J Lab Clin Med. 1954;44(2):301–307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Keane PJ, Kerr A, New PB. Crown Gall of Stone Fruit .2. Identification and Nomenclature of Agrobacterium Isolates. Australian J Biol Sci. 1970; 23(3):585-&.
- 65.Schweizer HP. The agmR gene, an environmentally responsive gene, complements defective glpR, which encodes the putative activator for glycerol metabolism in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1991;173(21):6798–6806. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.21.6798-6806.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Markel E, Maciak C, Butcher BG, Myers CR, Stodghill P, Bao Z, Cartinhour S, Swingle B. An extracytoplasmic function sigma factor-mediated cell surface signaling system in Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato DC3000 regulates gene expression in response to heterologous siderophores. J Bacteriol. 2011;193(20):5775–5783. doi: 10.1128/JB.05114-11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Swingle B, Thete D, Moll M, Myers CR, Schneider DJ, Cartinhour S. Characterization of the PvdS-regulated promoter motif in Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato DC3000 reveals regulon members and insights regarding PvdS function in other pseudomonads. Mol Microbiol. 2008;68(4):871–889. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2008.06209.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Vencato M, Tian F, Alfano JR, Buell CR, Cartinhour S, DeClerck GA, Guttman DS, Stavrinides J, Joardar V, Lindeberg M, et al. Bioinformatics-enabled identification of the HrpL regulon and type III secretion system effector proteins of Pseudomonas syringae pv. phaseolicola 1448A. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2006;19(11):1193–1206. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-19-1193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Moll S, Schneider DJ, Stodghill P, Myers CR, Cartinhour SW, Filiatrault MJ. Contruction of an rsmX co-variance model and identification of five rsmX non-coding RNAs in Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato DC3000. RNA Biol. 2010;7(5):1–9. doi: 10.4161/rna.7.5.12687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Argaman L, Hershberg R, Vogel J, Bejerano G, Wagner EG, Margalit H, Altuvia S. Novel small RNA-encoding genes in the intergenic regions of Escherichia coli. Curr Biol. 2001;11(12):941–950. doi: 10.1016/S0960-9822(01)00270-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Park SH, Butcher BG, Anderson Z, Pellegrini N, Bao Z, D’Amico K, Filiatrault MJ. Analysis of the small RNA P16/RgsA in the plant pathogen Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato strain DC3000. Microbiology. 2013;159(Pt 2):296–306. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.063826-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Schafer A, Tauch A, Jager W, Kalinowski J, Thierbach G, Puhler A. Small mobilizable multi-purpose cloning vectors derived from the Escherichia coli plasmids pK18 and pK19: selection of defined deletions in the chromosome of Corynebacterium glutamicum. Gene. 1994;145(1):69–73. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(94)90324-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.West SE, Schweizer HP, Dall C, Sample AK, Runyen-Janecky LJ. Construction of improved Escherichia-Pseudomonas shuttle vectors derived from pUC18/19 and sequence of the region required for their replication in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Gene. 1994;148(1):81–86. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(94)90237-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Ishiga Y, Ishiga T, Uppalapati SR, Mysore KS. Arabidopsis seedling flood-inoculation technique: a rapid and reliable assay for studying plant-bacterial interactions. Plant Methods. 2011;7:32. doi: 10.1186/1746-4811-7-32. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Merritt JH, Kadouri DE, O’Toole GA. Growing and analyzing static biofilms. Curr Protoc Microbiol. 2005; Chapter 1:Unit 1B.1.doi:10.1002/9780471729259.mc01b01s00. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 76.O’Toole GA, Pratt LA, Watnick PI, Newman DK, Weaver VB, Kolter R. Genetic approaches to study of biofilms. Methods Enzymol. 1999;310:91–109. doi: 10.1016/S0076-6879(99)10008-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article and its supplementary information files.


