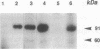
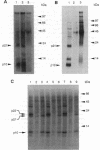
Abstract
Agrobacterium tumefaciens initiates the expression of pathogenic genes (vir genes) in response to host-derived phenolic signals through a two-component regulatory system consisting of VirA and VirG. alpha-Bromoacetosyringone (ASBr) was developed as an inhibitor of this induction process and found to be a specific and irreversible inhibitor of vir gene induction in this pathogen. Formal replacement of one of the methoxy groups of ASBr with iodine gave an equally effective inhibitor that could carry an 125I label. We report here that the resulting radiolabeled inhibitor does not react with the sensory component of this system, VirA, either in vivo or in vitro. Rather, two small proteins, p10 and p21, bind labeled inhibitor in vivo in a time period that is consistent with the exposure time required for the inhibition of vir gene expression. Labeling to these proteins was protected by preexposure to ASBr but not by alpha-bromo-3,5-dimethoxyacetophenone, a compound of comparable chemical reactivity but previously shown not to inhibit vir gene expression. Our findings suggest that proteins that are not tumor-inducing plasmid-encoded mediate vir gene activation in a step prior to the VirA/VirG two-component regulatory system.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bourret R. B., Borkovich K. A., Simon M. I. Signal transduction pathways involving protein phosphorylation in prokaryotes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:401–441. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.002153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cangelosi G. A., Ankenbauer R. G., Nester E. W. Sugars induce the Agrobacterium virulence genes through a periplasmic binding protein and a transmembrane signal protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(17):6708–6712. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.17.6708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cangelosi G. A., Best E. A., Martinetti G., Nester E. W. Genetic analysis of Agrobacterium. Methods Enzymol. 1991;204:384–397. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)04020-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C. Y., Winans S. C. Controlled expression of the transcriptional activator gene virG in Agrobacterium tumefaciens by using the Escherichia coli lac promoter. J Bacteriol. 1991 Feb;173(3):1139–1144. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.3.1139-1144.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Close T. J., Zaitlin D., Kado C. I. Design and development of amplifiable broad-host-range cloning vectors: analysis of the vir region of Agrobacterium tumefaciens plasmid pTiC58. Plasmid. 1984 Sep;12(2):111–118. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(84)90057-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooley M. B., D'Souza M. R., Kado C. I. The virC and virD operons of the Agrobacterium Ti plasmid are regulated by the ros chromosomal gene: analysis of the cloned ros gene. J Bacteriol. 1991 Apr;173(8):2608–2616. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.8.2608-2616.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ditta G., Stanfield S., Corbin D., Helinski D. R. Broad host range DNA cloning system for gram-negative bacteria: construction of a gene bank of Rhizobium meliloti. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7347–7351. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess K. M., Dudley M. W., Lynn D. G., Joerger R. D., Binns A. N. Mechanism of phenolic activation of Agrobacterium virulence genes: development of a specific inhibitor of bacterial sensor/response systems. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 1;88(17):7854–7858. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.17.7854. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang Y., Morel P., Powell B., Kado C. I. VirA, a coregulator of Ti-specified virulence genes, is phosphorylated in vitro. J Bacteriol. 1990 Feb;172(2):1142–1144. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.2.1142-1144.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jin S. G., Prusti R. K., Roitsch T., Ankenbauer R. G., Nester E. W. Phosphorylation of the VirG protein of Agrobacterium tumefaciens by the autophosphorylated VirA protein: essential role in biological activity of VirG. J Bacteriol. 1990 Sep;172(9):4945–4950. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.9.4945-4950.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jin S., Roitsch T., Ankenbauer R. G., Gordon M. P., Nester E. W. The VirA protein of Agrobacterium tumefaciens is autophosphorylated and is essential for vir gene regulation. J Bacteriol. 1990 Feb;172(2):525–530. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.2.525-530.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knauf V. C., Nester E. W. Wide host range cloning vectors: a cosmid clone bank of an Agrobacterium Ti plasmid. Plasmid. 1982 Jul;8(1):45–54. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(82)90040-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leroux B., Yanofsky M. F., Winans S. C., Ward J. E., Ziegler S. F., Nester E. W. Characterization of the virA locus of Agrobacterium tumefaciens: a transcriptional regulator and host range determinant. EMBO J. 1987 Apr;6(4):849–856. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04830.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melchers L. S., Regensburg-Tuïnk T. J., Bourret R. B., Sedee N. J., Schilperoort R. A., Hooykaas P. J. Membrane topology and functional analysis of the sensory protein VirA of Agrobacterium tumefaciens. EMBO J. 1989 Jul;8(7):1919–1925. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03595.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milburn M. V., Privé G. G., Milligan D. L., Scott W. G., Yeh J., Jancarik J., Koshland D. E., Jr, Kim S. H. Three-dimensional structures of the ligand-binding domain of the bacterial aspartate receptor with and without a ligand. Science. 1991 Nov 29;254(5036):1342–1347. doi: 10.1126/science.1660187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orr J. D., Lynn D. G. Biosynthesis of dehydrodiconiferyl alcohol glucosides: implications for the control of tobacco cell growth. Plant Physiol. 1992 Jan;98(1):343–352. doi: 10.1104/pp.98.1.343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn M. J., Gander J. E., Parisi E., Carson J. Mechanism of assembly of the outer membrane of Salmonella typhimurium. Isolation and characterization of cytoplasmic and outer membrane. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jun 25;247(12):3962–3972. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stachel S. E., Nester E. W. The genetic and transcriptional organization of the vir region of the A6 Ti plasmid of Agrobacterium tumefaciens. EMBO J. 1986 Jul;5(7):1445–1454. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04381.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teutonico R. A., Dudley M. W., Orr J. D., Lynn D. G., Binns A. N. Activity and accumulation of cell division-promoting phenolics in tobacco tissue cultures. Plant Physiol. 1991 Sep;97(1):288–297. doi: 10.1104/pp.97.1.288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward J. E., Jr, Dale E. M., Christie P. J., Nester E. W., Binns A. N. Complementation analysis of Agrobacterium tumefaciens Ti plasmid virB genes by use of a vir promoter expression vector: virB9, virB10, and virB11 are essential virulence genes. J Bacteriol. 1990 Sep;172(9):5187–5199. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.9.5187-5199.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winans S. C., Ebert P. R., Stachel S. E., Gordon M. P., Nester E. W. A gene essential for Agrobacterium virulence is homologous to a family of positive regulatory loci. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8278–8282. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winans S. C., Kerstetter R. A., Ward J. E., Nester E. W. A protein required for transcriptional regulation of Agrobacterium virulence genes spans the cytoplasmic membrane. J Bacteriol. 1989 Mar;171(3):1616–1622. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.3.1616-1622.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winans S. C. Two-way chemical signaling in Agrobacterium-plant interactions. Microbiol Rev. 1992 Mar;56(1):12–31. doi: 10.1128/mr.56.1.12-31.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]