Abstract
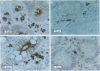
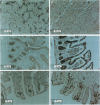
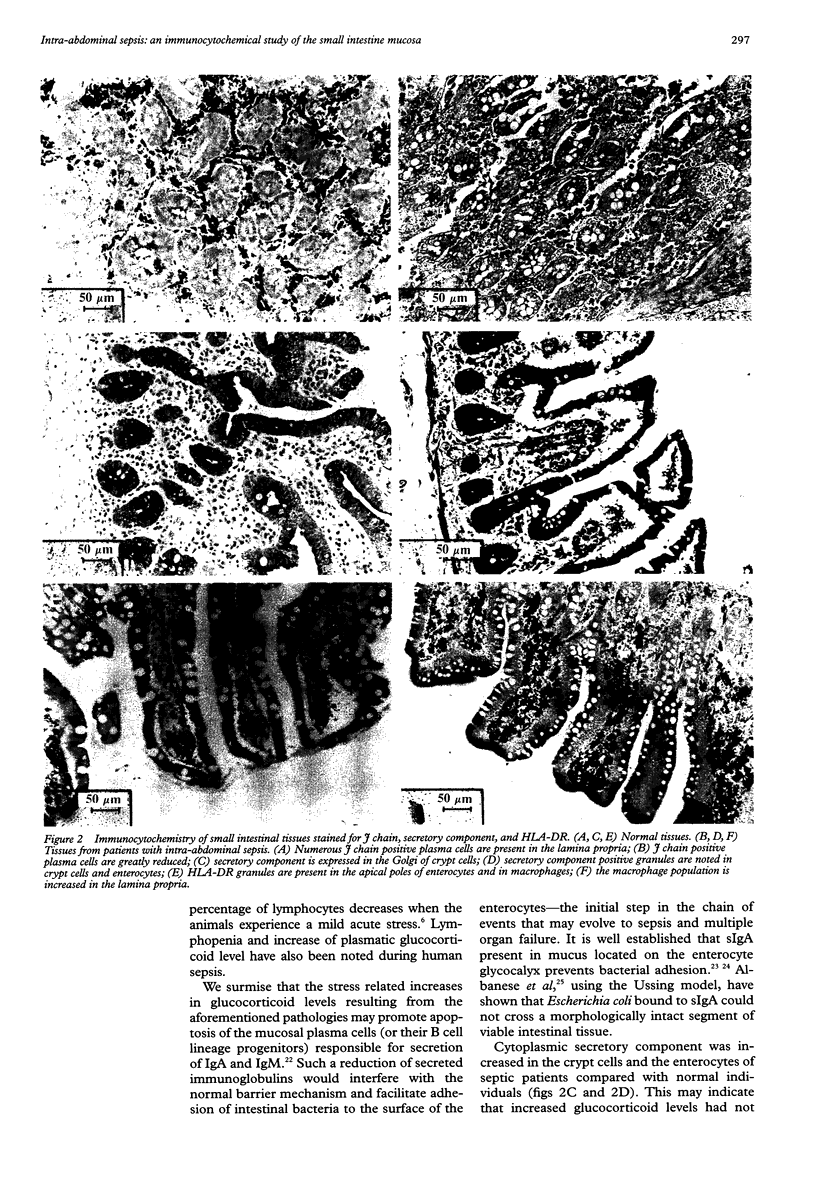
AIM: To investigate immunocytochemical changes in intestinal tissues from patients with intra-abdominal sepsis, and to relate the changes to the possibility of enhanced bacterial adhesion and translocation. METHODS: Tissues from 17 patients suffering from intra-abdominal sepsis and from controls were sectioned and stained immunocytochemically for IgA, IgM, secretory component, J chain, and HLA-DR. Differences in the distribution and characteristics of positively staining cells between the patient groups were assessed. RESULTS: Patients with intra-abdominal sepsis had noticeable reductions in numbers of IgA and IgM plasma cells, reduced J chain staining, and had little immunoglobulin on the surfaces of enterocytes. In contrast, HLA-DR positive cells were increased in the sepsis compared with the control group. The plasma cells present showed cytological changes suggestive of apoptosis. CONCLUSIONS: Stress associated with sepsis and its immediate causes might result in increased plasma glucocorticoid levels that bring about apoptosis of mucosal plasma cells (or their precursors). The consequent reduction in expression of IgA and IgM may favour bacterial adhesion to the enterocytes and facilitate bacterial translocation into the tissues.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albanese C. T., Smith S. D., Watkins S., Kurkchubasche A., Simmons R. L., Rowe M. I. Effect of secretory IgA on transepithelial passage of bacteria across the intact ileum in vitro. J Am Coll Surg. 1994 Dec;179(6):679–688. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexander J. W., Boyce S. T., Babcock G. F., Gianotti L., Peck M. D., Dunn D. L., Pyles T., Childress C. P., Ash S. K. The process of microbial translocation. Ann Surg. 1990 Oct;212(4):496–512. doi: 10.1097/00000658-199010000-00012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alverdy J. C., Aoys E., Moss G. S. Total parenteral nutrition promotes bacterial translocation from the gut. Surgery. 1988 Aug;104(2):185–190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arends M. J., Wyllie A. H. Apoptosis: mechanisms and roles in pathology. Int Rev Exp Pathol. 1991;32:223–254. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-364932-4.50010-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ayala A., Perrin M. M., Chaudry I. H. Defective macrophage antigen presentation following haemorrhage is associated with the loss of MHC class II (Ia) antigens. Immunology. 1990 May;70(1):33–39. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baue A. E. The horror autotoxicus and multiple-organ failure. Arch Surg. 1992 Dec;127(12):1451–1462. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1992.01420120085016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg R. D., Garlington A. W. Translocation of certain indigenous bacteria from the gastrointestinal tract to the mesenteric lymph nodes and other organs in a gnotobiotic mouse model. Infect Immun. 1979 Feb;23(2):403–411. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.2.403-411.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandtzaeg P., Nilssen D. E., Rognum T. O., Thrane P. S. Ontogeny of the mucosal immune system and IgA deficiency. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 1991 Sep;20(3):397–439. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cech A. C., Shou J., Gallagher H., Daly J. M. Glucocorticoid receptor blockade reverses postinjury macrophage suppression. Arch Surg. 1994 Dec;129(12):1227–1232. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1994.01420360013001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deitch E. A., Berg R., Specian R. Endotoxin promotes the translocation of bacteria from the gut. Arch Surg. 1987 Feb;122(2):185–190. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1987.01400140067008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deitch E. A. Simple intestinal obstruction causes bacterial translocation in man. Arch Surg. 1989 Jun;124(6):699–701. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1989.01410060065013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhabhar F. S., Miller A. H., McEwen B. S., Spencer R. L. Effects of stress on immune cell distribution. Dynamics and hormonal mechanisms. J Immunol. 1995 May 15;154(10):5511–5527. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fertsch D., Schoenberg D. R., Germain R. N., Tou J. Y., Vogel S. N. Induction of macrophage Ia antigen expression by rIFN-gamma and down-regulation by IFN-alpha/beta and dexamethasone are mediated by changes in steady-state levels of Ia mRNA. J Immunol. 1987 Jul 1;139(1):244–249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox A. D., Kripke S. A., De Paula J., Berman J. M., Settle R. G., Rombeau J. L. Effect of a glutamine-supplemented enteral diet on methotrexate-induced enterocolitis. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 1988 Jul-Aug;12(4):325–331. doi: 10.1177/0148607188012004325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones W. G., 2nd, Minei J. P., Barber A. E., Rayburn J. L., Fahey T. J., 3rd, Shires G. T., 3rd, Shires G. T. Bacterial translocation and intestinal atrophy after thermal injury and burn wound sepsis. Ann Surg. 1990 Apr;211(4):399–405. doi: 10.1097/00000658-199004000-00004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maejima K., Deitch E. A., Berg R. D. Bacterial translocation from the gastrointestinal tracts of rats receiving thermal injury. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):6–10. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.6-10.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall J. C., Christou N. V., Horn R., Meakins J. L. The microbiology of multiple organ failure. The proximal gastrointestinal tract as an occult reservoir of pathogens. Arch Surg. 1988 Mar;123(3):309–315. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1988.01400270043006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mestecky J., Lue C., Russell M. W. Selective transport of IgA. Cellular and molecular aspects. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 1991 Sep;20(3):441–471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Motyka B., Bhogal H. S., Reynolds J. D. Apoptosis of ileal Peyer's patch B cells is increased by glucocorticoids or anti-immunoglobulin antibodies. Eur J Immunol. 1995 Jul;25(7):1865–1871. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830250711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norvell A., Mandik L., Monroe J. G. Engagement of the antigen-receptor on immature murine B lymphocytes results in death by apoptosis. J Immunol. 1995 May 1;154(9):4404–4413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petty H. R., Martin S. M. Combinative ligand-receptor interactions: effects of cAMP, epinephrine, and met-enkephalin on RAW264 macrophage morphology, spreading, adherence, and microfilaments. J Cell Physiol. 1989 Feb;138(2):247–256. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041380205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes R. S., Karnovsky M. J. Loss of macromolecular barrier function associated with surgical trauma to the intestine. Lab Invest. 1971 Sep;25(3):220–229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rush B. F., Jr, Sori A. J., Murphy T. F., Smith S., Flanagan J. J., Jr, Machiedo G. W. Endotoxemia and bacteremia during hemorrhagic shock. The link between trauma and sepsis? Ann Surg. 1988 May;207(5):549–554. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198805000-00009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder D. S., Unanue E. R. Corticosteroids inhibit murine macrophage Ia expression and interleukin 1 production. J Immunol. 1982 Nov;129(5):1803–1805. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]