Abstract
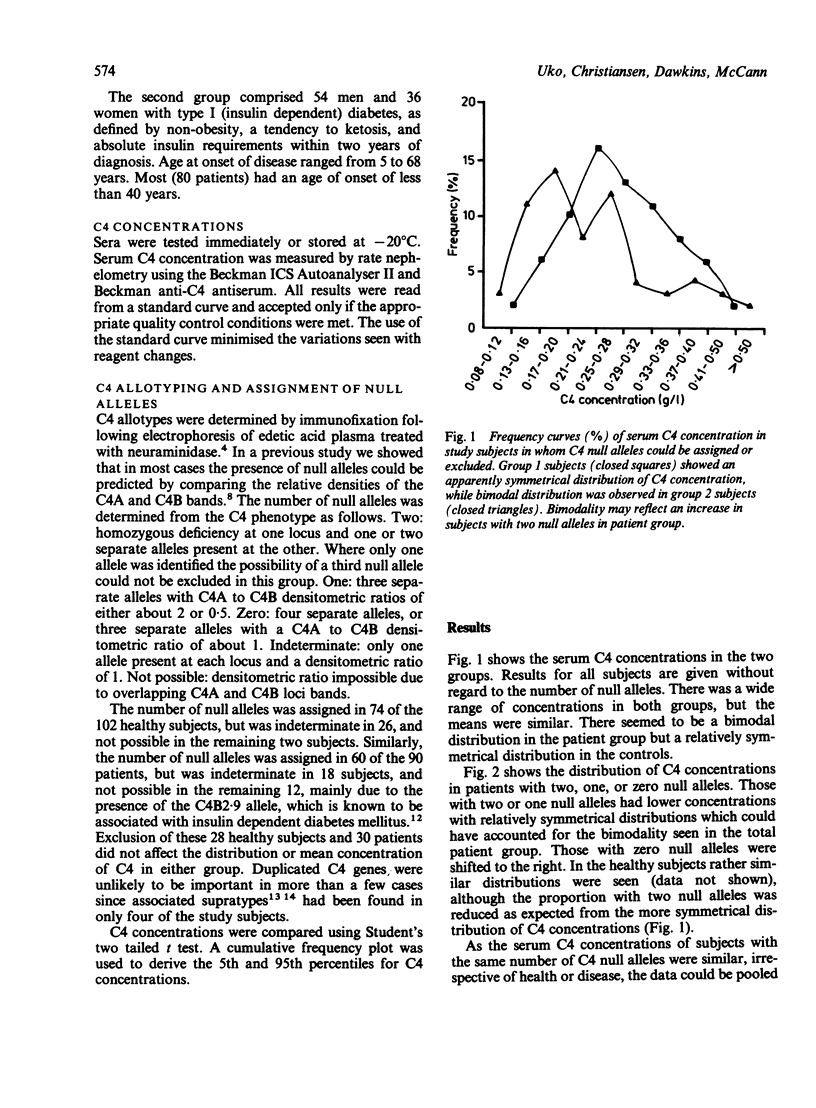
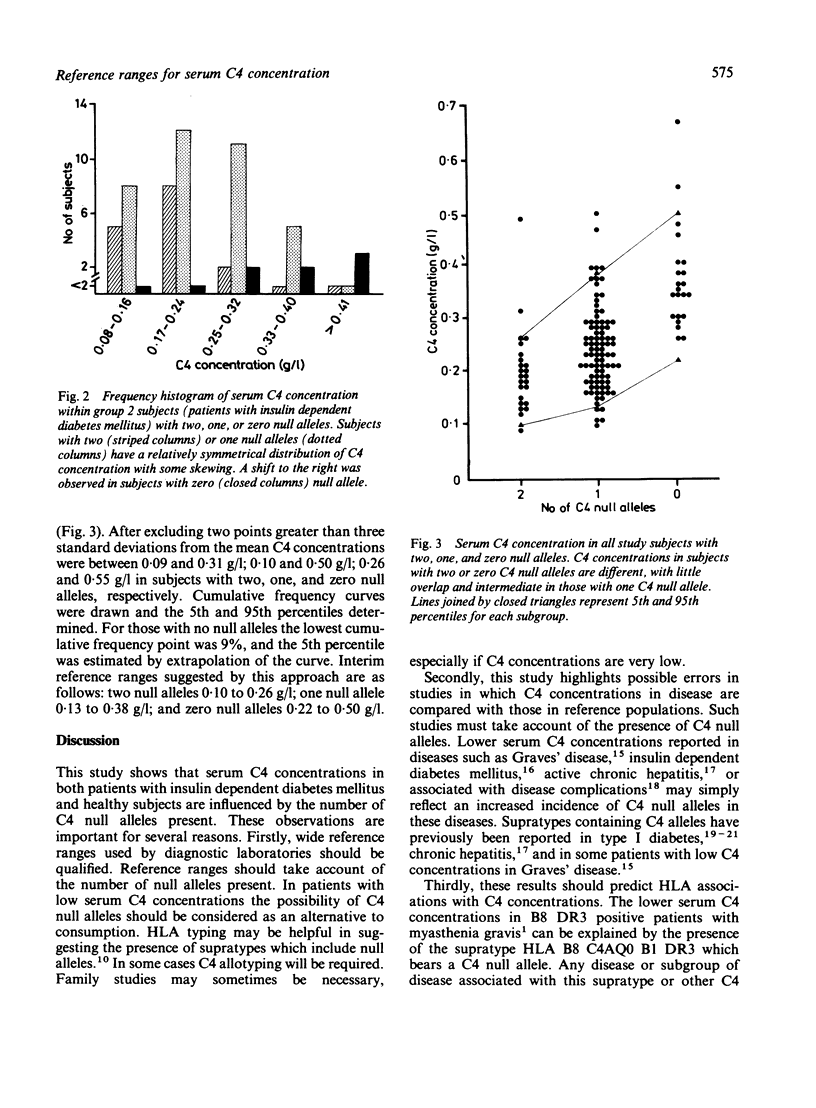
Serum C4 concentrations were measured in 102 healthy subjects and 90 subjects with type I diabetes mellitus. A wide range was observed in the group as a whole (0.08-0.67 g/l; mean = 0.26 g/l; SEM = 0.01 g/l). After C4 allotyping it was possible to subgroup 134 of these subjects according to the number of C4 null alleles present. C4 concentrations in the group with two null alleles were lower than in the group without null alleles (mean 0.2 v 0.37 g/l; p less than 0.001). C4 concentrations in the group with one C4 null allele were intermediate and significantly different from those of the group without null alleles (mean 0.24 v 0.37 g/l; p less than 0.001). Appropriate analysis has defined reference ranges for serum C4 concentrations in subjects with two, one, or zero C4 null alleles. Interpretation of low serum C4 concentrations should take account of the number of C4 null alleles present.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Awdeh Z. L., Alper C. A. Inherited structural polymorphism of the fourth component of human complement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3576–3580. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Awdeh Z. L., Ochs H. D., Alper C. A. Genetic analysis of C4 deficiency. J Clin Invest. 1981 Jan;67(1):260–263. doi: 10.1172/JCI110021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnett A. H., Mijovic C., Fletcher J., Chesner I., Kulkuska-Langlands B. M., Holder R., Bradwell A. R. Low plasma C4 concentrations: association with microangiopathy in insulin dependent diabetes. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1984 Oct 13;289(6450):943–945. doi: 10.1136/bmj.289.6450.943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christiansen F. T., Dawkins R. L., Uko G., McCluskey J., Kay P. H., Zilko P. J. Complement allotyping in SLE: association with C4A null. Aust N Z J Med. 1983 Oct;13(5):483–488. doi: 10.1111/j.1445-5994.1983.tb02699.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christiansen F. T., Houliston J. B., Dawkins R. L. HLA, anti-DNA, and complement in myasthenia gravis. Muscle Nerve. 1978 Nov-Dec;1(6):467–470. doi: 10.1002/mus.880010605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniels C. A., Borsos T., Rapp H. J., Snyderman R., Notkins A. L. Neutralization of sensitized virus by purified components of complement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Mar;65(3):528–535. doi: 10.1073/pnas.65.3.528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins B. R., Houliston J. B., Dawkins R. L. Distribution of HLA A, B and C antigens in an Australian population. Hum Genet. 1979 Nov;52(2):193–201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mannik M., Arend M. P., Hall A. P., Gilliland B. C. Studies on antigen-antibody complexes. I. Elimination of soluble complexes from rabbit circulation. J Exp Med. 1971 Apr 1;133(4):713–739. doi: 10.1084/jem.133.4.713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCluskey J., McCann V. J., Kay P. H., Zilko P. J., Christiansen F. T., O'Neill G. J., Dawkins R. L. HLA and complement allotypes in Type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes. Diabetologia. 1983 Mar;24(3):162–165. doi: 10.1007/BF00250155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill G. J., Yang S. Y., Dupont B. Two HLA-linked loci controlling the fourth component of human complement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):5165–5169. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.5165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olaisen B., Teisberg P., Jonassen R. The C4 system: quantitative studies of different genotypes. Immunobiology. 1980;158(1-2):82–85. doi: 10.1016/S0171-2985(80)80044-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raum D., Awdeh Z., Alper C. A. BF types and the mode of inheritance of insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM). Immunogenetics. 1981;12(1-2):59–74. doi: 10.1007/BF01561651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rich S., O'Neill G., Dalmasso A. P., Nerl C., Barbosa J. Complement and HLA. Further definition of high-risk haplotypes in insulin-dependent diabetes. Diabetes. 1985 May;34(5):504–509. doi: 10.2337/diab.34.5.504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby R. J., Dawkins R. L., Wetherall J. D., Hawkins B. R. HLA in systemic lupus erythematosus: influence on severity. Tissue Antigens. 1978 Jul;12(1):25–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tom W., Farid N. R. Reduced C4 in HLA-B8 positive patients with Graves' disease. Hum Hered. 1981;31(4):227–231. doi: 10.1159/000153213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uko G., Christiansen F. T., Dawkins R. L., Kay P. H. Low serum C4 concentrations in insulin dependent diabetes mellitus. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1983 May 28;286(6379):1748–1749. doi: 10.1136/bmj.286.6379.1748-b. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vergani D., Wells L., Larcher V. F., Nasaruddin B. A., Davies E. T., Mieli-Vergani G., Mowat A. P. Genetically determined low C4: a predisposing factor to autoimmune chronic active hepatitis. Lancet. 1985 Aug 10;2(8450):294–298. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)90348-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch T. R., Beischel L., Berry A., Forristal J., West C. D. The effect of null C4 alleles on complement function. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1985 Mar;34(3):316–325. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(85)90180-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilton A. N., Cobain T. J., Dawkins R. L. Family studies of IgA deficiency. Immunogenetics. 1985;21(4):333–342. doi: 10.1007/BF00430799. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


