Current learning tools such as photographs, cadavers, and computer models are not sufficient for learning the comprehensive anatomy of the kidney and its surroundings. The objective of this research was to aid medical students by presenting tutorial software that contains peeled and piled volume models of the kidney. The sectioned images of donated female cadaver (age at death, 26 years; cause of death, stomach cancer; kidney pathology, none) were stacked to reconstruct three-dimensional volume model (voxel size, 0.2 mm) (1). Peeling and piling of the model were continuously carried out (intervals, 0.4 mm) to explore the inside and outside of the kidney (2).
For convenient browsing, 61 peeled and piled models (from −12 mm to +12 mm) in anterior, posterior, medial, and lateral views were put into software (Figs. 1 and 2). "Browsing software (Male - Peeled and piled kidney) (118 MB)" can be downloaded from the website (anatomy.co.kr) or directly from the address (http://vkh.ajou.ac.kr/Browsing_software_(kidney)_setup.exe) without charge or registration.
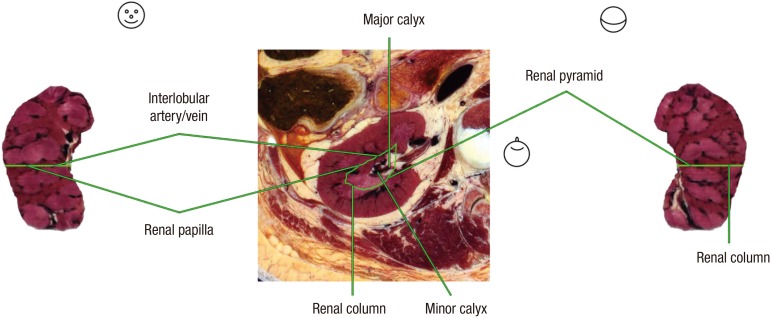
Fig. 1. The peeled (−12 mm) model of right kidney reconstructed by computer software (left and right). The level of peeling is indicated with green line on the reference sectioned image (center). The renal cortex (renal column) is red, while the renal medulla (renal pyramid, renal papilla) is pink. The renal column includes the interlobular artery and vein. Head shapes are appended to represent the viewpoints of the volume model and the sectioned image: anterior view (left), horizontal view (center), and posterior view (right).
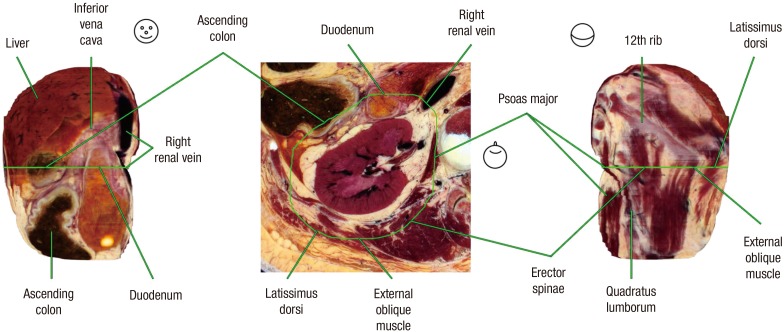
Fig. 2. The piled (+12 mm) model of right kidney. The followings are found on the anterior surface of the kidney: liver (superolateral), inferior vena cava and renal vein (superomedial), ascending colon (inferolateral), and the duodenum (inferomedial); On the posterior surface, we identify the followings: 12th rib (superior), latissimus dorsi (lateral), erector spinae (medial), quadratus lumborum (inferolateral), psoas major (inferomedial), and external oblique muscle (posterior).
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
Raw data of the Visible Korean Human were acquired by the assistance from the Korea Institute of Science and Technology Information. Raw data of the Visible Korean Human were acquired by the assistance from the Korea Institute of Science and Technology Information.
Footnotes
Funding: This work was funded by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MSIP) (No. 2015R1A2A2A01008248, 2015R1A5A7037630). This research was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (No. 2015R1D1A4A01020277).
References
- 1.Park HS, Choi DH, Park JS. Improved sectioned images and surface models of the whole female body. Int J Morphol. 2015;33:1323–1332. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Kwon K, Shin DS, Shin BS, Park HS, Lee S, Jang HG, Park JS, Chung MS. Virtual endoscopic and laparoscopic exploration of stomach wall based on a cadaver’s sectioned images. J Korean Med Sci. 2015;30:658–661. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2015.30.5.658. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]