FIG 3 .
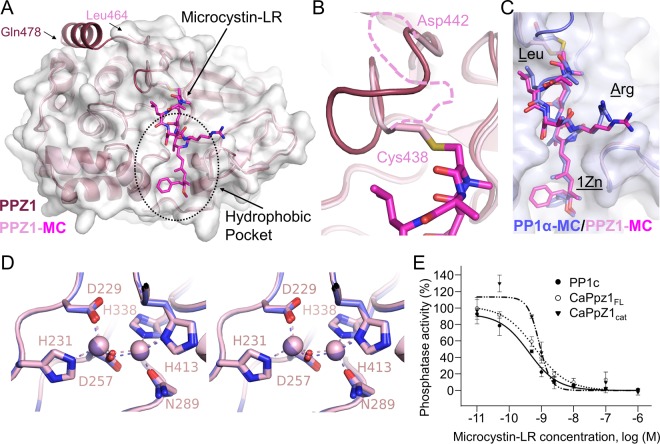
The PPZ1-specific helix is dynamic. (A) Overlay of free PPZ1 (dark pink) and MC-bound PPZ1 (light pink). The C-terminal residues of both proteins are labeled. The gray surface corresponds to the PPZ1-MC complex, illustrating that the PPZ1-specific helix was not ordered and thus not modeled (see the text for details). The PPZ1 hydrophobic pocket is indicated by a dashed circle. (B) Enlarged view of the covalent bond between Cys438 and MC, resulting in a change in conformation of the β12-β13 loop. (Residues 439 to 441 were not visible in the PPZ1-MC structure and are indicated by a pink dashed line.) (C) Overlay of MC from PPZ1 (light pink) and PP1α (blue). The Leu and Arg residues in microcystin-LR are labeled, as is the 1Zn [(2S,3S,4E,6E,8S,9S)-3-amino-9-methoxy-2,6,8-trimethyl-10-phenyldeca-4,6-dienoic acid]. (D) Stereo image of the PPZ1 and PP1α metal-bound active sites. Bound Mn2+ ions are shown as spheres. (E) Dose-response curves reporting the inhibition of PP1c, PPZ1FL, and PPZ1cat activities by the MC toxin; 32P-labeled MLC20 was used as a substrate. The phosphatase activities of each enzyme without toxin were set to 100% activity. The data represent the means ± standard errors (SE) from 3 experiments.